
How to Use TIP-122: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TIP-122 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TIP-122 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TIP-122 is a high-power NPN Darlington transistor manufactured by STMicroelectronics. It is designed for use in switching and amplification applications, capable of handling high currents and voltages. The TIP-122 is particularly well-suited for driving motors, solenoids, and other high-power devices in industrial and hobbyist projects.
Explore Projects Built with TIP-122
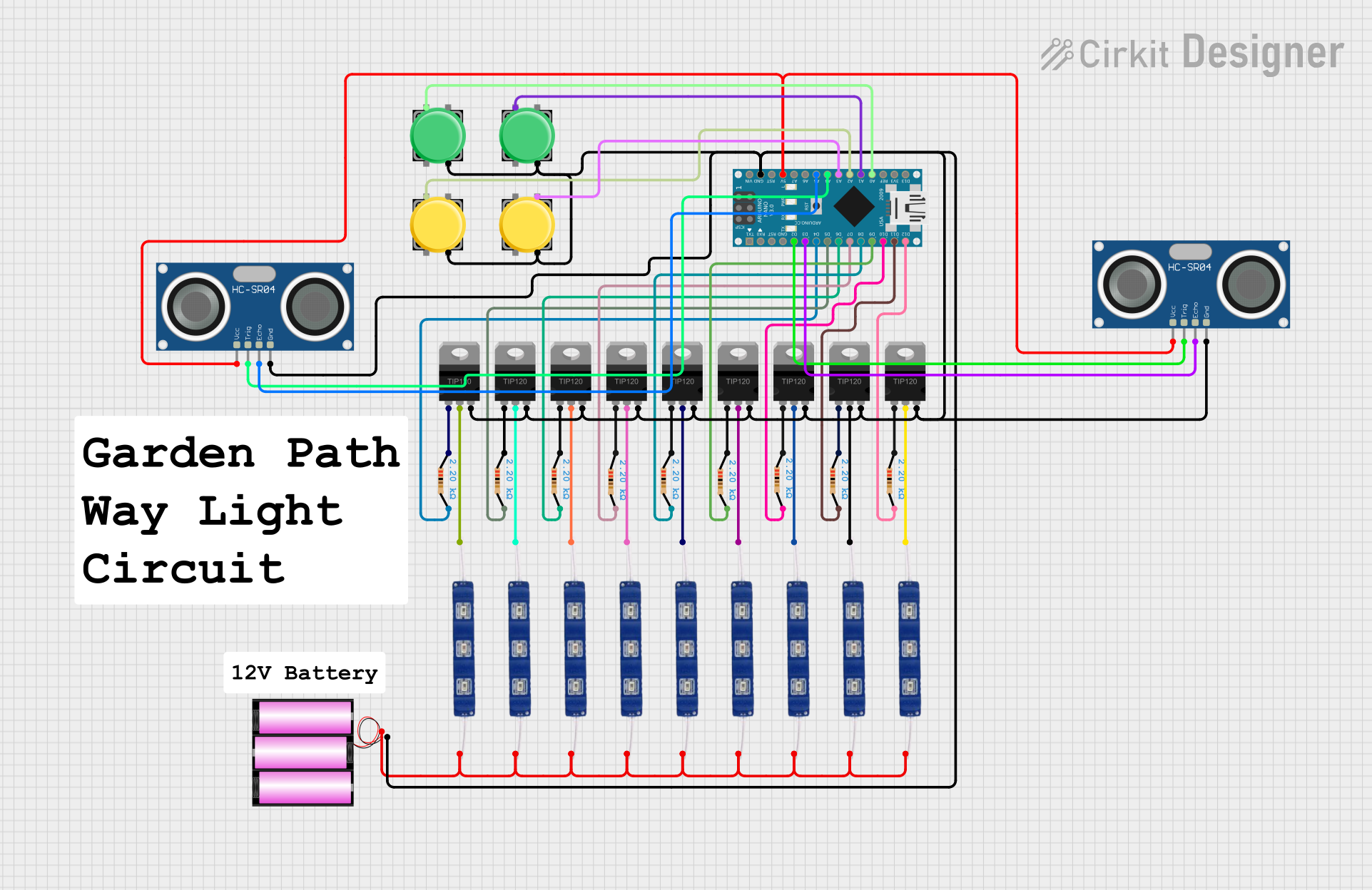
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer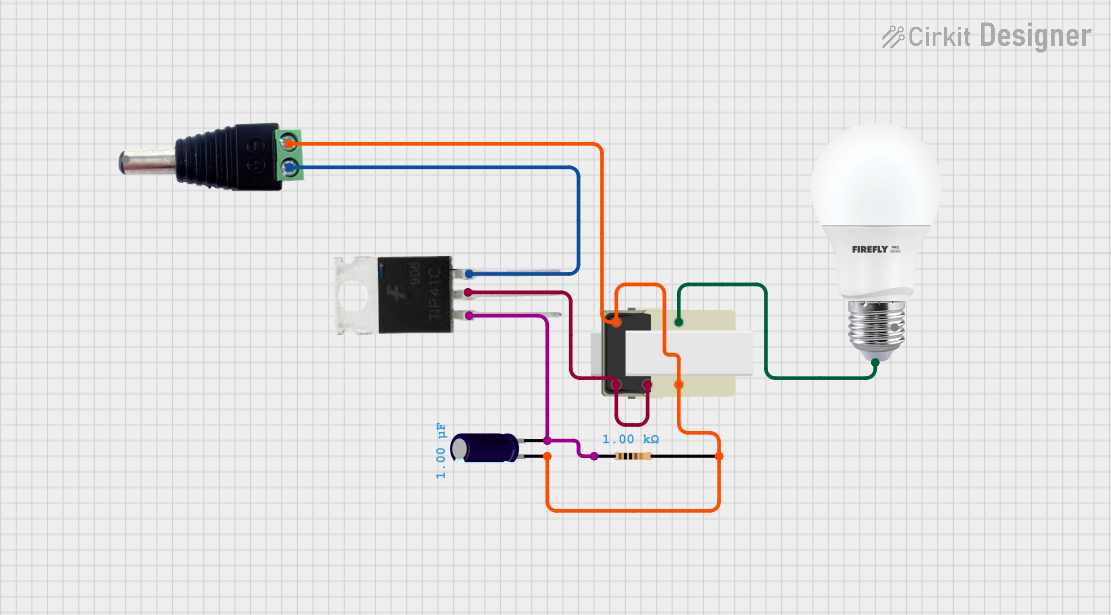
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer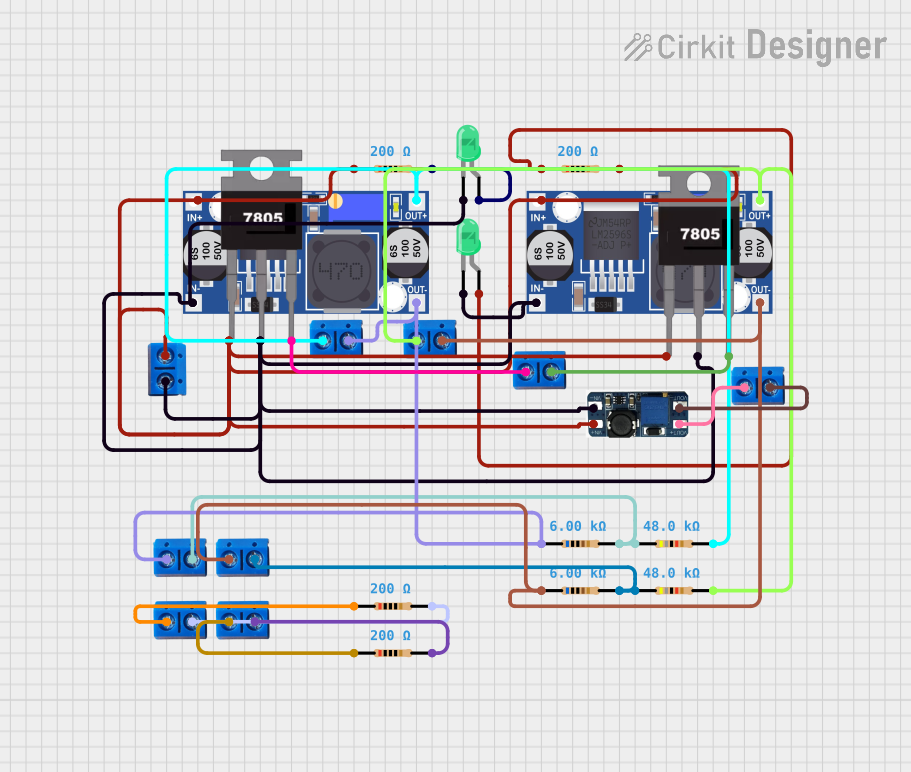
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TIP-122

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Motor control and speed regulation
- Solenoid and relay driving
- High-power LED driving
- Audio amplification
- General-purpose switching in high-current circuits
Technical Specifications
The TIP-122 is a robust component with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Part ID | TIP122 |
| Transistor Type | NPN Darlington |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 100V |
| Maximum Collector Current (IC) | 5A |
| Maximum Base Current (IB) | 120mA |
| Maximum Power Dissipation (PD) | 65W |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 1000 (minimum) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -65°C to +150°C |
| Package Type | TO-220 |
Pin Configuration
The TIP-122 is housed in a TO-220 package with three pins. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base (B) | Controls the transistor's operation |
| 2 | Collector (C) | Current flows into this pin |
| 3 | Emitter (E) | Current flows out of this pin |
Usage Instructions
The TIP-122 is straightforward to use in circuits, but proper design considerations are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
How to Use the TIP-122 in a Circuit
Base Resistor: Always use a base resistor to limit the current flowing into the base pin. The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law: [ R_B = \frac{V_{IN} - V_{BE}}{I_B} ] where ( V_{IN} ) is the input voltage, ( V_{BE} ) is the base-emitter voltage (approximately 2.5V for the TIP-122), and ( I_B ) is the desired base current.
