
How to Use esp32: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
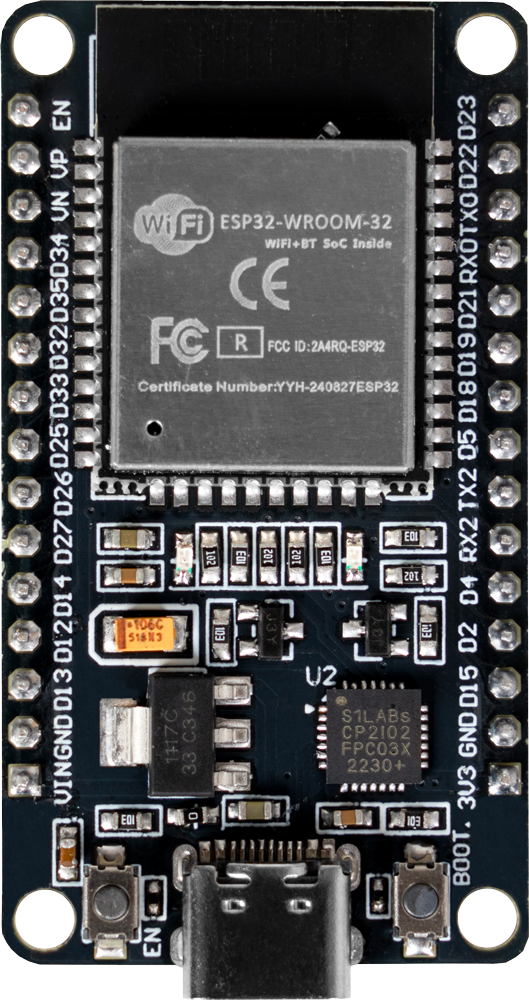
 Design with esp32 in Cirkit Designer
Design with esp32 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power system on a chip (SoC) developed by Espressif Systems. It features integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it an ideal choice for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, smart devices, and embedded systems. The ESP32 is highly versatile, offering dual-core processing, a wide range of GPIO pins, and support for various communication protocols.
Explore Projects Built with esp32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer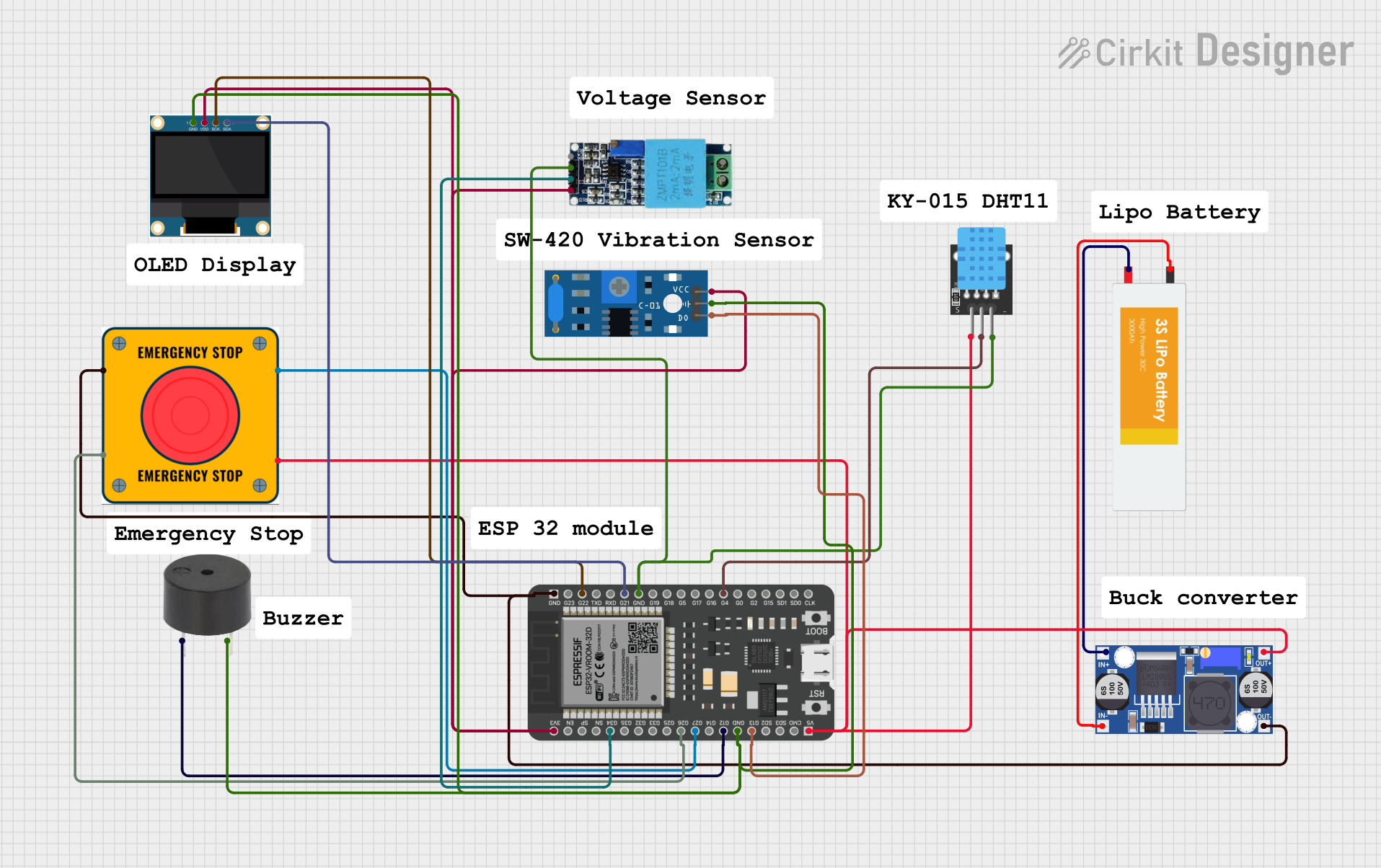
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer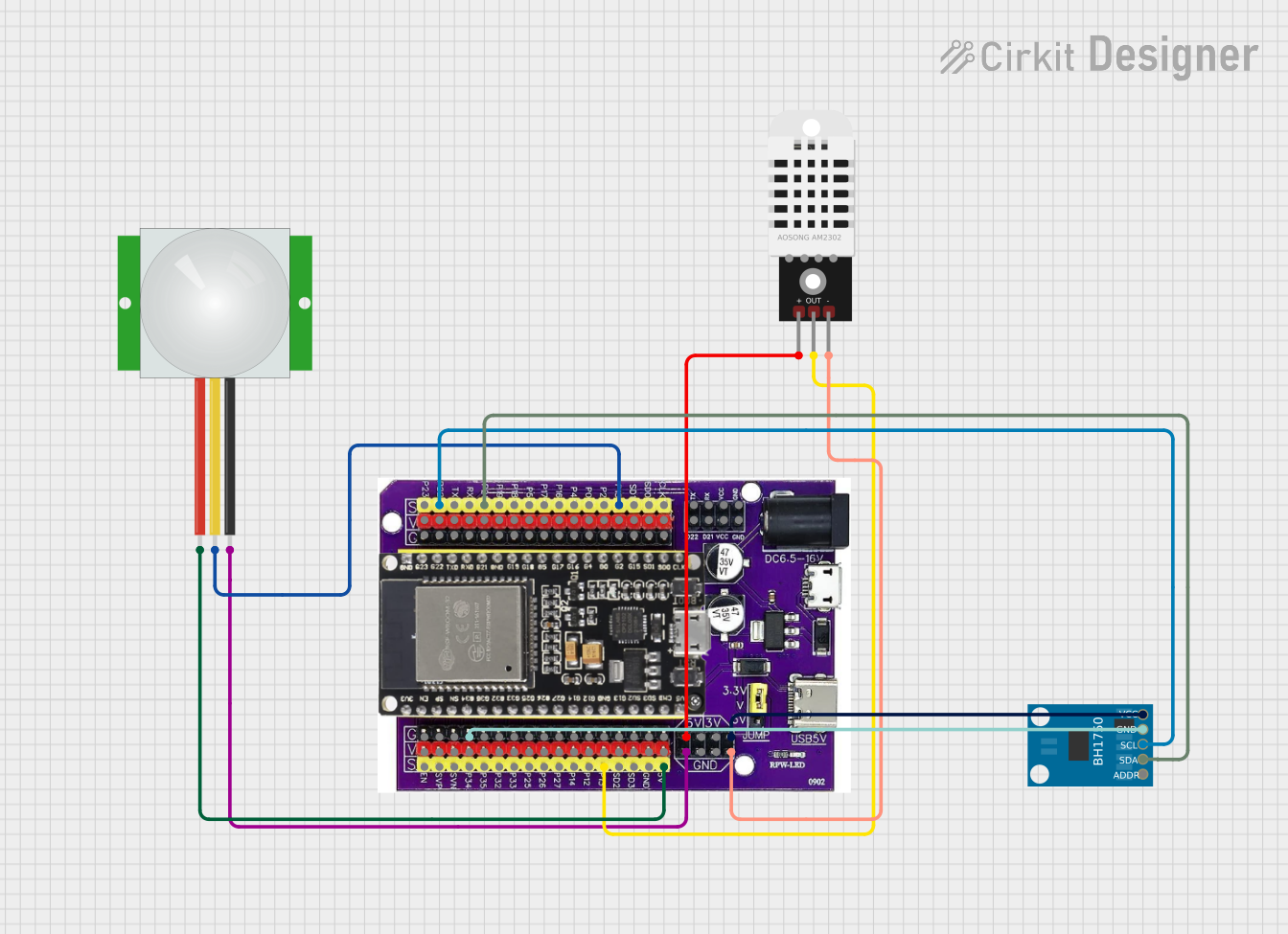
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer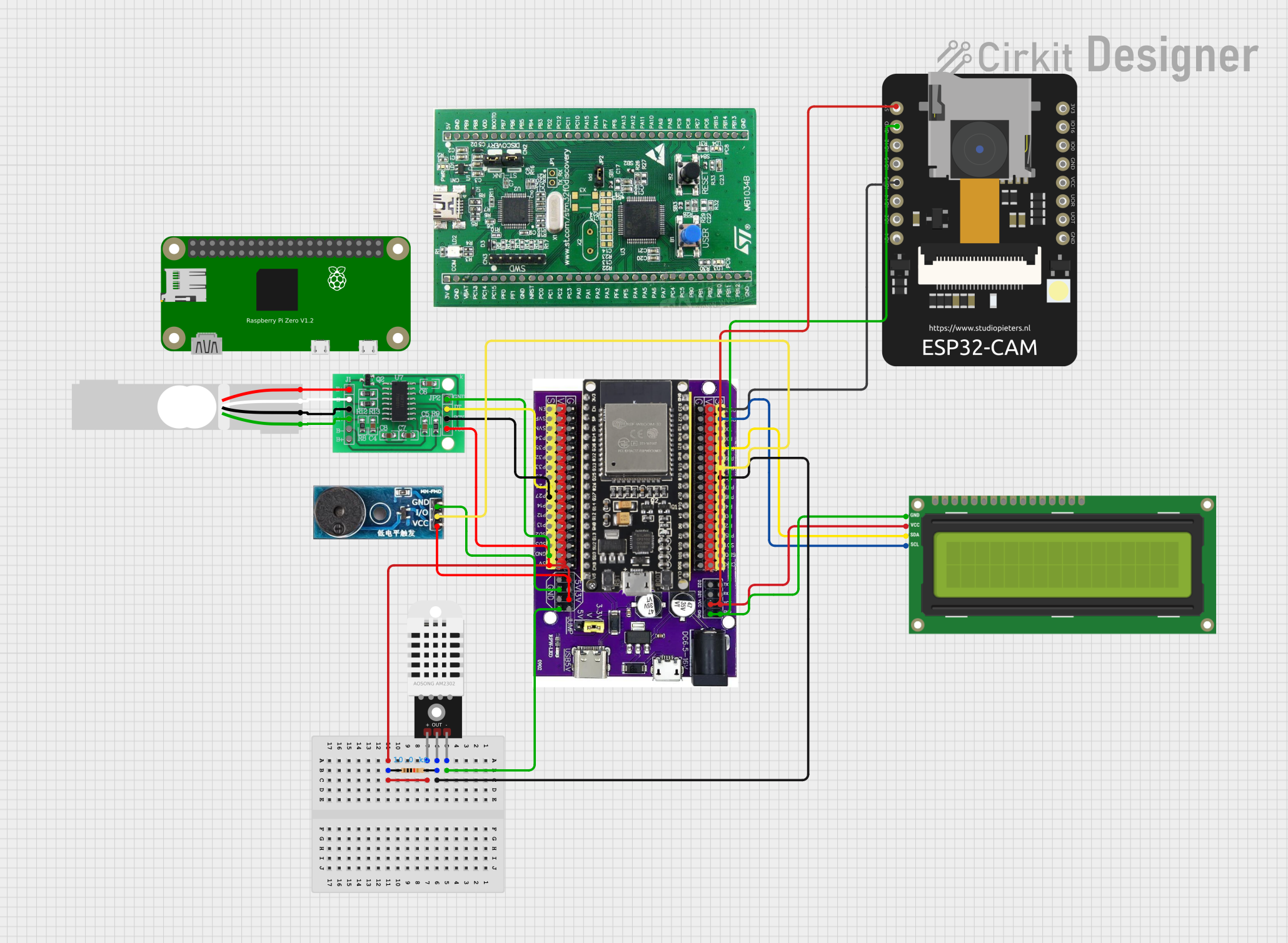
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with esp32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices (e.g., smart home systems, sensors, and actuators)
- Wearable technology
- Wireless communication hubs
- Robotics and automation
- Data logging and remote monitoring
- Prototyping and educational projects
Technical Specifications
The ESP32 is packed with features that make it a powerful and flexible component for a wide range of applications. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | Xtensa® dual-core 32-bit LX6 processor (up to 240 MHz) |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB (varies by module) |
| SRAM | 520 KB |
