
How to Use TB6600: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with TB6600 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TB6600 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TB6600 is a high-performance stepper motor driver designed to control bipolar stepper motors with precision and reliability. It supports adjustable current settings, microstepping capabilities, and includes built-in thermal protection, making it a versatile choice for demanding applications. The TB6600 is widely used in CNC machines, 3D printers, robotics, and other motion control systems where precise motor control is essential.
Explore Projects Built with TB6600
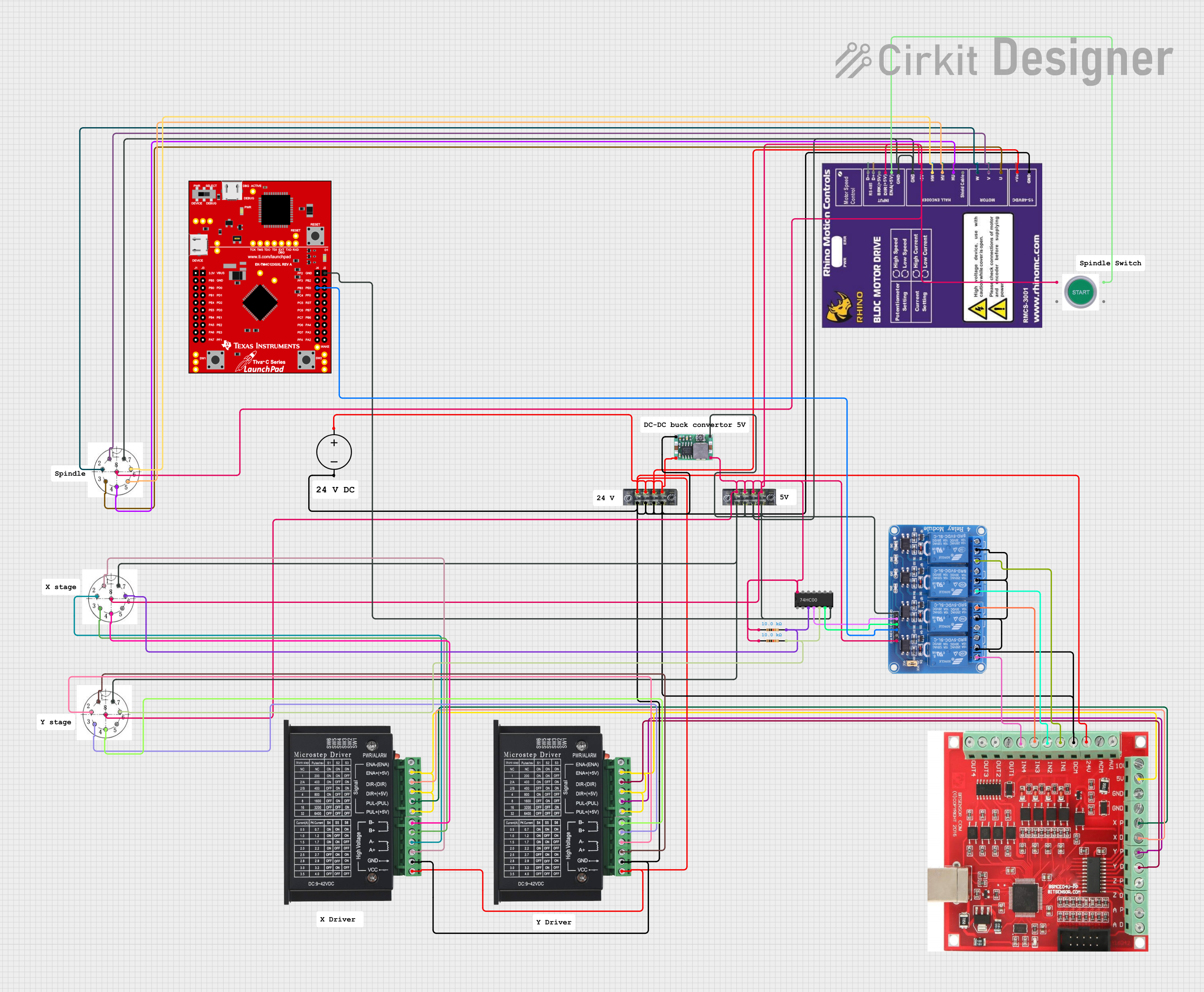
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer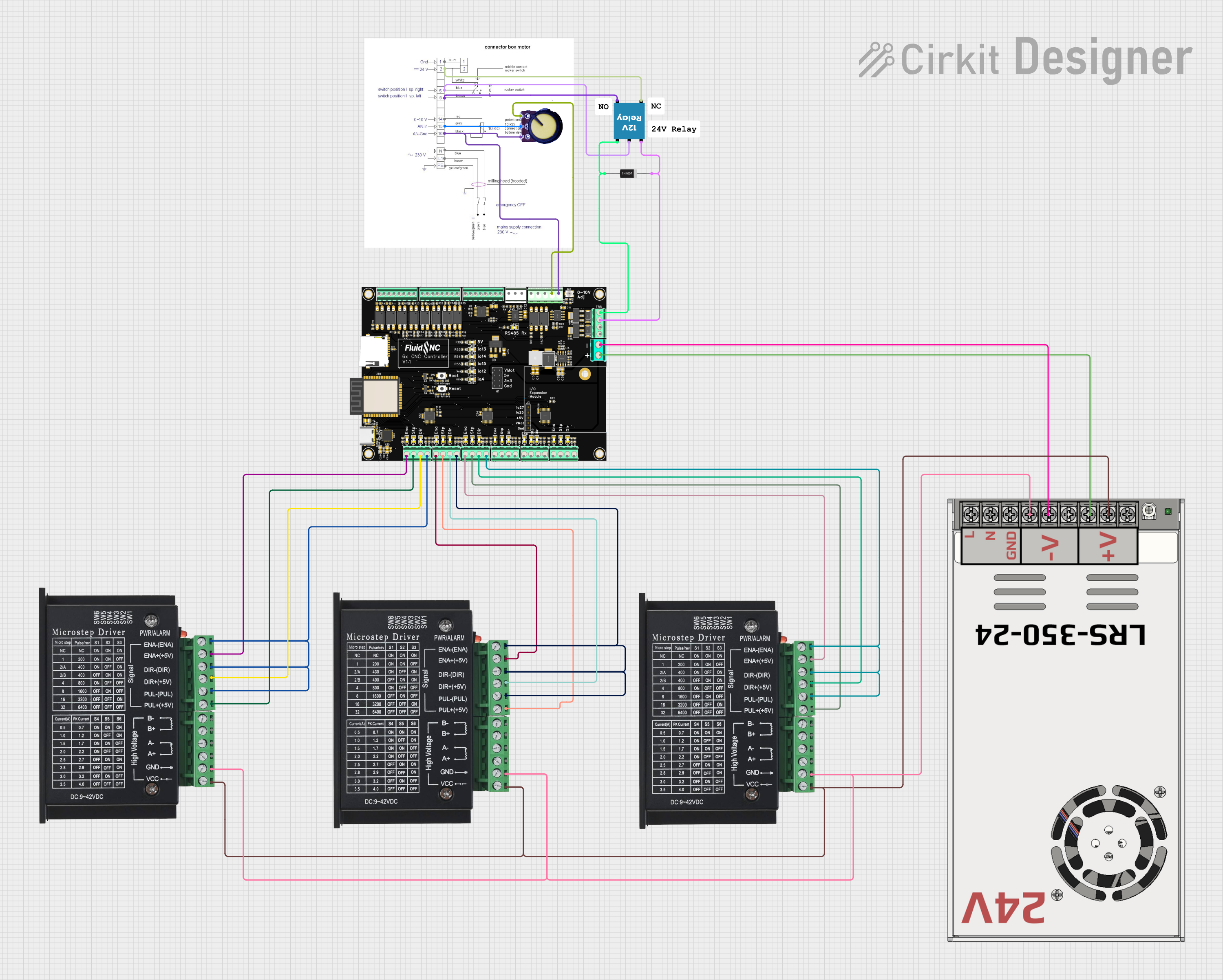
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer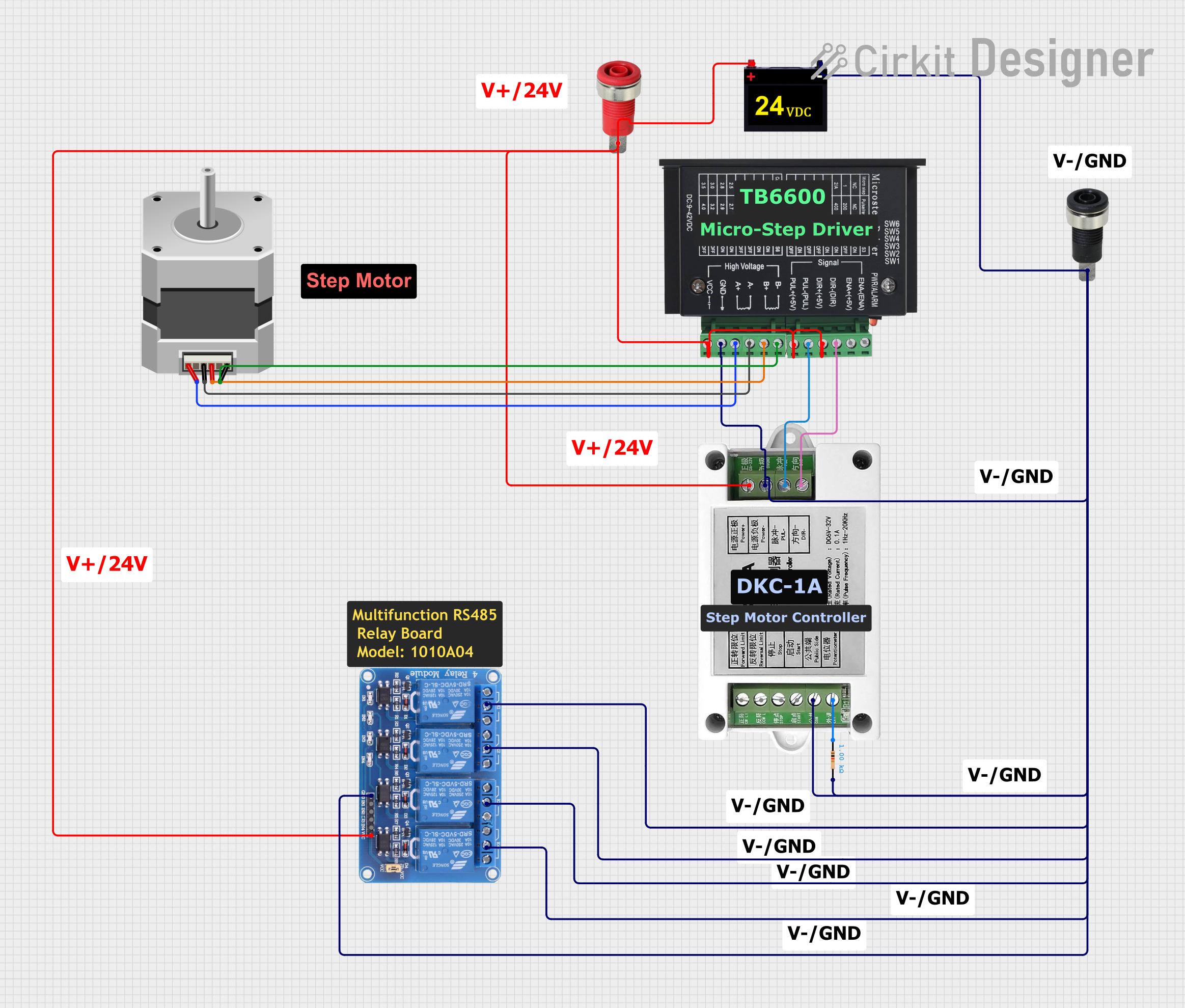
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TB6600

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- CNC machines for precise cutting and engraving
- 3D printers for accurate layer deposition
- Robotics for controlled motion
- Automated conveyor systems
- Industrial automation projects
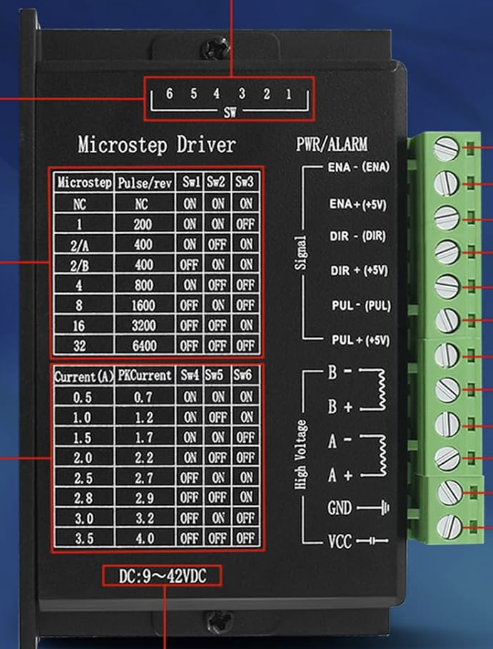
Technical Specifications
The TB6600 stepper motor driver is designed to handle a wide range of stepper motors and offers robust performance. Below are its key technical details:
Key Specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 9V to 42V DC |
| Output Current Range | 0.5A to 4.0A (adjustable) |
| Microstepping Modes | Full, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16 |
