
How to Use BTS7960: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with BTS7960 in Cirkit Designer
Design with BTS7960 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BTS7960 is a high-current H-bridge motor driver designed for driving DC motors and other inductive loads. Manufactured by an unknown Chinese manufacturer under the part ID "motorcontroller," this component is widely used in robotics, automation, and other applications requiring precise motor control. It supports bidirectional motor control and features built-in protection mechanisms, including overcurrent, overtemperature, and undervoltage protection, ensuring reliable operation in demanding environments.
Explore Projects Built with BTS7960
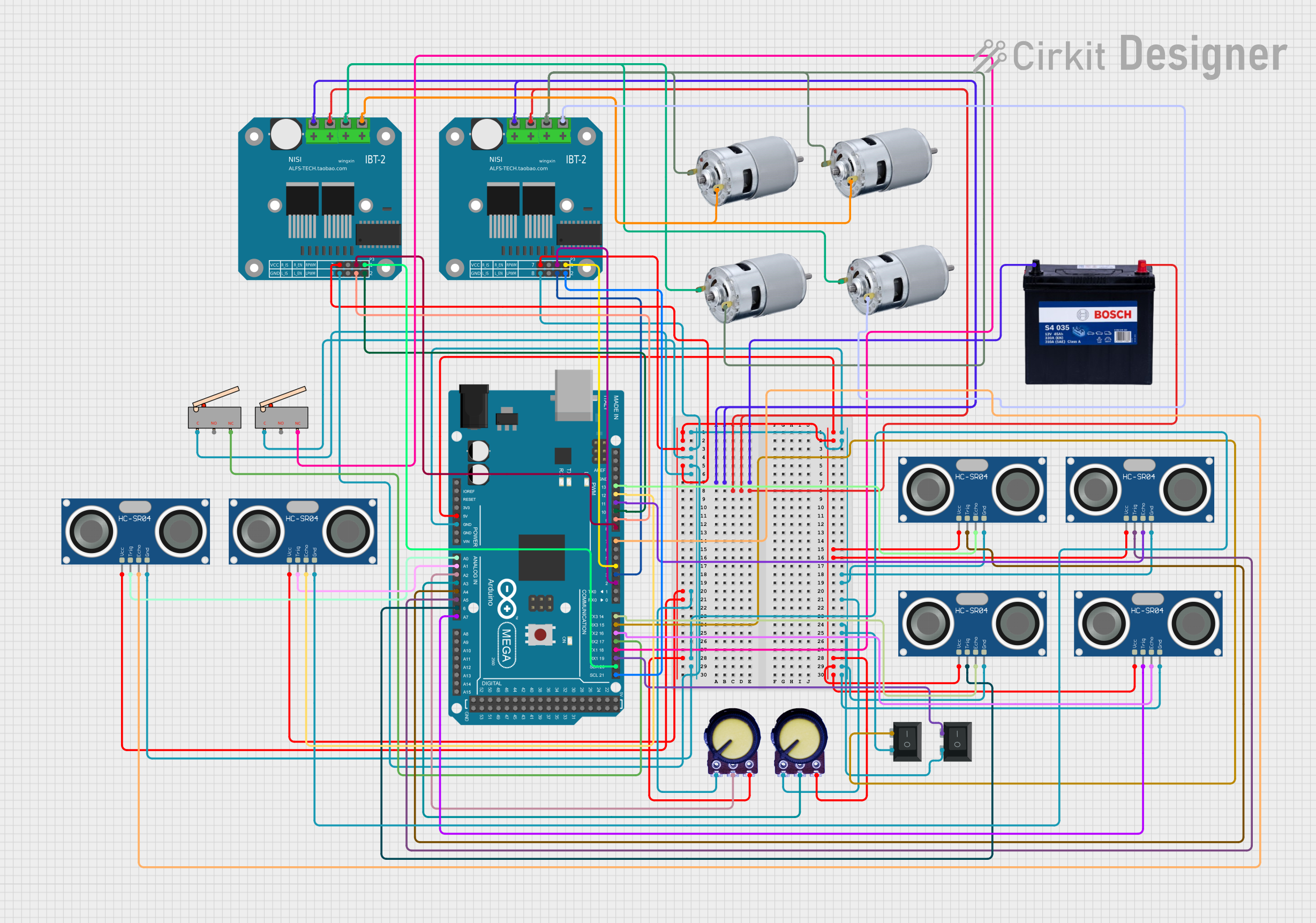
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer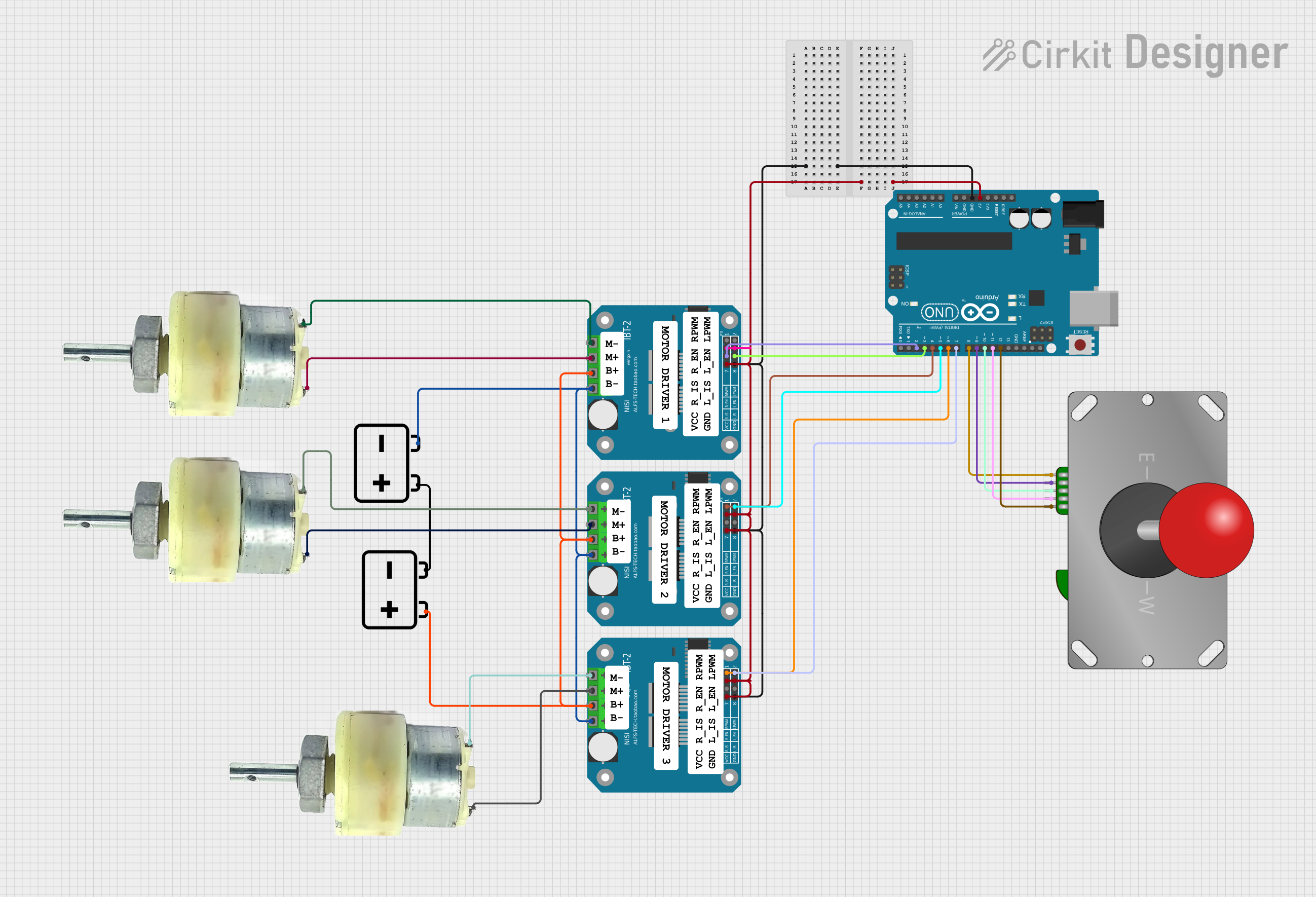
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer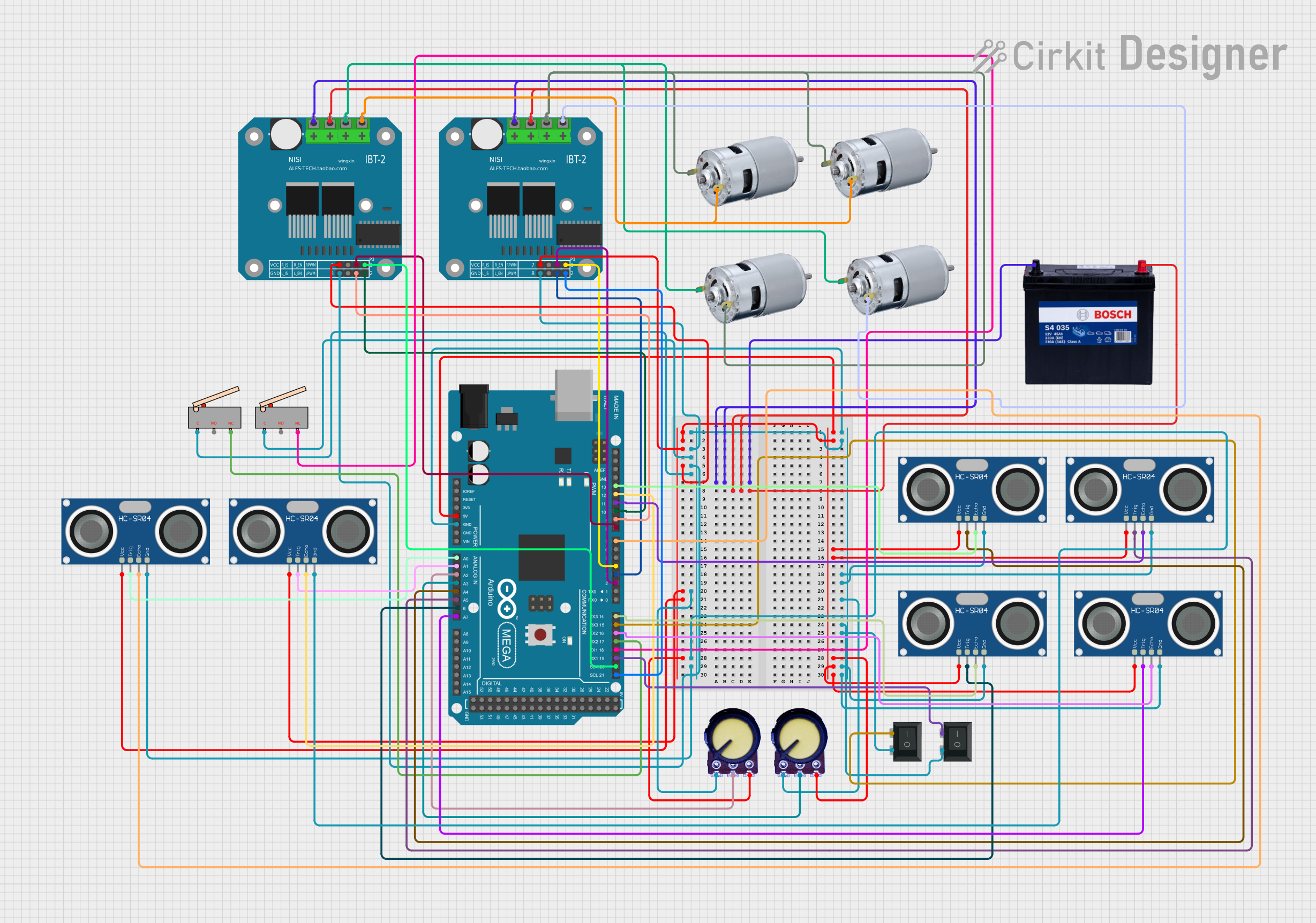
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer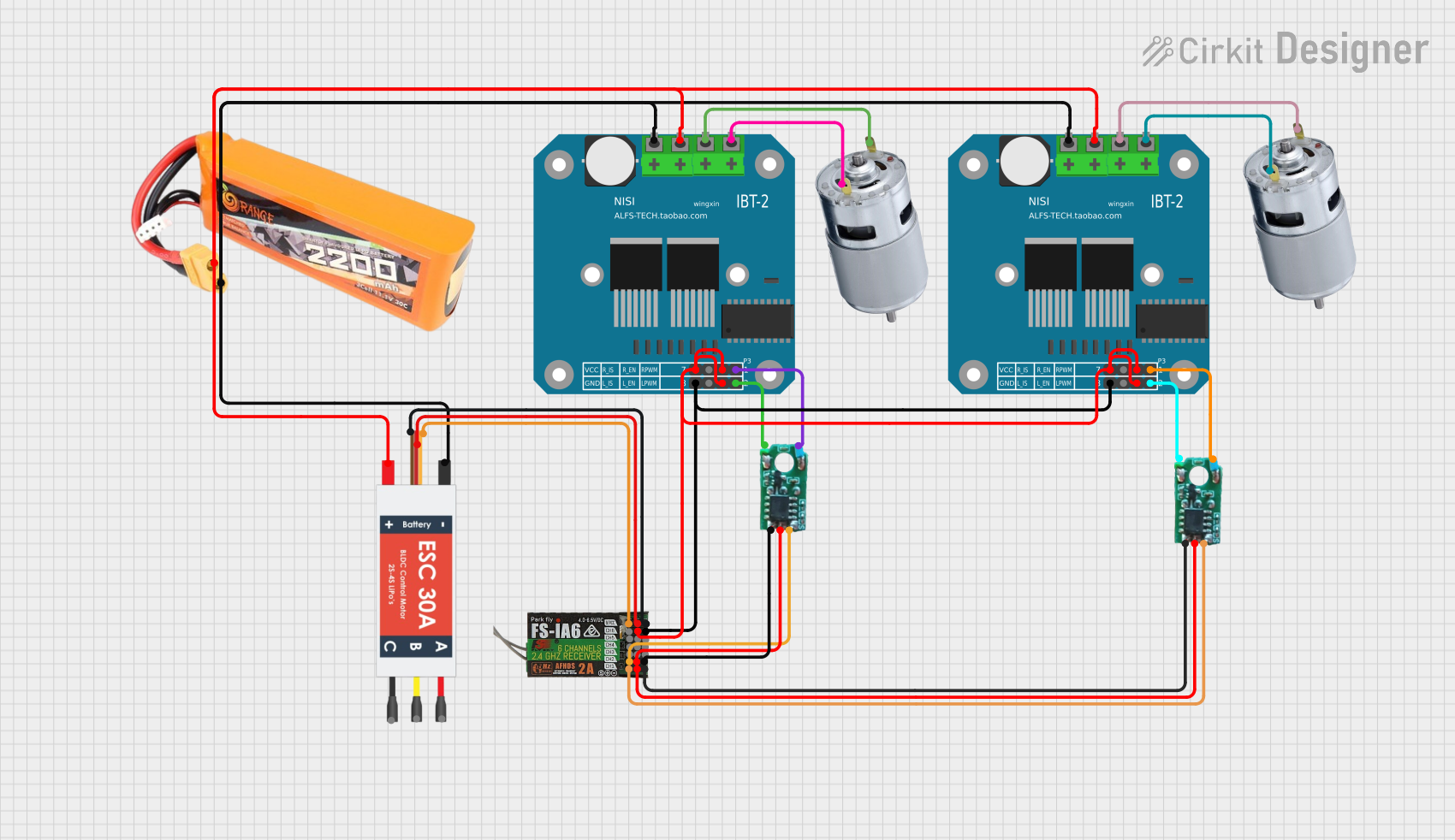
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BTS7960

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics (e.g., motorized arms, wheeled robots)
- Industrial automation systems
- Electric vehicles and carts
- Conveyor belts and other motorized machinery
