
How to Use Pimorini PGA2350: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
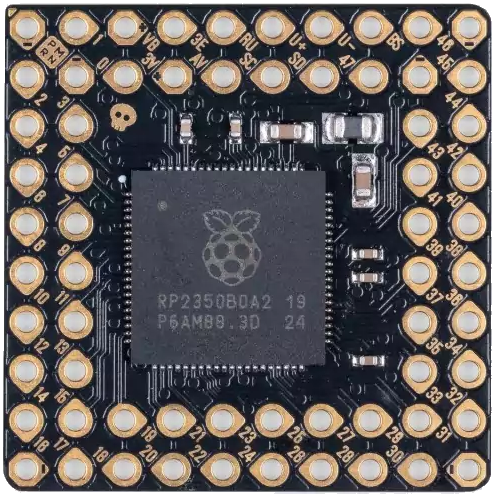
 Design with Pimorini PGA2350 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Pimorini PGA2350 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Pimorini PGA2350 is a high-performance programmable gain amplifier (PGA) designed specifically for audio applications. It allows precise control of signal gain, making it ideal for scenarios where audio signal levels need to be adjusted dynamically while maintaining exceptional sound quality. The PGA2350 is widely used in audio processing systems, mixers, and preamplifiers due to its low noise, high fidelity, and ease of integration.
Explore Projects Built with Pimorini PGA2350
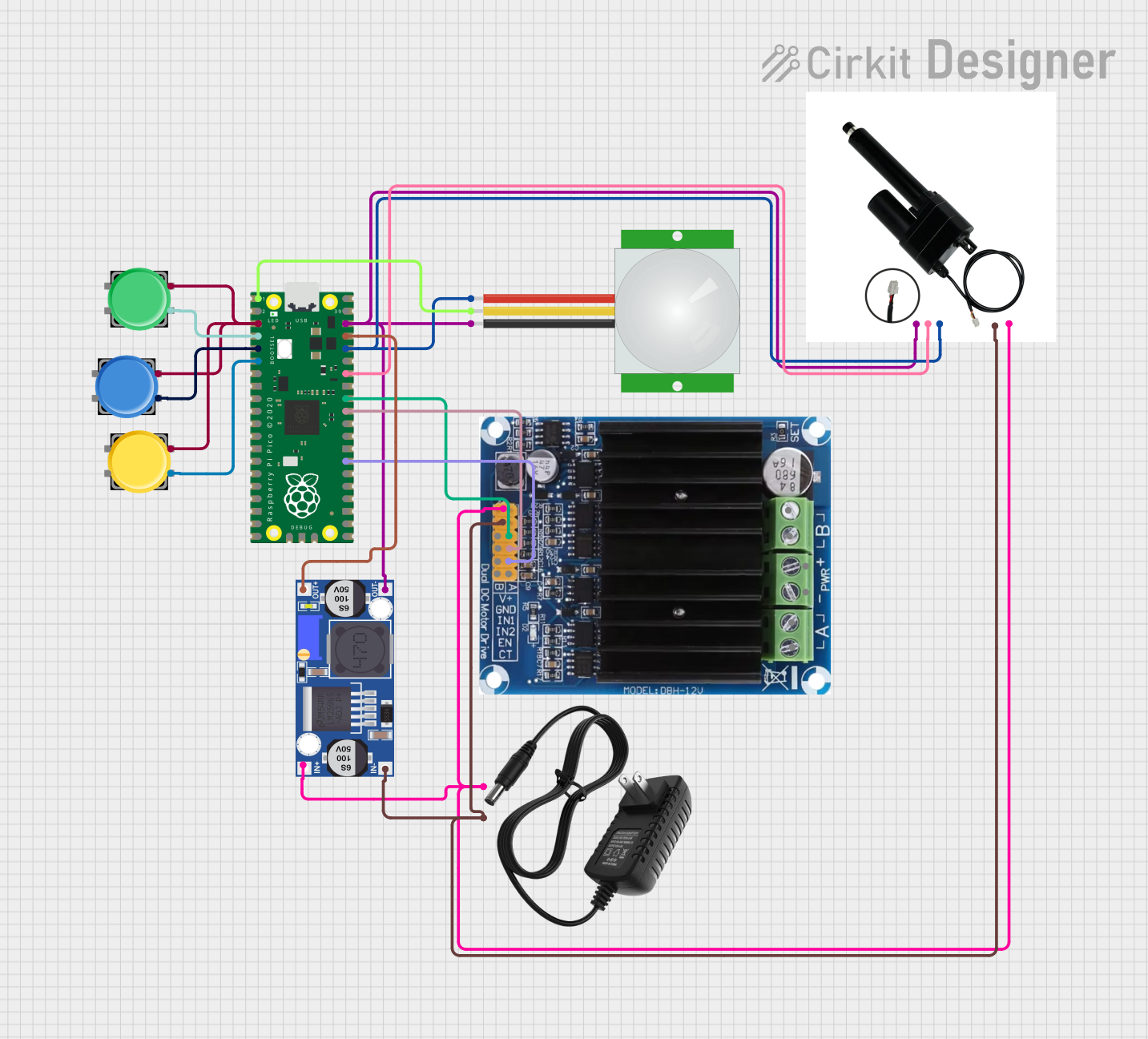
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer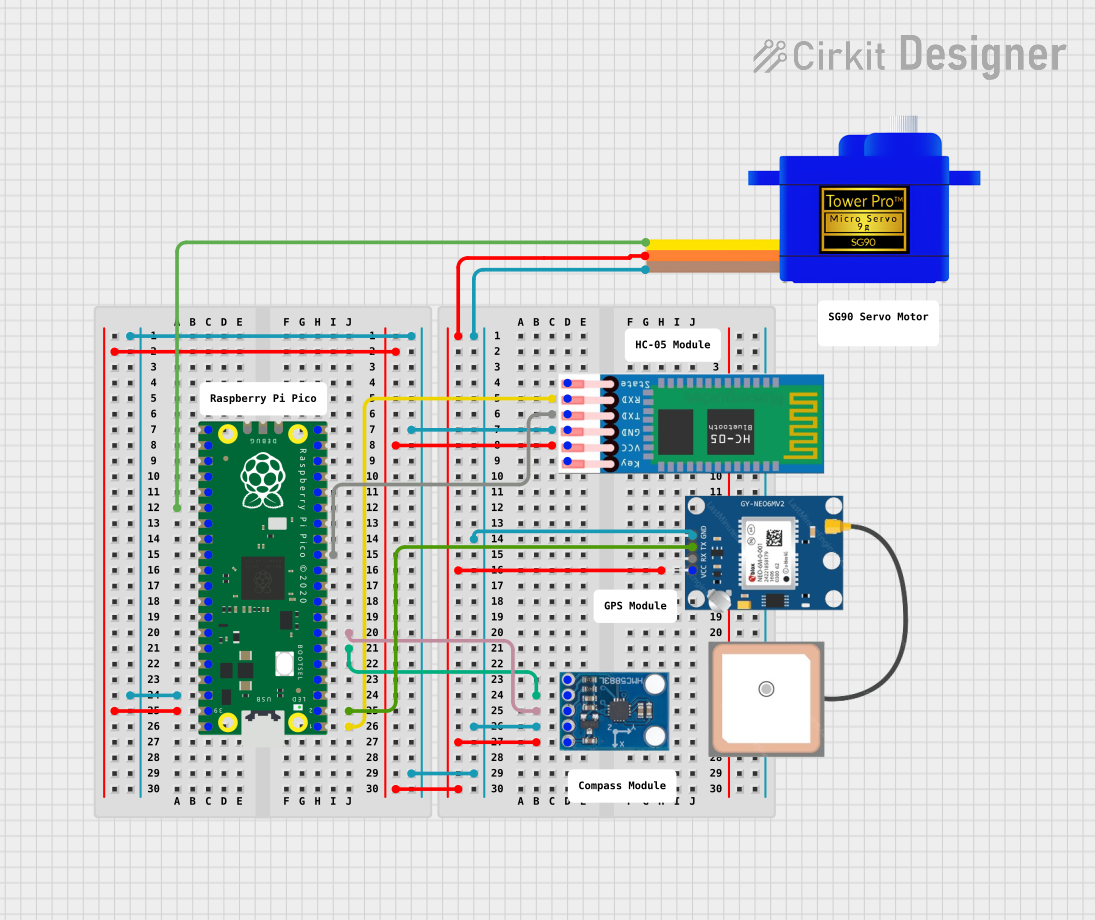
