
How to Use Temperature Sensor : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
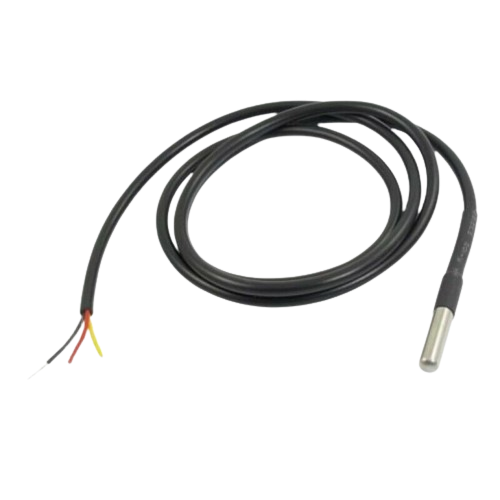

 Design with Temperature Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Temperature Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A temperature sensor is a device that measures the temperature of an environment or object and converts it into a readable signal, such as an analog voltage or digital data. These sensors are widely used in applications such as HVAC systems, weather stations, industrial processes, and consumer electronics. They are essential for monitoring and controlling temperature in various systems to ensure safety, efficiency, and performance.
Common types of temperature sensors include thermistors, thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and integrated circuit (IC) temperature sensors. Each type has its own advantages and is suited for specific use cases.
Explore Projects Built with Temperature Sensor
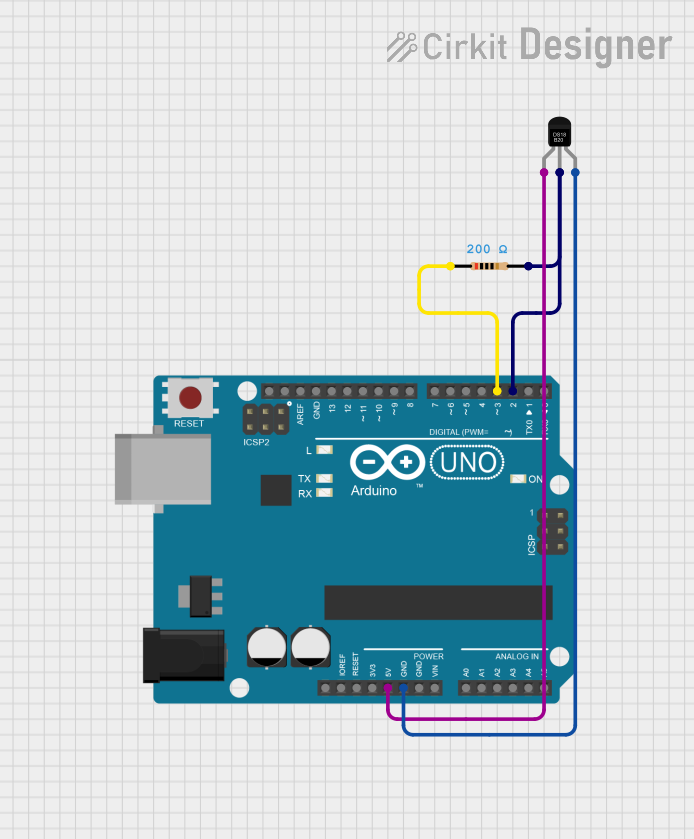
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer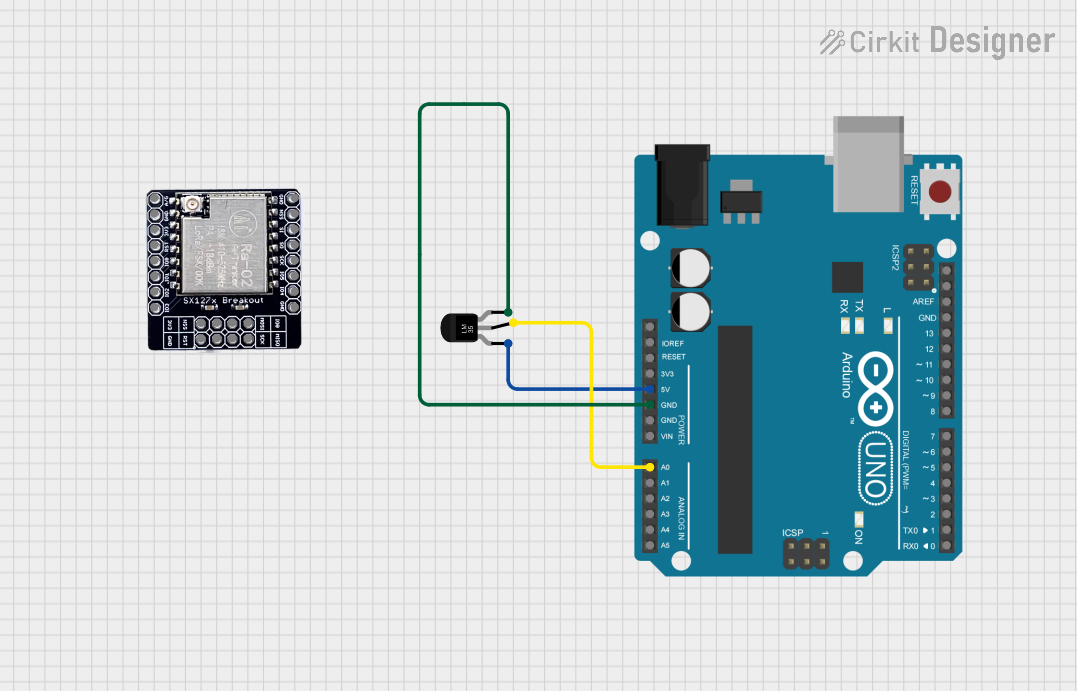
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer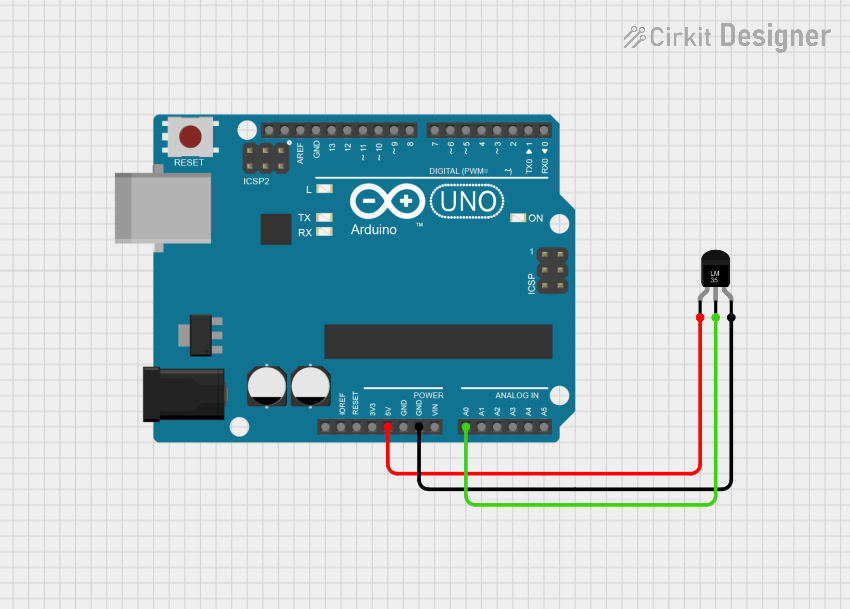
