
How to Use USB power&data: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with USB power&data in Cirkit Designer
Design with USB power&data in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The USB Power & Data interface is a versatile and widely used electronic component that combines power delivery and data transfer capabilities in a single connection. It is a cornerstone of modern electronics, enabling devices to communicate with each other while simultaneously receiving electrical power. This dual functionality makes it an essential component in applications ranging from charging mobile devices to connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and external storage devices.
Explore Projects Built with USB power&data

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer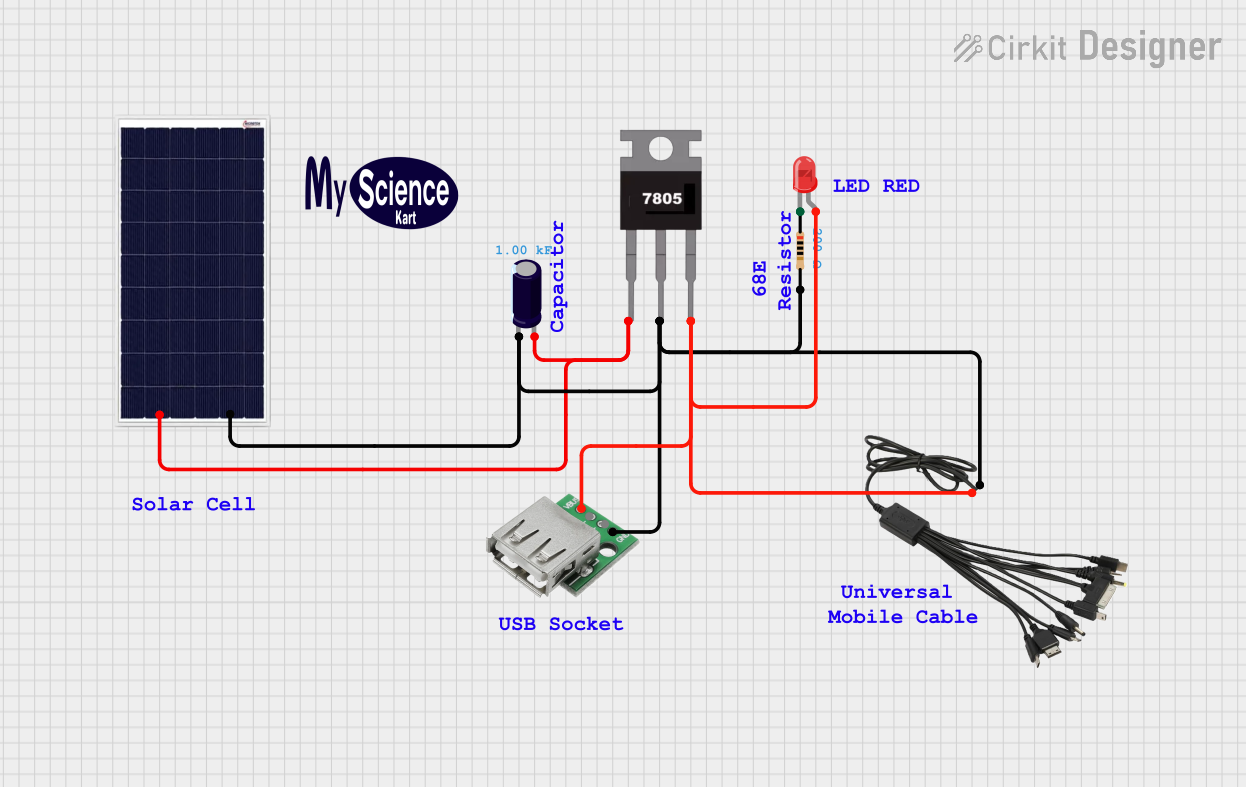
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer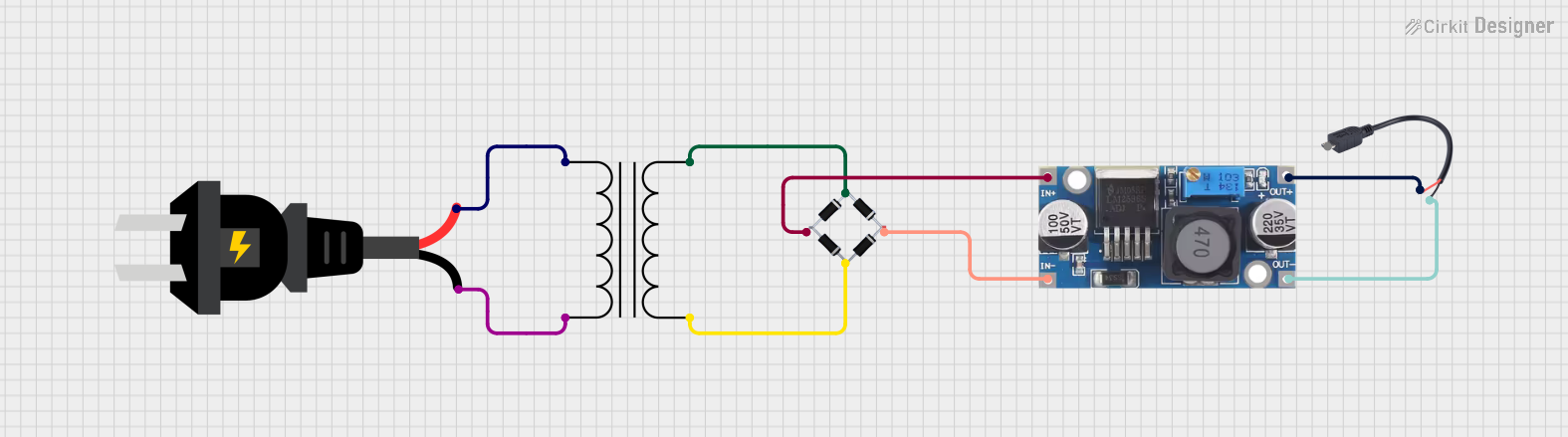
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer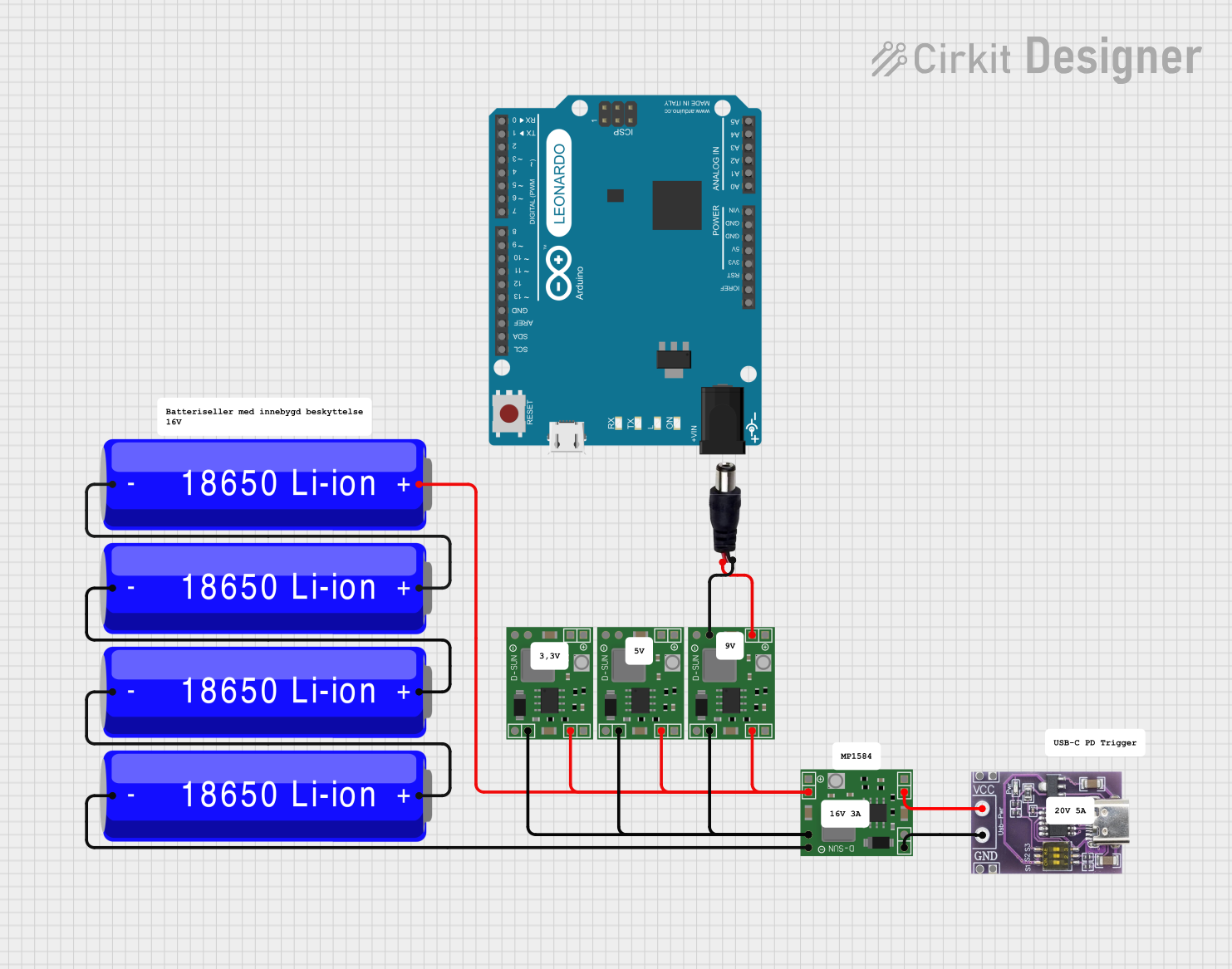
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with USB power&data

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging and powering portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
- Data transfer between computers and peripherals (e.g., printers, external hard drives).
