
How to Use TB6612FNG : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TB6612FNG in Cirkit Designer
Design with TB6612FNG in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TB6612FNG, manufactured by SparkFun, is a dual H-bridge motor driver IC designed for controlling two DC motors or one stepper motor. It supports PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for precise speed control and direction management. The IC is compact, efficient, and includes built-in protection features such as thermal shutdown and overcurrent protection, making it ideal for robotics, automation, and other motor control applications.
Explore Projects Built with TB6612FNG

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer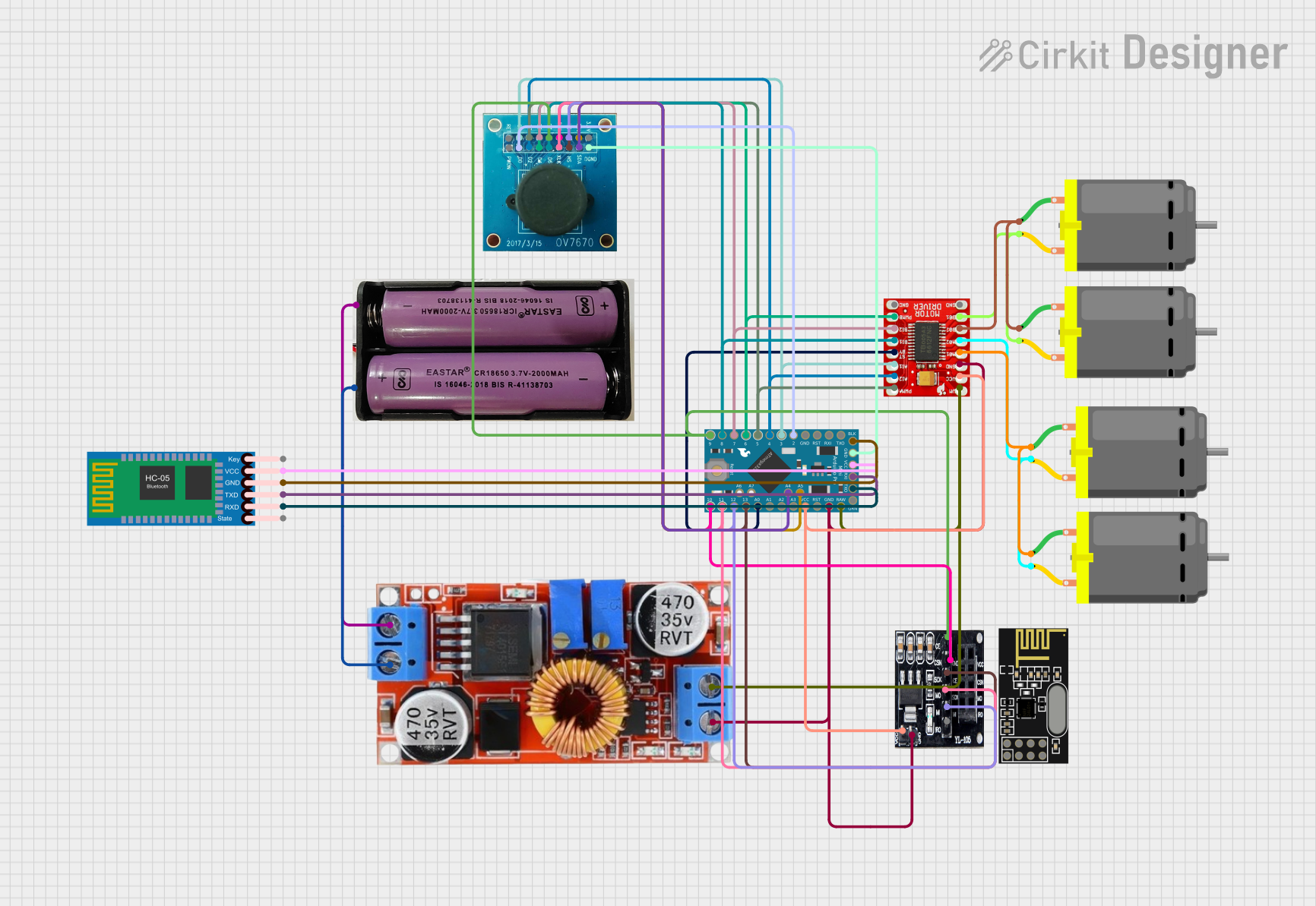
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer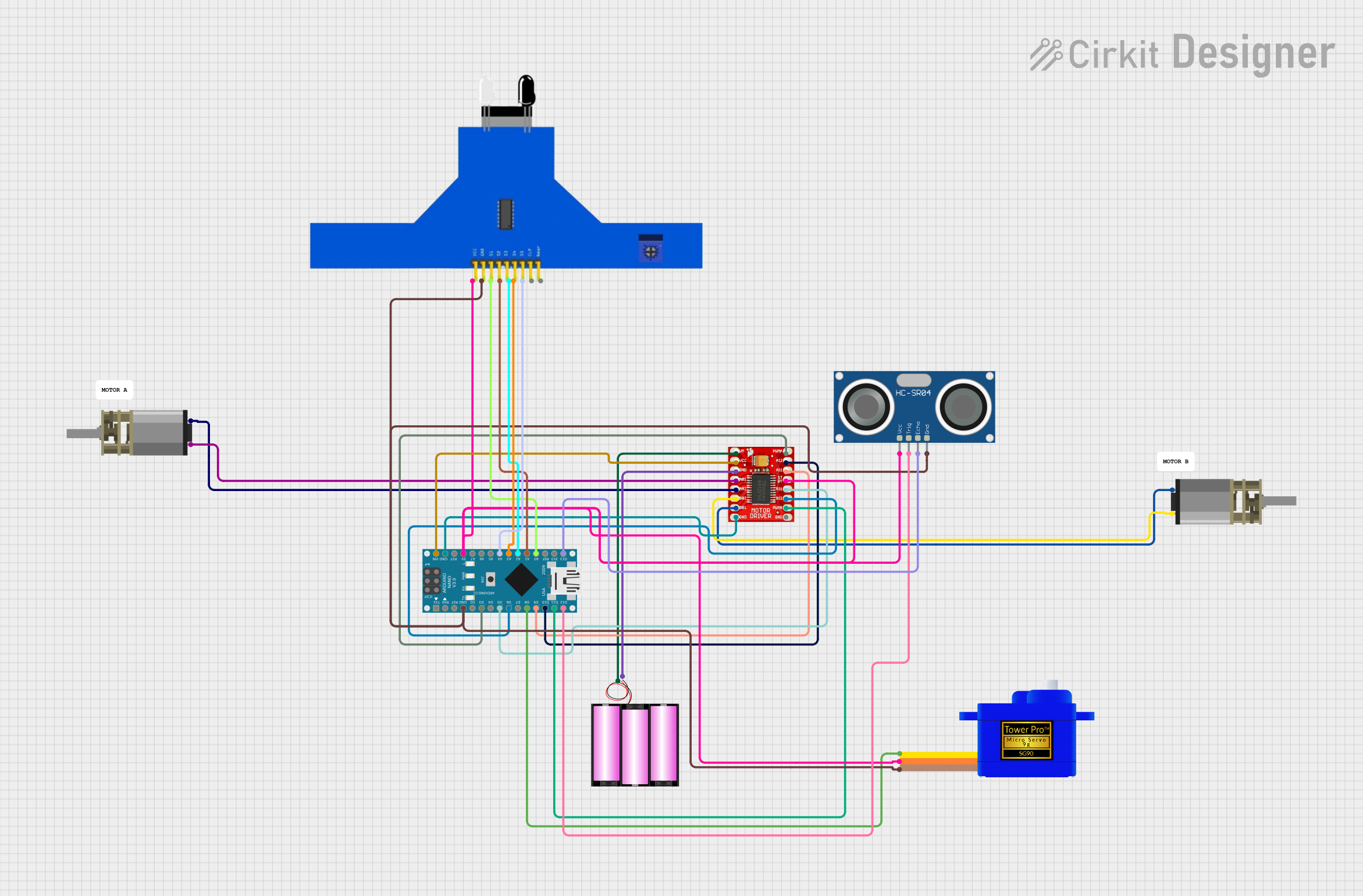
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer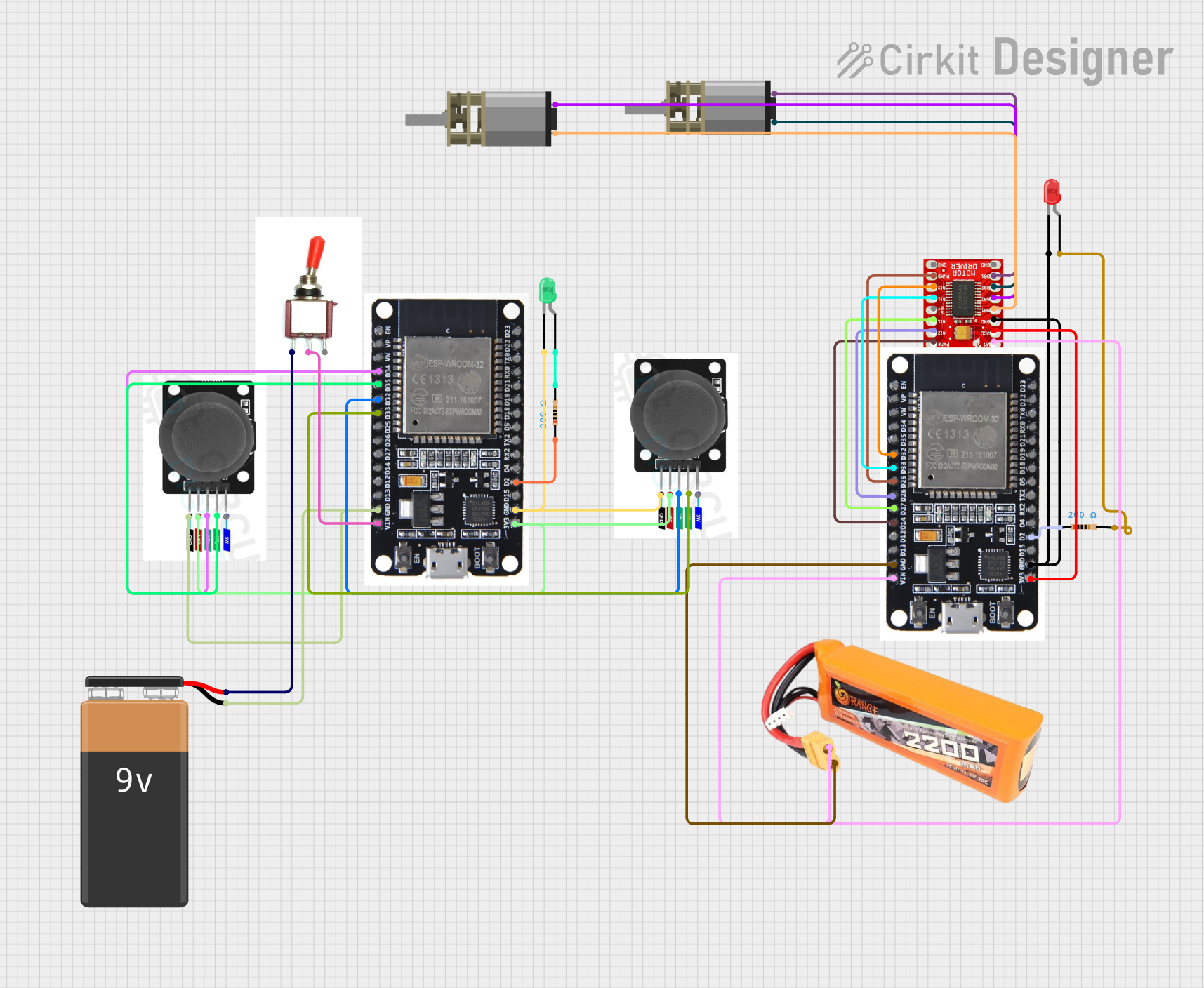
