
How to Use TSOP38238 IR Receiver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with TSOP38238 IR Receiver in Cirkit Designer
Design with TSOP38238 IR Receiver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TSOP38238 is an infrared (IR) receiver module designed for remote control applications. It operates at a carrier frequency of 38 kHz, making it compatible with most standard IR remote controls. The module is equipped with a built-in preamplifier and demodulator, which filters out ambient light interference and provides a clean digital output signal. This makes it ideal for use in consumer electronics, home automation systems, and robotics.
Explore Projects Built with TSOP38238 IR Receiver
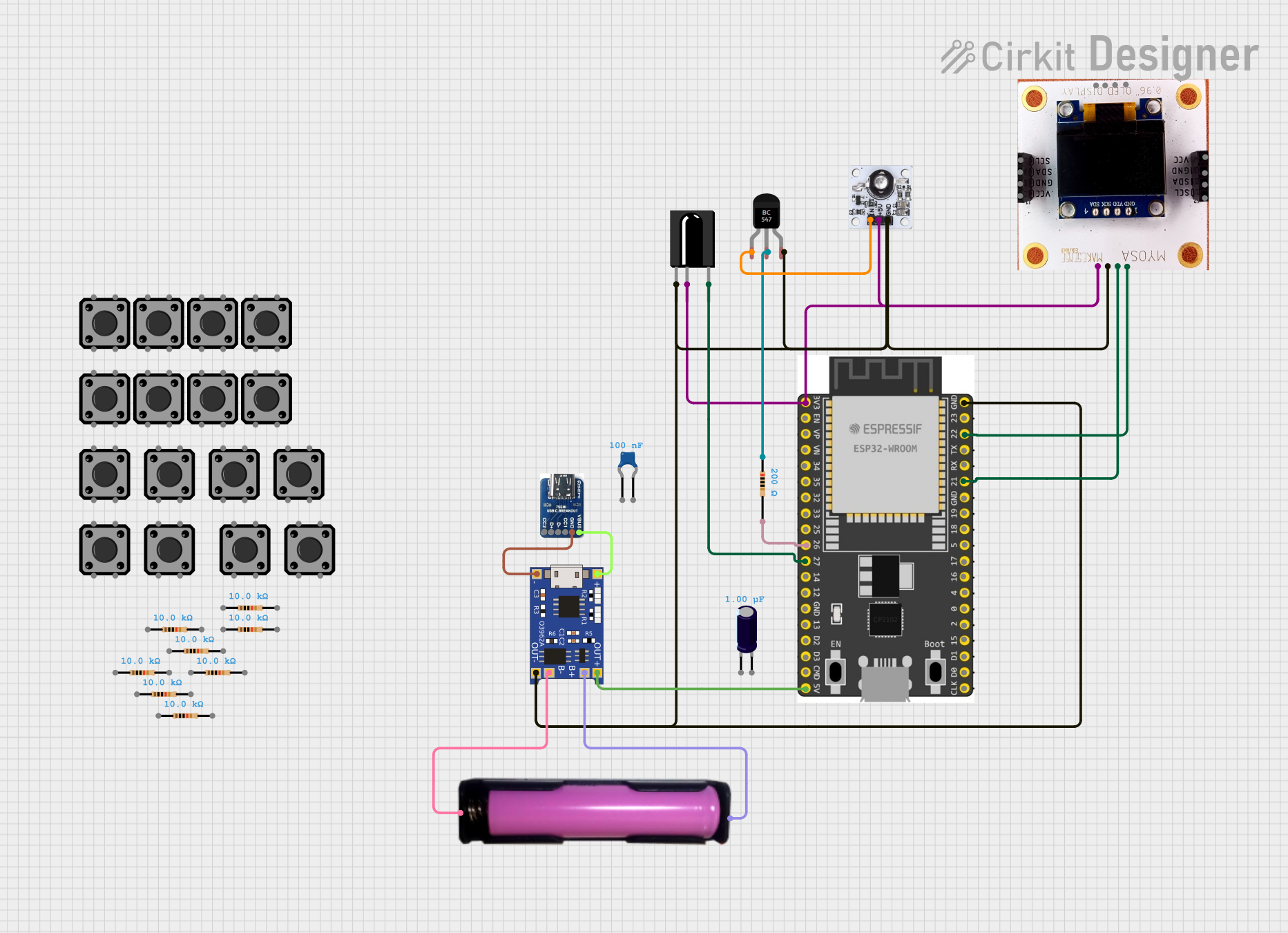
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer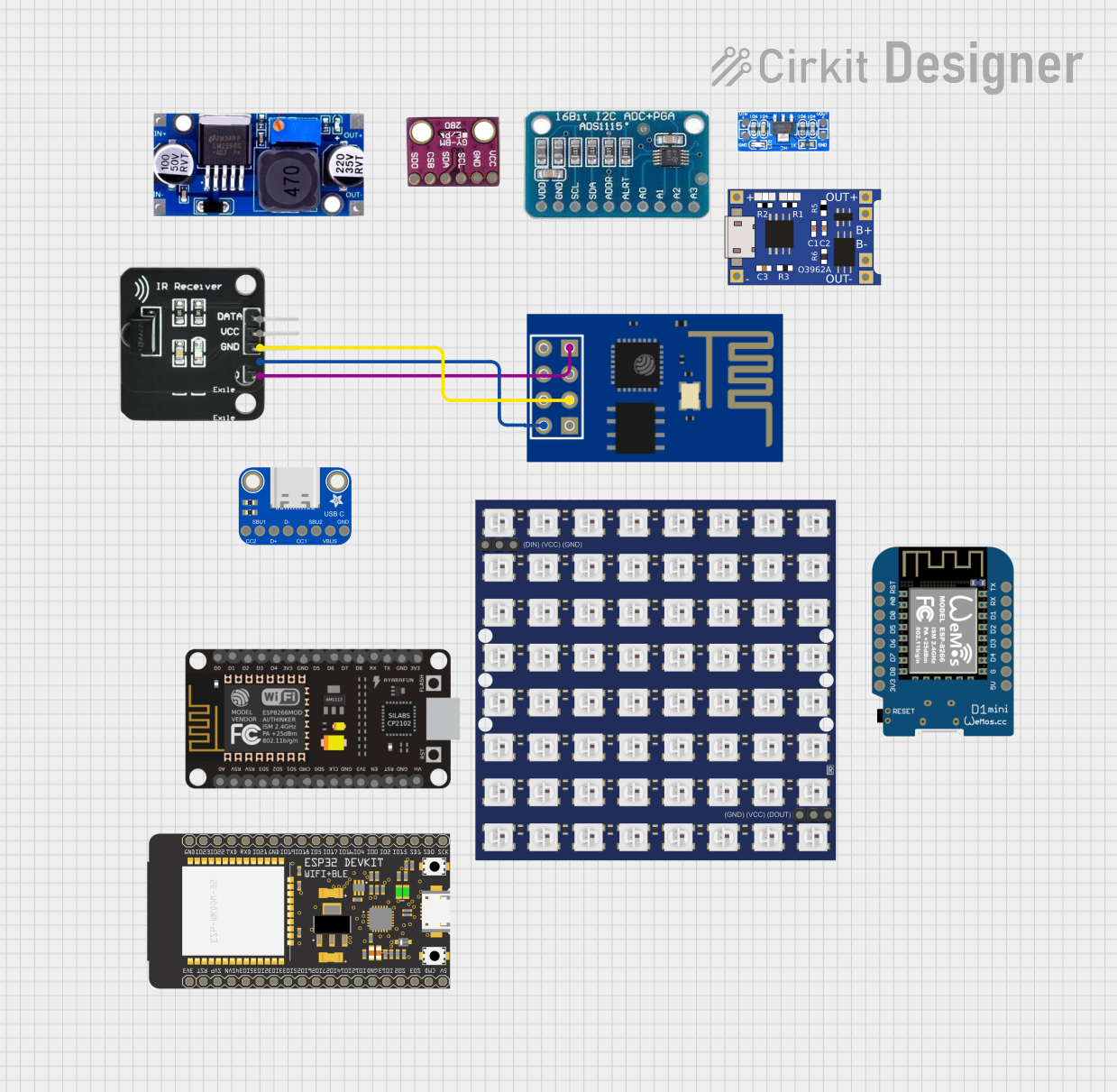
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer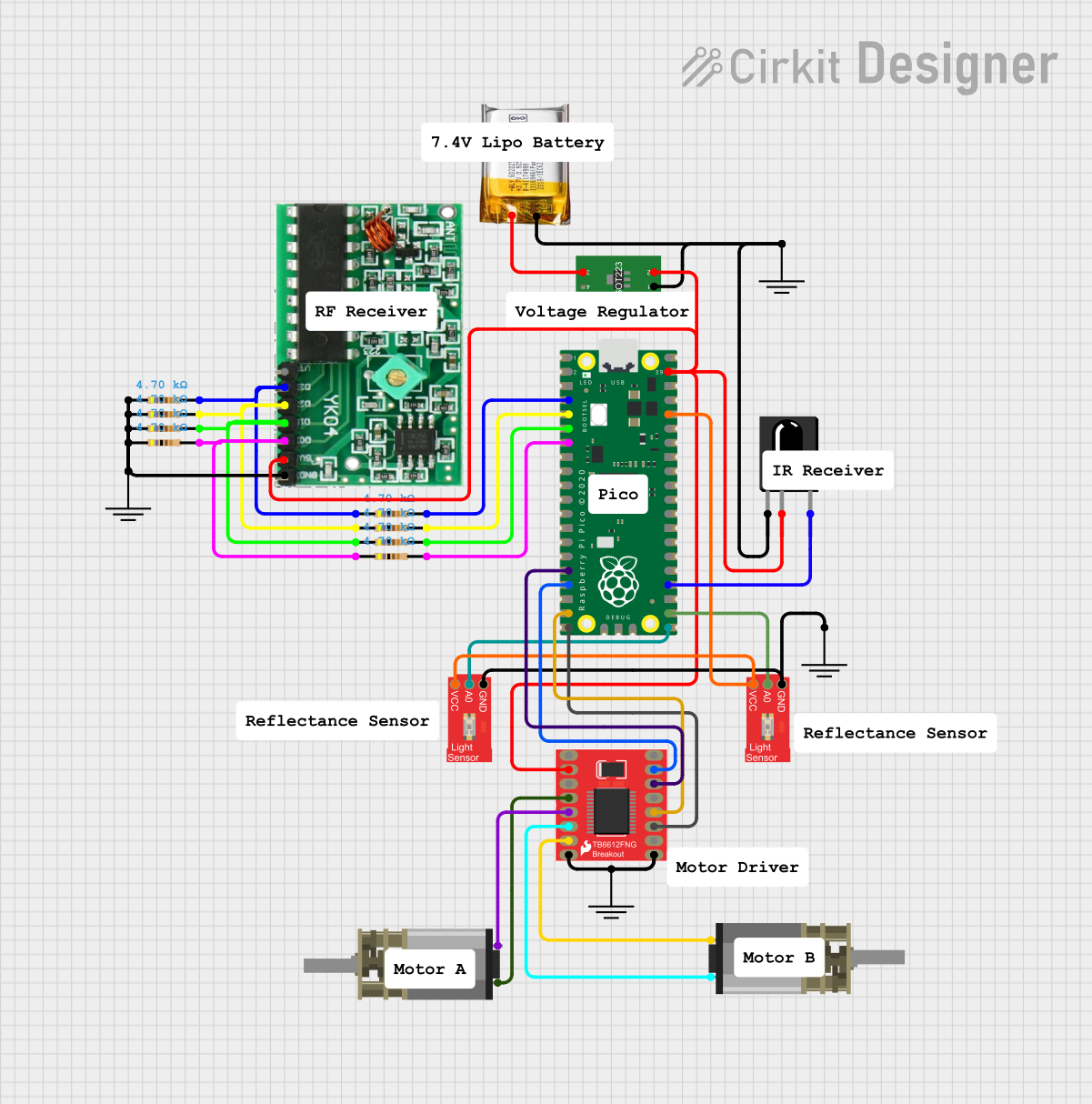
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer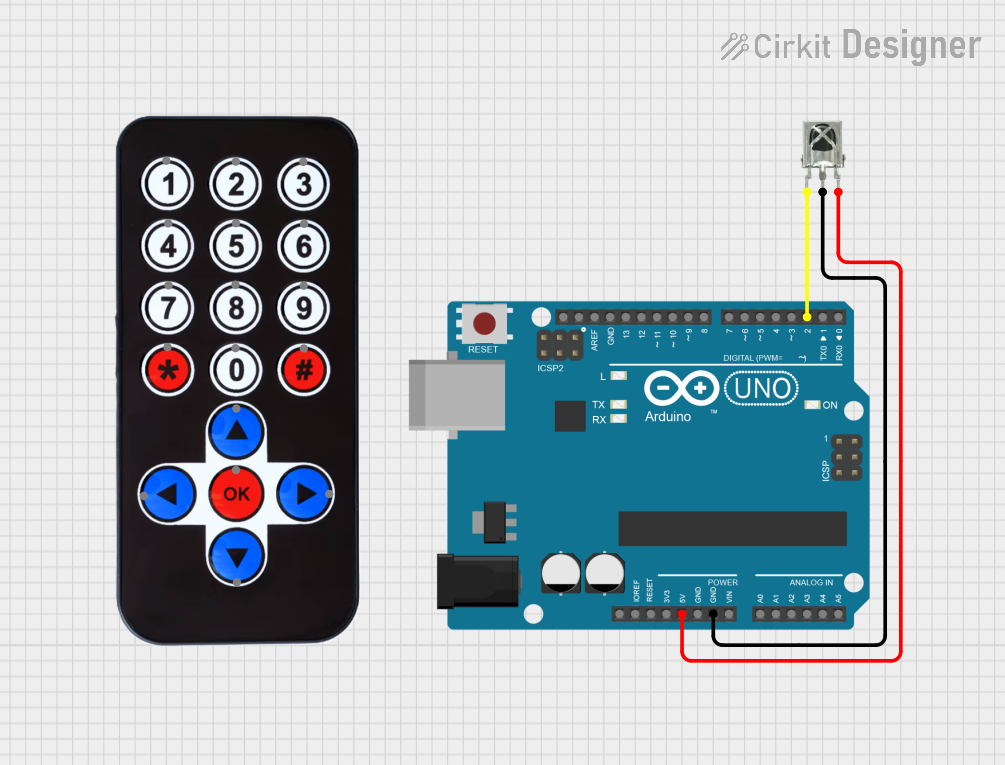
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TSOP38238 IR Receiver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Remote control signal reception for TVs, audio systems, and set-top boxes
- IR-based communication in home automation systems
- Obstacle detection and line-following robots
- Wireless data transmission in embedded systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the TSOP38238 IR receiver:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier Frequency | 38 kHz |
