
How to Use 3P Breaker: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 3P Breaker in Cirkit Designer
Design with 3P Breaker in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 3P (three-pole) breaker is a protective device designed to safeguard electrical circuits by interrupting the flow of current in the event of an overload or short circuit. It is specifically engineered for three-phase systems, which are commonly used in industrial, commercial, and large-scale residential applications. The 3P breaker ensures the safety of equipment and personnel by isolating all three phases simultaneously when a fault is detected.
Explore Projects Built with 3P Breaker
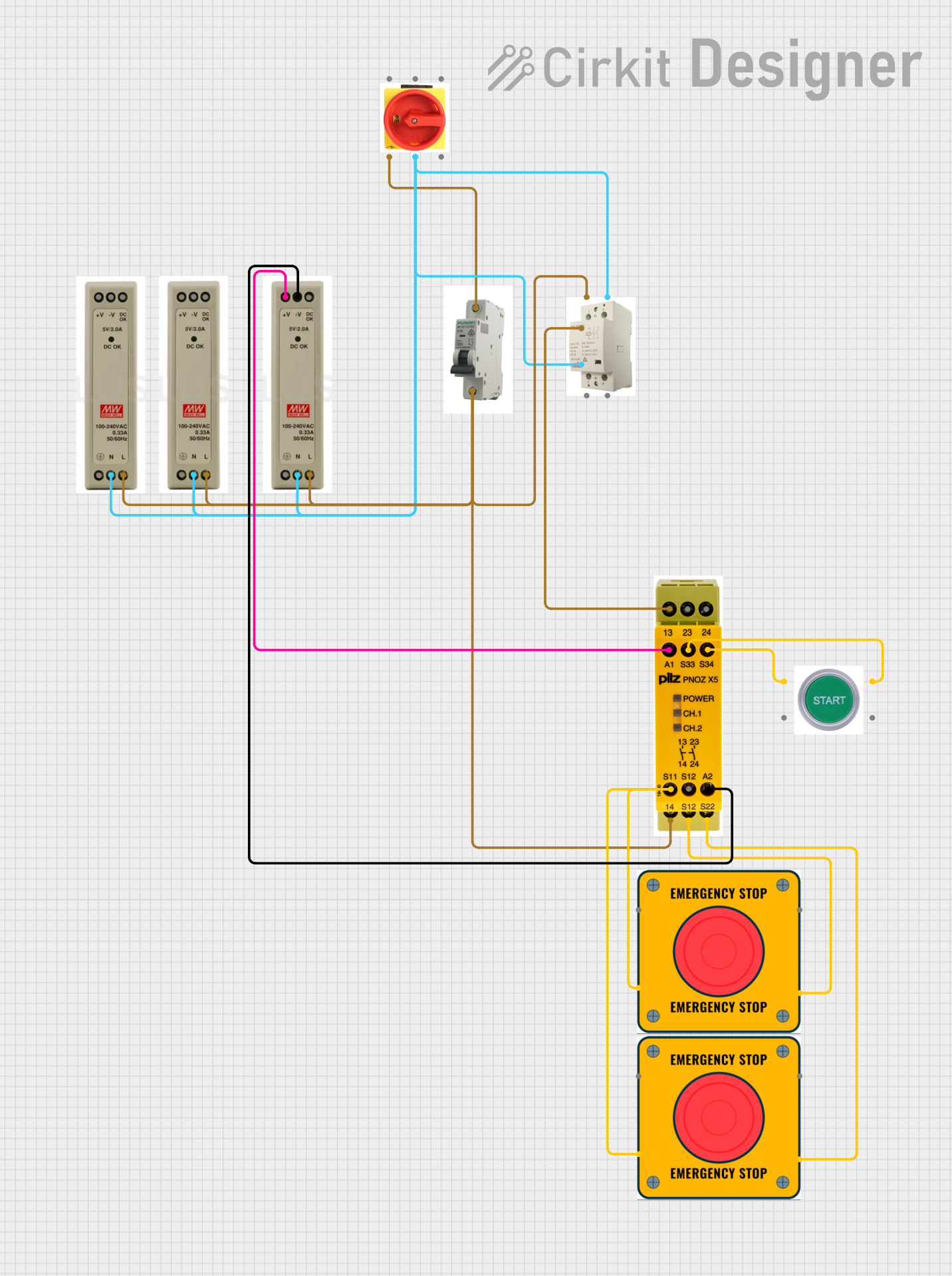
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer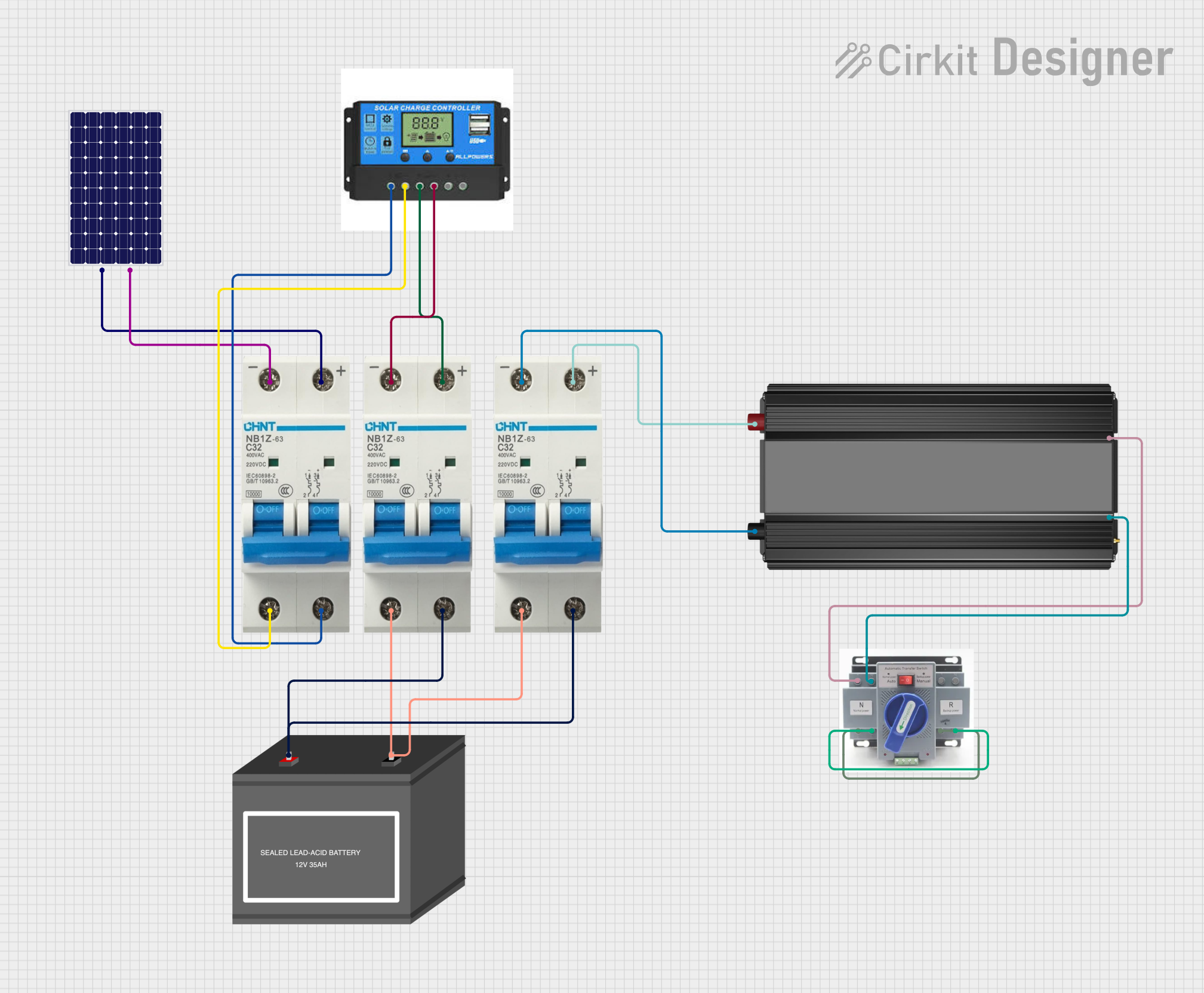
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer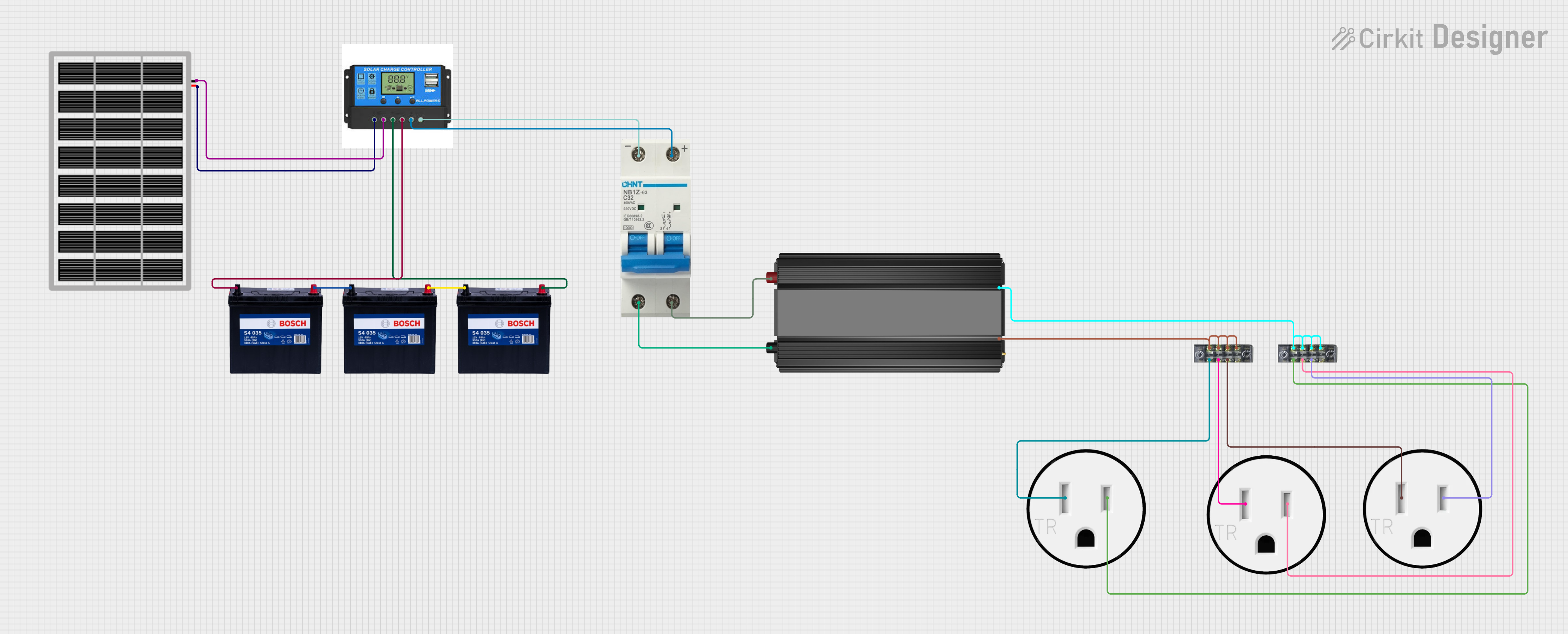
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer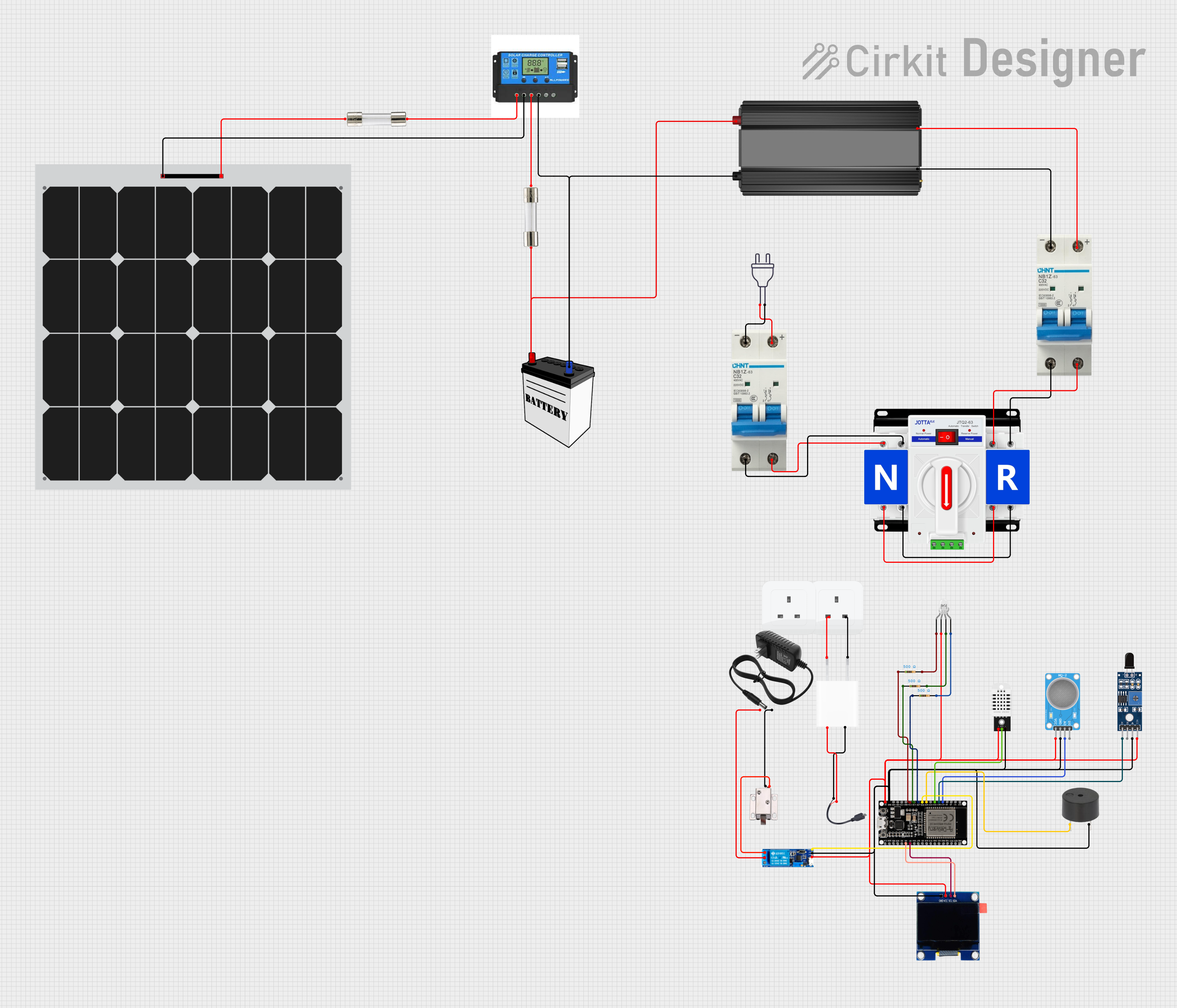
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 3P Breaker

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Protection of three-phase motors and machinery
- Distribution panel protection in industrial and commercial buildings
- Safeguarding HVAC systems and large electrical appliances
- Overload and short-circuit protection in three-phase power systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a typical 3P breaker:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 400V AC (typical for three-phase systems) |
| Rated Current | 10A to 125A (varies by model) |
| Breaking Capacity | 6kA to 50kA (depending on application) |
| Number of Poles | 3 |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Trip Mechanism | Thermal-magnetic or electronic |
| Mounting Type | DIN rail or panel-mounted |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
| Standards Compliance | IEC 60947-2, UL 489 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 3P breaker has three input terminals and three output terminals, corresponding to the three phases of the electrical system.
