
How to Use Optocoupler 4n35: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
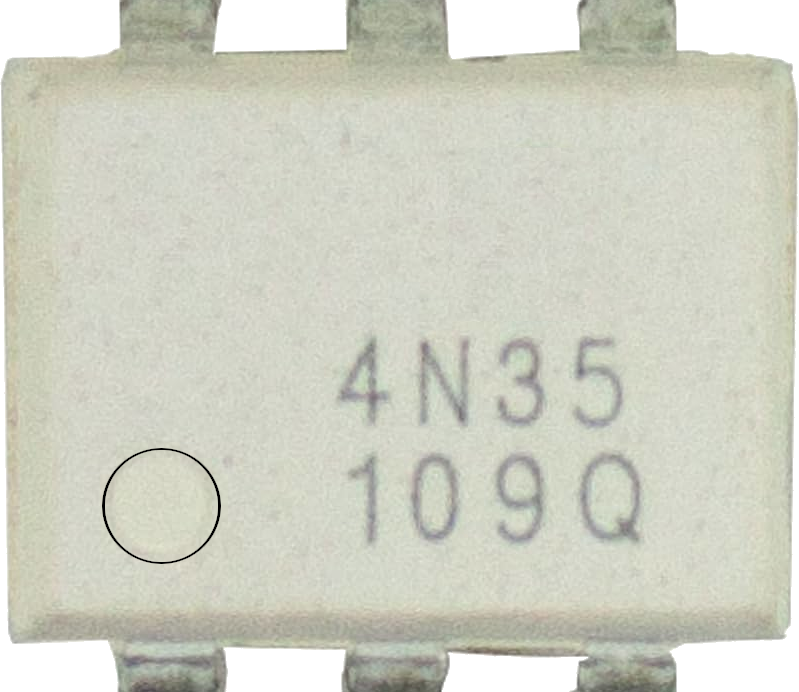
 Design with Optocoupler 4n35 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Optocoupler 4n35 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Optocoupler 4N35 is an optoelectronic device that uses light to transfer electrical signals between two isolated circuits. It consists of an infrared LED and a phototransistor housed in a single package. This design allows for electrical isolation between the input and output, making it ideal for protecting sensitive components from high voltages or noisy signals.
Explore Projects Built with Optocoupler 4n35
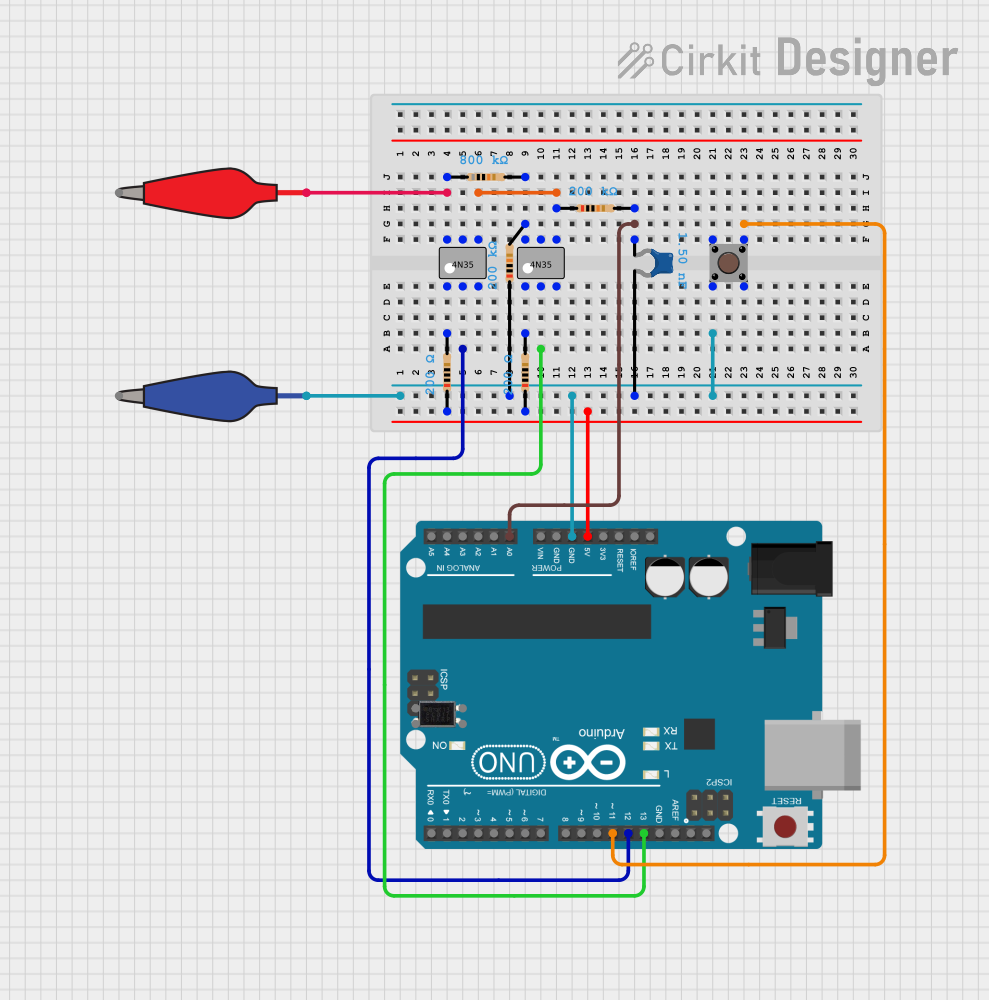
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer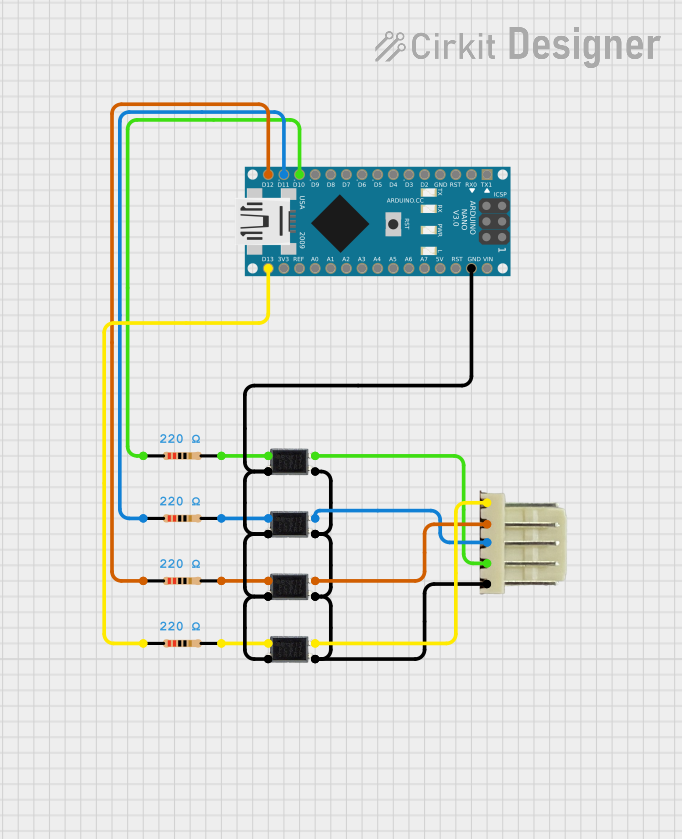
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer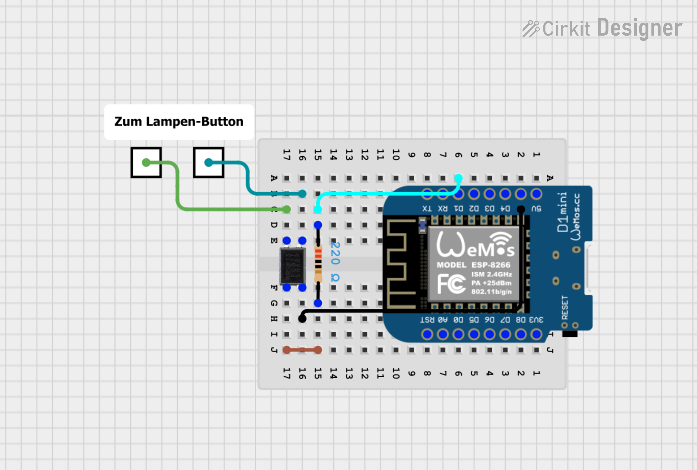
