
How to Use Connection Node 1pin: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Connection Node 1pin in Cirkit Designer
Design with Connection Node 1pin in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Connection Node 1pin is a simple yet versatile electronic component designed to establish a single-point electrical connection in a circuit. It serves as a fundamental building block for integrating various components, enabling seamless connectivity in both prototyping and permanent circuit designs. Its compact design and ease of use make it an essential component for hobbyists, engineers, and educators alike.
Explore Projects Built with Connection Node 1pin
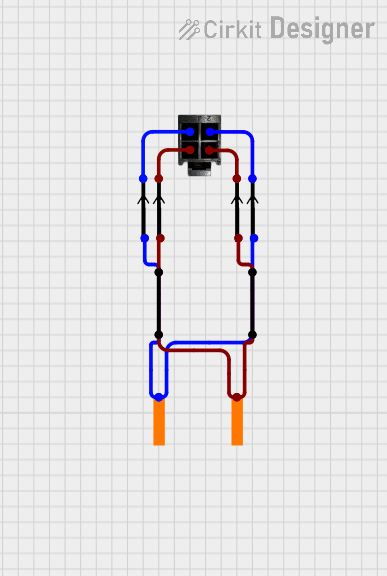
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer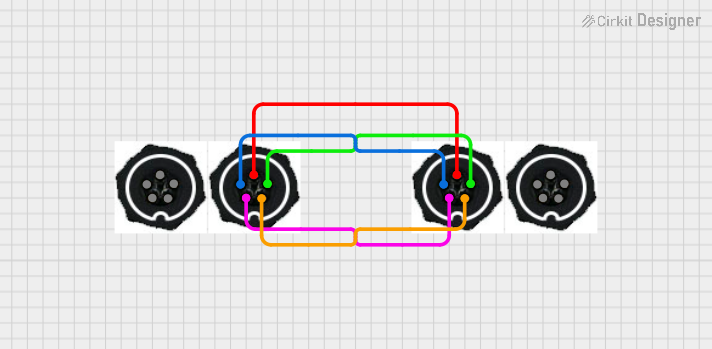
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer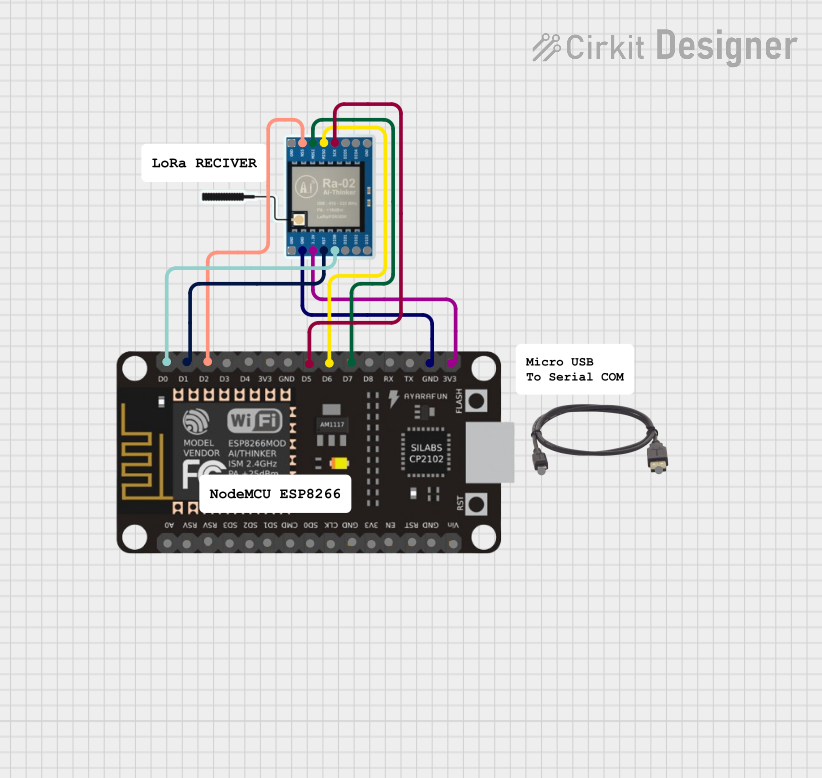
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer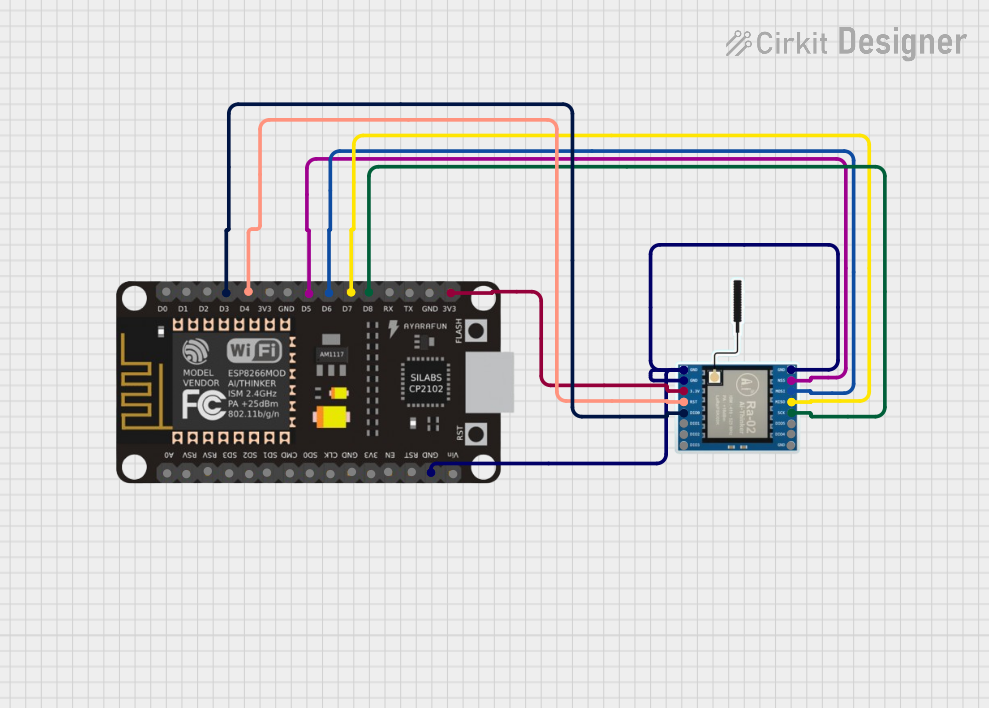
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Connection Node 1pin

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Prototyping: Used on breadboards or perfboards to connect wires or components.
- Signal Distribution: Acts as a junction for distributing signals or power to multiple components.
- Testing and Debugging: Provides a convenient point for connecting test probes or measuring instruments.
- Permanent Installations: Used in soldered circuits for reliable single-pin connections.
Technical Specifications
The Connection Node 1pin is a passive component with no active electrical properties. Below are its key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Material | Copper (with optional tin plating) |
| Maximum Current Rating | 3A |
| Maximum Voltage Rating | 50V |
| Pin Diameter | 0.8mm |
| Mounting Type | Through-hole or solderable |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Connection Node 1pin has a single pin, which serves as the electrical connection point. Below is the pin description:
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Electrical connection point (input/output) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Prototyping on a Breadboard:
- Insert the pin into a breadboard hole to establish a connection.
- Connect wires or components to the same breadboard row to complete the circuit.
Soldering in Permanent Circuits:
- Place the pin through a hole in a printed circuit board (PCB).
- Solder the pin to the PCB pad to secure the connection.
Signal or Power Distribution:
- Use the node as a junction point by connecting multiple wires to it.
