
How to Use BC547 Transistor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with BC547 Transistor in Cirkit Designer
Design with BC547 Transistor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BC547 is a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) widely used in low-power amplification and switching applications. It is a reliable and versatile component, making it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike. With a maximum collector current of 100 mA and a voltage rating of 45 V, the BC547 is suitable for a variety of electronic circuits, including signal amplification, small motor control, and digital switching.
Explore Projects Built with BC547 Transistor
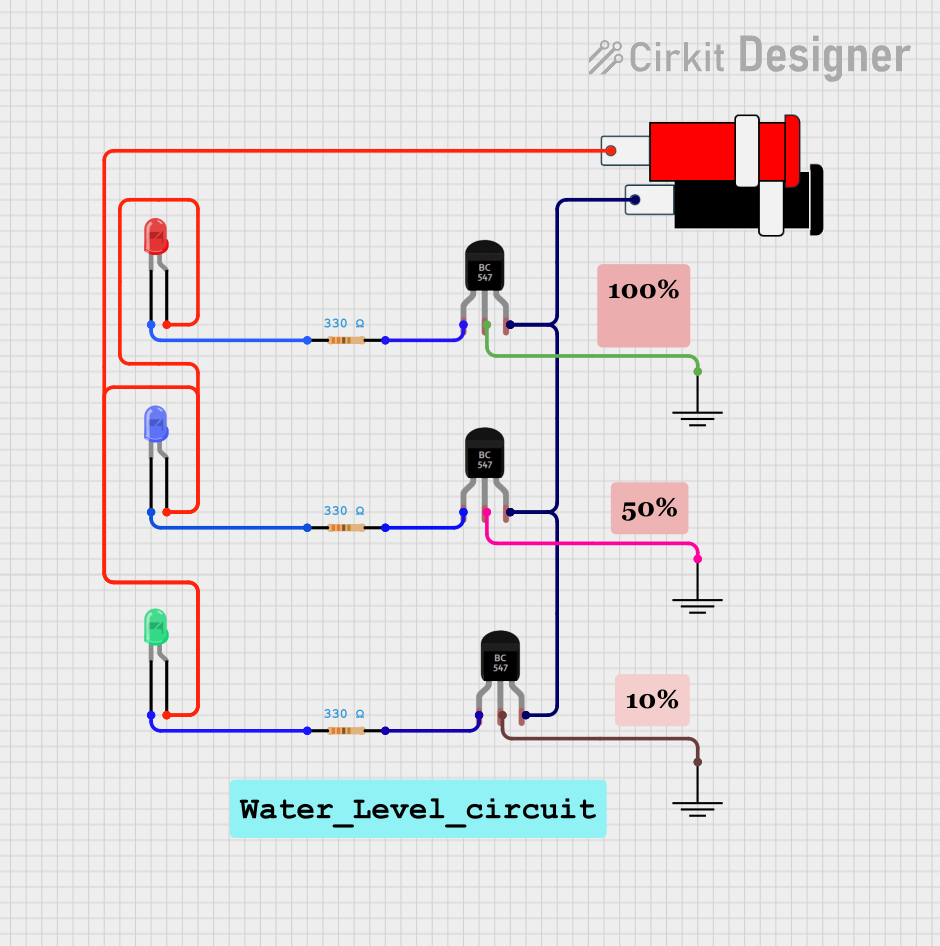
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer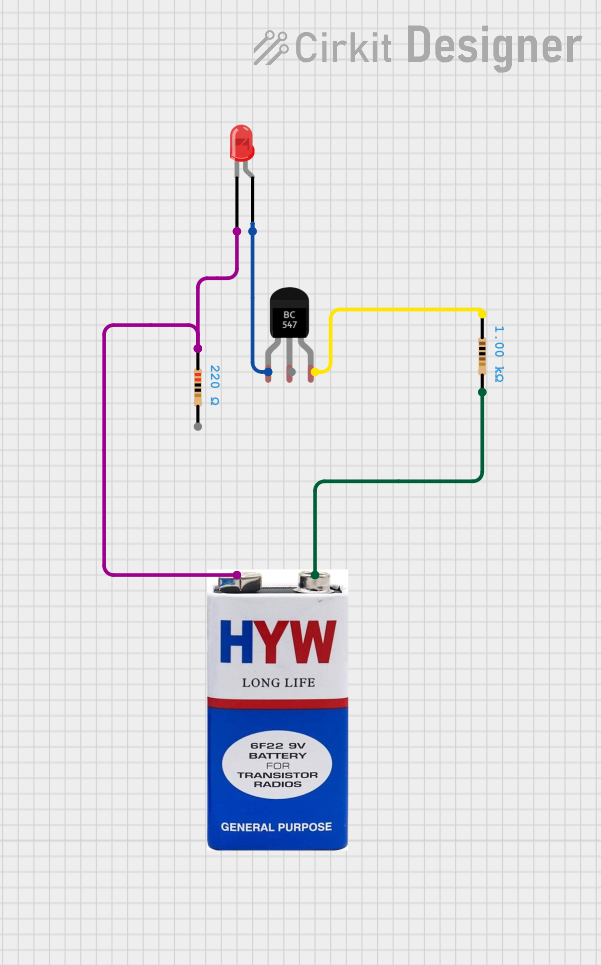
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer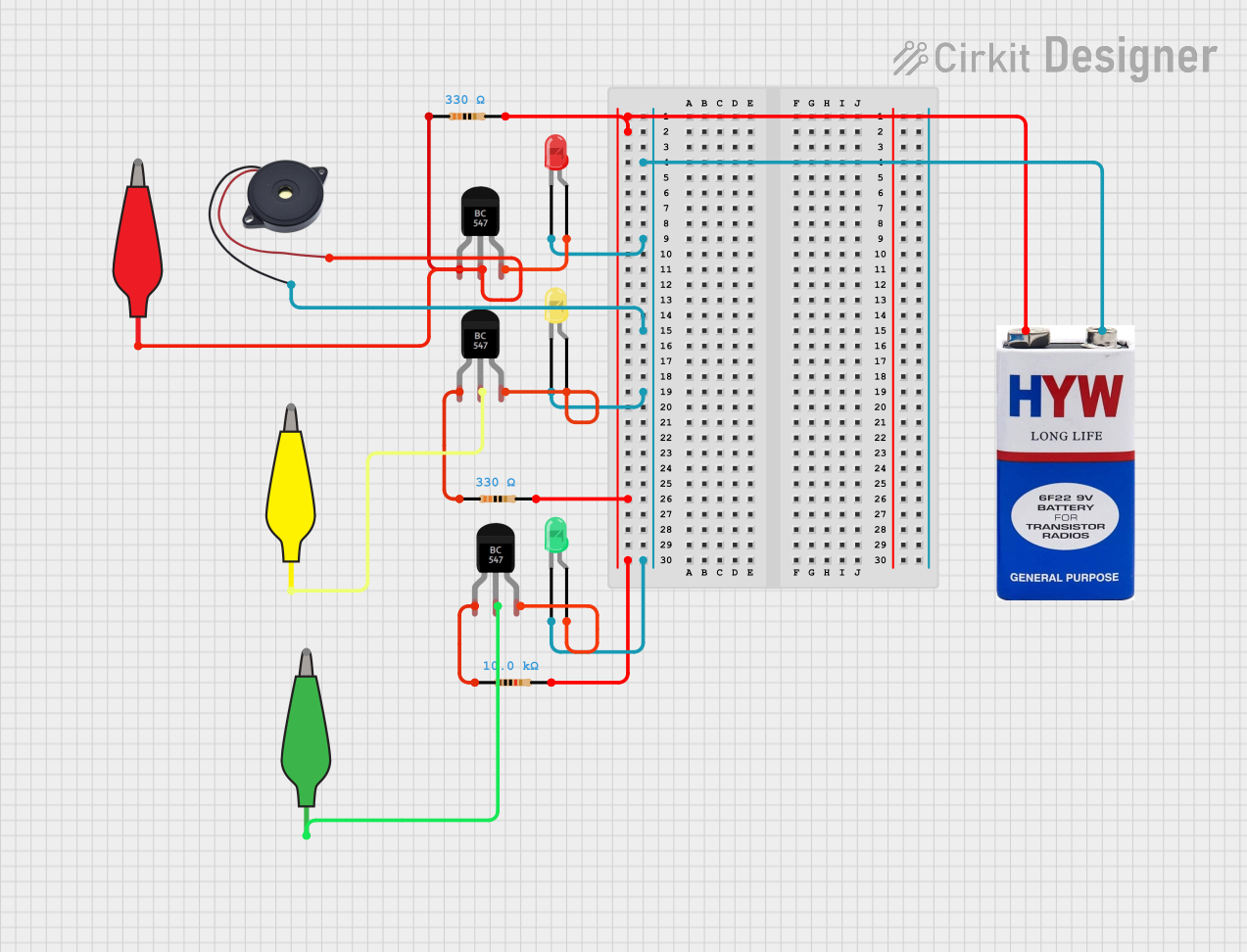
