
How to Use ESP32-DevKitM-1: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
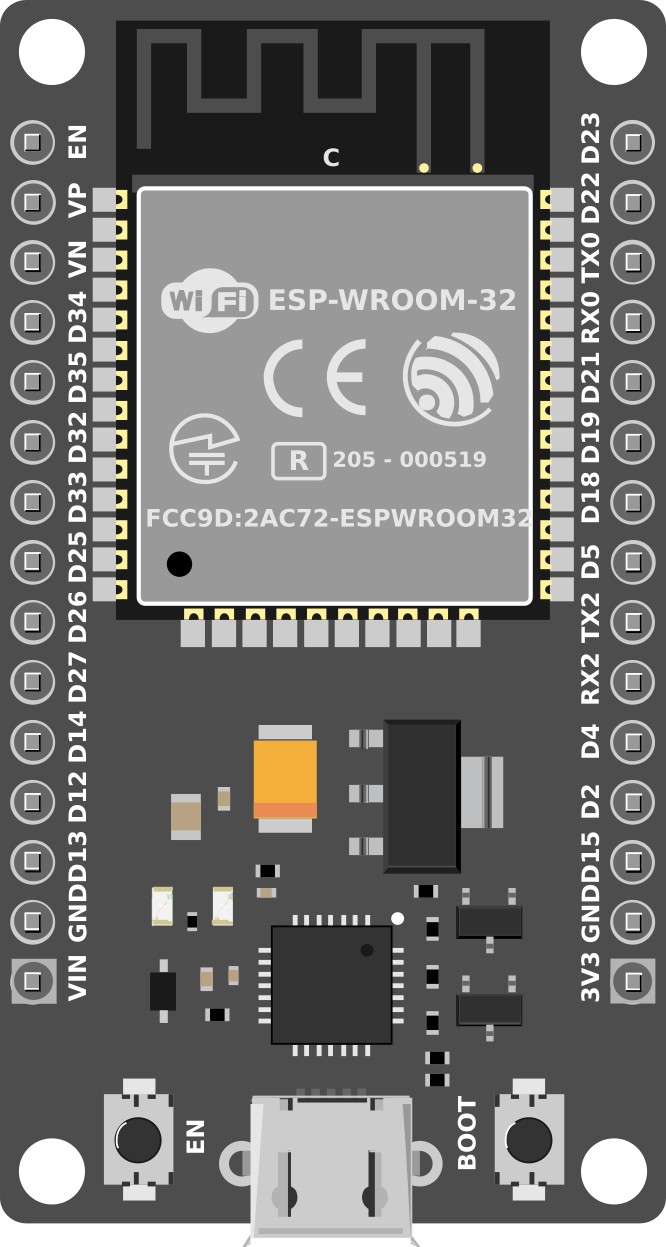
 Design with ESP32-DevKitM-1 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32-DevKitM-1 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32-DevKitM-1 is a compact development board based on the ESP32-MINI-1 module, which integrates the powerful ESP32 chip. This board is equipped with dual-mode Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it