
How to Use LED Board: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with LED Board in Cirkit Designer
Design with LED Board in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The LED Board by Arron is a versatile and efficient lighting solution designed for a variety of applications. This electronic component is widely used for illumination, signaling, and decorative purposes. Its low power consumption and long lifespan make it a popular choice for projects ranging from simple DIY crafts to complex industrial systems.
Explore Projects Built with LED Board
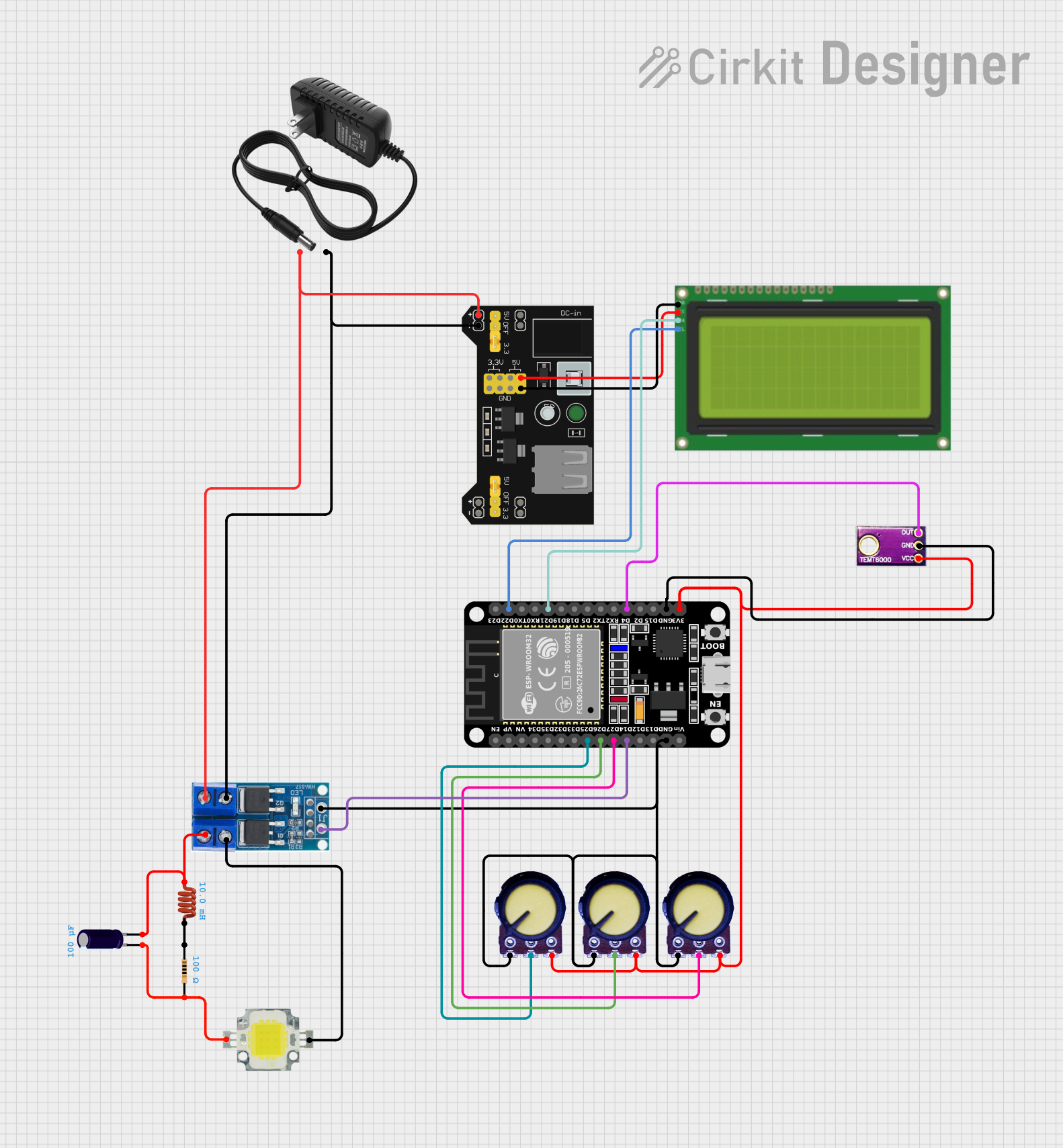
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer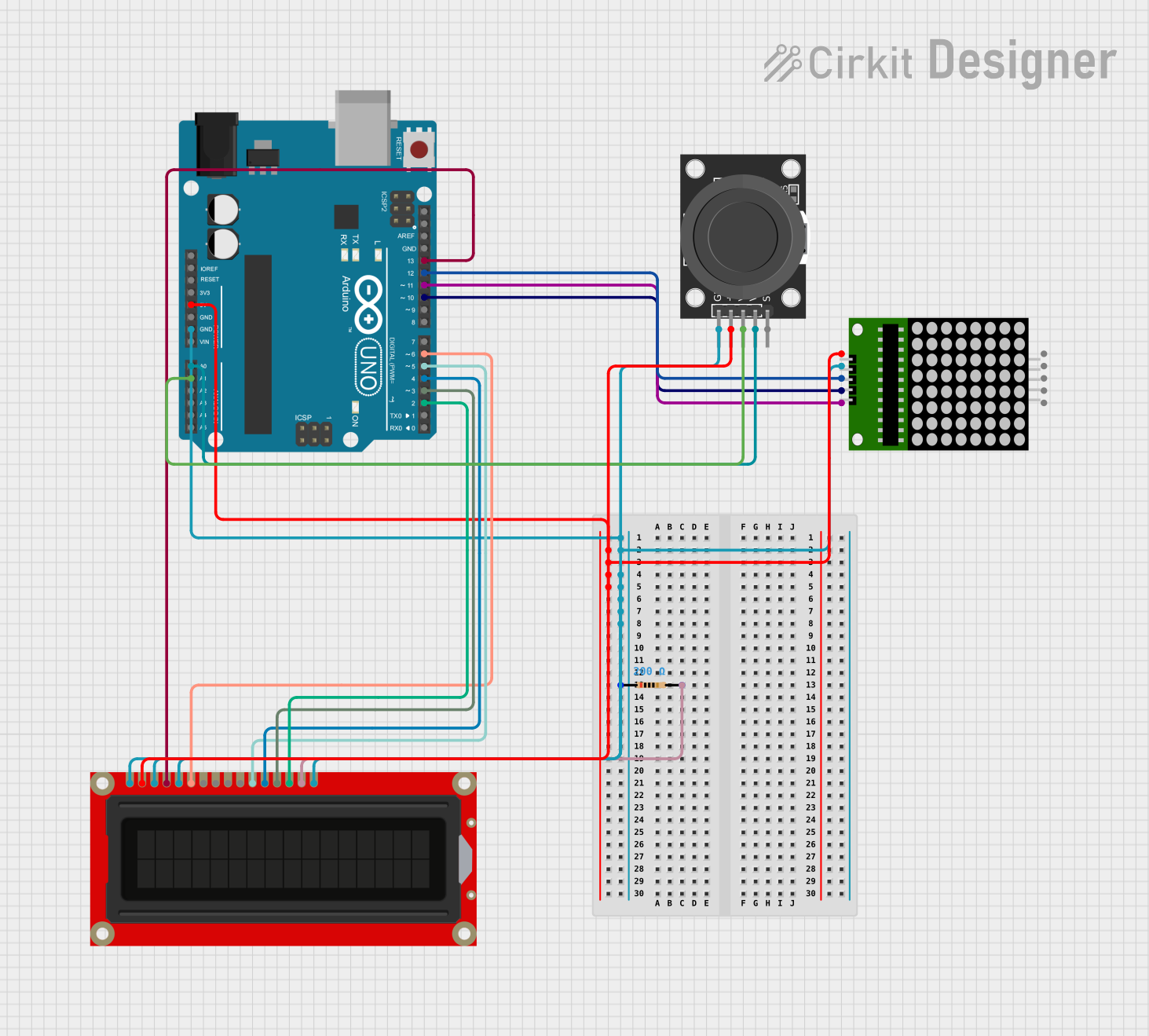
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer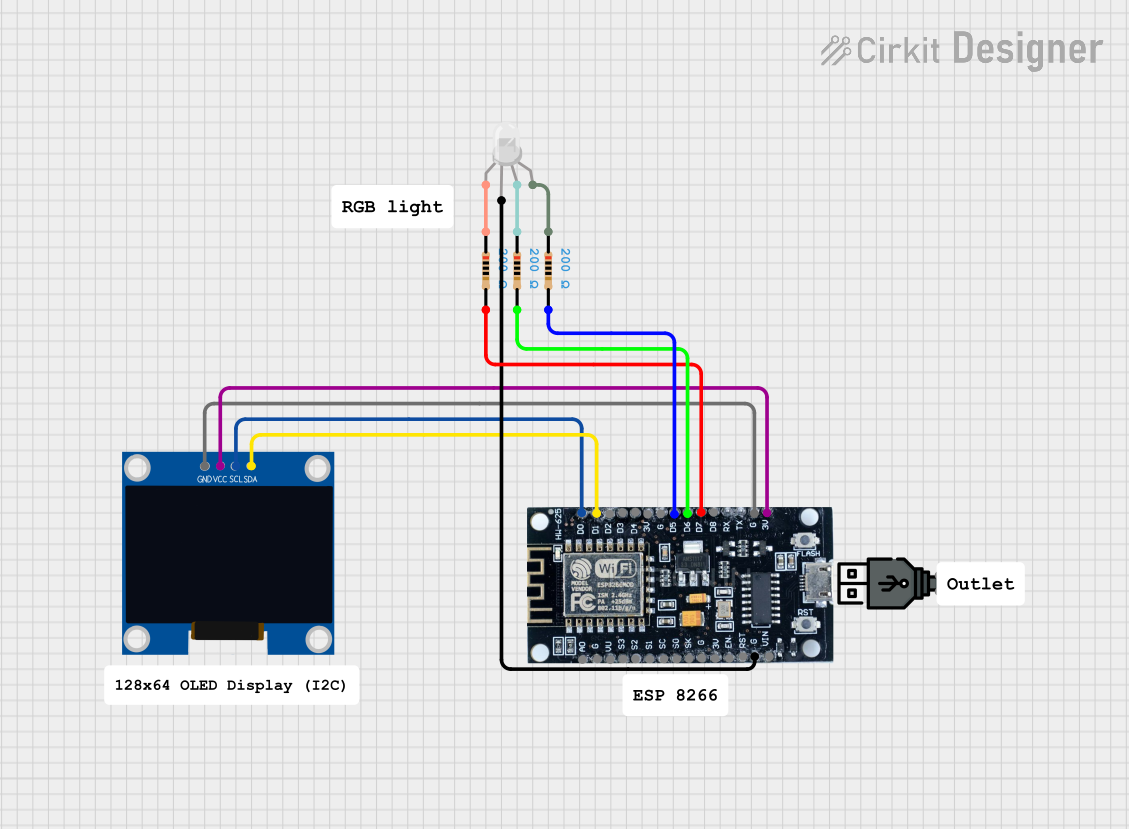
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with LED Board

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Indicator lights for electronic devices
- Backlighting for LCD or display panels
- Decorative lighting for events and venues
- Educational projects and hobbyist circuits
- Prototyping for product development
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: Typically 2V to 3.6V per LED
- Forward Current: Recommended 20mA per LED
- Power Ratings: Varies with the number and type of LEDs used
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode (+) | Connect to positive voltage |
| 2 | Cathode (-) | Connect to ground |
