
How to Use Battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with Battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A battery is a device that stores electrical energy in chemical form and provides a voltage to power electronic circuits. It is a fundamental component in electronics, enabling portable and backup power solutions. Batteries come in various types, such as alkaline, lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and lead-acid, each suited for specific applications.
Common applications of batteries include:
- Powering portable electronic devices (e.g., smartphones, laptops, and remote controls)
- Providing backup power for critical systems (e.g., uninterruptible power supplies)
- Supplying energy for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage
- Enabling small-scale electronics like sensors and microcontrollers
Explore Projects Built with Battery
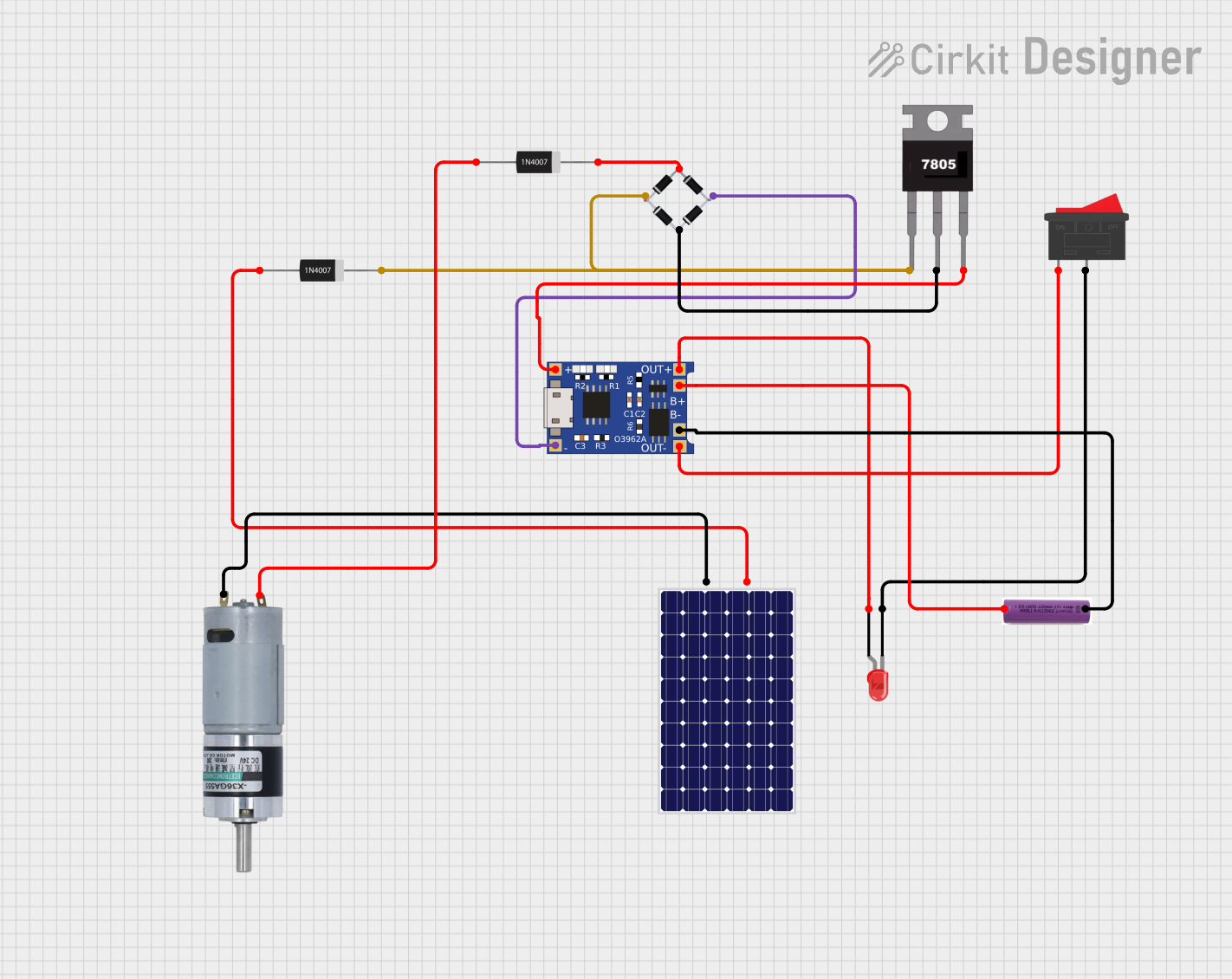
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer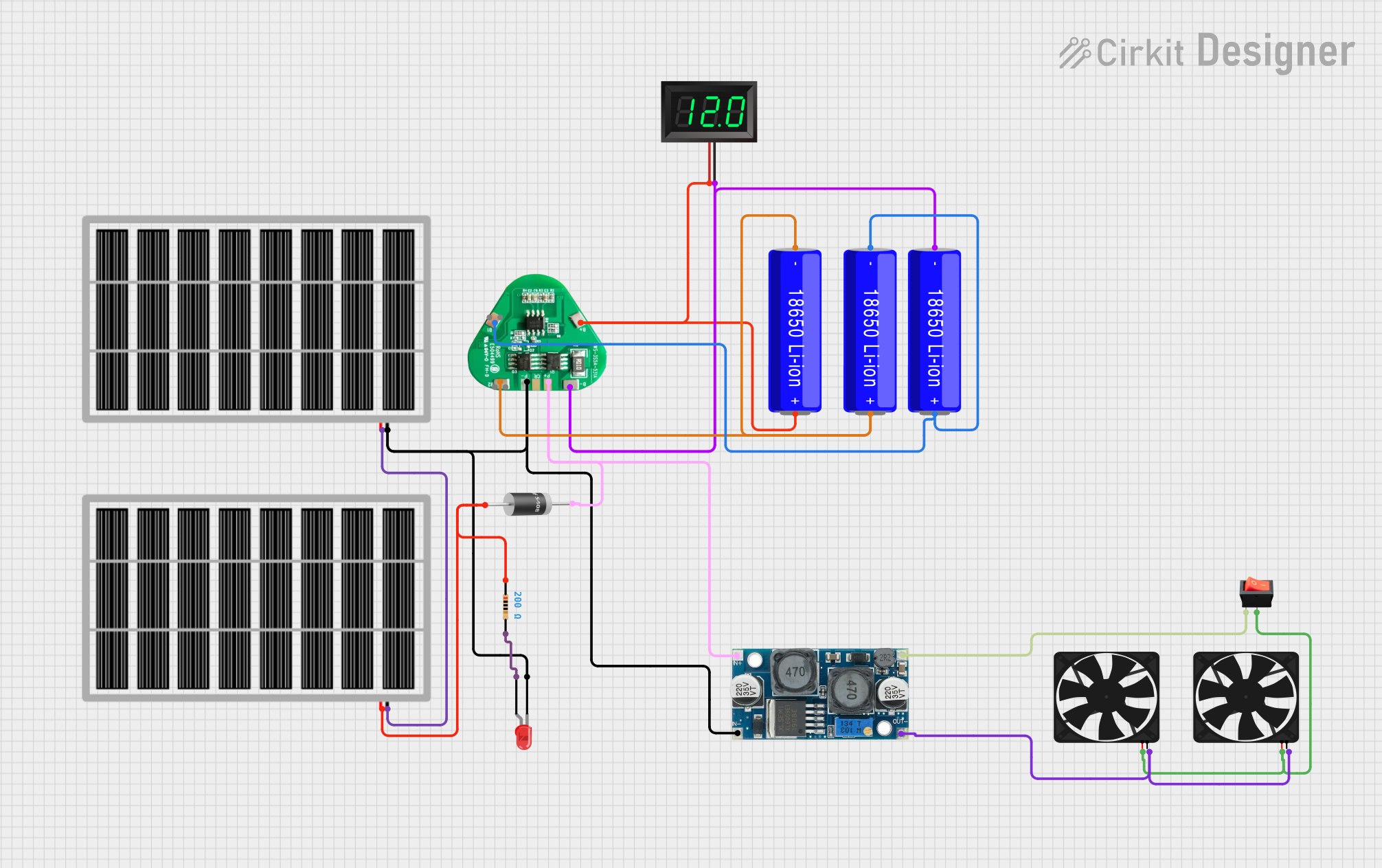
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer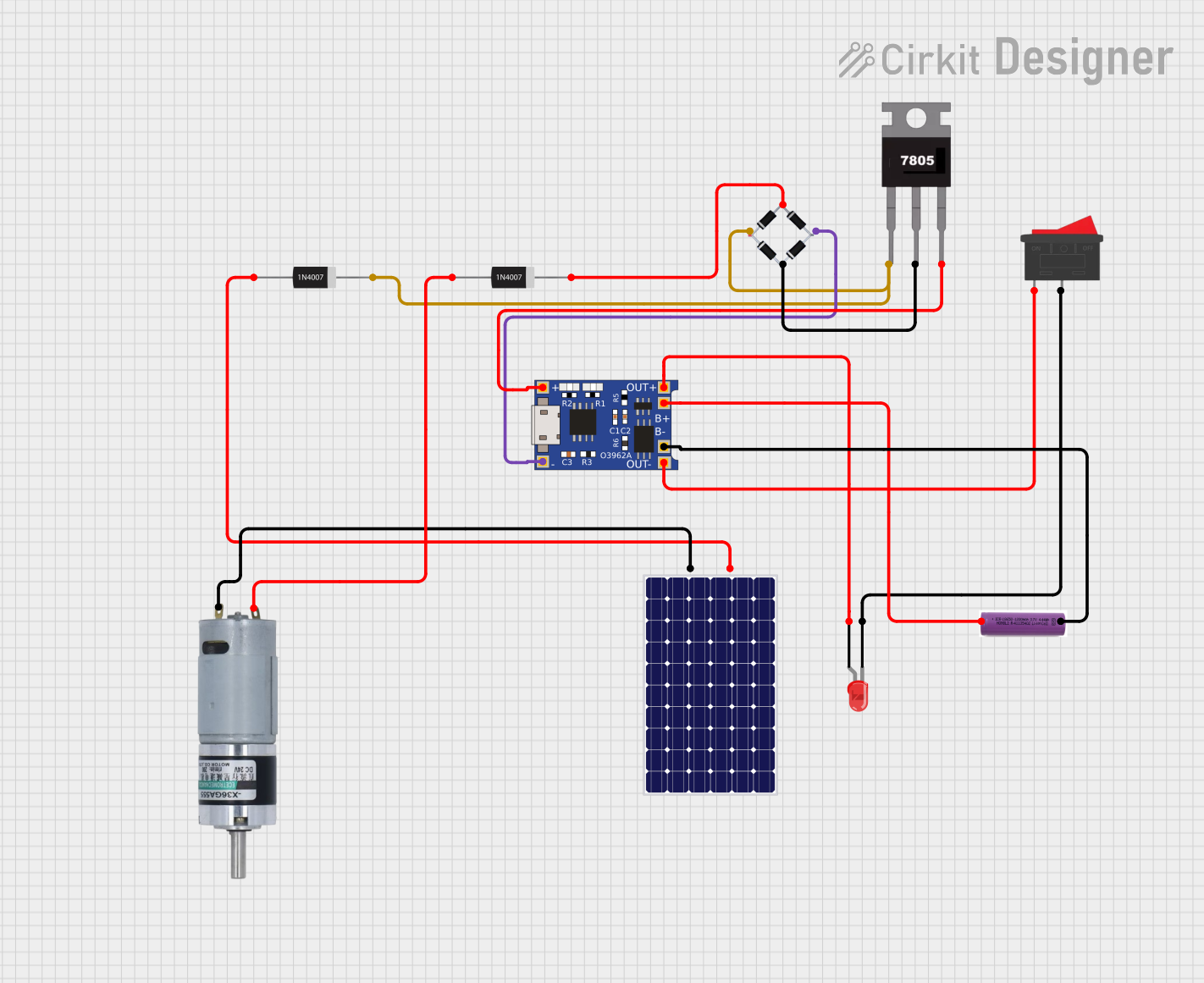
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The specifications of a battery depend on its type and intended use. Below are general technical details for batteries:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | The typical voltage output of the battery (e.g., 1.5V, 3.7V, 12V). |
