
How to Use 10a Fuse: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 10a Fuse in Cirkit Designer
Design with 10a Fuse in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 10A fuse is a safety device designed to protect electrical circuits by interrupting the flow of current when it exceeds 10 amps. This prevents damage to sensitive components, reduces the risk of overheating, and minimizes fire hazards. Fuses are essential in a wide range of applications, including automotive systems, household appliances, industrial equipment, and electronic circuits.
Explore Projects Built with 10a Fuse
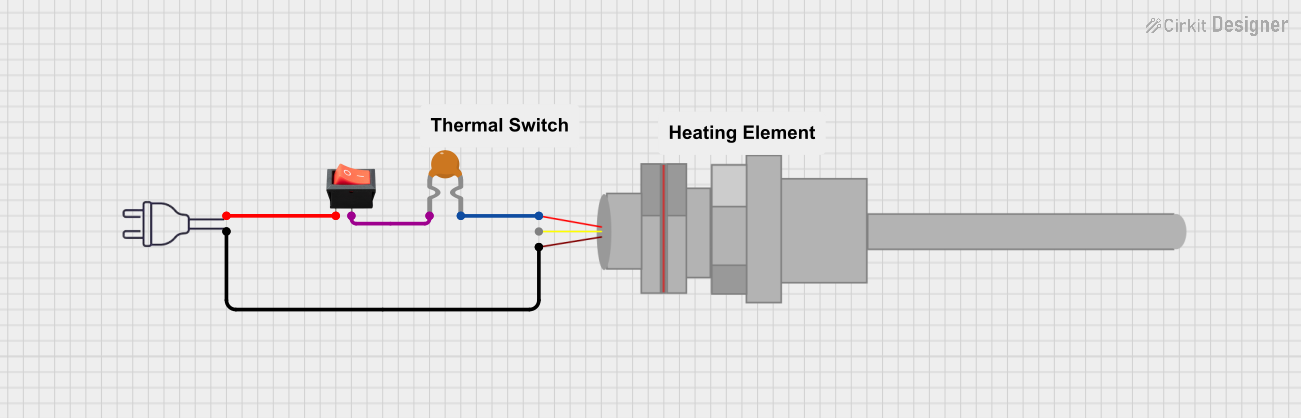
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer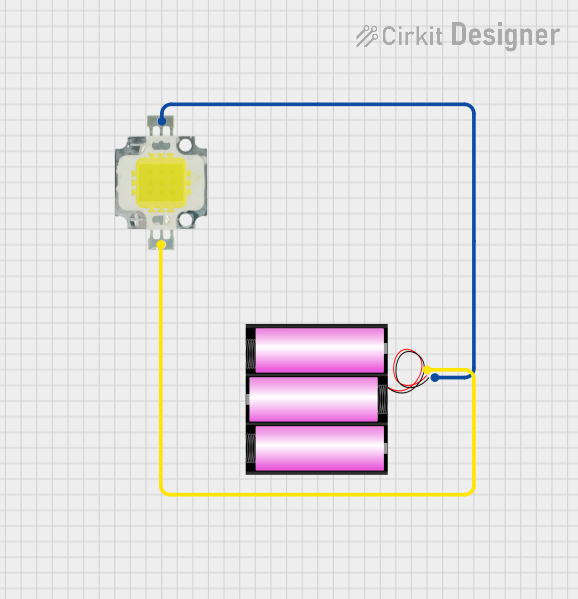
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer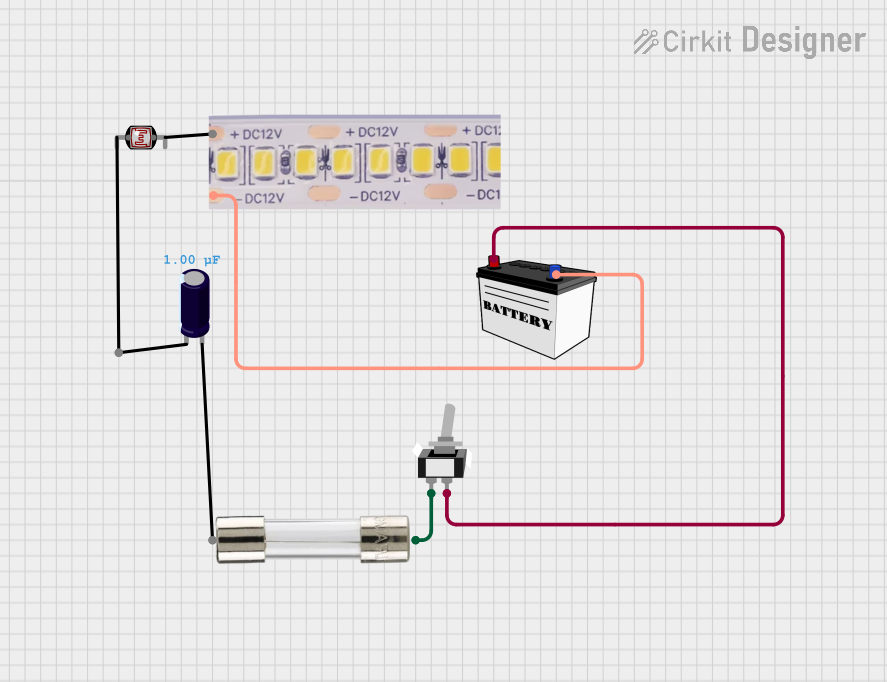
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 10a Fuse

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive Systems: Protects wiring and components in vehicles.