- DIY motor control projects
Technical Specifications
The BTS7960 is a robust motor driver with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage (Vcc) | 5V (logic level) |
| Motor Voltage (VM) | 6V to 27V |
| Continuous Output Current | Up to 43A |
| Peak Output Current | 50A |
| PWM Frequency | Up to 25kHz |
| Logic Input Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Overcurrent Protection | Yes |
| Overtemperature Protection | Yes |
| Undervoltage Protection | Yes |
Pin Configuration
The BTS7960 module typically comes with a 12-pin interface. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power Input | 5V logic power supply input. |
| GND | Power Input | Ground connection for logic and motor power. |
| RPWM | Logic Input | PWM signal input for controlling motor speed in one direction. |
| LPWM | Logic Input | PWM signal input for controlling motor speed in the opposite direction. |
| R_EN | Logic Input | Enable pin for the right side of the H-bridge. Active HIGH. |
| L_EN | Logic Input | Enable pin for the left side of the H-bridge. Active HIGH. |
| R_IS | Analog Output | Current sense output for the right side of the H-bridge. |
| L_IS | Analog Output | Current sense output for the left side of the H-bridge. |
| VM+ | Power Input | Positive terminal for motor power supply (6V to 27V). |
| VM- | Power Input | Negative terminal for motor power supply (connected to GND). |
| MOTOR+ | Power Output | Positive terminal for the motor connection. |
| MOTOR- | Power Output | Negative terminal for the motor connection. |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the BTS7960 to a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect a 6V to 27V power source to the
VM+andVM-pins. Ensure the power supply can handle the motor's current requirements. - Logic Power: Provide a 5V logic power supply to the
VCCpin and connect theGNDpin to the ground of your microcontroller. - Motor Connection: Connect the motor terminals to the
MOTOR+andMOTOR-pins. - Control Signals: Use the
RPWMandLPWMpins to send PWM signals for speed control. Use theR_ENandL_ENpins to enable or disable the respective sides of the H-bridge.
Example: Using BTS7960 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example Arduino sketch to control a motor using the BTS7960:
// Define control pins for the BTS7960
#define RPWM 9 // PWM pin for forward direction
#define LPWM 10 // PWM pin for reverse direction
#define R_EN 8 // Enable pin for forward direction
#define L_EN 7 // Enable pin for reverse direction