| Capacity | The amount of charge the battery can store, measured in milliamp-hours (mAh) or amp-hours (Ah). |
| Chemistry | The chemical composition of the battery (e.g., lithium-ion, alkaline). |
| Rechargeability | Indicates whether the battery is rechargeable or single-use. |
| Operating Temperature | The temperature range within which the battery operates efficiently. |
| Shelf Life | The duration the battery can be stored without significant capacity loss. |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Batteries typically have two terminals: positive (+) and negative (-). The table below describes these terminals:
| Terminal | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | (+) | The terminal where current flows out of the battery in a conventional circuit. |
| Negative | (-) | The terminal where current flows into the battery in a conventional circuit. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use a Battery in a Circuit
- Identify the Battery Type: Choose a battery with the appropriate voltage and capacity for your circuit.
- Connect the Terminals:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the positive rail of the circuit.
- Connect the negative terminal to the ground (GND) rail.
- Use a Battery Holder: For safety and convenience, use a battery holder or clip to secure the battery in place.
- Add Protection: Include a fuse or current-limiting resistor to prevent overcurrent or short circuits.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Match Voltage Requirements: Ensure the battery voltage matches the requirements of your circuit to avoid damage.
- Avoid Overdischarge: For rechargeable batteries, avoid discharging below the recommended voltage to prevent damage.
- Monitor Temperature: Do not expose batteries to extreme heat or cold, as this can reduce performance and lifespan.
- Dispose Properly: Follow local regulations for disposing of batteries, especially rechargeable ones, to prevent environmental harm.
Example: Connecting a Battery to an Arduino UNO
To power an Arduino UNO with a 9V battery, follow these steps:
- Connect the positive terminal of the 9V battery to the Arduino's VIN pin.
- Connect the negative terminal to the GND pin.
Here is an example Arduino sketch to blink an LED while powered by a battery:
// This code blinks an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO.
// Ensure the Arduino is powered by a 9V battery connected to VIN and GND.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output for the LED
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Battery Drains Quickly:
- Cause: High current draw or a faulty circuit.
- Solution: Check the circuit for short circuits or reduce the load on the battery.
Battery Overheats:
- Cause: Overcurrent or exposure to high temperatures.
- Solution: Use a current-limiting resistor or ensure proper ventilation.
Device Does Not Power On:
- Cause: Incorrect battery polarity or insufficient voltage.
- Solution: Verify the battery is installed correctly and meets the voltage requirements.
Rechargeable Battery Does Not Charge:
- Cause: Faulty charger or battery degradation.
- Solution: Test with a different charger or replace the battery if it is old.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a higher voltage battery than specified for my device?
A: No, using a higher voltage battery can damage your device. Always use a battery with the recommended voltage.
Q: How do I know when to replace a battery?
A: Replace the battery when it no longer holds a charge or when the device performance degrades significantly.
Q: Can I mix different types of batteries in a device?
A: No, mixing battery types (e.g., alkaline and NiMH) can cause uneven discharge and damage the device.
Q: How do I store batteries safely?
A: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and flammable materials. Keep them out of reach of children.