
How to Use TPS61023: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TPS61023 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TPS61023 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TPS61023 is a high-efficiency, synchronous boost converter designed to step up low input voltages to higher output voltages. It is particularly well-suited for applications powered by single-cell lithium-ion batteries. With its wide input voltage range (0.5 V to 5.5 V), adjustable output voltage, and integrated power switches, the TPS61023 is an excellent choice for portable and battery-powered devices. Its compact size and high efficiency make it ideal for applications such as wearable devices, IoT sensors, and portable medical equipment.
Explore Projects Built with TPS61023
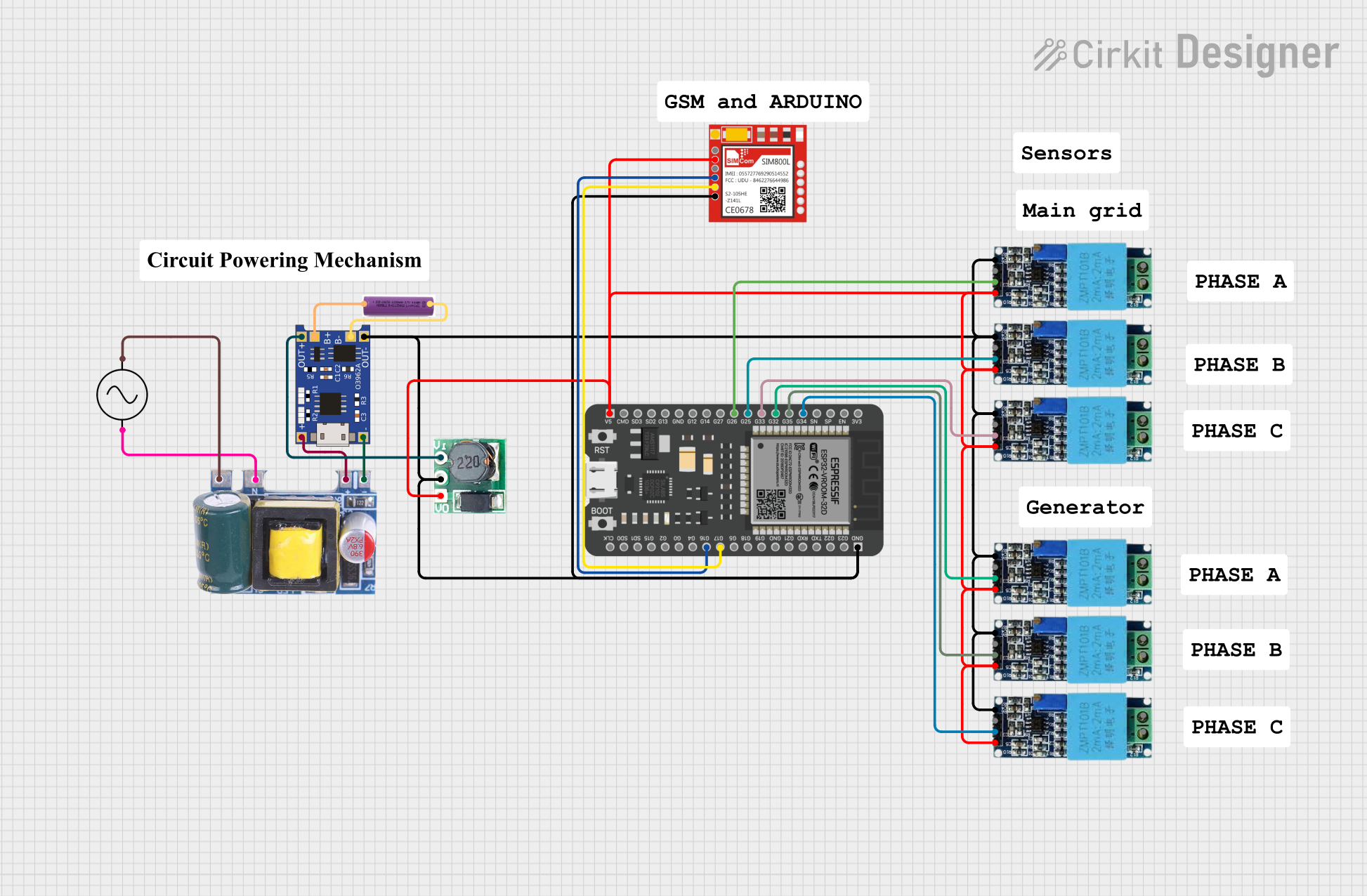
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer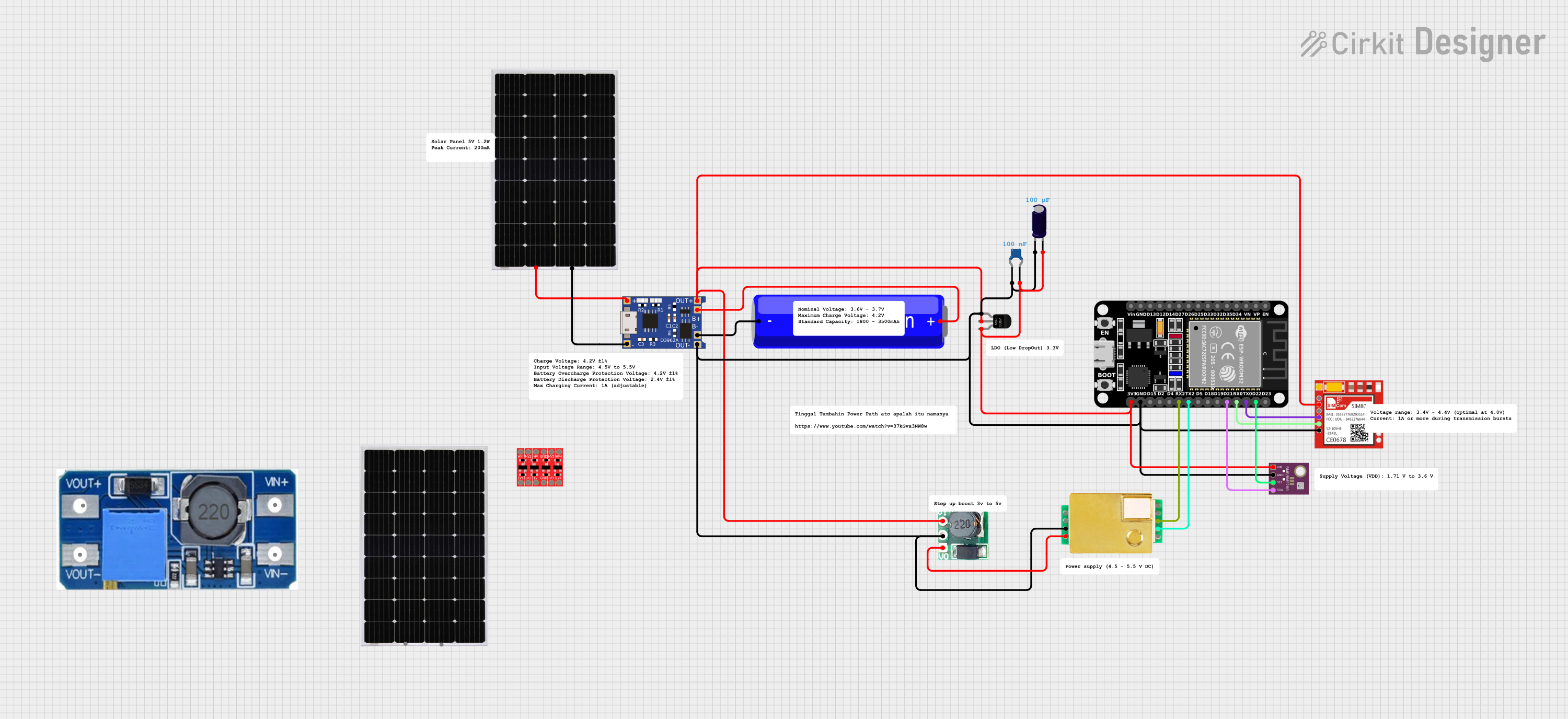
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TPS61023

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Wearable electronics
- IoT devices and sensors
- Portable medical equipment
- Battery-powered devices
- Wireless communication modules
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 0.5 V to 5.5 V |
| Output Voltage Range | 1.8 V to 5.5 V (adjustable) |
| Maximum Output Current | Up to 2 A (depending on input/output conditions) |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% |
| Switching Frequency | 2.4 MHz |
| Quiescent Current (Iq) | 15 µA (typical) |
| Package Type | 2 mm × 1.5 mm WSON-6 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TPS61023 is available in a 6-pin WSON package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SW | Switching node. Connect to the inductor and diode. |
| 2 | GND | Ground. Connect to the system ground plane. |
| 3 | FB | Feedback pin. Connect to a resistor divider to set the output voltage. |
| 4 | EN | Enable pin. Drive high to enable the device, low to disable it. |
| 5 | VIN | Input voltage supply. Connect to the input power source. |
| 6 | VOUT | Output voltage. Connect to the load and output capacitor. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TPS61023 in a Circuit
Input and Output Capacitors:
- Place a low-ESR ceramic capacitor (e.g., 10 µF) close to the VIN pin to stabilize the input voltage.
