
How to Use 5v DC Power Supply: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 5v DC Power Supply in Cirkit Designer
Design with 5v DC Power Supply in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 5V DC Power Supply is a device designed to convert AC voltage from the mains into a stable 5V DC output. It is widely used in powering electronic circuits, microcontrollers, sensors, and other low-voltage devices. This component ensures a reliable and consistent power source, making it an essential part of many electronic projects and systems.
Explore Projects Built with 5v DC Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer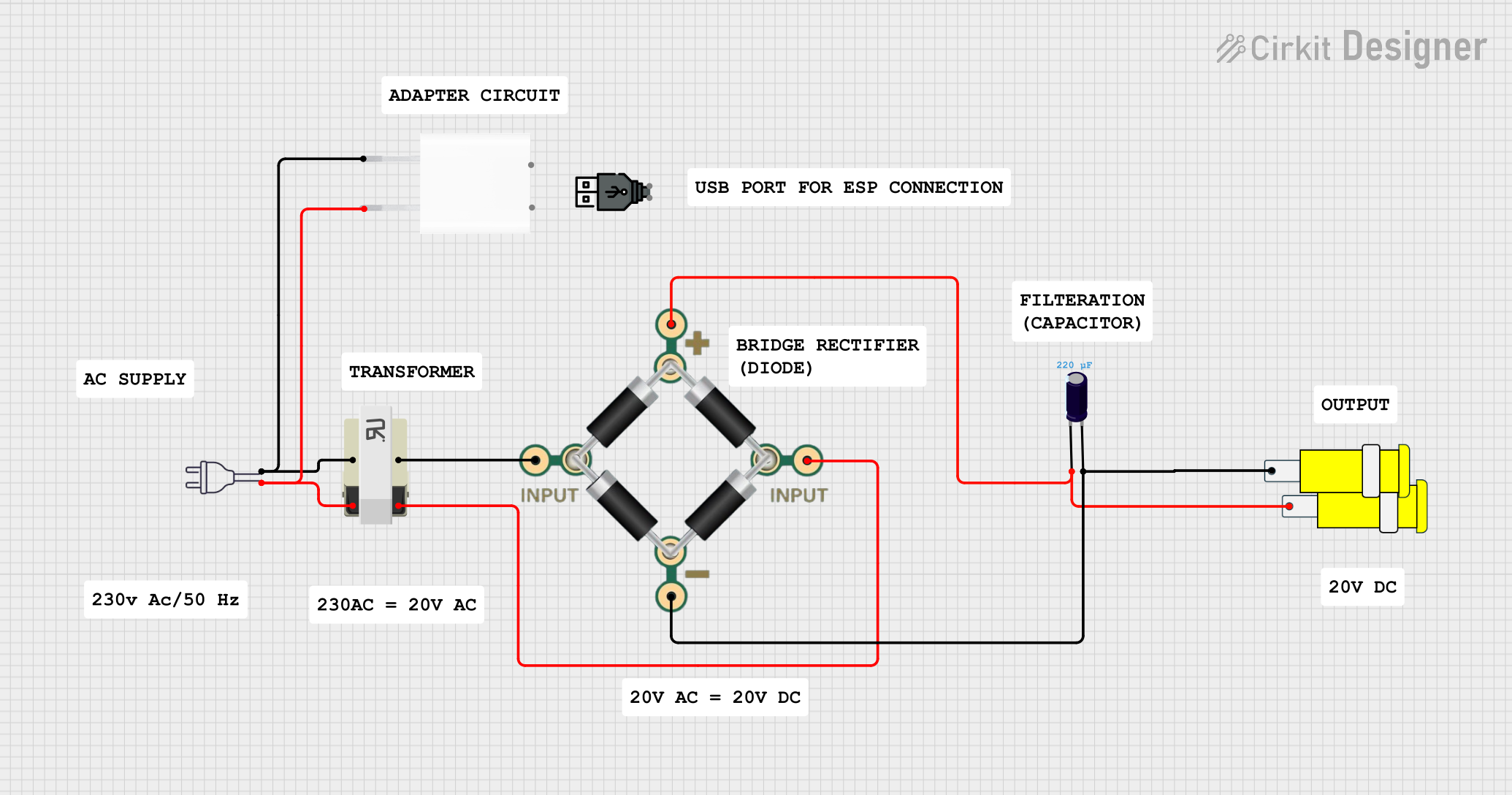
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 5v DC Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and ESP32
- Supplying power to sensors, modules, and small electronic devices
- Charging USB-powered devices
- Providing a stable voltage source for prototyping and testing circuits
- Used in embedded systems and IoT applications
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the 5V DC Power Supply:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 100-240V AC (50/60Hz) |
| Output Voltage | 5V DC |
| Output Current | Typically 1A to 3A (varies by model) |
| Power Rating | 5W to 15W (depending on current) |
| Efficiency | ≥ 80% |
| Ripple and Noise | ≤ 50mV |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to 50°C |
| Storage Temperature | -20°C to 85°C |
| Protection Features | Overload, short circuit, overvoltage |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 5V DC Power Supply typically has the following connections:
| Pin/Connector | Description |
|---|---|
| AC Input (L, N) | Live (L) and Neutral (N) terminals for AC mains input |
| Ground (GND) | Ground connection for the DC output |
| DC Output (+5V) | Positive 5V DC output terminal |
For USB-based 5V DC power supplies, the pinout is as follows:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| VBUS | +5V DC output |
| GND | Ground connection |
| D+ | Data line (not used for power) |
| D- | Data line (not used for power) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 5V DC Power Supply in a Circuit
Connect the AC Input:
- Ensure the power supply is rated for your local mains voltage (e.g., 110V or 220V).
- Connect the Live (L) and Neutral (N) terminals to the AC mains using appropriate wiring.
- If the power supply has a plug, simply connect it to a wall socket.
Connect the DC Output:
- Identify the positive (+5V) and ground (GND) terminals on the power supply.
- Connect the +5V terminal to the positive power rail of your circuit.
- Connect the GND terminal to the ground rail of your circuit.
Power On:
- Turn on the power supply (if it has a switch) or plug it into the mains.