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TB6612FNG

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics: Driving wheels or actuators
- Automation systems: Conveyor belts or small machinery
- DIY projects: Remote-controlled cars, drones, or robotic arms
- Stepper motor control for CNC machines or 3D printers
Technical Specifications
The TB6612FNG is a versatile motor driver with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage (Vcc) | 2.7V to 5.5V |
| Motor Voltage (VM) | 4.5V to 13.5V |
| Output Current (per channel) | 1.2A (continuous), 3.2A (peak) |
| Control Interface | PWM and digital logic |
| Standby Current | 1 µA (typical) |
| Built-in Protections | Thermal shutdown, overcurrent, low voltage |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | HTSSOP-20 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TB6612FNG has 20 pins, with the following configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AIN1 | Input signal for Motor A direction control |
| 2 | AIN2 | Input signal for Motor A direction control |
| 3 | PWMA | PWM input for Motor A speed control |
| 4 | AO1 | Output 1 for Motor A |
| 5 | AO2 | Output 2 for Motor A |
| 6 | VM | Motor power supply (4.5V to 13.5V) |
| 7 | GND | Ground |
| 8 | STBY | Standby control (active HIGH to enable the IC) |
| 9 | Vcc | Logic power supply (2.7V to 5.5V) |
| 10 | BIN1 | Input signal for Motor B direction control |
| 11 | BIN2 | Input signal for Motor B direction control |
| 12 | PWMB | PWM input for Motor B speed control |
| 13 | BO1 | Output 1 for Motor B |
| 14 | BO2 | Output 2 for Motor B |
| 15 | NC | No connection |
| 16 | NC | No connection |
| 17 | NC | No connection |
| 18 | NC | No connection |
| 19 | NC | No connection |
| 20 | NC | No connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TB6612FNG in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the motor power supply (VM) to the VM pin (4.5V to 13.5V).