Heat Dissipation: The TIP-122 can dissipate up to 65W of power. For high-power applications, attach a heatsink to the TO-220 package to prevent overheating.
Load Connection: Connect the load (e.g., motor, LED, or relay) between the collector pin and the positive supply voltage. The emitter pin should be connected to ground.
Switching: To turn the transistor on, apply a sufficient voltage to the base pin. To turn it off, ensure the base pin is at 0V.
Example: Controlling a Motor with Arduino UNO
The TIP-122 can be used to control a DC motor with an Arduino UNO. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the motor's positive terminal to the collector pin of the TIP-122.
- Connect the emitter pin to ground.
- Connect the base pin to an Arduino digital pin (e.g., D9) through a 1kΩ resistor.
- Connect a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4007) across the motor terminals to protect the transistor from voltage spikes.
Arduino Code
// TIP-122 Motor Control Example
// This code demonstrates how to control a motor using the TIP-122 transistor
// and an Arduino UNO. The motor speed is controlled via PWM.
const int motorPin = 9; // TIP-122 base connected to pin D9 through a resistor
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT); // Set motorPin as an output
}
void loop() {
// Gradually increase motor speed
for (int speed = 0; speed <= 255; speed++) {
analogWrite(motorPin, speed); // Write PWM signal to motorPin
delay(10); // Small delay for smooth acceleration
}
delay(1000); // Run motor at full speed for 1 second
// Gradually decrease motor speed
for (int speed = 255; speed >= 0; speed--) {
analogWrite(motorPin, speed); // Write PWM signal to motorPin
delay(10); // Small delay for smooth deceleration
}
delay(1000); // Pause before repeating the cycle
}
Important Considerations
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum voltage (100V) or current (5A) ratings to avoid damaging the transistor.
- Flyback Diode: Always use a flyback diode when driving inductive loads (e.g., motors or relays) to protect the TIP-122 from voltage spikes.
- Heatsink: Use a heatsink for high-power applications to prevent overheating.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Transistor Overheating
- Cause: Excessive power dissipation or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Attach a heatsink to the TIP-122 and ensure proper ventilation.
Motor Not Running
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient base current.
- Solution: Double-check the circuit connections and ensure the base resistor value is appropriate.
Low Output Current
- Cause: Insufficient base drive or damaged transistor.
- Solution: Verify the base resistor value and replace the transistor if necessary.
Voltage Spikes Damaging the Transistor
- Cause: Inductive load without a flyback diode.
- Solution: Add a flyback diode across the load terminals.
FAQs
Q: Can the TIP-122 be used for audio amplification?
A: Yes, the TIP-122 can be used in audio amplifier circuits, but it is more commonly used for switching applications due to its high current handling capability.
Q: What is the difference between the TIP-122 and TIP-120?
A: The TIP-122 has a slightly higher current gain (hFE) compared to the TIP-120, making it more efficient in certain applications.
Q: Can I use the TIP-122 without a heatsink?
A: For low-power applications, a heatsink may not be necessary. However, for high-power applications, a heatsink is essential to prevent overheating.
Q: What is the maximum PWM frequency for the TIP-122?
A: The TIP-122 can handle PWM frequencies up to a few kHz. For higher frequencies, consider using a MOSFET instead.