- Verify the output voltage using a multimeter before connecting sensitive devices.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Check the Current Rating: Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current for your circuit. Exceeding the rated current may cause overheating or damage.
- Avoid Short Circuits: Double-check all connections to prevent short circuits, which can damage the power supply and connected devices.
- Use Proper Heat Dissipation: If the power supply operates at high currents, ensure adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Isolation: For safety, use an isolated power supply to avoid electrical shocks or interference with other devices.
- Fuse Protection: Consider adding a fuse on the AC input side for additional protection.
Example: Using with an Arduino UNO
The 5V DC Power Supply can be used to power an Arduino UNO via its 5V pin. Below is an example of how to connect it:
- Connect the +5V output of the power supply to the 5V pin on the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the GND output of the power supply to the GND pin on the Arduino UNO.
Sample Arduino Code
// Example code to blink an LED using an Arduino UNO powered by a 5V DC power supply
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: The power supply is not connected to the mains or the input voltage is incorrect.
- Solution: Verify the AC input connections and ensure the mains voltage matches the power supply's input rating.
Output Voltage Too Low or Unstable:
- Cause: The load exceeds the power supply's current rating.
- Solution: Reduce the load or use a power supply with a higher current rating.
Overheating:
- Cause: Insufficient ventilation or excessive load.
- Solution: Ensure proper airflow around the power supply and reduce the load if necessary.
Short Circuit Protection Triggered:
- Cause: A short circuit in the connected circuit.
- Solution: Inspect the circuit for wiring errors and fix any shorts before reconnecting the power supply.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this power supply to charge a USB device?
A: Yes, if the power supply has a USB output or you use a USB adapter, it can charge USB devices that require 5V.
Q: Is it safe to leave the power supply on for extended periods?
A: Yes, as long as the power supply is operating within its rated specifications and has proper ventilation.
Q: Can I use this power supply with a breadboard?
A: Yes, you can connect the +5V and GND outputs to the power rails of a breadboard to power your circuit.
Q: What happens if I connect a device that requires more than the rated current?
A: The power supply may shut down, overheat, or become damaged. Always ensure the load does not exceed the power supply's current rating.