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer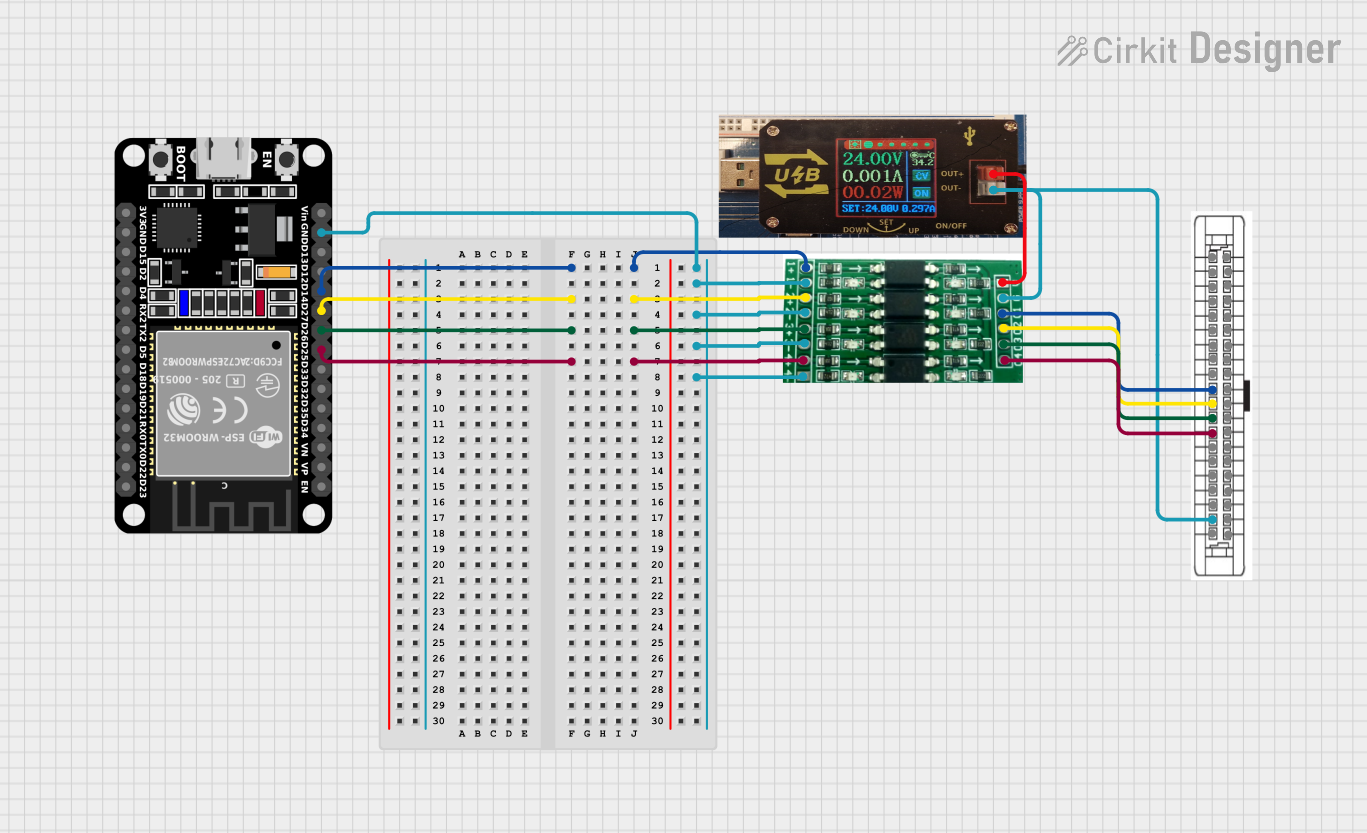
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Optocoupler 4n35

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Signal isolation in microcontroller circuits
- Protection of low-voltage circuits from high-voltage systems
- Noise suppression in industrial control systems
- Data communication between systems with different ground potentials
- Motor control and power supply circuits
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the 4N35 optocoupler:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input LED Forward Voltage | 1.2V (typical), 1.5V (maximum) |
| Input LED Forward Current | 10mA (typical), 50mA (maximum) |
| Output Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE) | 30V (maximum) |
| Output Collector Current | 100mA (maximum) |
| Current Transfer Ratio (CTR) | 100% to 200% |
| Isolation Voltage | 5000V RMS |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to +100°C |
| Package Type | 6-pin DIP |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 4N35 optocoupler has a 6-pin Dual Inline Package (DIP). The pinout is as follows:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode (A) | Positive terminal of the internal LED. Connect to the input signal. |
| 2 | Cathode (K) | Negative terminal of the internal LED. Connect to ground or the return path. |
| 3 | NC (No Connect) | Not connected internally. Leave unconnected or use for mechanical stability. |
| 4 | Emitter (E) | Emitter of the phototransistor. Connect to the output circuit. |
| 5 | Collector (C) | Collector of the phototransistor. Connect to the output circuit. |
| 6 | Base (B) | Base of the phototransistor. Typically left unconnected for normal operation. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 4N35 in a Circuit
Input Side (LED):
- Connect the anode (Pin 1) to the positive side of the input signal through a current-limiting resistor.