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer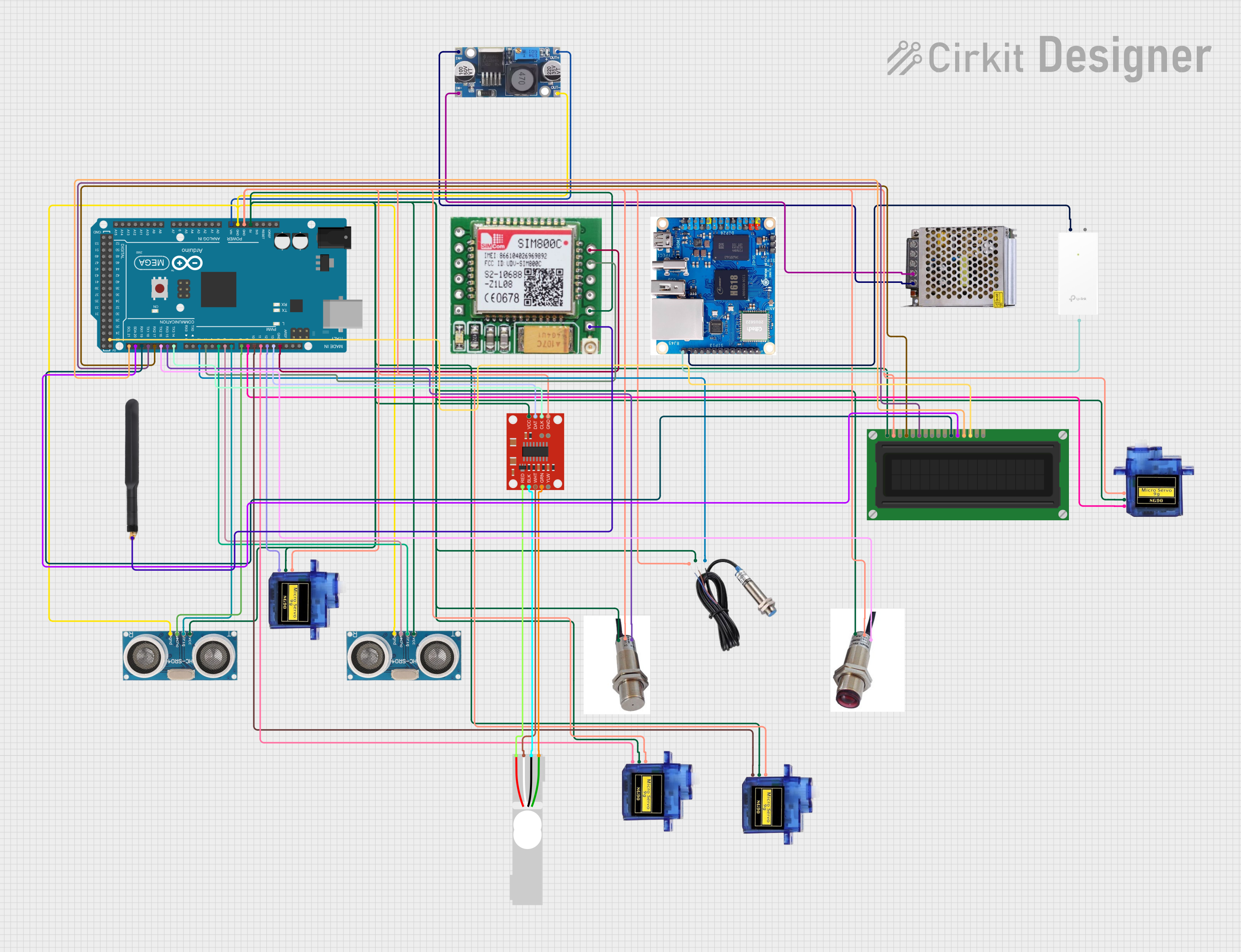
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Pimorini PGA2350

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Audio signal processing in professional and consumer audio equipment
- Volume control in audio amplifiers and mixers
- Preamplifiers for microphones and other audio input devices
- Dynamic range adjustment in audio systems
- High-fidelity audio systems requiring precise gain control
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the Pimorini PGA2350:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (VDD) | 2.7V to 5.5V |
| Gain Range | -95.5 dB to +31.5 dB (0.5 dB steps) |
| Input Impedance | 10 kΩ |
| Output Impedance | 100 Ω |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio | 120 dB |
| Total Harmonic Distortion | 0.0004% |
| Control Interface | SPI |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | 16-pin SSOP |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Pimorini PGA2350 features a 16-pin SSOP package. The pinout and descriptions are as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Positive supply voltage |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | INL+ | Left channel positive input |
| 4 | INL- | Left channel negative input |
| 5 | INR+ | Right channel positive input |
| 6 | INR- | Right channel negative input |
| 7 | OUTL | Left channel output |
| 8 | OUTR | Right channel output |
| 9 | SCLK | SPI clock input |
| 10 | SDI | SPI data input |
| 11 | CS | Chip select (active low) |
| 12 | MUTE | Mute control (active high) |
| 13 | NC | No connection |
| 14 | NC | No connection |
| 15 | NC | No connection |
| 16 | NC | No connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the PGA2350 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a stable power supply within the range of 2.7V to 5.5V. Connect the GND pin to the circuit ground.
