
How to Use GT-U7 GPS Module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
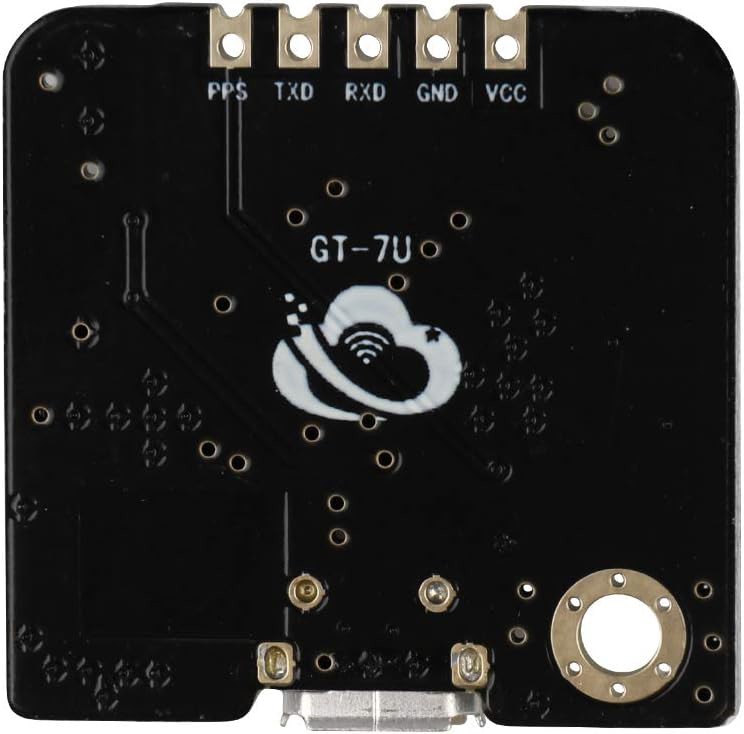

 Design with GT-U7 GPS Module in Cirkit Designer
Design with GT-U7 GPS Module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The GT-U7 GPS Module, manufactured by Deegoo-FPV, is a compact and efficient device designed to provide accurate positioning and timing information using GPS signals. It features a built-in ceramic antenna and supports multiple satellite navigation systems, ensuring reliable performance in various environments. The module is easy to integrate into electronic projects, making it a popular choice for applications such as navigation, vehicle tracking, drones, robotics, and other location-based services.
Explore Projects Built with GT-U7 GPS Module
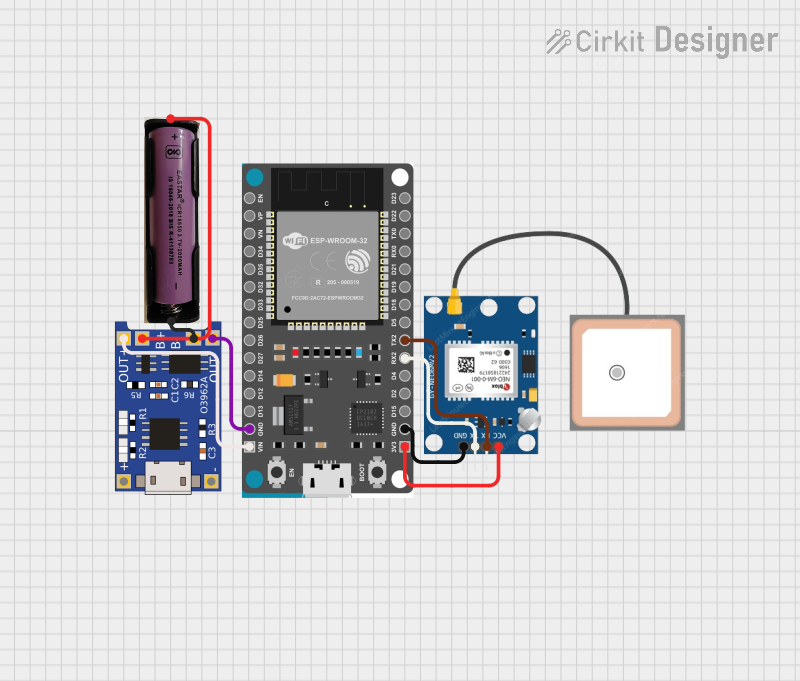
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer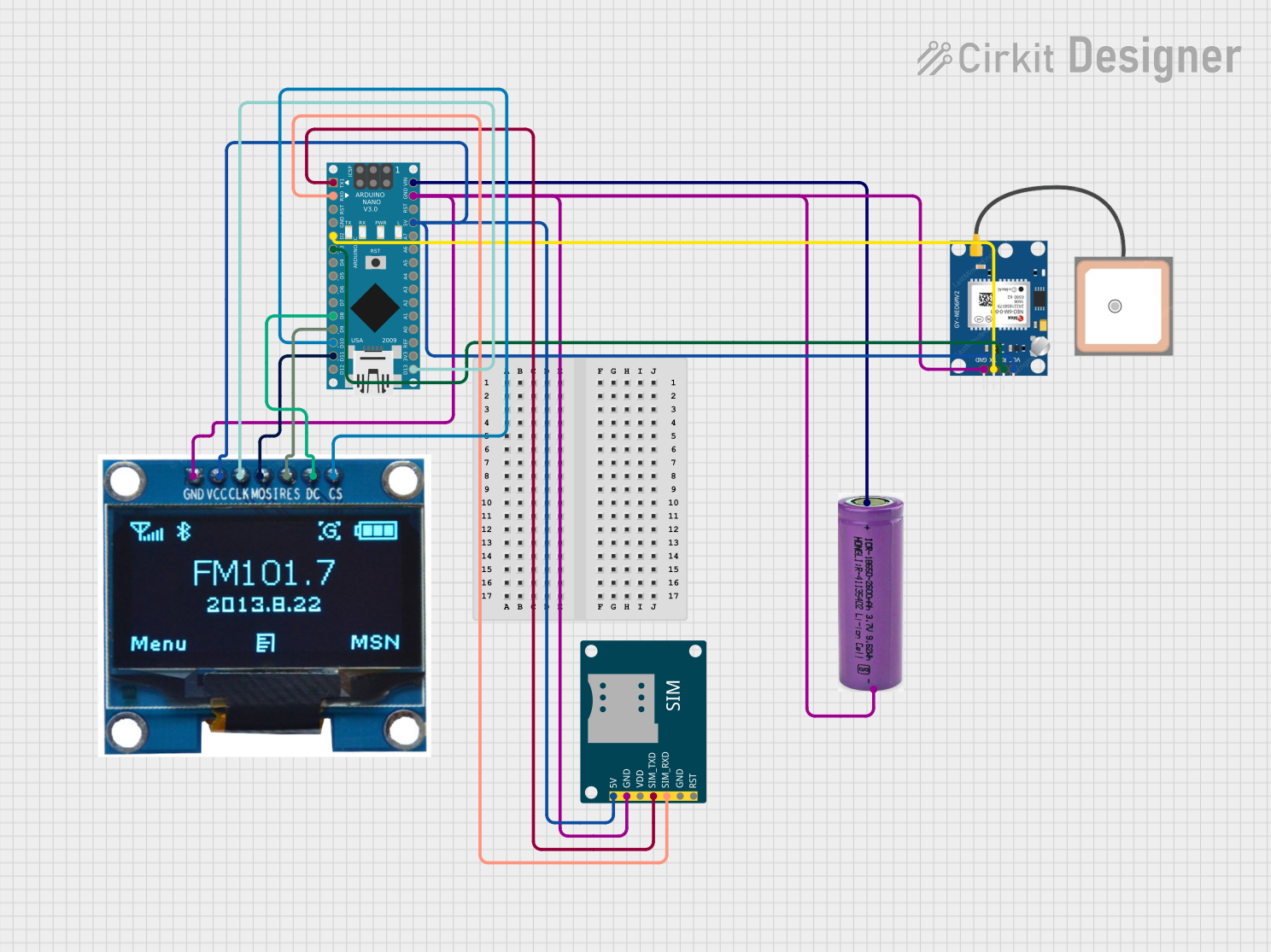
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer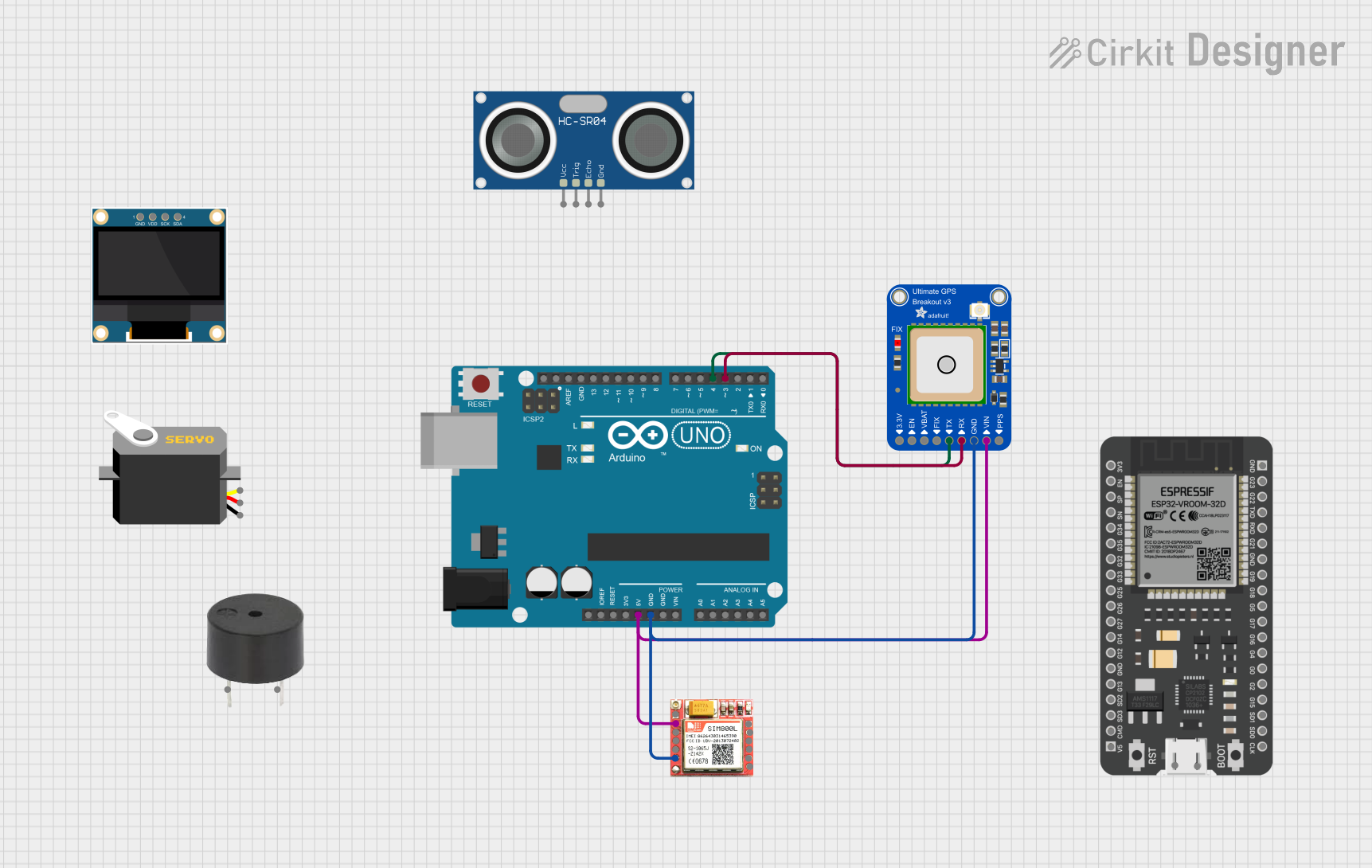
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer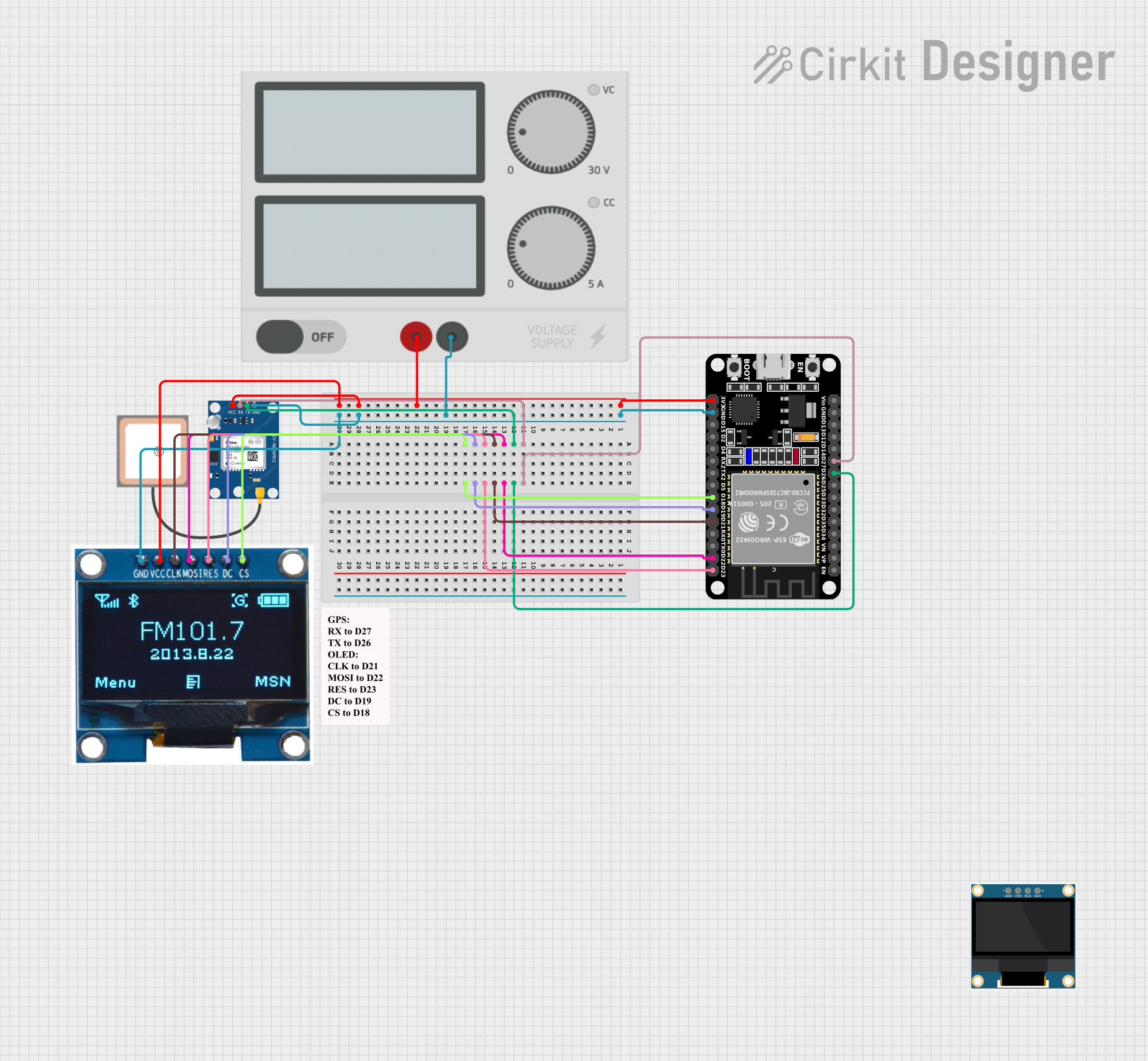
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GT-U7 GPS Module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- GPS navigation systems