- Use a similar capacitor (e.g., 22 µF) at the VOUT pin to stabilize the output voltage.
Inductor Selection:
- Choose an inductor with a saturation current higher than the peak current of the TPS61023.
- A typical value is 1 µH to 2.2 µH, depending on the application.
Feedback Resistor Divider:
- Use two resistors to set the output voltage via the FB pin. The output voltage is determined by the formula: [ V_{OUT} = V_{FB} \times \left(1 + \frac{R1}{R2}\right) ] where ( V_{FB} ) is typically 0.8 V.
Enable Pin:
- Drive the EN pin high (logic level 1) to enable the device. Pull it low (logic level 0) to disable it.
PCB Layout:
- Minimize the loop area of the input capacitor, inductor, and output capacitor to reduce noise.
- Place the feedback resistors close to the FB pin to minimize noise interference.
Example: Connecting TPS61023 to an Arduino UNO
The TPS61023 can be used to power an Arduino UNO from a single-cell lithium-ion battery. Below is an example circuit and Arduino code to enable the TPS61023.
Circuit Connections
- Connect the battery's positive terminal to the VIN pin.
- Connect the GND pin to the battery's negative terminal and the Arduino GND.
- Set the output voltage to 5 V using the feedback resistor divider.
- Connect the VOUT pin to the Arduino's 5 V input pin.
Arduino Code Example
// Example code to enable the TPS61023 via the EN pin
// This code assumes the EN pin is connected to Arduino pin 7.
#define EN_PIN 7 // Define the EN pin connected to Arduino pin 7
void setup() {
pinMode(EN_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set EN pin as output
digitalWrite(EN_PIN, HIGH); // Enable the TPS61023
}
void loop() {
// The TPS61023 remains enabled, providing 5 V to the Arduino.
// Add your application code here.
}
Important Considerations
- Ensure the input voltage does not exceed 5.5 V to avoid damaging the device.
- Select components (capacitors, inductors, resistors) with appropriate ratings for your application.
- Avoid long PCB traces for the SW pin to minimize EMI.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No output voltage | EN pin is not enabled | Ensure the EN pin is driven high (logic level 1). |
| Output voltage is unstable | Insufficient output capacitance | Use a low-ESR ceramic capacitor with a higher value (e.g., 22 µF). |
| Device overheating | Inductor saturation or high load current | Use an inductor with a higher saturation current and check load current. |
| Low efficiency | Incorrect component selection | Use recommended inductor and capacitor values for your application. |
FAQs
Can the TPS61023 output 5 V from a 1.8 V input?
- Yes, the TPS61023 can boost a 1.8 V input to 5 V, provided the load current is within the device's capability.
What is the maximum output current?
- The maximum output current depends on the input voltage and output voltage. Refer to the datasheet for detailed current capability charts.
Can I use the TPS61023 for 3.3 V output?
- Yes, you can configure the feedback resistor divider to set the output voltage to 3.3 V.
How do I calculate the feedback resistors?
- Use the formula ( V_{OUT} = V_{FB} \times (1 + R1/R2) ), where ( V_{FB} ) is 0.8 V.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the TPS61023 into your designs and troubleshoot common issues.