
How to Use TP4056: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
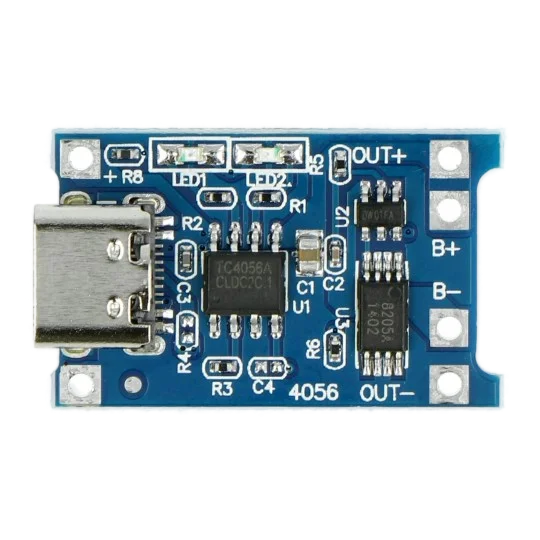
 Design with TP4056 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TP4056 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TP4056 is a lithium-ion battery charger IC designed to provide a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile. It is specifically tailored for charging single-cell lithium-ion batteries with high efficiency and safety. The IC integrates features such as over-voltage protection, under-voltage lockout, and thermal regulation, making it a reliable choice for battery charging applications.
Explore Projects Built with TP4056

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer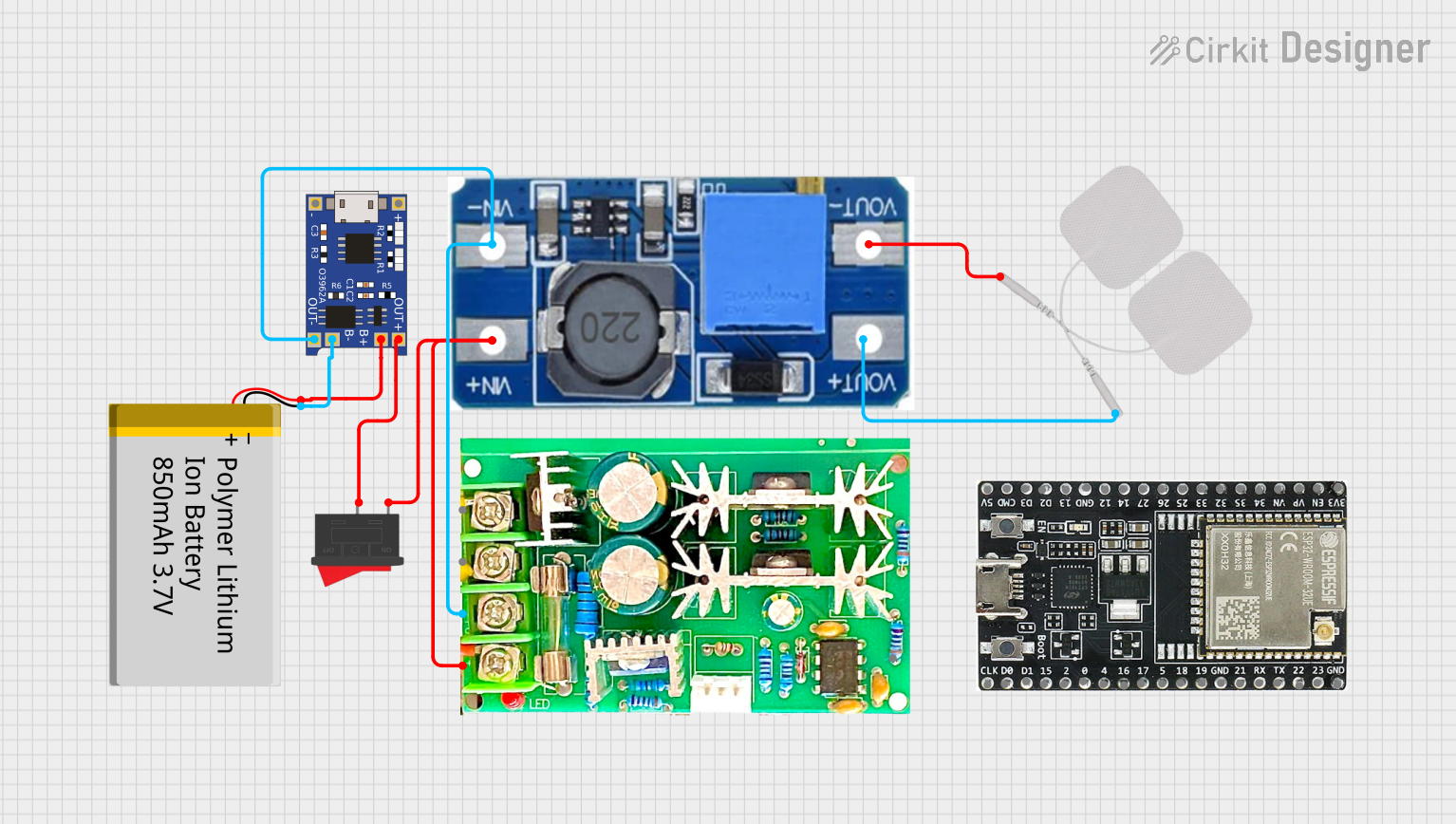
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TP4056

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries
- Power banks and portable battery packs
- USB-powered charging circuits
- Wearable devices and IoT gadgets
- DIY electronics projects
Technical Specifications
The TP4056 is a compact and efficient IC with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.0V to 8.0V |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2V ± 1% |
| Maximum Charging Current | 1A (adjustable via external resistor) |
| Charging Method | Constant Current/Constant Voltage (CC/CV) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Standby Current | < 2µA |
| Package Type | SOP-8 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TP4056 comes in an 8-pin SOP package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TEMP | Temperature sense input. Connect to an NTC thermistor for battery temperature monitoring. |
| 2 | PROG | Programs the charging current. Connect a resistor to ground to set the current. |
| 3 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the circuit ground. |
| 4 | VCC | Input supply voltage. Connect to a 4.0V–8.0V power source. |
| 5 | BAT | Battery connection pin. Connect directly to the positive terminal of the battery. |
| 6 | STDBY | Open-drain status output. Indicates charging status (low = charging, high = standby). |
| 7 | CHRG | Open-drain status output. Indicates charging in progress (low = charging). |
| 8 | CE | Chip enable. Active low. Pull low to enable the IC, or high to disable it. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TP4056 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect a 5V DC power source (e.g., USB) to the VCC pin. Ensure the input voltage is within the 4.0V–8.0V range.
- Battery Connection: Connect the positive terminal of the lithium-ion battery to the BAT pin and the negative terminal to GND.
- Programming Charging Current: Use a resistor (RPROG) between the PROG pin and GND to set the charging current. The charging current can be calculated using the formula: [ I_{CHG} = \frac{1200}{R_{PROG}} ] For example, a 1.2kΩ resistor sets the charging current to 1A.
- Status LEDs: Connect LEDs to the CHRG and STDBY pins (with appropriate current-limiting resistors) to indicate charging status:
- CHRG pin low: Charging in progress.
- STDBY pin low: Charging complete.
