
How to Use Power Supply Bench: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Power Supply Bench in Cirkit Designer
Design with Power Supply Bench in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A bench power supply is an essential piece of equipment in any electronics lab. It provides adjustable direct current (DC) voltage and current to power and test electronic circuits and components. Bench power supplies are commonly used in research and development, manufacturing, and educational settings where precise control of power parameters is necessary.
Explore Projects Built with Power Supply Bench
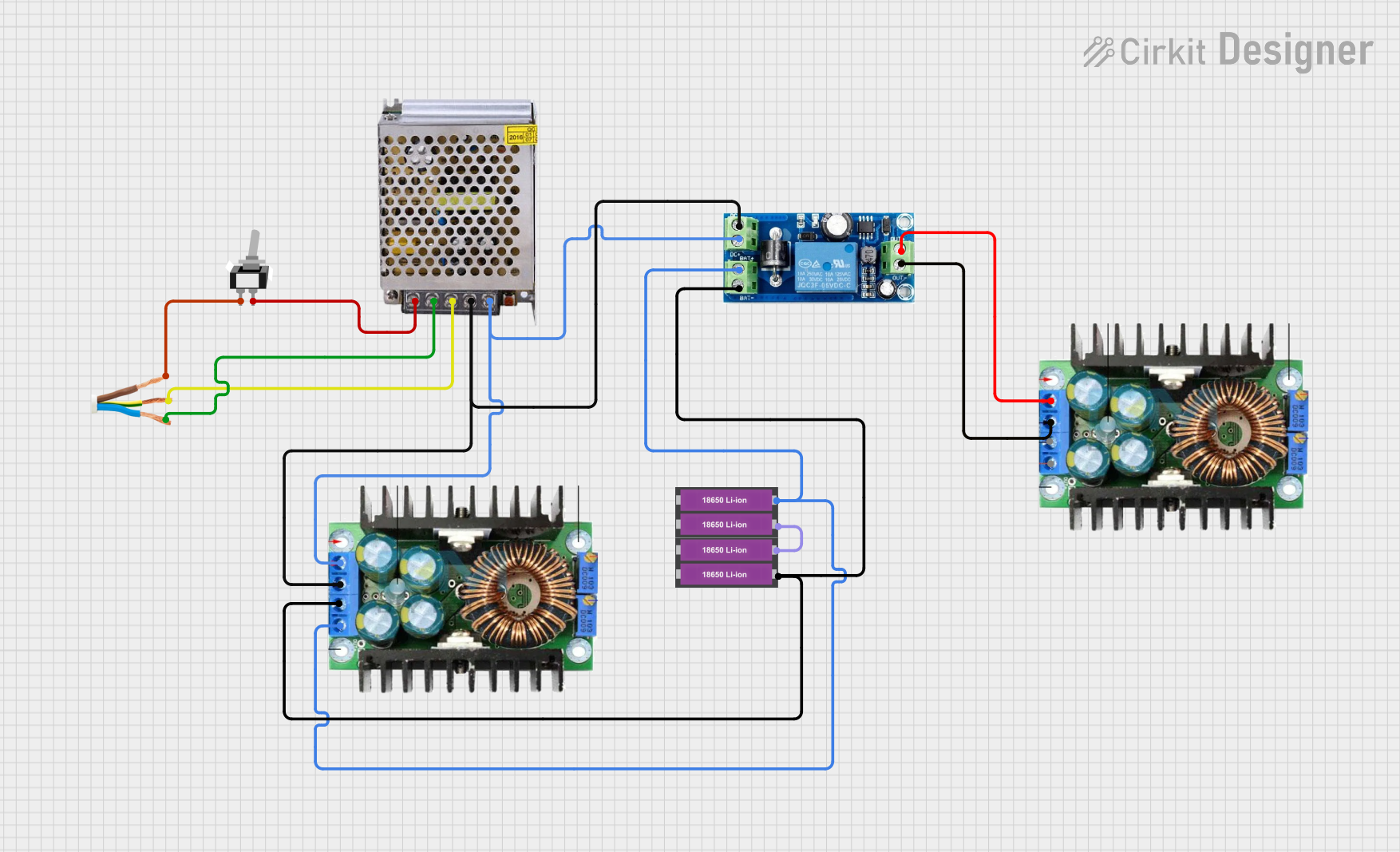
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer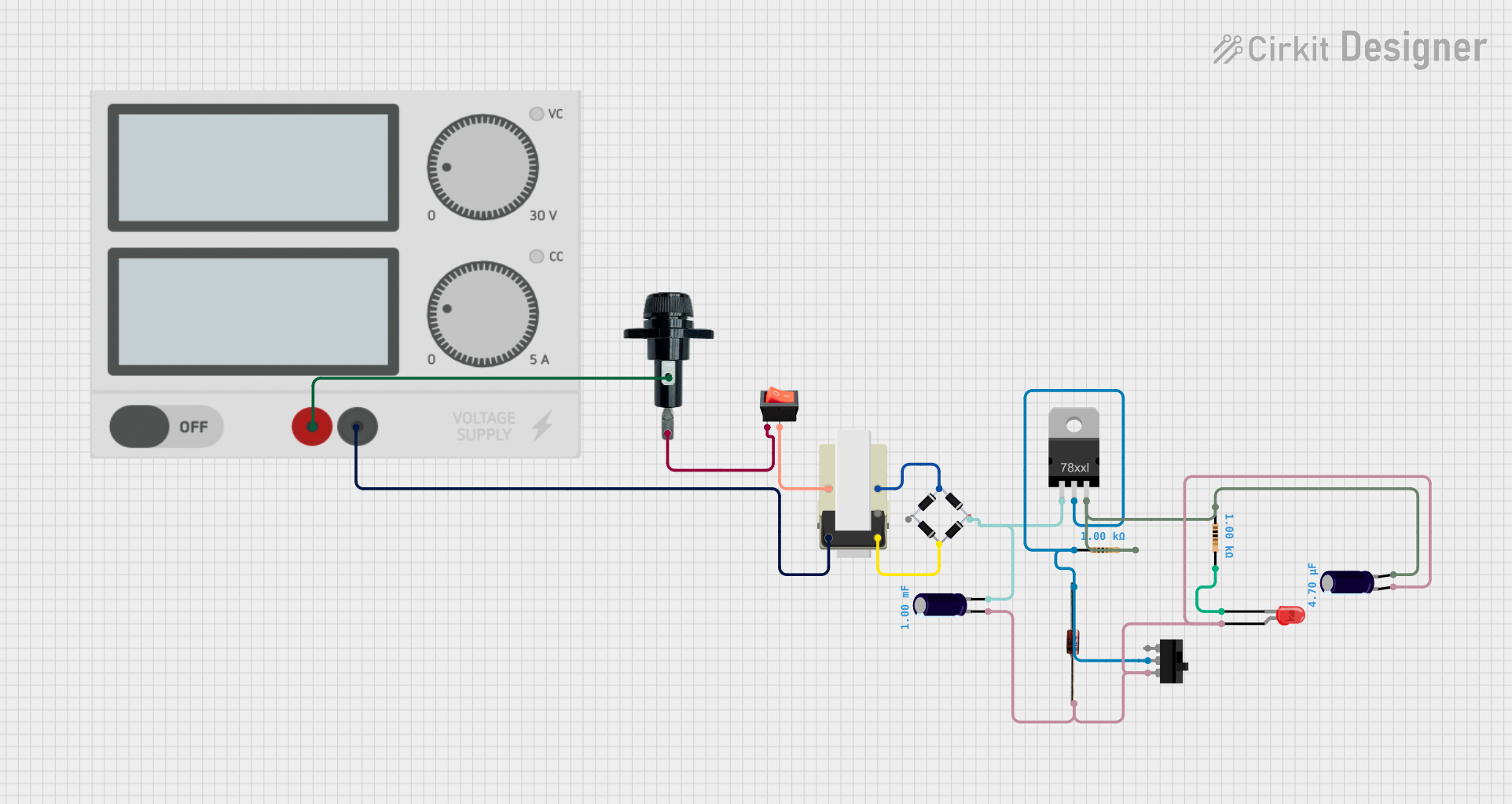
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Power Supply Bench

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Circuit Testing: Powering prototype circuits during design and testing.
- Educational Purposes: Teaching students about electronics and circuit design.
- Component Testing: Checking the functionality of electronic components.
- Battery Charging: Providing controlled charging to batteries.
- Repair Services: Troubleshooting and repairing electronic devices.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Output Voltage Range | 0-30V (adjustable) |
| Output Current Range | 0-5A (adjustable) |
| Voltage Regulation | <0.01% + 2mV |
| Current Regulation | <0.2% + 2mA |
| Ripple & Noise | <1mV rms |
| Display Accuracy | ±0.5% for voltage, ±1% for current |
| Load Stability | ±0.01% + 2mV (voltage), ±0.1% + 2mA (current) |
| Power Effect | <0.01% + 2mV (voltage), <0.1% + 2mA (current) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin/Output | Description |
|---|---|
| +V | Positive voltage output terminal |
| -V | Negative voltage output terminal |
| GND | Ground terminal |
| SET V | Voltage setting control input |
| SET I | Current setting control input |
| ON/OFF | Power on/off switch |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Power Supply: Plug the bench power supply into an AC outlet.
- Set Voltage and Current: Before connecting your device, set the desired voltage and current limits using the control knobs or buttons.
- Connect the Device: Attach the positive lead from the power supply to the positive input of your device and the negative lead to the negative input or ground.