| Terminal Label | Description |
|---|---|
| L1 (Input) | Phase 1 input terminal |
| L2 (Input) | Phase 2 input terminal |
| L3 (Input) | Phase 3 input terminal |
| T1 (Output) | Phase 1 output terminal |
| T2 (Output) | Phase 2 output terminal |
| T3 (Output) | Phase 3 output terminal |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 3P Breaker in a Circuit
- Determine the Specifications: Select a 3P breaker with the appropriate voltage, current, and breaking capacity for your application.
- Mount the Breaker: Install the breaker on a DIN rail or panel, ensuring it is securely fastened.
- Connect the Input Terminals: Connect the three-phase power supply to the input terminals (L1, L2, L3) of the breaker.
- Connect the Output Terminals: Connect the load (e.g., motor, equipment) to the output terminals (T1, T2, T3).
- Test the Circuit: After installation, test the circuit to ensure proper operation and that the breaker trips under fault conditions.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Select the Correct Breaker: Ensure the breaker’s rated current and breaking capacity match the requirements of your system.
- Proper Wiring: Use appropriately rated cables for the connections to avoid overheating or voltage drops.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically inspect the breaker for signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the rated current of the breaker to prevent nuisance tripping or damage.
- Safety First: Always disconnect power before installing or servicing the breaker.
Example: Connecting a 3P Breaker to an Arduino-Controlled System
While a 3P breaker is not directly controlled by an Arduino, it can be used in conjunction with an Arduino-based monitoring system. For example, you can use current sensors to monitor the load and trigger an alert if the current exceeds a threshold.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_INA219.h>
// Create an INA219 current sensor object
Adafruit_INA219 ina219;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
// Wait for the serial connection to initialize
}
// Initialize the INA219 sensor
if (!ina219.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to find INA219 chip");
while (1) {
delay(10); // Halt if the sensor is not detected
}
}
Serial.println("INA219 sensor initialized.");
}
void loop() {
float current_mA = ina219.getCurrent_mA(); // Read current in milliamps
// Print the current reading to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current_mA);
Serial.println(" mA");
// Check if the current exceeds a safe threshold
if (current_mA > 1000) { // Example threshold: 1000 mA
Serial.println("Warning: Overcurrent detected!");
// Add code here to trigger an alert or take action
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Breaker trips frequently | Overload or short circuit in the system | Check the load and wiring for faults |
| Breaker does not trip during a fault | Faulty breaker or incorrect rating | Replace the breaker or verify ratings |
| Overheating of terminals | Loose connections or undersized cables | Tighten connections or use proper cables |
| Difficulty in mounting | Incompatible mounting type | Verify the mounting type (DIN rail or panel) |
FAQs
Can a 3P breaker be used in a single-phase system?
Yes, but it is not recommended as it is designed for three-phase systems. For single-phase systems, use a single-pole or double-pole breaker.What is the difference between thermal-magnetic and electronic trip mechanisms?
Thermal-magnetic breakers use a bimetallic strip and magnetic coil for tripping, while electronic breakers use sensors and microprocessors for precise control.How do I calculate the correct breaker size for my system?
Determine the total load current and select a breaker with a rated current slightly higher than the load, but within safe limits.Can I reset a tripped 3P breaker?
Yes, after addressing the fault, you can reset the breaker by switching it off and then back on.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use and maintain a 3P breaker in your electrical systems.