| Control Signal Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Step Frequency | Up to 200 kHz |
| Protection Features | Overheat, overcurrent, and |
| short-circuit protection | |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to +45°C |
| Dimensions | 96mm x 56mm x 33mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions:
The TB6600 has several input and output terminals for connecting to the stepper motor, power supply, and control signals. Below is the pin configuration:
Input Terminals:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PUL+ | Positive terminal for the pulse signal (step signal) |
| PUL- | Negative terminal for the pulse signal |
| DIR+ | Positive terminal for the direction signal |
| DIR- | Negative terminal for the direction signal |
| ENA+ | Positive terminal for the enable signal (optional, used to enable/disable) |
| ENA- | Negative terminal for the enable signal |
Output Terminals:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| A+ | Positive terminal for one coil of the stepper motor |
| A- | Negative terminal for one coil of the stepper motor |
| B+ | Positive terminal for the other coil of the stepper motor |
| B- | Negative terminal for the other coil of the stepper motor |
Power Terminals:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Positive terminal for the power supply (9V to 42V DC) |
| GND | Ground terminal for the power supply |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TB6600 in a Circuit:
Connect the Stepper Motor:
- Connect the stepper motor's two coils to the A+/A- and B+/B- terminals of the TB6600.
- Ensure the wiring matches the motor's datasheet to avoid incorrect connections.