- Audio Inputs: Connect the audio signal sources to the INL+/- and INR+/- pins for the left and right channels, respectively.
- Audio Outputs: Connect the OUTL and OUTR pins to the next stage of the audio system (e.g., speakers or further amplification stages).
- SPI Control: Use the SCLK, SDI, and CS pins to interface with a microcontroller or other SPI master device. The SPI interface is used to program the gain settings.
- Mute Function: Use the MUTE pin to enable or disable the mute function. Pull the pin high to mute the output or low to enable audio output.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF and 10 µF) close to the VDD pin to ensure stable operation and minimize noise.
- Input Coupling: Use coupling capacitors on the input pins to block DC offsets from the audio source.
- Output Loading: Ensure the output impedance matches the load impedance for optimal performance.
- SPI Configuration: Configure the SPI interface with the correct clock polarity and phase (CPOL = 0, CPHA = 0).
- Gain Settings: Program the desired gain level using the SPI interface. The gain can be adjusted in 0.5 dB steps from -95.5 dB to +31.5 dB.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the PGA2350 using an Arduino UNO via SPI:
#include <SPI.h>
// Define SPI pins for the PGA2350
const int CS_PIN = 10; // Chip select pin
void setup() {
// Initialize SPI communication
SPI.begin();
pinMode(CS_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Set CS pin high (inactive)
// Set SPI settings: 1 MHz clock, MSB first, SPI mode 0
SPI.beginTransaction(SPISettings(1000000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
}
void setGain(float gain) {
// Convert gain to PGA2350 register value
int gainValue = (int)((gain + 95.5) * 2); // Gain in 0.5 dB steps
byte highByte = (gainValue >> 8) & 0xFF; // High byte of gain value
byte lowByte = gainValue & 0xFF; // Low byte of gain value
// Send gain value to PGA2350
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, LOW); // Activate chip select
SPI.transfer(highByte); // Send high byte
SPI.transfer(lowByte); // Send low byte
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Deactivate chip select
}
void loop() {
// Example: Set gain to 10 dB
setGain(10.0);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Ensure the MUTE pin is pulled low to enable audio output.
- Verify that the input and output connections are correct.
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the specified range.
Distorted Audio:
- Verify that the gain setting is appropriate for the input signal level.
- Check for proper decoupling and coupling capacitor placement.
SPI Communication Failure:
- Ensure the SPI clock, data, and chip select connections are correct.
- Verify that the SPI settings (clock speed, polarity, and phase) match the PGA2350 requirements.
Excessive Noise:
- Use proper grounding techniques to minimize noise.
- Ensure the input signal source is clean and free of interference.
FAQs
Q: Can the PGA2350 be used with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the PGA2350 operates with a supply voltage as low as 2.7V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.
Q: What is the maximum gain setting of the PGA2350?
A: The maximum gain is +31.5 dB, adjustable in 0.5 dB steps.
Q: Is the PGA2350 suitable for stereo audio applications?
A: Yes, the PGA2350 supports independent left and right channel inputs and outputs, making it ideal for stereo audio systems.