Note: The pin configuration may vary depending on the specific LED board model. Refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for exact details.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply matches the voltage requirements of the LED board. Exceeding the voltage rating can damage the LEDs.
- Current Limiting: Always use a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED to prevent excessive current flow.
- Wiring: Connect the anode pin to the positive side of the power supply through a current-limiting resistor, and the cathode pin to the ground.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: LEDs generate heat; ensure adequate cooling if the LED board is used at high brightness levels for extended periods.
- Dimming: Use a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal to dim the LEDs if required.
- Handling: Avoid static discharge by grounding yourself before handling the LED board.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the LED pin
const int ledPin = 13; // Most Arduino UNOs have an onboard LED on pin 13
void setup() {
// Set the LED pin as an output
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the LED on
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Turn the LED off
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Note: The above code is for an onboard LED. For an external LED board, replace ledPin with the appropriate pin connected to the anode of the LED board.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- LEDs not lighting up: Check if the power supply is correctly connected and within the specified voltage range. Ensure the current-limiting resistor is in place.
- LEDs too dim: Confirm that the current-limiting resistor value is not too high, which can limit the current flow and reduce brightness.
- LEDs burning out: Ensure that the voltage and current do not exceed the maximum ratings specified for the LED board.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-check connections: Verify that all connections are secure and correctly oriented.
- Measure voltage and current: Use a multimeter to check that the voltage across and current through the LEDs are within specifications.
- Resistor calculations: Use Ohm's law (V = IR) to calculate the correct resistor value for the desired current.
FAQs
Q: Can I power multiple LED boards in series? A: It's possible, but ensure that the power supply can handle the combined voltage requirements of all the LED boards.
Q: How do I change the color of the LEDs? A: The LED color is determined by the semiconductor material and cannot be changed. To use different colors, you need to use a different LED board with the desired color LEDs.
Q: Can I use a 9V battery to power the LED board? A: Yes, but you must use an appropriate current-limiting resistor to bring the voltage down to the LED's operating range and limit the current to the recommended level.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the Arron LED Board. For further assistance, consult the manufacturer's datasheet or contact technical support.