- Connect the logic power supply (Vcc) to the Vcc pin (2.7V to 5.5V).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the circuit.
Motor Connections:
- For Motor A, connect the motor terminals to AO1 and AO2.
- For Motor B, connect the motor terminals to BO1 and BO2.
Control Signals:
- Use the AIN1 and AIN2 pins to control the direction of Motor A.
- Use the BIN1 and BIN2 pins to control the direction of Motor B.
- Provide PWM signals to PWMA and PWMB for speed control of Motor A and Motor B, respectively.
Standby Mode:
- To enable the IC, set the STBY pin HIGH. To disable the IC, set it LOW.
Example Circuit:
- Connect the TB6612FNG to an Arduino UNO or similar microcontroller for control.
- Use digital pins on the microcontroller to send PWM and direction signals.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the motor power supply (VM) and logic power supply (Vcc) are within the specified voltage ranges.
- Use decoupling capacitors near the VM and Vcc pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum continuous current rating of 1.2A per channel to prevent overheating.
- Use proper heat dissipation techniques if operating near the peak current limit.
- Always set the STBY pin HIGH to enable the IC before sending control signals.
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example Arduino sketch to control two DC motors using the TB6612FNG:
// Define motor control pins
const int AIN1 = 2; // Motor A direction control pin 1
const int AIN2 = 3; // Motor A direction control pin 2
const int PWMA = 5; // Motor A speed control (PWM) pin
const int BIN1 = 4; // Motor B direction control pin 1
const int BIN2 = 7; // Motor B direction control pin 2
const int PWMB = 6; // Motor B speed control (PWM) pin
const int STBY = 8; // Standby control pin
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(AIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWMB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(STBY, OUTPUT);
// Enable the motor driver
digitalWrite(STBY, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Motor A: Forward at 50% speed
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW);
analogWrite(PWMA, 128); // 50% duty cycle (0-255)
// Motor B: Reverse at 75% speed
digitalWrite(BIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN2, HIGH);
analogWrite(PWMB, 192); // 75% duty cycle (0-255)
delay(2000); // Run motors for 2 seconds
// Stop both motors
analogWrite(PWMA, 0);
analogWrite(PWMB, 0);
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Motors Not Running:
- Ensure the STBY pin is set HIGH to enable the IC.
- Verify that the motor power supply (VM) and logic power supply (Vcc) are connected and within the specified voltage ranges.
- Check the PWM signals and direction control pins for proper configuration.
Overheating:
- Ensure the current drawn by the motors does not exceed the maximum continuous current rating of 1.2A per channel.
- Use heat sinks or proper ventilation if operating near the peak current limit.
Erratic Motor Behavior:
- Check for loose connections or poor soldering.
- Add decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins to reduce noise.
FAQs
Q: Can the TB6612FNG drive stepper motors?
A: Yes, the TB6612FNG can drive a single stepper motor by controlling the two H-bridges. You will need to sequence the control signals appropriately.
Q: What happens if the IC overheats?
A: The TB6612FNG has a built-in thermal shutdown feature that disables the outputs to protect the IC. Allow the IC to cool down before resuming operation.
Q: Can I use the TB6612FNG with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the TB6612FNG supports logic levels as low as 2.7V, making it compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers.