
How to Use Wemos D1 battery shield: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Wemos D1 battery shield in Cirkit Designer
Design with Wemos D1 battery shield in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Wemos D1 Battery Shield is a compact and efficient power management module designed specifically for the Wemos D1 Mini development board. It allows users to power their Wemos D1 Mini using a rechargeable lithium-ion or lithium-polymer battery, making it ideal for portable and low-power IoT applications. The shield includes a battery connector, charging circuitry, and a USB port for charging the connected battery.
Explore Projects Built with Wemos D1 battery shield
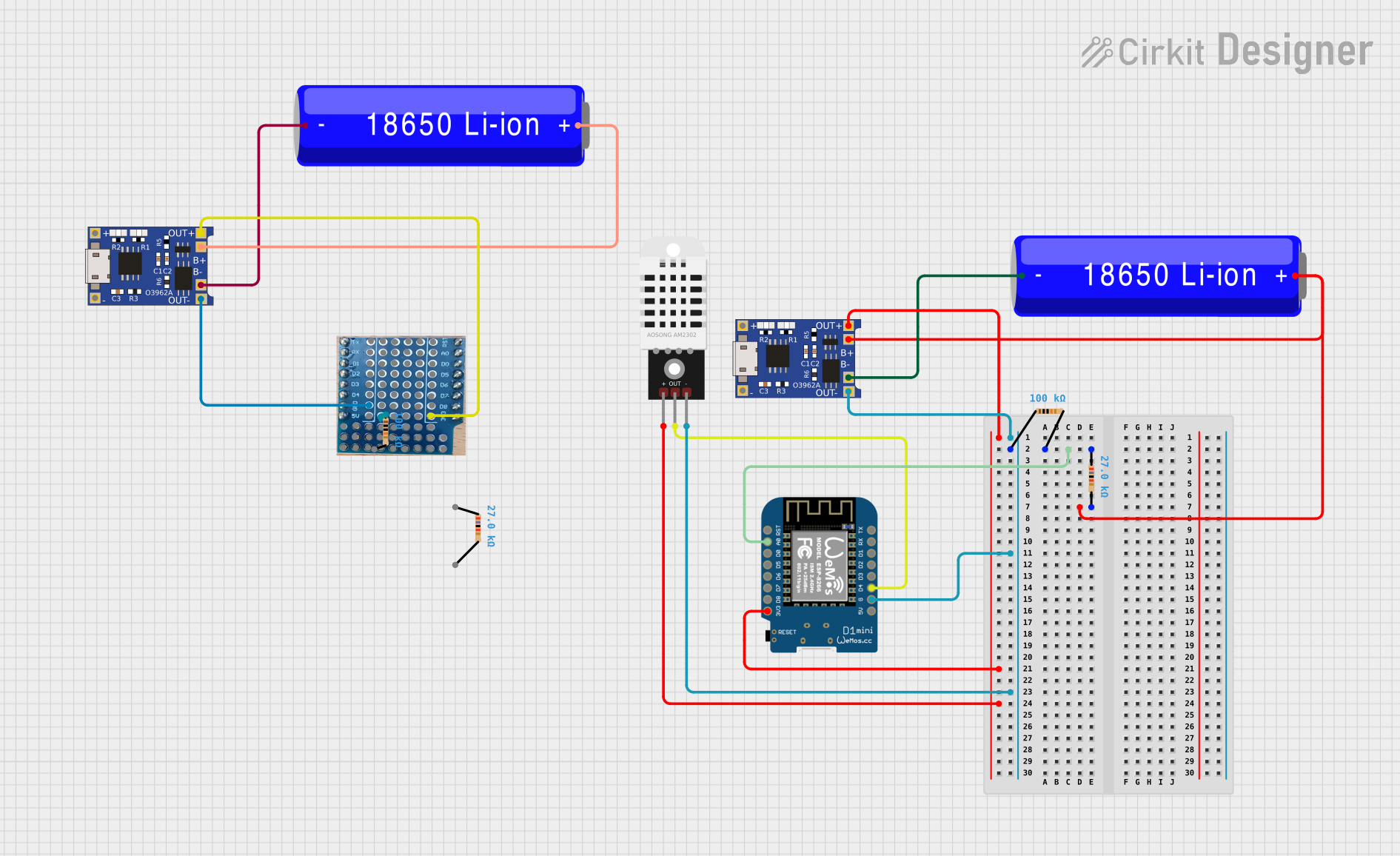
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer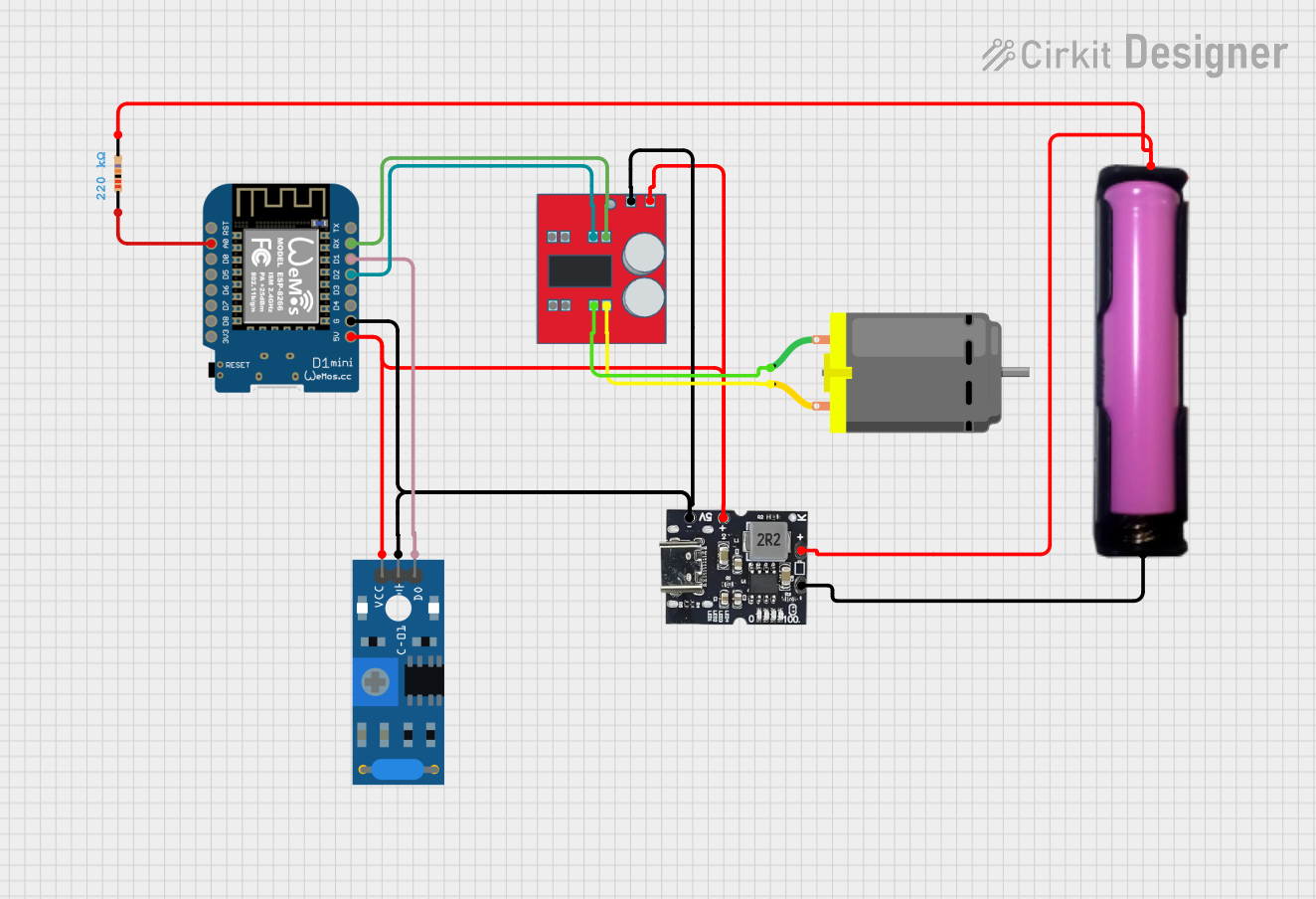
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer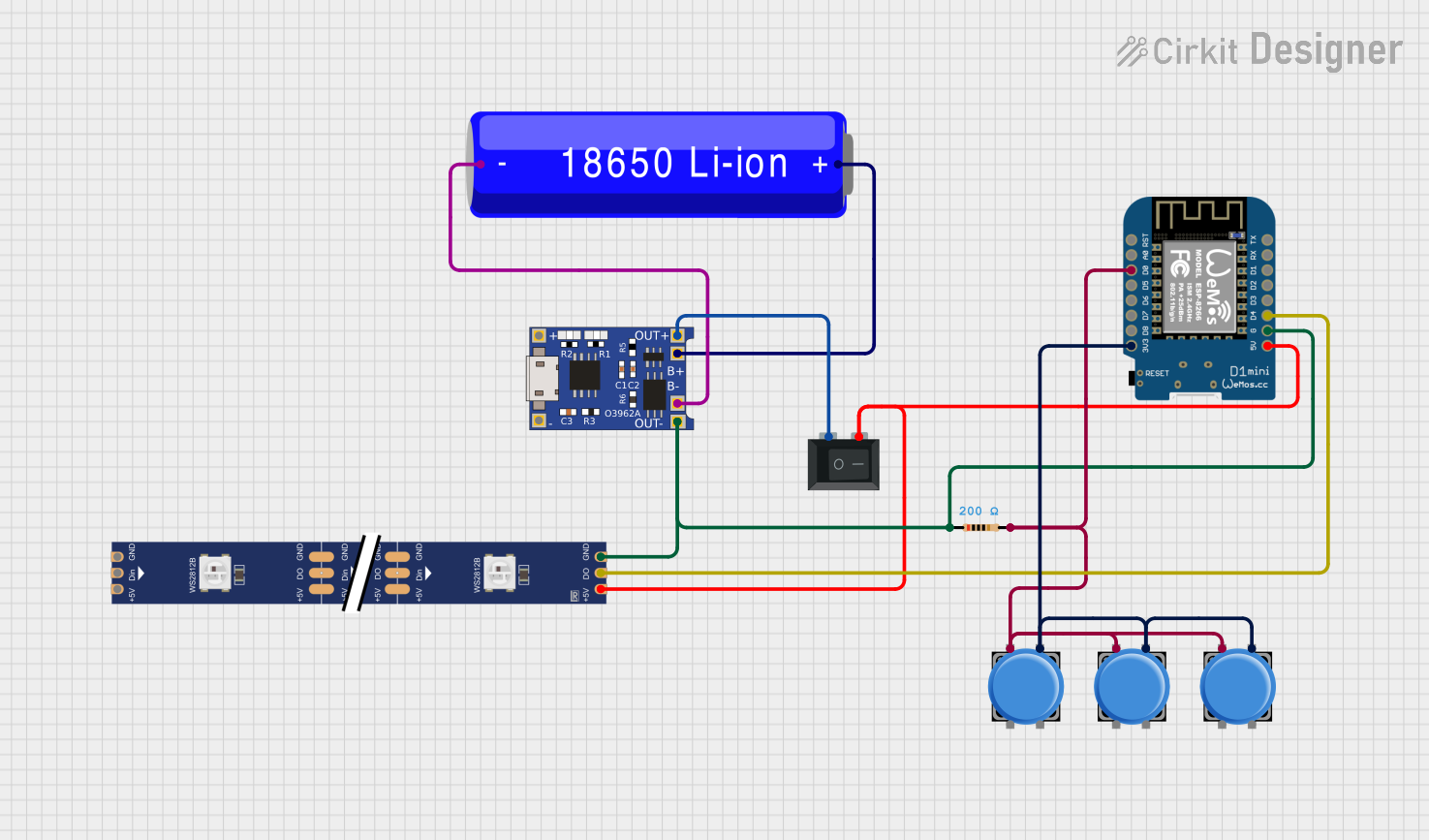
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer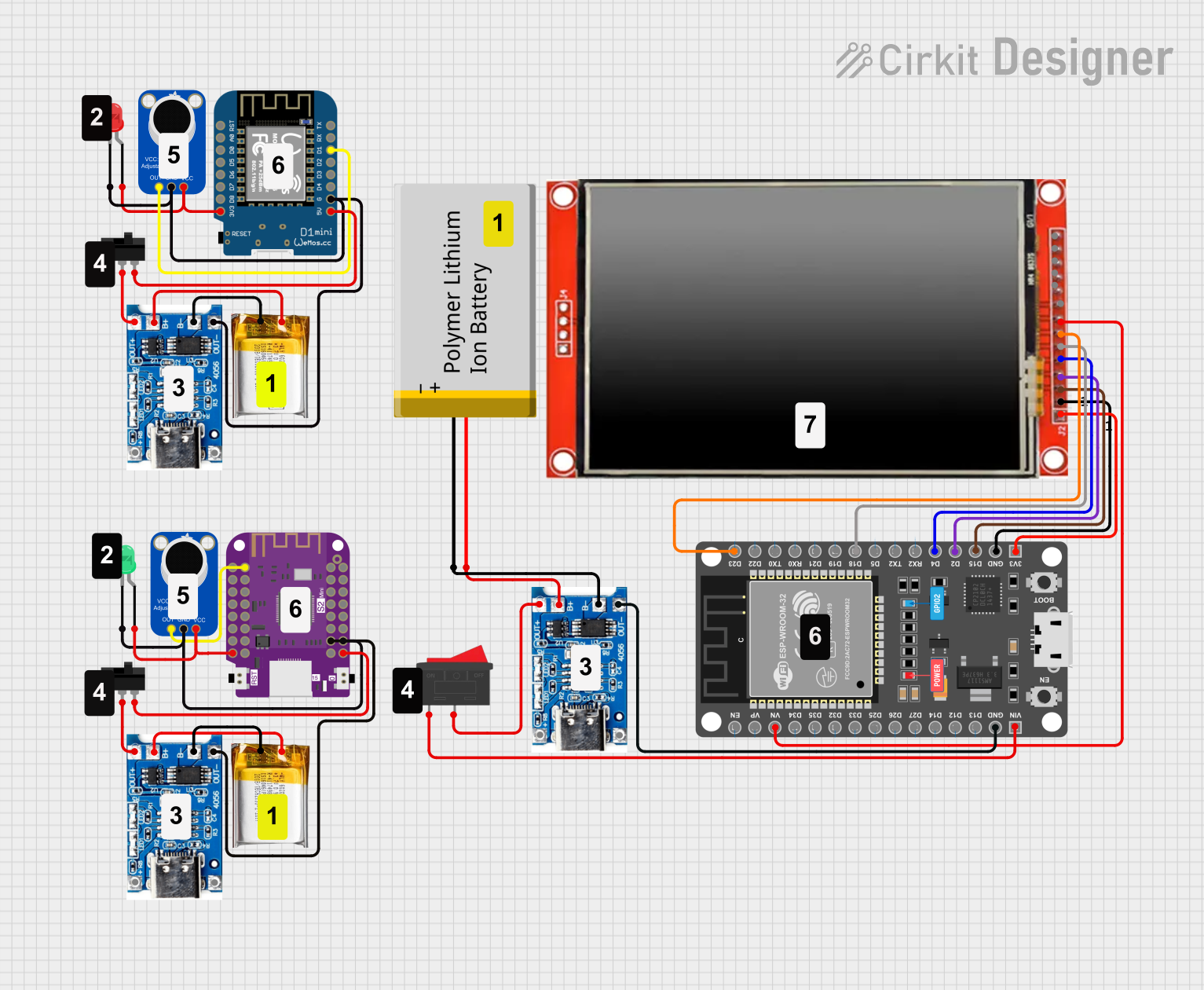
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Wemos D1 battery shield

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Portable IoT devices and projects