Power Supply:
- Connect a DC power supply (9V to 42V) to the VCC and GND terminals.
- Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current for the motor and driver.
Control Signals:
- Connect the PUL+, DIR+, and ENA+ terminals to the control board (e.g., Arduino UNO).
- Connect the corresponding PUL-, DIR-, and ENA- terminals to the ground of the control board.
Set the Current and Microstepping:
- Use the DIP switches on the TB6600 to configure the desired current limit and microstepping mode.
- Refer to the TB6600 datasheet for the DIP switch settings.
Test the Setup:
- Send pulse and direction signals from the control board to the TB6600.
- Observe the motor's movement to ensure proper operation.
Important Considerations:
- Heat Dissipation: The TB6600 can generate heat during operation. Use a heatsink or active cooling if necessary.
- Signal Voltage: Ensure the control signals (PUL, DIR, ENA) are within the 3.3V to 5V range.
- Wiring: Double-check all connections before powering the circuit to avoid damage to the driver or motor.
Example Code for Arduino UNO:
Below is an example code to control a stepper motor using the TB6600 and an Arduino UNO:
// Define control pins for the TB6600
const int stepPin = 3; // Pin connected to PUL+ (Pulse)
const int dirPin = 4; // Pin connected to DIR+ (Direction)
void setup() {
// Set the control pins as outputs
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
// Set initial direction
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH); // HIGH for one direction, LOW for the other
}
void loop() {
// Generate step pulses
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH); // Set step pin HIGH
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait for 500 microseconds
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW); // Set step pin LOW
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait for 500 microseconds
}
Notes:
- Adjust the
delayMicroseconds()value to control the motor speed. - Change the
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH/LOW)to reverse the motor's direction.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
Motor Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify all connections, especially the motor coils and control signals.
Driver Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Reduce the current setting using the DIP switches or add a heatsink/fan.
Erratic Motor Movement:
- Cause: Noise in control signals or incorrect microstepping settings.
- Solution: Use shielded cables for control signals and verify DIP switch settings.
No Response from Driver:
- Cause: Incorrect power supply voltage or damaged driver.
- Solution: Check the power supply voltage and replace the driver if necessary.
FAQs:
Q: Can the TB6600 drive unipolar stepper motors?
A: No, the TB6600 is designed for bipolar stepper motors only.Q: What is the maximum step frequency supported?
A: The TB6600 supports step frequencies up to 200 kHz.Q: Can I use a 12V power supply with the TB6600?
A: Yes, the TB6600 supports input voltages from 9V to 42V DC.Q: How do I enable/disable the driver?
A: Use the ENA+ and ENA- terminals. Leave them disconnected if not needed.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the TB6600 stepper motor driver in your projects.