| Wi-Fi | 802.11 b/g/n (2.4 GHz) |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 4.2 and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3 V |
| GPIO Pins | Up to 34 GPIO pins (multiplexed with other functions) |
| Communication Protocols | UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, CAN, PWM, ADC, DAC |
| ADC Resolution | 12-bit (up to 18 channels) |
| DAC Resolution | 8-bit (2 channels) |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low power consumption with multiple power modes |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 125°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32 has a variety of pins that can be used for different purposes. Below is a table summarizing the key pins and their functions:
| Pin Name | Function |
|---|---|
| GPIO0 | General-purpose I/O, boot mode selection |
| GPIO2 | General-purpose I/O, often used for onboard LEDs |
| GPIO12-15 | General-purpose I/O, SPI interface |
| GPIO21 | General-purpose I/O, I2C SDA |
| GPIO22 | General-purpose I/O, I2C SCL |
| GPIO34-39 | Input-only pins, often used for ADC |
| EN | Enable pin, used to reset the chip |
| 3V3 | 3.3V power supply |
| GND | Ground |
Note: The exact pinout may vary depending on the ESP32 module or development board you are using (e.g., ESP32-WROOM-32, ESP32-WROVER).
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP32 in a Circuit
Powering the ESP32:
- The ESP32 operates at 3.3V. Ensure your power supply provides a stable 3.3V to the
3V3pin. - Avoid supplying 5V directly to the GPIO pins, as this may damage the chip.
- The ESP32 operates at 3.3V. Ensure your power supply provides a stable 3.3V to the
Connecting to Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins for connecting sensors, actuators, and other peripherals.