- Connect the cathode (Pin 2) to ground or the return path of the input circuit.
- Calculate the resistor value to limit the LED current to 10mA (typical). Use the formula: [ R = \frac{V_{in} - V_f}{I_f} ] where ( V_{in} ) is the input voltage, ( V_f ) is the forward voltage of the LED (1.2V), and ( I_f ) is the desired forward current (e.g., 10mA).
Output Side (Phototransistor):
- Connect the collector (Pin 5) to the positive supply voltage of the output circuit through a pull-up resistor.
- Connect the emitter (Pin 4) to ground.
- The pull-up resistor value depends on the desired output current and voltage levels.
Isolation:
- Ensure that the input and output circuits share no direct electrical connection to maintain isolation.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the 4N35 optocoupler to isolate a digital input signal for an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Diagram
- Input Side:
- Connect a 5V signal to the anode (Pin 1) through a 470Ω resistor.
- Connect the cathode (Pin 2) to ground.
- Output Side:
- Connect the collector (Pin 5) to the Arduino's 5V pin through a 10kΩ pull-up resistor.
- Connect the emitter (Pin 4) to the Arduino's ground.
- Connect the collector (Pin 5) to a digital input pin (e.g., D2) on the Arduino.
Arduino Code
// Example code for using the 4N35 optocoupler with Arduino UNO
const int optoInputPin = 2; // Digital pin connected to the optocoupler output
void setup() {
pinMode(optoInputPin, INPUT); // Set the optocoupler output pin as input
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int optoState = digitalRead(optoInputPin); // Read the optocoupler output state
// Print the state to the Serial Monitor
if (optoState == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Input signal is HIGH");
} else {
Serial.println("Input signal is LOW");
}
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before reading again
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a current-limiting resistor on the LED side to prevent damage.
- Ensure the pull-up resistor on the phototransistor side is appropriately sized for your circuit.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum voltage and current ratings to prevent permanent damage.
- For high-speed applications, consider the switching speed of the optocoupler, as it may introduce delays.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Check the input LED circuit. Ensure the current-limiting resistor is correctly calculated and the LED is forward-biased.
- Verify the pull-up resistor on the output side is connected properly.
Output Signal is Always HIGH or LOW:
- Ensure the input signal is within the operating range of the LED.
- Check for loose connections or incorrect wiring.
Slow Response Time:
- The 4N35 is not designed for high-speed applications. If faster switching is required, consider using a high-speed optocoupler.
Excessive Heat:
- Ensure the input and output currents do not exceed the maximum ratings.
- Verify that the circuit design includes appropriate resistors to limit current.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the 4N35 for AC signal isolation?
A: Yes, the 4N35 can be used for AC signal isolation, but you will need to use a rectifier circuit on the input side to drive the LED.
Q: What is the purpose of the base pin (Pin 6)?
A: The base pin is typically left unconnected in most applications. However, it can be used to control the phototransistor's gain if needed.
Q: Can the 4N35 handle high voltages?
A: The 4N35 provides isolation up to 5000V RMS, but the phototransistor side is limited to a maximum collector-emitter voltage of 30V.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the 4N35 optocoupler in your electronic projects for signal isolation and protection.