| Supply Voltage (VCC) | 2.5 V to 5.5 V |
| Supply Current | 0.35 mA (typical) |
| Output Voltage (High) | VCC - 0.2 V (typical) |
| Output Voltage (Low) | < 0.2 V |
| Reception Distance | Up to 45 meters (depending on IR emitter) |
| Viewing Angle | ±45° |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | Epoxy package with 3 pins |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TSOP38238 has three pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | OUT | Digital output signal (active low) |
| 2 | GND | Ground (0 V reference) |
| 3 | VCC | Supply voltage (2.5 V to 5.5 V) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TSOP38238 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a regulated power supply (2.5 V to 5.5 V). Ensure the supply voltage matches the requirements of your microcontroller or circuit.
- Ground Connection: Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Output Signal: Connect the OUT pin to a digital input pin of your microcontroller or to the input of a logic circuit. The output is active low, meaning it goes low when an IR signal is detected.
- Decoupling Capacitor: Place a 100 nF ceramic capacitor between VCC and GND, as close to the TSOP38238 as possible, to filter out power supply noise.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ambient Light: Avoid placing the TSOP38238 in direct sunlight or near strong artificial light sources, as these can interfere with IR signal reception.
- IR Emitter Compatibility: Ensure the IR emitter operates at a carrier frequency of 38 kHz for optimal performance.
- Viewing Angle: Position the TSOP38238 to face the IR emitter directly for maximum reception range.
- Pull-Up Resistor: If the output pin is connected to a high-impedance input, consider using a pull-up resistor (e.g., 10 kΩ) to ensure a stable high state when no signal is received.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the TSOP38238 to an Arduino UNO and read IR signals:
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the TSOP38238's VCC pin to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- Connect the GND pin to the Arduino's GND pin.
- Connect the OUT pin to digital pin 2 on the Arduino.
Arduino Code
#include <IRremote.h> // Include the IRremote library
const int RECV_PIN = 2; // TSOP38238 OUT pin connected to Arduino pin 2
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN); // Create an IR receiver object
decode_results results; // Variable to store decoded IR data
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the IR receiver
Serial.println("IR Receiver is ready");
}
void loop() {
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) { // Check if an IR signal is received
Serial.print("IR Code: ");
Serial.println(results.value, HEX); // Print the received code in HEX format
irrecv.resume(); // Prepare to receive the next signal
}
}
Notes:
- Install the
IRremotelibrary in the Arduino IDE before uploading the code. - The received IR codes can be used to identify specific buttons on a remote control.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Signal Detected:
- Ensure the IR emitter is operating at 38 kHz.
- Check the wiring and ensure the TSOP38238 is powered correctly.
- Verify that the IR emitter is within the module's viewing angle and range.
Interference from Ambient Light:
- Avoid direct sunlight or strong artificial light sources.
- Use an IR emitter with a narrow beam angle to reduce interference.
Unstable Output:
- Add a 100 nF decoupling capacitor between VCC and GND.
- Use a pull-up resistor on the OUT pin if connected to a high-impedance input.
Short Reception Range:
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the specified range.
- Verify the IR emitter's power and alignment with the TSOP38238.
FAQs
Q1: Can the TSOP38238 work with any IR remote control?
A1: The TSOP38238 is compatible with most IR remote controls that operate at a carrier frequency of 38 kHz.
Q2: What is the maximum range of the TSOP38238?
A2: The maximum range is up to 45 meters, depending on the power and alignment of the IR emitter.
Q3: Can I use the TSOP38238 with a 3.3 V microcontroller?
A3: Yes, the TSOP38238 operates with supply voltages as low as 2.5 V, making it compatible with 3.3 V systems.
Q4: How do I decode the received IR signals?
A4: Use an IR library (e.g., IRremote for Arduino) to decode the received signals into recognizable codes.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the TSOP38238 IR receiver into your projects and troubleshoot any issues that arise.