- Household Appliances: Ensures safe operation of devices like microwaves and washing machines.
- Industrial Equipment: Safeguards heavy machinery from electrical overloads.
- Electronic Circuits: Prevents damage to sensitive components in DIY and professional projects.
Technical Specifications
The 10A fuse is available in various types, such as glass tube, ceramic, and blade fuses. Below are the general technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Current | 10A |
| Rated Voltage | Typically 250V AC or 32V DC |
| Breaking Capacity | Varies (e.g., 35A, 100A) |
| Fuse Type | Fast-blow or slow-blow |
| Material | Glass, ceramic, or plastic |
| Dimensions | Varies by type (e.g., 5x20mm for glass fuses) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Fuses do not have pins in the traditional sense but are connected via terminals or clips. Below is a description of the connection points:
| Connection Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Input side of the fuse (connected to power) |
| Terminal 2 | Output side of the fuse (connected to load) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 10A Fuse in a Circuit
- Determine the Fuse Type: Select the appropriate type (fast-blow or slow-blow) based on the application. Fast-blow fuses are ideal for circuits with steady current, while slow-blow fuses are better for circuits with inrush currents.
- Check the Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the fuse's voltage and current ratings match the circuit requirements.
- Install the Fuse:
- For glass or ceramic fuses, use a fuse holder or clips.
- For blade fuses, insert them into the designated fuse box or socket.
- Test the Circuit: After installation, power on the circuit and verify proper operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same type, current rating, and voltage rating.
- Avoid bypassing the fuse, as this defeats its safety purpose.
- Ensure the fuse is securely mounted to prevent loose connections.
- For circuits with high inrush currents (e.g., motors), use a slow-blow fuse to prevent nuisance tripping.
Example: Using a 10A Fuse with an Arduino UNO
When connecting an Arduino UNO to a power supply, a 10A fuse can protect the circuit from accidental short circuits or overcurrent. Below is an example circuit:
- Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to one side of the 10A fuse.
- Connect the other side of the fuse to the VIN pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the negative terminal of the power supply to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
// Example Arduino code to demonstrate a simple LED circuit
// This assumes the 10A fuse is protecting the power supply to the Arduino.
const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED pin on Arduino UNO
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Fuse Blows Repeatedly:
- Cause: Circuit is drawing more than 10A.
- Solution: Check for short circuits or reduce the load on the circuit.
Fuse Does Not Blow When Expected:
- Cause: Incorrect fuse type or rating.
- Solution: Verify the fuse's current and voltage ratings match the circuit requirements.
Loose Connections:
- Cause: Fuse is not securely mounted.
- Solution: Ensure the fuse is properly seated in its holder or socket.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a higher-rated fuse (e.g., 15A) instead of a 10A fuse?
A: No, using a higher-rated fuse compromises the safety of the circuit and may allow excessive current to flow, causing damage or fire.Q: How do I know if a fuse is blown?
A: For glass fuses, inspect the filament inside; if it is broken, the fuse is blown. For other types, use a multimeter to check for continuity.Q: Can I reuse a blown fuse?
A: No, fuses are single-use components and must be replaced once blown.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use a 10A fuse in your circuits.