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer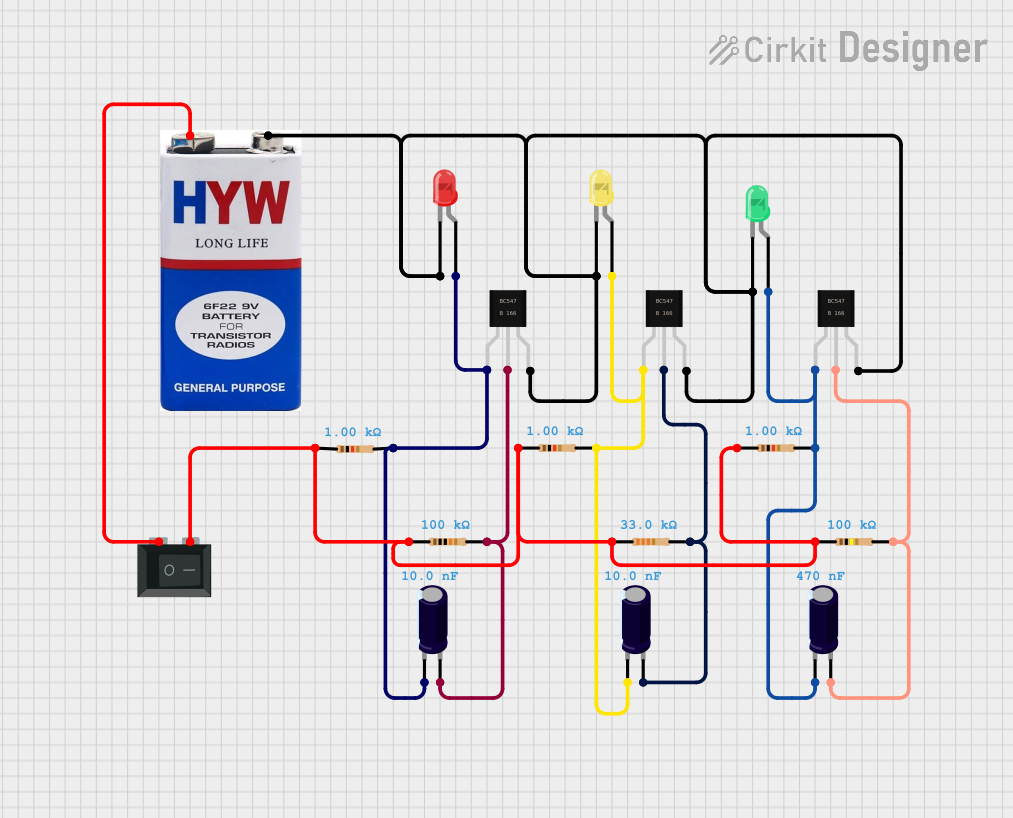
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BC547 Transistor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Signal amplification in audio and RF circuits
- Switching small loads such as LEDs or relays
- Oscillator circuits
- Voltage regulation and current limiting
- General-purpose low-power electronic projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the BC547 transistor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Transistor Type | NPN |
| Maximum Collector Current (Ic) | 100 mA |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce) | 45 V |
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (Vcb) | 50 V |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (Veb) | 6 V |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 110 to 800 (varies by model) |
| Power Dissipation (Ptot) | 500 mW |
| Transition Frequency (ft) | 150 MHz |
| Package Type | TO-92 |
Pin Configuration
The BC547 transistor comes in a TO-92 package with three pins. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Collector | Current flows out of this pin. |
| 2 | Base | Controls the transistor's operation. |
| 3 | Emitter | Current flows into this pin. |
Below is a visual representation of the pinout (viewed from the flat side of the TO-92 package):
_______
| |
| |
|_______|
| | |
1 2 3
C B E
Usage Instructions
How to Use the BC547 in a Circuit
The BC547 transistor operates as a current-controlled device. A small current applied to the base pin (B) controls a larger current flowing between the collector (C) and emitter (E). Below are the steps to use the BC547 in a circuit:
Determine the Operating Region:
- Cutoff Region: The transistor is OFF (no current flows from collector to emitter).
