
How to Use Tinkerboard S: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
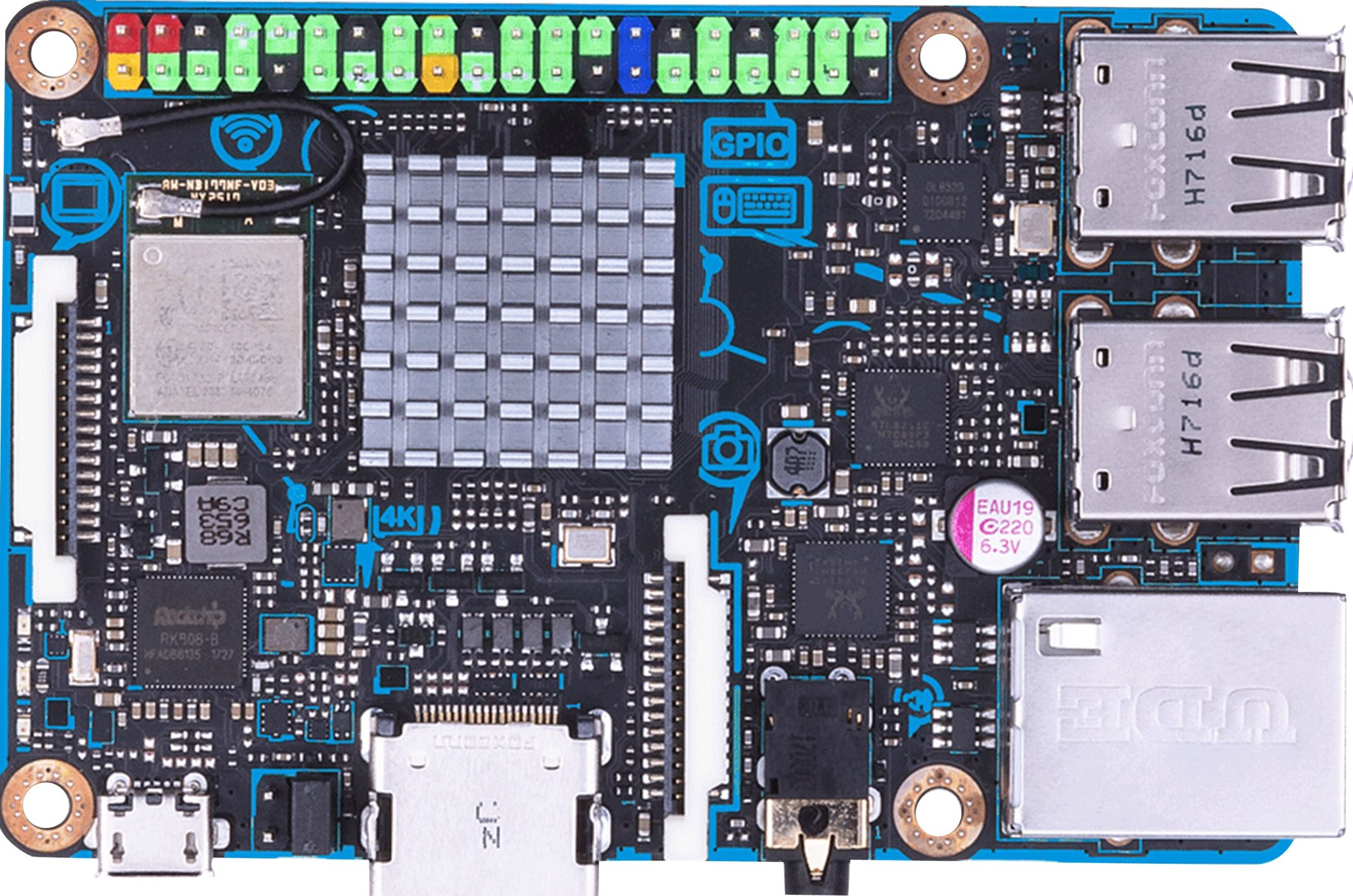
 Design with Tinkerboard S in Cirkit Designer
Design with Tinkerboard S in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ASUS Tinkerboard S is a powerful single-board computer that offers enhanced performance and robustness for hobbyists, makers, and professionals alike. It is equipped with a quad-core ARM Cortex-A17 CPU, making it suitable for a variety of applications ranging from DIY projects to Internet of Things (IoT) implementations. Its compatibility with various operating systems and the inclusion of onboard storage make it a versatile choice for projects that require a compact yet powerful computing solution.