an excellent choice for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Its small form factor and versatile GPIO pins allow developers to interface with a wide range of sensors, actuators, and other peripherals.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32-DevKitM-1
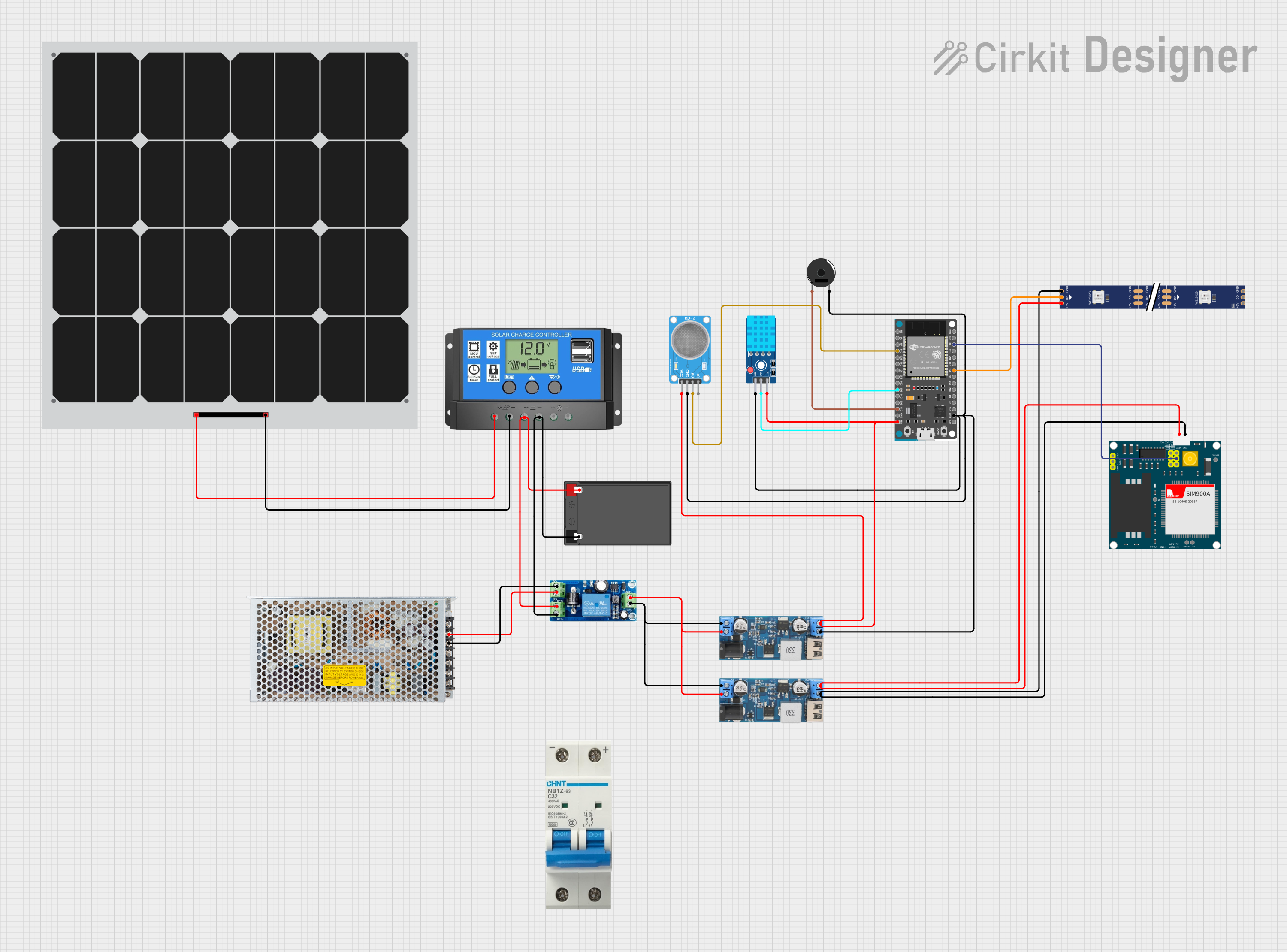
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer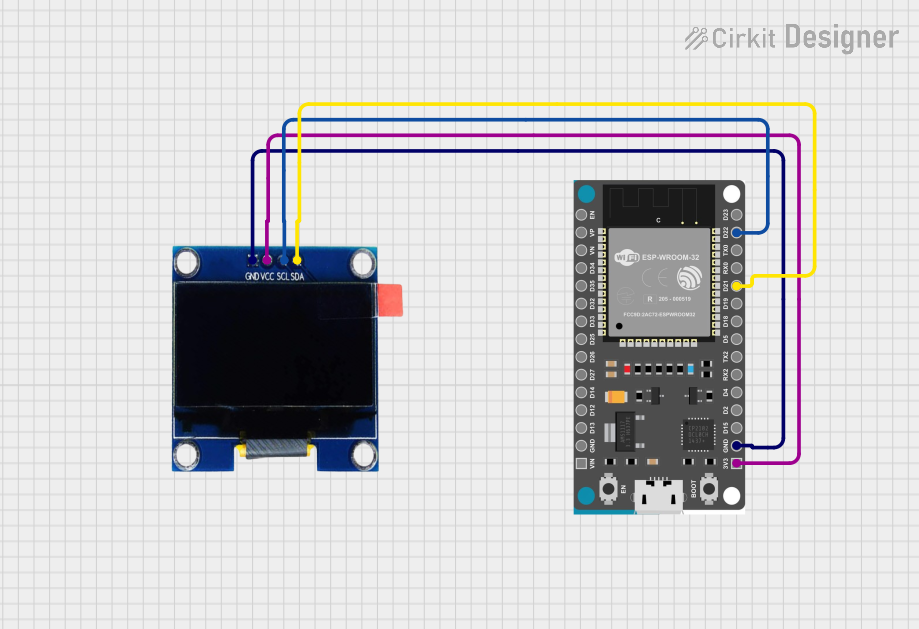
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer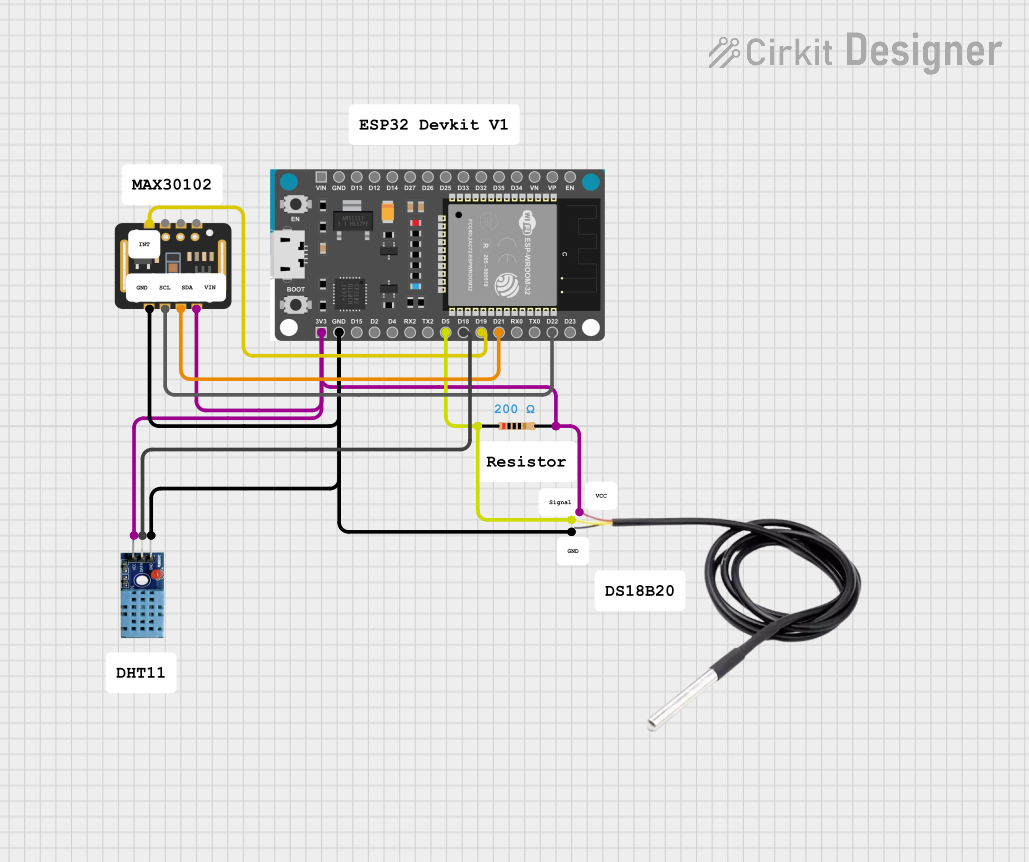