- Active Region: The transistor amplifies the input signal.
- Saturation Region: The transistor is fully ON, acting as a closed switch.
Base Resistor Calculation: To prevent damage to the transistor, a resistor is typically connected to the base pin. The value of the base resistor (Rb) can be calculated using the formula: [ R_b = \frac{V_{in} - V_{be}}{I_b} ] Where:
- ( V_{in} ) = Input voltage to the base
- ( V_{be} ) = Base-emitter voltage (typically 0.7 V for BC547)
- ( I_b ) = Base current (( I_b = \frac{I_c}{h_{FE}} ))
Connect the Circuit:
- Connect the collector to the load (e.g., an LED with a current-limiting resistor).
- Connect the emitter to ground.
- Apply a small current to the base through a resistor to control the transistor.
Example: Controlling an LED with an Arduino UNO
The BC547 can be used to control an LED with an Arduino UNO. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Connections:
- Collector (C): Connect to one terminal of the LED (with a 220 Ω resistor in series).
- Emitter (E): Connect to ground.
- Base (B): Connect to an Arduino digital pin (e.g., pin 9) through a 1 kΩ resistor.
Arduino Code:
// Define the pin connected to the BC547 base
const int transistorBasePin = 9;
void setup() {
// Set the transistor base pin as an output
pinMode(transistorBasePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the LED ON by sending a HIGH signal to the transistor base
digitalWrite(transistorBasePin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the LED ON for 1 second
// Turn the LED OFF by sending a LOW signal to the transistor base
digitalWrite(transistorBasePin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the LED OFF for 1 second
}
Important Considerations:
- Do not exceed the maximum voltage or current ratings to avoid damaging the transistor.
- Always use a base resistor to limit the base current.
- Ensure proper heat dissipation if the transistor operates near its maximum power rating.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
The transistor does not turn ON:
- Check the base resistor value. Ensure the base current is sufficient to drive the transistor.
- Verify the input voltage to the base pin is at least 0.7 V.
The transistor overheats:
- Ensure the collector current does not exceed 100 mA.
- Check for proper heat dissipation and avoid operating near the maximum power rating.
The load does not operate as expected:
- Verify the connections to the collector and emitter pins.
- Ensure the load is within the transistor's current and voltage limits.
The transistor is damaged:
- Check for accidental reverse polarity or excessive voltage/current.
- Replace the transistor and verify the circuit design.
FAQs:
Q1: Can the BC547 be used to drive a motor?
A1: The BC547 can drive small motors with a current requirement below 100 mA. For larger motors, use a transistor with a higher current rating.
Q2: What is the difference between BC547 and BC548?
A2: The BC547 and BC548 are similar, but the BC548 has a slightly higher voltage rating and is optimized for different applications. Always check the datasheet for specific differences.
Q3: Can the BC547 amplify audio signals?
A3: Yes, the BC547 is commonly used for low-power audio signal amplification in preamplifier circuits.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the BC547 transistor in your electronic projects!