- Battery-powered sensor nodes
- Wearable electronics
- Remote monitoring systems
- Prototyping low-power wireless applications
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Wemos D1 Battery Shield:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage (USB) | 5V (via Micro-USB port) |
| Battery Type | Lithium-ion or Lithium-polymer (LiPo) |
| Battery Connector | JST 2.0 (PH2.0) |
| Charging Current | 500mA (default) |
| Output Voltage | 3.3V or 5V (regulated) |
| Output Current | Up to 1A |
| Charging Indicator LEDs | Red (charging), Blue (fully charged) |
| Dimensions | 34.2mm x 25.6mm x 8mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Wemos D1 Battery Shield has a simple pin layout that matches the Wemos D1 Mini. Below is a table describing the key pins:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 5V | Provides a regulated 5V output from the battery or USB input. |
| 3V3 | Provides a regulated 3.3V output from the battery or USB input. |
| GND | Ground connection. |
| BAT | Direct connection to the battery's positive terminal. |
| USB | Direct connection to the USB input voltage (5V). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Wemos D1 Battery Shield in a Circuit
- Connect a Battery: Attach a compatible lithium-ion or lithium-polymer battery to the JST 2.0 connector on the shield.
- Stack the Shield: Place the Wemos D1 Battery Shield on top of the Wemos D1 Mini, ensuring the pins align correctly.
- Power the Board: The shield will automatically supply power to the Wemos D1 Mini from the connected battery or USB input.
- Charge the Battery: Connect a 5V power source (e.g., a USB charger) to the Micro-USB port on the shield to charge the battery. The red LED will light up during charging, and the blue LED will light up when the battery is fully charged.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Selection: Use only lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries with a nominal voltage of 3.7V and a JST 2.0 connector.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the maximum output current of 1A to prevent damage to the shield or battery.
- Heat Management: Ensure proper ventilation during charging to avoid overheating.
- Polarity Check: Double-check the battery polarity before connecting it to the shield to prevent damage.