- Temperature Monitoring: Optionally, connect an NTC thermistor to the TEMP pin for battery temperature monitoring. If unused, connect TEMP to GND.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Thermal Management: Ensure proper heat dissipation, as the IC may heat up during high-current charging. Use a heat sink or adequate PCB copper area for thermal regulation.
- Battery Protection: Use a protection circuit module (PCM) with the battery to prevent over-discharge and over-current conditions.
- Input Voltage: Avoid exceeding the maximum input voltage of 8.0V to prevent damage to the IC.
- Current Limiting: Do not exceed the maximum charging current of 1A to ensure safe operation.
Example: Using TP4056 with Arduino UNO
The TP4056 can be used in conjunction with an Arduino UNO to monitor the charging status of a battery. Below is an example code snippet:
// TP4056 Status Monitoring with Arduino UNO
// Connect CHRG pin to Arduino pin 2 and STDBY pin to Arduino pin 3
#define CHRG_PIN 2 // CHRG pin of TP4056 connected to Arduino digital pin 2
#define STDBY_PIN 3 // STDBY pin of TP4056 connected to Arduino digital pin 3
void setup() {
pinMode(CHRG_PIN, INPUT); // Set CHRG pin as input
pinMode(STDBY_PIN, INPUT); // Set STDBY pin as input
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int chrgStatus = digitalRead(CHRG_PIN); // Read CHRG pin status
int stdbyStatus = digitalRead(STDBY_PIN); // Read STDBY pin status
if (chrgStatus == LOW) {
Serial.println("Battery is charging...");
} else if (stdbyStatus == LOW) {
Serial.println("Battery is fully charged.");
} else {
Serial.println("No battery connected or charging stopped.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before checking again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
IC Overheating
- Cause: High charging current or insufficient heat dissipation.
- Solution: Reduce the charging current by increasing the RPROG resistor value. Ensure proper PCB design for heat dissipation.
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient input voltage.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the input voltage is within the 4.0V–8.0V range.
Status LEDs Not Working
- Cause: Incorrect LED connections or missing current-limiting resistors.
- Solution: Check the LED polarity and ensure resistors are properly connected.
Charging Stops Prematurely
- Cause: Battery protection circuit triggered or thermal regulation activated.
- Solution: Check the battery's protection circuit and ensure proper thermal management.
FAQs
Can the TP4056 charge multiple batteries in series? No, the TP4056 is designed for single-cell lithium-ion batteries only. Charging multiple cells in series requires a specialized multi-cell charger.
What happens if the input voltage exceeds 8.0V? Exceeding 8.0V can damage the IC. Always use a regulated power supply within the specified range.
Can I use the TP4056 without a thermistor? Yes, if temperature monitoring is not required, connect the TEMP pin to GND.
How do I adjust the charging current? Use the formula ( I_{CHG} = \frac{1200}{R_{PROG}} ) to calculate the required resistor value for the desired charging current.