
How to Use Pump: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Pump in Cirkit Designer
Design with Pump in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A pump is an electronic component designed to move fluids, either liquids or gases, through mechanical action. Pumps can be found in a variety of applications, from industrial systems and household appliances to automotive and aerospace technologies. They are essential in systems that require fluid circulation, such as water cooling systems in computers, fuel delivery systems in vehicles, and irrigation systems in agriculture.
Explore Projects Built with Pump
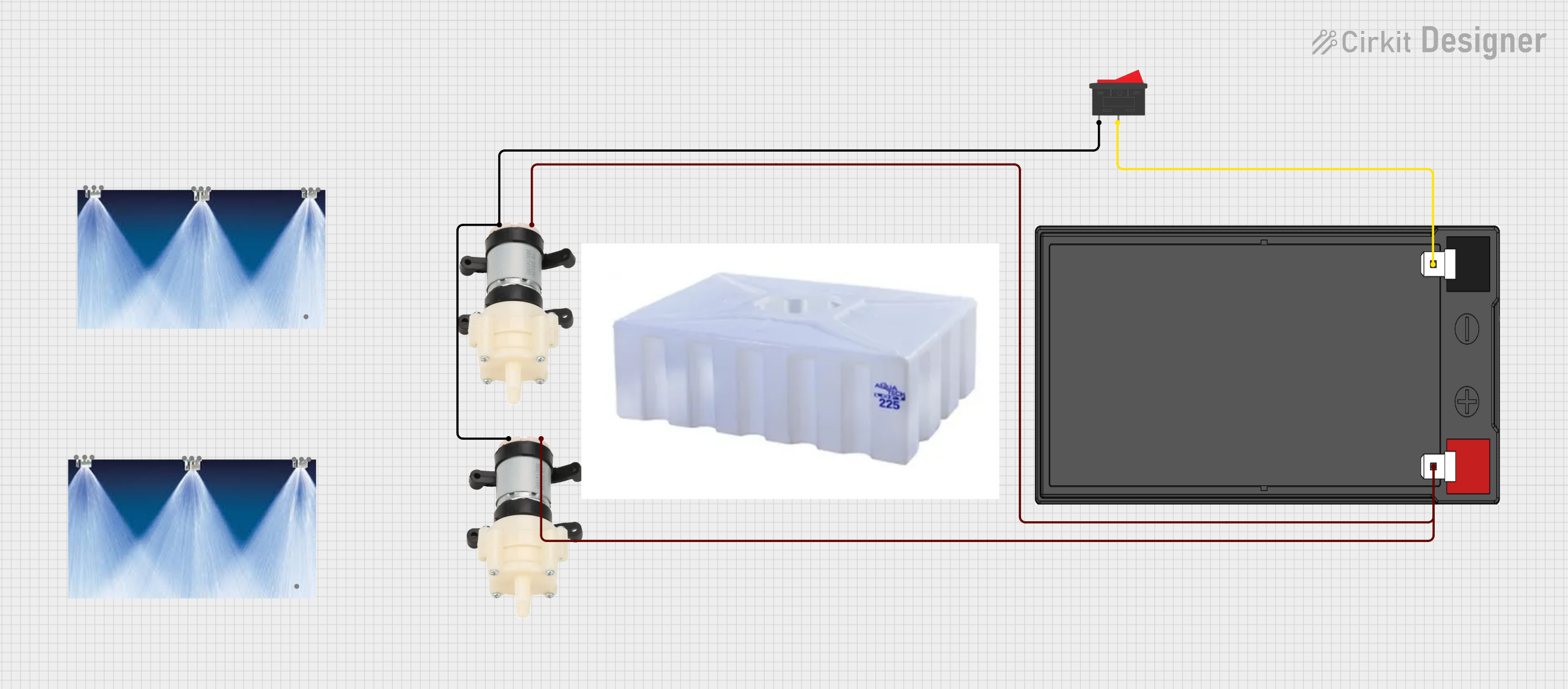
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer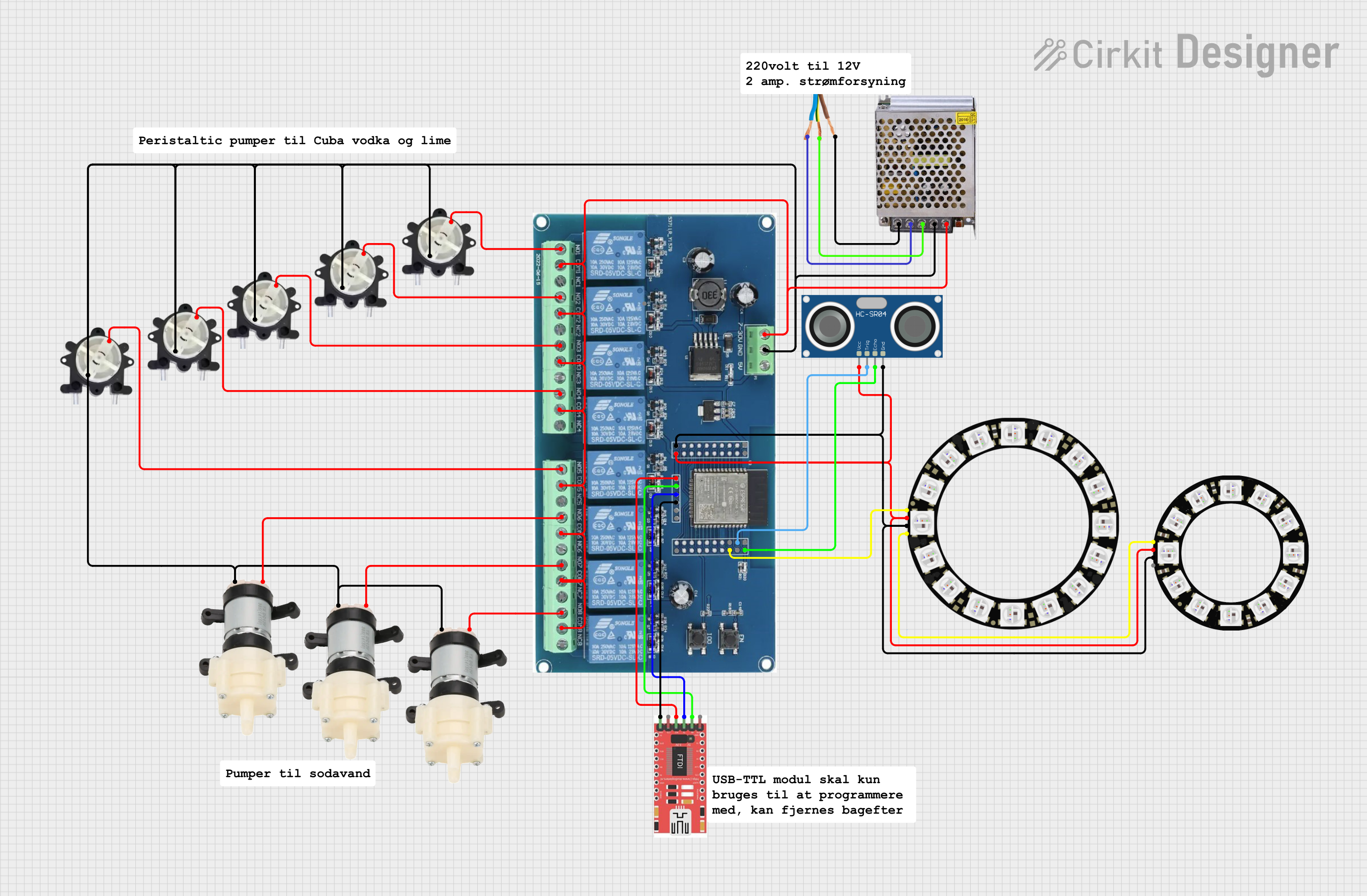
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer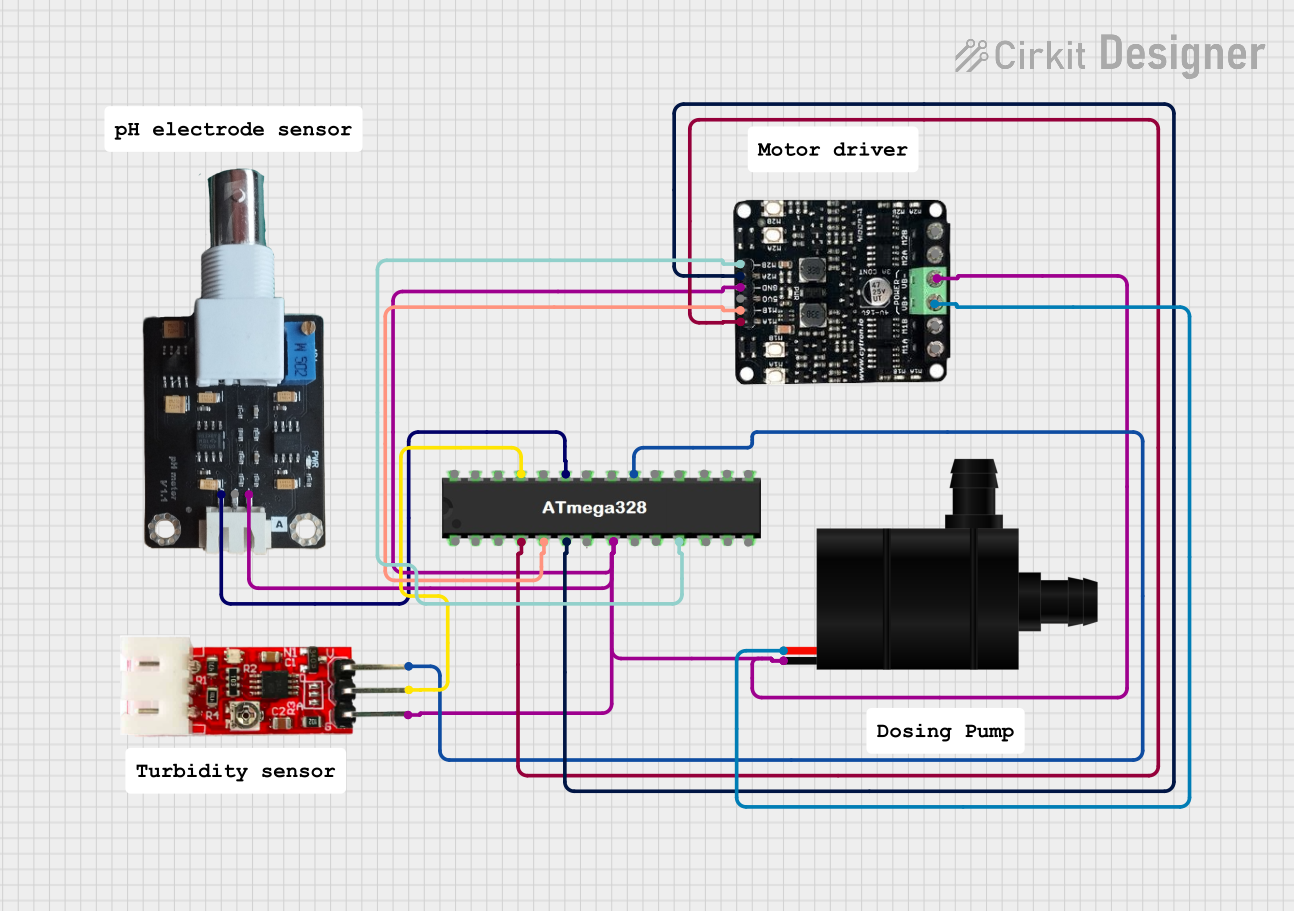
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer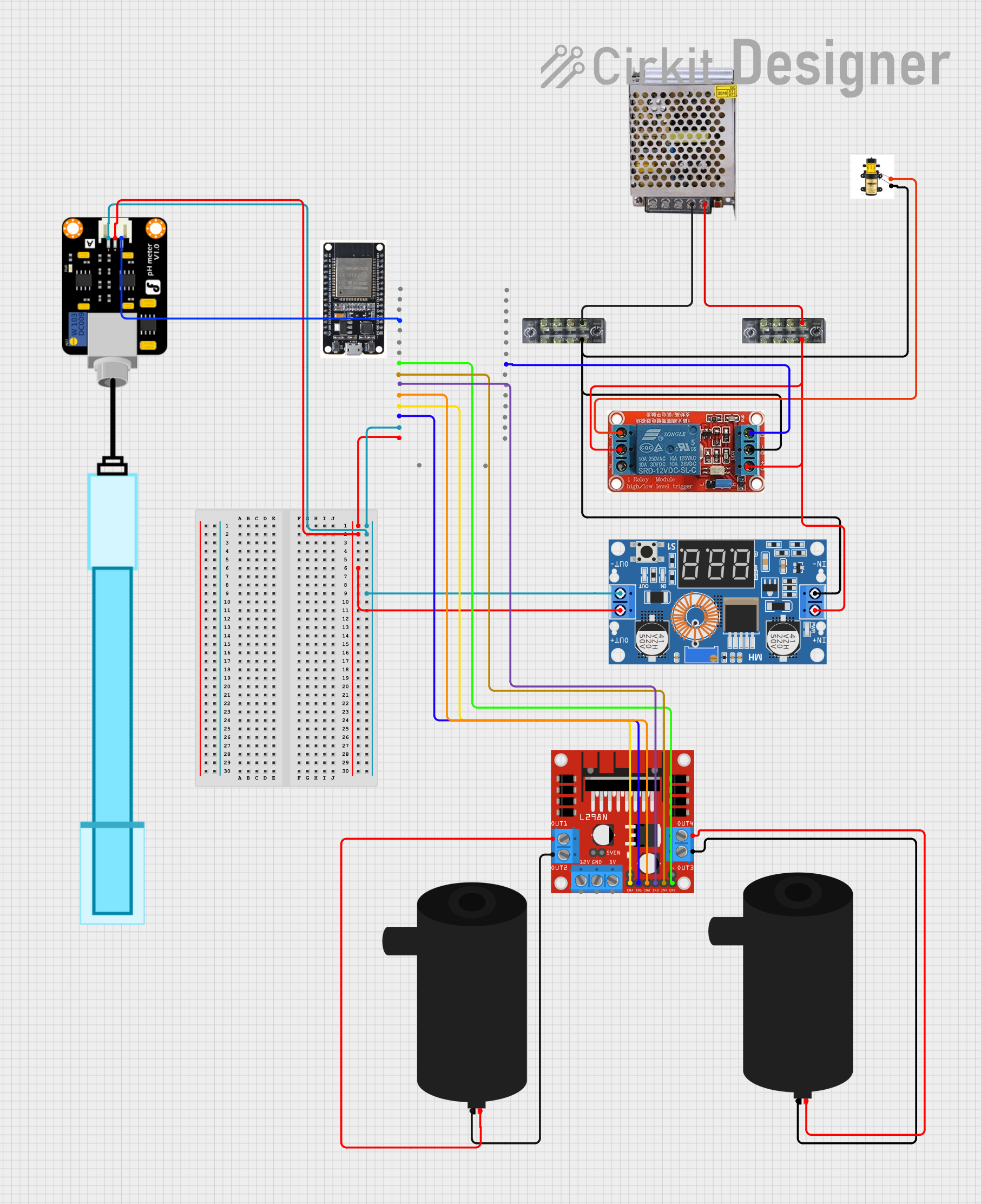
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Pump

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
General Specifications
- Operating Voltage Range: Typically 3V to 12V DC for small electronic pumps