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(RPWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LPWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_EN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_EN, OUTPUT);
// Enable both sides of the H-bridge
digitalWrite(R_EN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(L_EN, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Run motor forward at 50% speed
analogWrite(RPWM, 128); // 50% duty cycle (128 out of 255)
analogWrite(LPWM, 0); // No reverse signal
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Example: Run motor in reverse at 75% speed
analogWrite(RPWM, 0); // No forward signal
analogWrite(LPWM, 192); // 75% duty cycle (192 out of 255)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(RPWM, 0);
analogWrite(LPWM, 0);
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Important Considerations
- Heat Dissipation: The BTS7960 can handle high currents, but it may generate significant heat. Use a heatsink or active cooling if necessary.
- Power Supply: Ensure the motor power supply can provide sufficient current for the motor's operation.
- PWM Frequency: Use a PWM frequency within the recommended range (up to 25kHz) for optimal performance.
- Protection Features: The built-in protection mechanisms are helpful, but avoid pushing the module to its absolute limits to ensure longevity.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Motor Not Running
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the power supply meets the motor's requirements.
Overheating
- Cause: Prolonged operation at high currents without proper cooling.
- Solution: Add a heatsink or active cooling to the module.
Erratic Motor Behavior
- Cause: Noise in the PWM signal or insufficient grounding.
- Solution: Use proper decoupling capacitors and ensure a solid ground connection.
No Response to PWM Signals
- Cause: Incorrect logic voltage levels or damaged module.
- Solution: Verify the logic voltage is 5V and test the module with a known working setup.
FAQs
Q: Can the BTS7960 drive stepper motors?
A: No, the BTS7960 is designed for DC motors and other inductive loads. Stepper motors require a dedicated stepper driver.
Q: What is the maximum motor voltage the BTS7960 can handle?
A: The BTS7960 supports motor voltages from 6V to 27V.
Q: Can I use the BTS7960 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the logic input pins are compatible with both 3.3V and 5V signals.
Q: How do I know if the module's protection features are active?
A: The module will automatically shut down or limit current when protection features are triggered. Check your circuit for faults if this occurs frequently.