- Vehicle and asset tracking
- Drones and UAVs
- Robotics and automation
- IoT devices requiring location data
- Time synchronization for embedded systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the GT-U7 GPS Module:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Deegoo-FPV |
| Part Number | GT-U7 |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V to 5.0V |
| Operating Current | 20mA (typical) |
| Communication Interface | UART (default baud rate: 9600 bps) |
| Positioning Accuracy | 2.5 meters (CEP) |
| Cold Start Time | < 35 seconds |
| Warm Start Time | < 10 seconds |
| Hot Start Time | < 1 second |
| Antenna | Built-in ceramic antenna |
| Dimensions | 25mm x 25mm x 8mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Supported Protocols | NMEA 0183, UBX |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The GT-U7 GPS Module has a 4-pin interface for easy connection to microcontrollers and other devices. Below is the pinout:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 5.0V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | TXD | UART Transmit (data output from the module) |
| 4 | RXD | UART Receive (data input to the module) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the GT-U7 GPS Module
- Power Supply: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5.0V power source and theGNDpin to ground. - UART Communication:
- Connect the
TXDpin of the module to the RX pin of your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO). - Connect the
RXDpin of the module to the TX pin of your microcontroller.
- Connect the
- Antenna Placement: Ensure the module's built-in antenna has a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS signal reception.
Example: Using GT-U7 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the GT-U7 GPS Module with an Arduino UNO to read GPS data:
Circuit Diagram:
- Connect
VCCto the Arduino's5Vpin. - Connect
GNDto the Arduino'sGNDpin. - Connect
TXDto the Arduino'sRXpin (pin 0). - Connect
RXDto the Arduino'sTXpin (pin 1).
Arduino Code:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Create a SoftwareSerial object for communication with the GT-U7 GPS Module
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(4, 3); // RX = pin 4, TX = pin 3
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize Serial Monitor at 9600 bps
gpsSerial.begin(9600); // Initialize GPS module communication at 9600 bps