- Current Consumption: Varies with size and model, from a few hundred milliamps to several amps
- Flow Rate: Dependent on the pump model, can range from less than 1 L/min to several L/min
- Maximum Head: The maximum height the pump can push the fluid, often measured in meters
- Operating Temperature Range: Usually from 0°C to 50°C for standard models
- Life Expectancy: Varies with usage, typically rated for several thousand hours of operation
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | V+ (Power Supply) | Connect to positive voltage |
| 2 | GND (Ground) | Connect to system ground |
Note: The actual pin configuration may vary depending on the pump model. Always refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for exact details.
Usage Instructions
Incorporating the Pump into a Circuit
Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply matches the voltage and current requirements of the pump. Overvoltage or excessive current can damage the pump.
Polarity: Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to the V+ pin and the negative terminal to the GND pin. Reversing the polarity may damage the pump.
Control: To control the pump with a microcontroller like an Arduino UNO, use a transistor or a relay module as a switch to handle the current required by the pump.
Protection: It is advisable to use a diode (flyback diode) across the pump terminals to protect against voltage spikes when the pump is turned off.
Tubing: Ensure that the tubing connected to the pump's inlet and outlet is secure to prevent leaks.
Best Practices
- Avoid running the pump dry, as this can cause premature wear or damage.
- Use a filter on the pump's inlet to prevent debris from entering and damaging the pump.
- Regularly check for any signs of wear or leaks and maintain the pump according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Example Arduino Code
// Define the pump control pin
const int pumpPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the pump control pin as an output
pinMode(pumpPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn on the pump for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(pumpPin, HIGH);
delay(5000);
// Turn off the pump
digitalWrite(pumpPin, LOW);
delay(10000); // Wait for 10 seconds before the next cycle
}
Note: The above code assumes the use of a relay or transistor to control the pump.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Pump does not start: Check the power supply for proper voltage and current. Ensure that the connections are secure and the polarity is correct.
- Low flow rate: Verify that the pump is not clogged and that the tubing is not kinked. Check if the filter is clean and unobstructed.
- Pump is noisy or vibrates excessively: Ensure that the pump is securely mounted and that there are no loose parts.
FAQs
Q: Can I run the pump continuously? A: It depends on the pump's design. Some pumps are rated for continuous operation, while others are intended for intermittent use. Check the manufacturer's specifications.
Q: Is it possible to control the flow rate of the pump? A: Yes, some pumps allow flow rate control either through pulse-width modulation (PWM) or by using a flow control valve.
Q: Can I use the pump for hot liquids? A: This depends on the pump's material and design. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for the maximum operating temperature.
Remember to consult the manufacturer's datasheet and documentation for specific information about the pump you are using. Proper installation and maintenance are key to ensuring the longevity and performance of your pump.