- Configure the pins in your code to match the required input/output functionality.
Programming the ESP32:
- The ESP32 can be programmed using the Arduino IDE, Espressif's ESP-IDF, or other compatible tools.
- Connect the ESP32 to your computer via a USB-to-serial adapter or a development board with a built-in USB interface.
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Setup:
- Use the built-in libraries (e.g.,
WiFi.hfor Wi-Fi andBluetoothSerial.hfor Bluetooth) to configure wireless communication.
- Use the built-in libraries (e.g.,
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected devices operate at 3.3V logic levels to avoid damaging the ESP32.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to prevent unexpected resets or malfunctions.
- GPIO Usage: Some GPIO pins have specific functions during boot (e.g., GPIO0 for boot mode selection). Avoid using these pins for general I/O unless necessary.
- Heat Management: The ESP32 can get warm during operation. Ensure proper ventilation or heat dissipation in your design.
Example: Connecting the ESP32 to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of using the ESP32 with the Arduino IDE to connect to a Wi-Fi network:
#include <WiFi.h> // Include the Wi-Fi library for ESP32
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication at 115200 baud
delay(1000); // Wait for a moment before starting
Serial.println("Connecting to Wi-Fi...");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password); // Start Wi-Fi connection
// Wait until the ESP32 connects to the Wi-Fi network