Serial.println("GT-U7 GPS Module Test");
Serial.println("Waiting for GPS data...");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the GPS module
while (gpsSerial.available()) {
char c = gpsSerial.read(); // Read one character from the GPS module
Serial.print(c); // Print the character to the Serial Monitor
// Note: The GPS module outputs NMEA sentences, which can be parsed
// for specific data like latitude, longitude, and time.
}
}
Important Considerations:
- Baud Rate: The default baud rate of the GT-U7 is 9600 bps. Ensure your microcontroller's UART settings match this.
- Signal Reception: For best results, place the module outdoors or near a window with a clear view of the sky.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid performance issues.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
No GPS Data Received:
- Ensure the module has a clear view of the sky.
- Verify the connections between the module and the microcontroller.
- Check that the baud rate is set correctly (default: 9600 bps).
Long Time to Acquire GPS Fix:
- This may occur during a cold start. Allow the module sufficient time to acquire satellite signals.
- Ensure the module is not obstructed by buildings, trees, or other objects.
Garbage Data in Serial Monitor:
- Verify that the baud rate in the Serial Monitor matches the baud rate of the GPS module.
- Check for loose or incorrect wiring.
Module Not Powering On:
- Confirm that the power supply voltage is within the specified range (3.3V to 5.0V).
- Check the connections to the
VCCandGNDpins.
FAQs:
Q1: Can the GT-U7 GPS Module be used indoors?
A1: While the module may work indoors, signal reception is significantly reduced. For best results, use the module outdoors or near a window.
Q2: How do I parse NMEA sentences from the module?
A2: NMEA sentences can be parsed using libraries like TinyGPS++ or by writing custom code to extract specific data fields.
Q3: Can I change the default baud rate of the module?
A3: Yes, the baud rate can be changed using specific UBX commands. Refer to the module's datasheet for details.
Q4: Does the module support other satellite systems like GLONASS?
A4: The GT-U7 primarily supports GPS signals. For multi-system support, check the module's datasheet or consider alternative models.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the GT-U7 GPS Module into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.