- Communication between microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino) and computers for programming and debugging.
- Powering and interfacing USB-powered sensors and modules in embedded systems.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Supply (Vbus): 5V DC (standard USB specification).
- Current Rating:
- USB 2.0: Up to 500mA.
- USB 3.0: Up to 900mA.
- USB-C (Power Delivery): Up to 5A (depending on the configuration).
- Data Transfer Speeds:
- USB 2.0: Up to 480 Mbps.
- USB 3.0: Up to 5 Gbps.
- USB 3.1/3.2: Up to 10 Gbps.
- USB 4.0: Up to 40 Gbps.
- Connector Types: USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, Micro-USB, Mini-USB.
- Operating Temperature Range: -20°C to 70°C (typical).
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The USB interface typically consists of four or more pins, depending on the version and connector type. Below is the pin configuration for standard USB 2.0 and USB-C connectors.
USB 2.0 Pinout
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vbus | +5V DC power supply |
| 2 | D- | Data line (negative) |
| 3 | D+ | Data line (positive) |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
USB-C Pinout (Simplified)
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A1, B1 | GND | Ground |
| A4, B4 | Vbus | +5V DC power supply |
| A6, B6 | D- | Data line (negative) |
| A7, B7 | D+ | Data line (positive) |
| A5, B5 | CC | Configuration channel for power delivery |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the USB Power & Data Interface in a Circuit
Power Delivery:
- Connect the Vbus pin to the power input of your device or circuit.
- Ensure the current draw does not exceed the USB port's rating (e.g., 500mA for USB 2.0).
- Use a voltage regulator if your circuit requires a voltage lower than 5V.
Data Transfer:
- Connect the D+ and D- pins to the corresponding data lines of your device.
- Ensure proper impedance matching (typically 90Ω differential) for high-speed data transfer.
Grounding:
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit to complete the electrical connection.
USB-C Specifics:
- For USB-C, use the CC pin to negotiate power delivery if higher currents or voltages are required.
- Use appropriate USB-C breakout boards or connectors for easier integration.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Cable Quality: Use high-quality USB cables to ensure reliable power delivery and data transfer.
- Overcurrent Protection: Include a fuse or current-limiting circuit to protect the USB port from damage.
- Signal Integrity: Keep data lines short and avoid running them parallel to power lines to minimize interference.
- USB Standards Compliance: Ensure your device complies with the USB standard to avoid compatibility issues.
Example: Connecting USB to an Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO can be powered and programmed via its USB interface. Below is an example of how to use the USB Power & Data interface with an Arduino UNO.
Code Example
// This example demonstrates serial communication between an Arduino UNO
// and a computer via the USB interface. The Arduino sends a message
// to the computer every second.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
while (!Serial) {
// Wait for the serial port to connect (for Leonardo/Micro boards)
}
Serial.println("USB Power & Data Interface Initialized");
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Hello from Arduino!"); // Send a message to the computer
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Device Not Recognized:
- Cause: Faulty cable or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Check the cable and ensure proper connections for Vbus, D+, D-, and GND.
Insufficient Power:
- Cause: Device draws more current than the USB port can supply.
- Solution: Use a powered USB hub or a USB-C power delivery adapter.
Data Transfer Errors:
- Cause: Signal interference or poor cable quality.
- Solution: Use shielded cables and ensure proper grounding.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the load or improve cooling.
FAQs
Q: Can I use USB to power high-current devices?
A: Standard USB ports are limited in current output. Use USB-C with power delivery for higher currents (up to 5A).Q: How do I identify the USB version of my device?
A: Check the device's documentation or look for color-coded connectors (e.g., blue for USB 3.0).Q: Can I extend USB cables for longer distances?
A: USB cables have a maximum length (e.g., 5m for USB 2.0). Use active USB extenders for longer distances.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and using the USB Power & Data interface effectively.