- Power On: Turn on the power supply. Monitor the voltage and current readings to ensure they match your requirements.
- Adjust as Needed: Fine-tune the voltage and current settings if necessary while observing the effect on your device.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Start Low: Begin with lower voltage and current settings before gradually increasing to the desired levels.
- Polarity Check: Ensure correct polarity when connecting the power supply to prevent damage.
- Overload Protection: Utilize the current limit function to prevent overloading your circuit.
- Cooling: Ensure proper ventilation around the power supply to prevent overheating.
- Regular Calibration: Periodically calibrate the power supply to maintain accuracy.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Inaccurate Voltage or Current: Check if the power supply needs calibration or if the measurement tools are accurate.
- No Output: Ensure the power supply is turned on and the output terminals are properly connected.
- Overheating: Reduce the load or improve ventilation around the power supply.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Device Not Powering On: Verify that the power supply is on and the output settings are correct.
- Unexpected Voltage Fluctuations: Check for loose connections and ensure the power supply is not overloaded.
- Power Supply Shuts Down: This could be due to over-temperature or over-current protection. Allow it to cool down and check if the current limit is set too low.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a bench power supply to power multiple devices at once? A: Yes, as long as the total power requirements do not exceed the power supply's maximum output.
Q: How do I know if my power supply is calibrated correctly? A: Compare the power supply's readings with a known accurate multimeter. If there is a significant discrepancy, calibration may be needed.
Q: What should I do if the power supply is not responding to control adjustments? A: Turn off the power supply, unplug it, and check for any internal issues like a blown fuse or loose connections. If the problem persists, consult the manufacturer's support.
Note: Always refer to the manufacturer's manual for specific troubleshooting related to your model of bench power supply.