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWi-Fi connected!");
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); // Print the assigned IP address
}
void loop() {
// Add your main code here
}
Tip: Ensure you have installed the ESP32 board package in the Arduino IDE before uploading the code.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
ESP32 Not Connecting to Wi-Fi:
- Double-check your SSID and password.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is operating at 2.4 GHz (ESP32 does not support 5 GHz networks).
- Move the ESP32 closer to the router to improve signal strength.
Frequent Resets or Instability:
- Verify that your power supply provides sufficient current (at least 500 mA).
- Check for loose connections or short circuits in your circuit.
Upload Errors in Arduino IDE:
- Ensure the correct board and COM port are selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Press and hold the
BOOTbutton on the ESP32 while uploading the code.
GPIO Pin Not Working:
- Confirm that the pin is not reserved for special functions (e.g., boot mode).
- Check your code for proper pin configuration.
FAQs
Q: Can the ESP32 operate on battery power?
A: Yes, the ESP32 can be powered by a battery. Use a voltage regulator to ensure a stable 3.3V supply.
Q: How do I reset the ESP32?
A: Press the EN (Enable) button on the development board to reset the ESP32.
Q: Can I use the ESP32 with 5V logic devices?
A: No, the ESP32 operates at 3.3V logic levels. Use a level shifter to interface with 5V devices.
Q: Is the ESP32 compatible with Arduino libraries?
A: Yes, many Arduino libraries are compatible with the ESP32, but some may require modifications.