- Stacking Order: If using multiple shields, ensure the Battery Shield is stacked at the bottom to provide power to the entire stack.
Example: Using the Wemos D1 Battery Shield with Arduino UNO Code
The Wemos D1 Mini can be programmed using the Arduino IDE. Below is an example code snippet to read the battery voltage using the BAT pin:
// Example code to read battery voltage on Wemos D1 Mini
// Ensure the BAT pin is connected to an analog input pin (e.g., A0).
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication at 115200 baud
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(A0); // Read the analog value from the BAT pin
float voltage = (rawValue / 1023.0) * 3.3 * 2;
// Convert raw value to voltage. Multiply by 2 due to voltage divider.
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: The Wemos D1 Mini has a built-in voltage divider on the A0 pin, so the input voltage is scaled down by a factor of 2. Adjust the calculation accordingly.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Faulty battery or incorrect connection.
- Solution: Verify the battery polarity and ensure it is securely connected to the JST 2.0 connector.
No Power Output
- Cause: Battery is depleted or not connected.
- Solution: Charge the battery using the Micro-USB port or check the battery connection.
Overheating During Charging
- Cause: Insufficient ventilation or high ambient temperature.
- Solution: Ensure proper airflow around the shield and avoid charging in hot environments.
Incorrect Voltage Readings
- Cause: Miscalculation in the voltage divider formula.
- Solution: Double-check the formula and ensure the correct scaling factor is applied.
FAQs
Can I use the shield without a battery? Yes, the shield can power the Wemos D1 Mini directly from the USB input without a battery.
What happens if both USB and battery are connected? The shield will prioritize USB power for the Wemos D1 Mini and charge the battery simultaneously.
Can I use a different type of battery? No, only lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries with a nominal voltage of 3.7V are supported.
What is the maximum battery capacity supported? There is no strict limit on capacity, but charging time will increase with higher-capacity batteries.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Wemos D1 Battery Shield into your projects and ensure reliable performance.