Explore Projects Built with Tinkerboard S
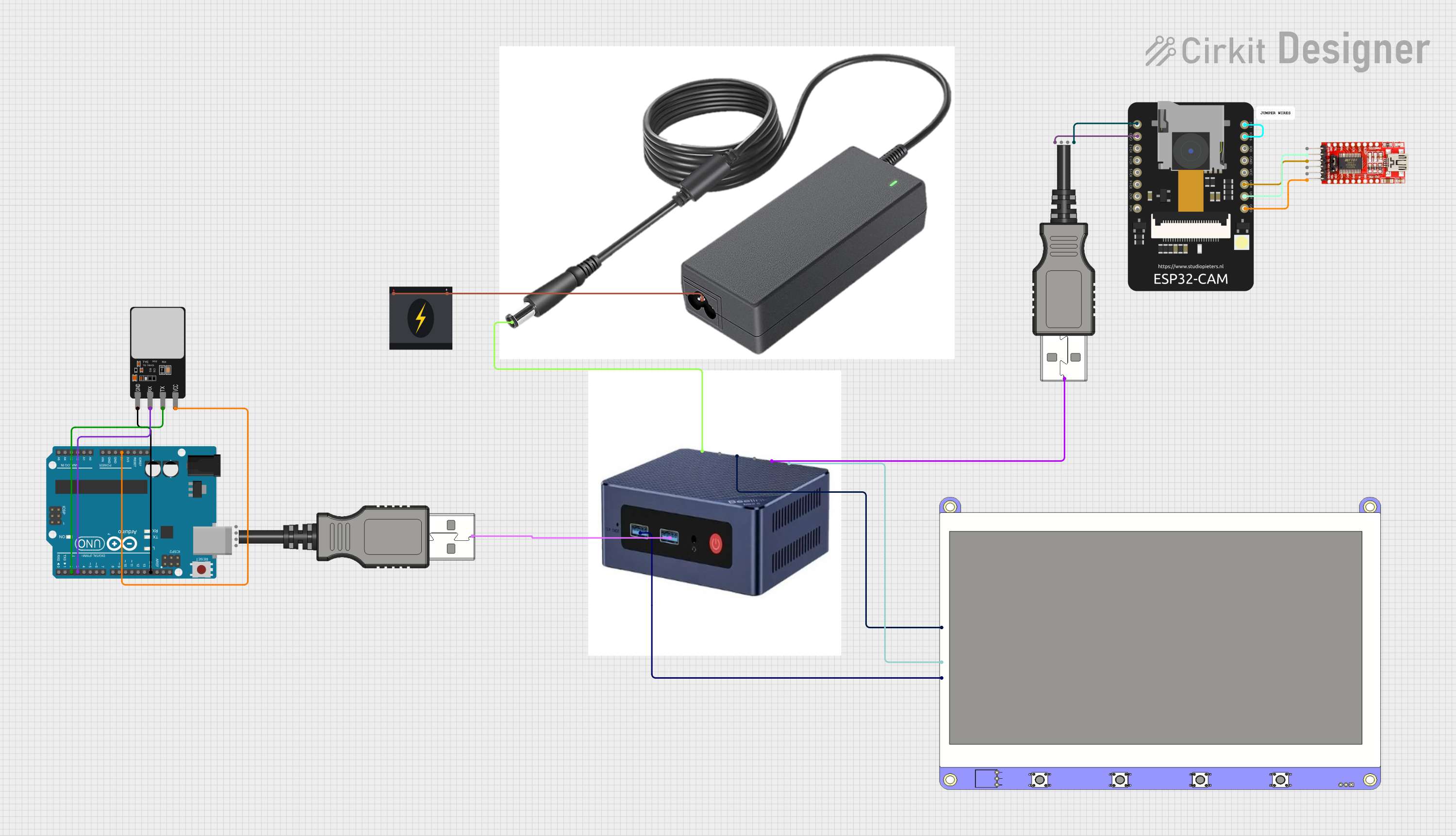
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer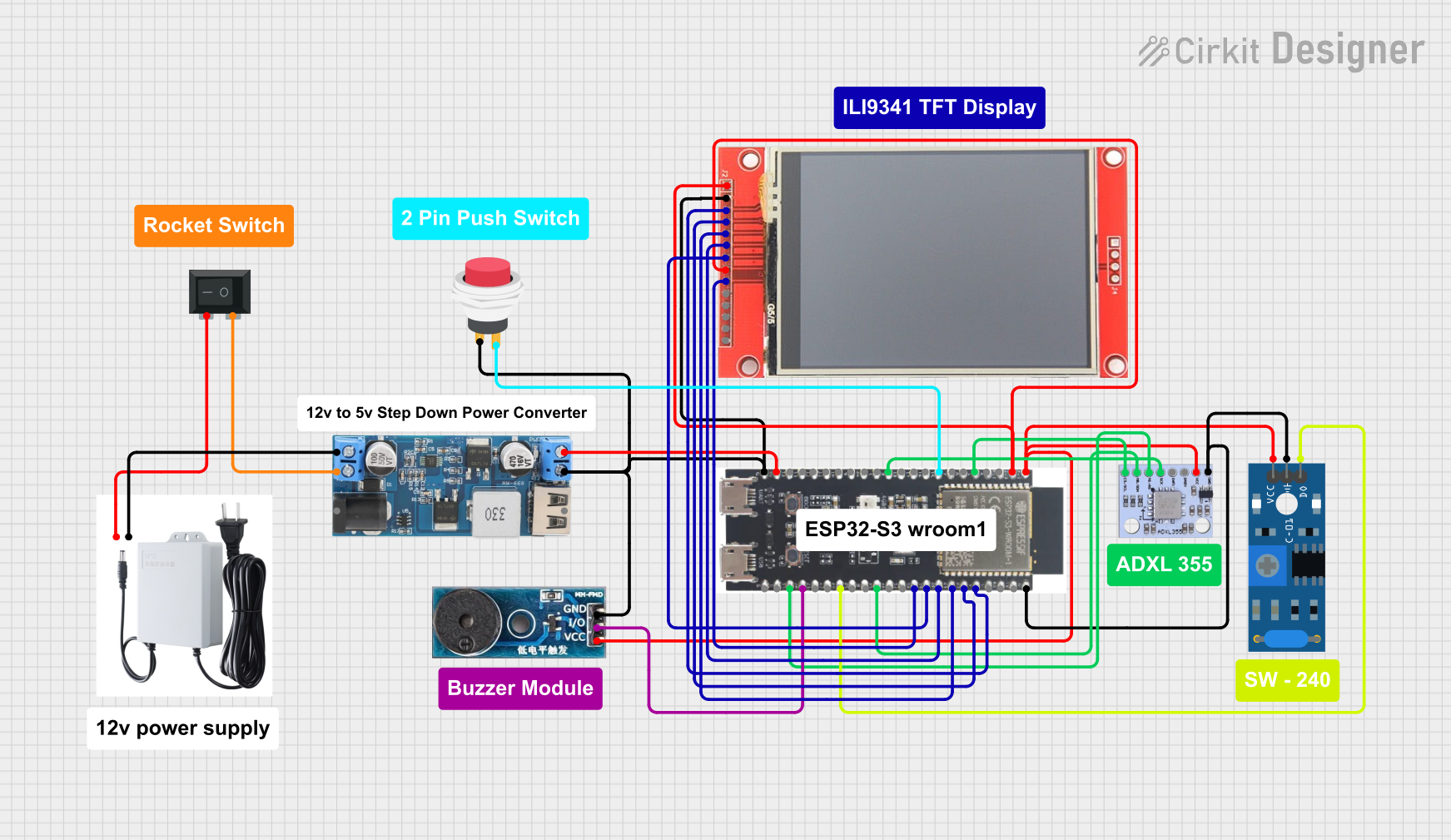
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer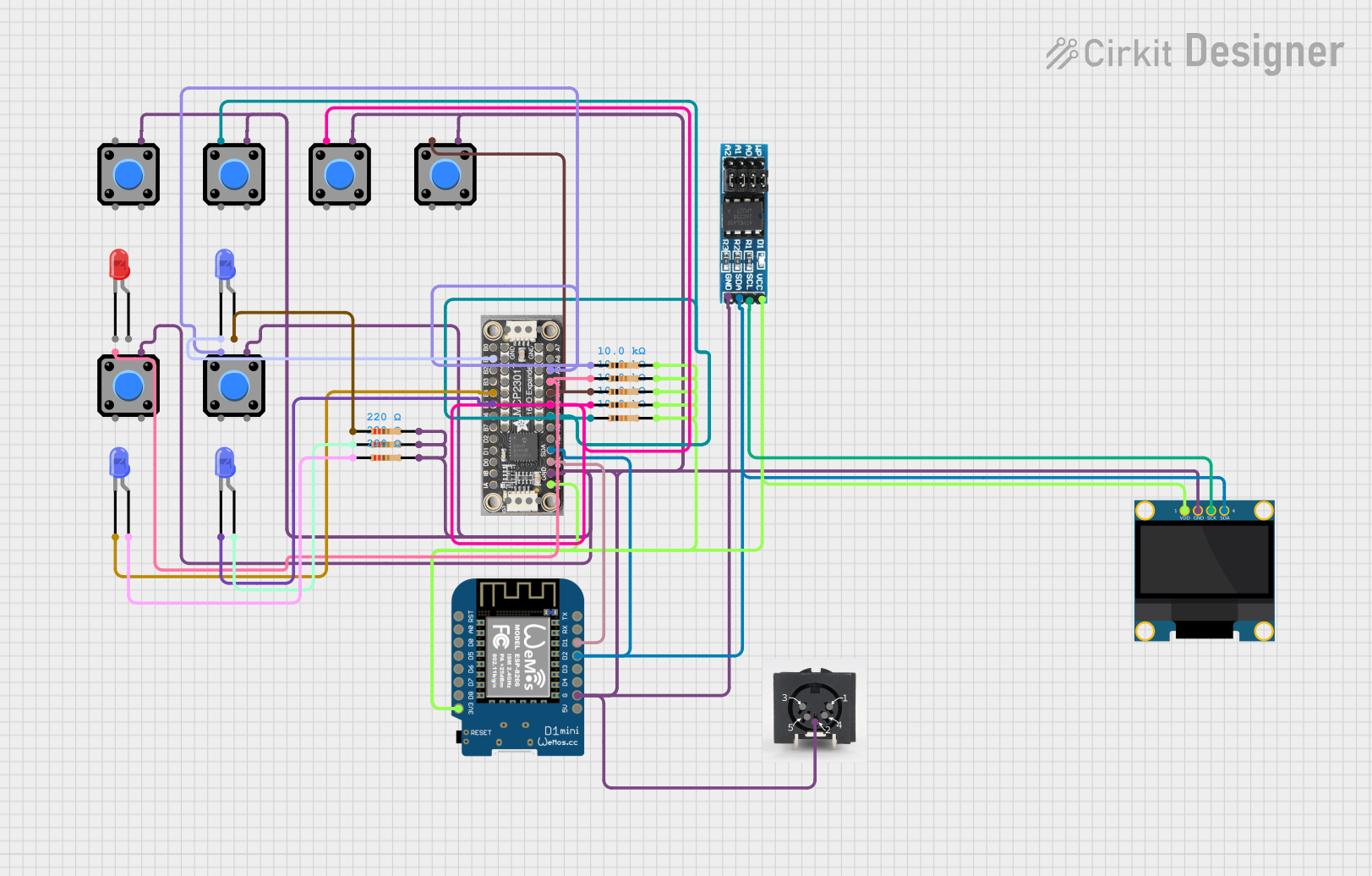
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer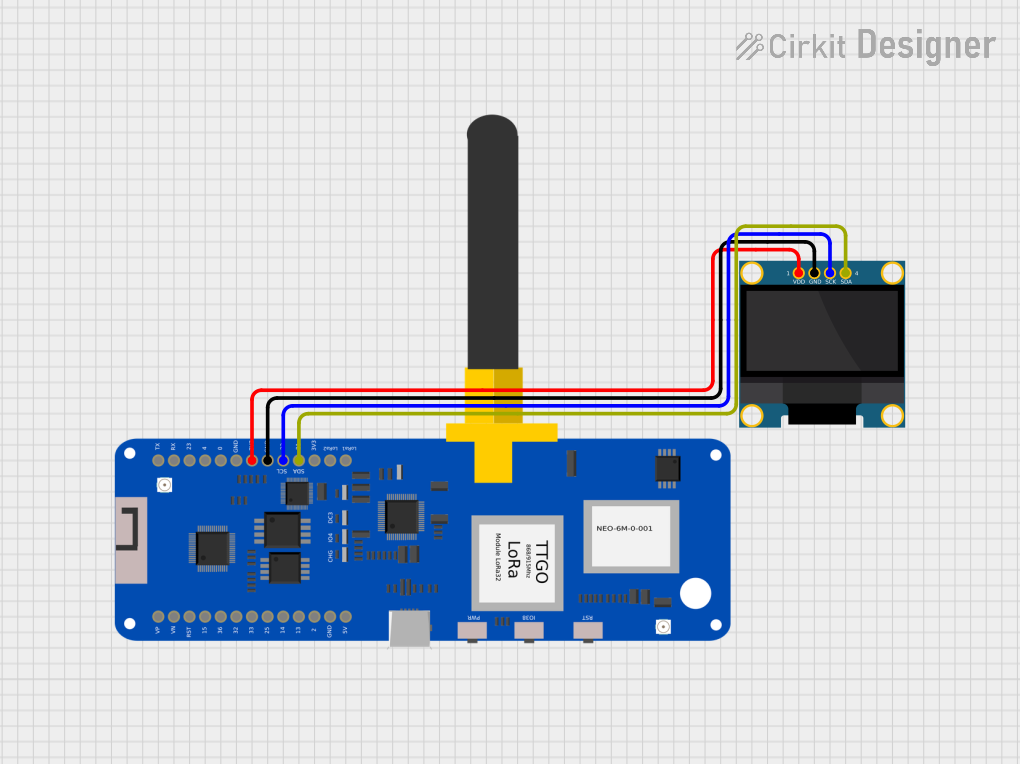
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Tinkerboard S

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems
- Media centers
- Educational platforms for coding and electronics
- Prototyping IoT devices
- Embedded computing projects
- Digital signage and kiosks
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- CPU: Rockchip RK3288, Quad-core ARM Cortex-A17
- GPU: ARM Mali-T764
- RAM: 2GB LPDDR3
- Storage: 16GB eMMC, Micro SD(TF) card slot
- Connectivity: Gigabit Ethernet, Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth 4.0 + EDR
- USB Ports: 4 x USB 2.0
- Video Output: HDMI 2.0 (up to 4K resolution)