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer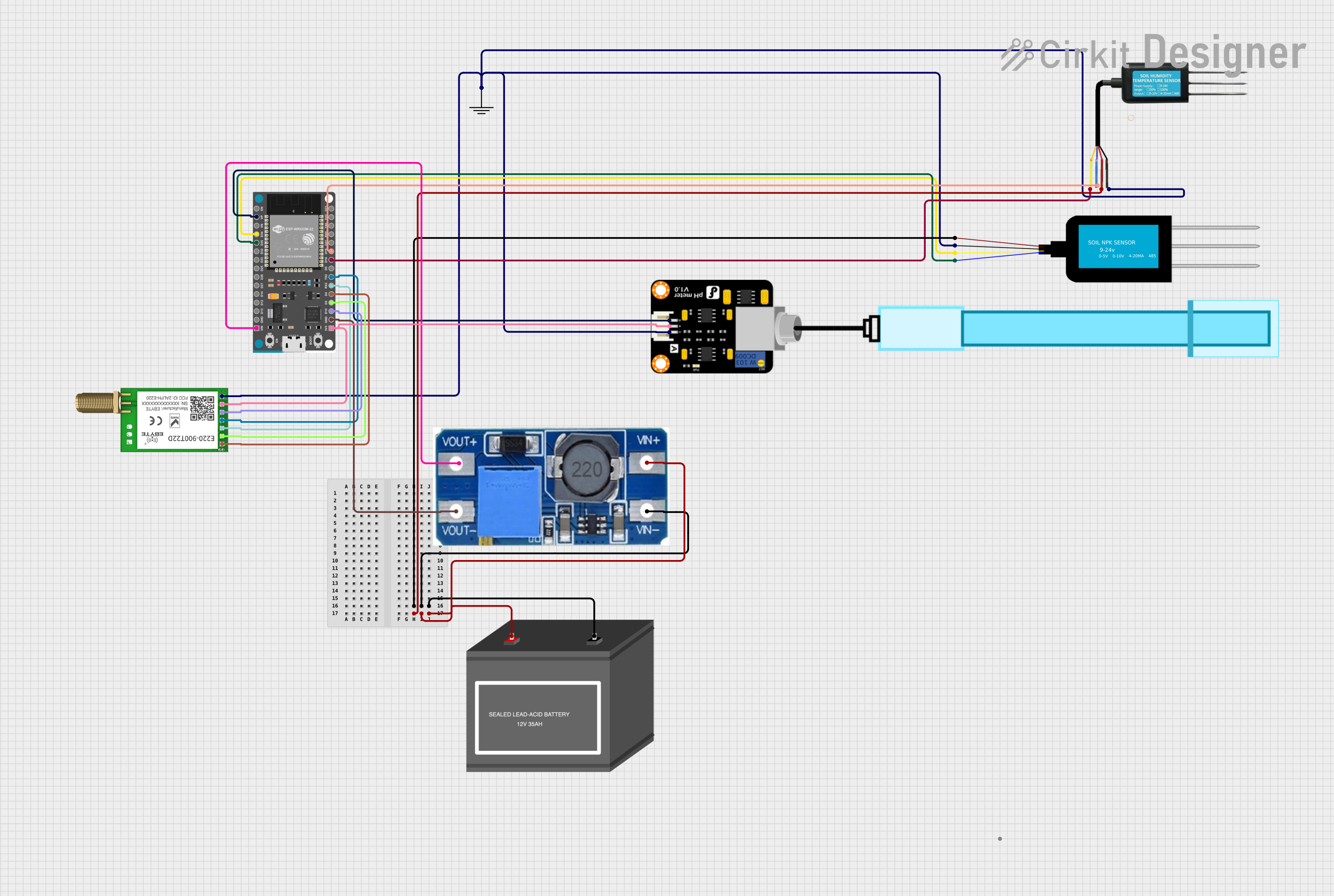
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32-DevKitM-1

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Smart home devices (e.g., connected lights, thermostats)
- Wearable electronics
- Industrial IoT systems
- Wireless data logging and monitoring
- Prototyping Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Wi-Fi-enabled devices
Technical Specifications
The ESP32-DevKitM-1 is designed to provide robust performance in a compact package. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ESP32-MINI-1 module (based on ESP32 chip)
- Wireless Connectivity: Wi-Fi (802.11 b/g/n) and Bluetooth (v4.2 BR/EDR and BLE)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage Range: 5V (via USB) or 3.3V (via external power supply)
- GPIO Pins: 15 (configurable for digital I/O, PWM, ADC, etc.)