- Ensure that the current and voltage do not exceed the component's ratings.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overloading: Ensure the current and voltage do not exceed the maximum ratings (3A and 50V).
- Secure Connections: When soldering, ensure a clean and solid solder joint to prevent loose connections.
- Prevent Short Circuits: Avoid accidental contact with other conductive materials.
- Use Heat Shrink Tubing: For added insulation, cover the pin with heat shrink tubing after soldering.
Example: Using with an Arduino UNO
The Connection Node 1pin can be used to connect external components to an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of connecting an LED to an Arduino using the node:
Circuit Setup
- Connect the positive leg of the LED to the Connection Node 1pin.
- Connect the node to a digital pin on the Arduino (e.g., pin 13).
- Connect the negative leg of the LED to a resistor (220Ω) and then to the Arduino's GND.
Arduino Code
// Example code to blink an LED connected via Connection Node 1pin
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the Connection Node 1pin
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Loose Connections:
- Issue: The pin feels loose in the breadboard or PCB.
- Solution: Ensure the pin is properly inserted. For PCBs, check the solder joint for cracks or weak connections.
Overheating:
- Issue: The node becomes hot during operation.
- Solution: Verify that the current and voltage do not exceed the component's ratings. Reduce the load if necessary.
Short Circuits:
- Issue: The circuit does not function, and components may overheat.
- Solution: Inspect the circuit for accidental contact between the pin and other conductive materials. Use insulation if needed.
Corrosion or Oxidation:
- Issue: The pin surface appears tarnished, affecting conductivity.
- Solution: Clean the pin with isopropyl alcohol or a fine abrasive material. Consider using a tin-plated version for better corrosion resistance.
FAQs
Q1: Can the Connection Node 1pin handle AC signals?
A1: Yes, it can handle both AC and DC signals, provided the voltage and current ratings are not exceeded.
Q2: Is the Connection Node 1pin reusable?
A2: Yes, it can be reused in prototyping applications. However, for soldered connections, desoldering may damage the pin.
Q3: Can I use this component for high-frequency signals?
A3: While it can handle high-frequency signals, its performance may vary depending on the circuit design and layout. For critical applications, consider components specifically designed for high-frequency use.
Q4: What tools are recommended for soldering this component?
A4: Use a soldering iron with a fine tip, solder wire, and flux for best results. Heat shrink tubing can be used for insulation after soldering.