- Audio: 3.5mm Audio Jack, HD Codec that supports up to 24-bit/192kHz audio
- GPIO: 40-pin header: up to 28 x GPIO pins, up to 2 x SPI bus, up to 2 x I2C bus, up to 4 x UART, up to 2 x PWM, up to 1 x PCM/I2S, up to 1 x SPDIF TX, up to 6 x ADC
- Power Supply: 5V/2-3A via Micro USB or GPIO
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V Power | 2 | 5V Power |
| 3 | GPIO2 (I2C SDA) | 4 | 5V Power |
| 5 | GPIO3 (I2C SCL) | 6 | Ground |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 39 | Ground | 40 | GPIO21 (PWM0) |
Note: The above table is a partial representation. Refer to the Tinkerboard S GPIO pinout diagram for the complete details.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Tinkerboard S in a Circuit
- Powering the Board: Connect a 5V/2-3A power supply to the Micro USB port or via the GPIO pins.
- Setting Up Storage: Use the onboard 16GB eMMC or insert a Micro SD card with a compatible OS image.
- Connecting Peripherals: Attach necessary peripherals such as keyboard, mouse, and display via USB ports and HDMI output.
- Programming: Access the board through SSH or a direct user interface to program and control the Tinkerboard S.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always handle the board with care to avoid static discharge or physical damage.
- Ensure the power supply is adequate and stable.
- Use heat sinks and proper ventilation if running CPU/GPU intensive tasks.
- Regularly update the operating system and software to maintain security and performance.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Board Does Not Power On: Check the power supply and cable connections. Ensure the power source meets the required specifications.
- No Video Output: Verify that the HDMI cable is properly connected and the display is powered on. Check the display settings in the OS.
- Inaccessible via Network: Ensure the Ethernet cable is connected and the network is functioning. Check Wi-Fi settings if using a wireless connection.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- If the board is unresponsive, attempt to power cycle by disconnecting and reconnecting the power supply.
- For network issues, try connecting to a different port on the router or use a different Wi-Fi network.
- Consult the Tinkerboard S forums and community for support on specific issues.
FAQs
Q: Can the Tinkerboard S run Android or Linux? A: Yes, the Tinkerboard S supports various versions of Android and Linux distributions that are compatible with the ARM architecture.
Q: Is the GPIO pinout compatible with the Raspberry Pi? A: While the Tinkerboard S has a similar 40-pin GPIO header, the pinout and functionality may differ. Always refer to the Tinkerboard S documentation for accurate pin assignments.
Q: Can I use the Tinkerboard S for commercial products? A: Yes, the Tinkerboard S is suitable for commercial applications, provided that you adhere to the relevant regulations and standards for your product.
For more detailed troubleshooting, refer to the official ASUS Tinkerboard S resources and community forums.