- Flash Memory: 4 MB
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to 85°C
- Dimensions: 48.0 mm x 25.5 mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32-DevKitM-1 features a 16-pin layout. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground pin |
| 2 | 3V3 | 3.3V power output |
| 3 | EN | Enable pin (active high, used to reset the chip) |
| 4 | IO0 | GPIO0 (can also be used for boot mode selection) |
| 5 | IO1 | GPIO1 (UART TX by default) |
| 6 | IO3 | GPIO3 (UART RX by default) |
| 7 | IO4 | GPIO4 (configurable digital I/O) |
| 8 | IO5 | GPIO5 (configurable digital I/O) |
| 9 | IO12 | GPIO12 (configurable digital I/O, ADC, or touch input) |
| 10 | IO13 | GPIO13 (configurable digital I/O, ADC, or touch input) |
| 11 | IO14 | GPIO14 (configurable digital I/O, ADC, or touch input) |
| 12 | IO15 | GPIO15 (configurable digital I/O, ADC, or touch input) |
| 13 | IO16 | GPIO16 (configurable digital I/O) |
| 14 | IO17 | GPIO17 (configurable digital I/O) |
| 15 | GND | Ground pin |
| 16 | 5V | 5V power input (via USB or external power supply) |
Usage Instructions
The ESP32-DevKitM-1 is versatile and easy to use in a variety of projects. Below are the steps and best practices for using this development board.
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the board to a computer or USB power source using a micro-USB cable.
- Alternatively, supply 3.3V directly to the 3V3 pin or 5V to the 5V pin.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF for development.
- Add the ESP32 board support package to the Arduino IDE via the Boards Manager.
- Select "ESP32 Dev Module" as the board type in the IDE.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, actuators, or other devices.
- Ensure that the voltage levels of connected peripherals are compatible with the 3.3V logic of the ESP32.
Uploading Code:
- Write your code in the Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF.
- Connect the board to your computer via USB and select the correct COM port.
- Click the upload button to flash the code onto the ESP32.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure that all connected peripherals operate at 3.3V logic levels to avoid damaging the board.
- Boot Mode: To enter bootloader mode, hold down the IO0 button while pressing the EN button.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid unexpected resets or instability.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth: Avoid placing the board in metal enclosures, as this can interfere with wireless signals.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
Below is an example of how to use the ESP32-DevKitM-1 to read data from a DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor and send it to a serial monitor:
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <DHT.h>
// Define the DHT sensor type and pin
#define DHTPIN 4 // GPIO4 is connected to the DHT sensor
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT11 sensor type
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
dht.begin(); // Initialize the DHT sensor
Serial.println("ESP32 DHT11 Example");
}
void loop() {
delay(2000); // Wait 2 seconds between readings
// Read temperature and humidity values
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
// Check if the readings are valid
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
// Print the readings to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.print("% Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println("°C");
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Board Not Detected by Computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
- Install the correct USB-to-serial driver for the ESP32.
Code Upload Fails:
- Check that the correct COM port and board type are selected in the IDE.
- Hold down the IO0 button while pressing the EN button to enter bootloader mode.
Wi-Fi Connection Issues:
- Verify the SSID and password in your code.
- Ensure the router is within range and supports 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi.
Unstable Operation:
- Use a stable power source with sufficient current (at least 500 mA).
- Avoid connecting peripherals that draw excessive current.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Debugging: Use the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE to print debug messages.
- Resetting the Board: Press the EN button to reset the ESP32 if it becomes unresponsive.
- Firmware Updates: Update the ESP32 firmware using the ESP-IDF tools for improved stability and features.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the ESP32-DevKitM-1 in your IoT and embedded systems projects.