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer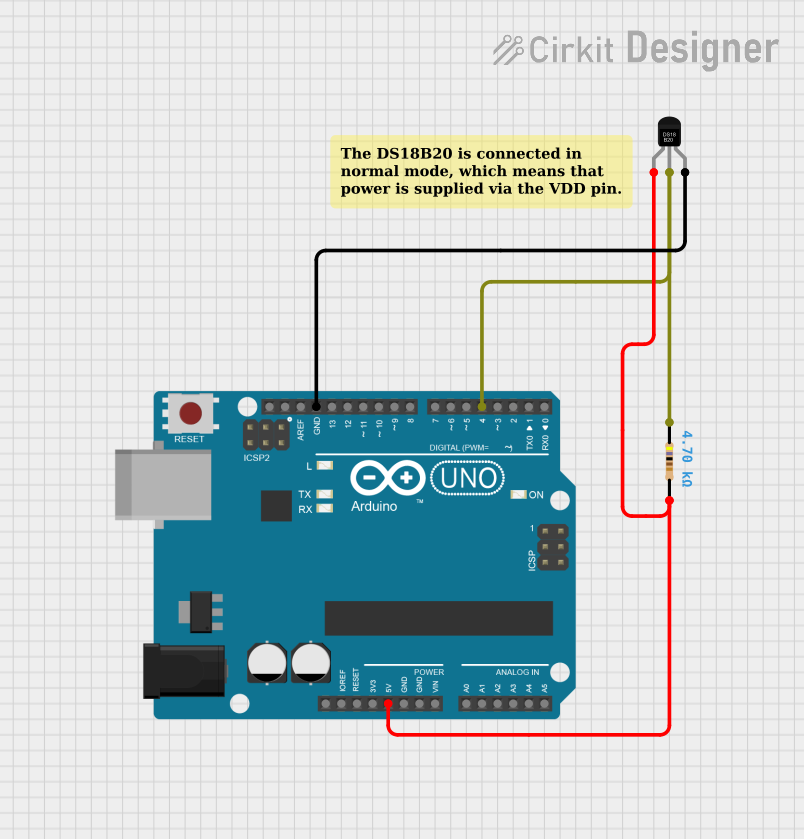
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Temperature Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a common IC-based temperature sensor, such as the LM35:
- Operating Voltage: 4V to 30V
- Output Signal: Analog voltage proportional to temperature
- Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
- Accuracy: ±0.5°C (typical at 25°C)
- Output Scale Factor: 10mV/°C
- Current Consumption: <60 µA
- Response Time: <1 second (typical)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The following table describes the pinout for a typical 3-pin temperature sensor like the LM35:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (4V to 30V) |
| 2 | VOUT | Analog output voltage proportional to temperature |
| 3 | GND | Ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the VCC pin to a stable power supply (e.g., 5V from an Arduino UNO) and the GND pin to the ground.
- Read the Output: Connect the VOUT pin to an analog input pin of a microcontroller or an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) to read the temperature.
- Calculate Temperature: For an LM35, the output voltage is directly proportional to the temperature in °C. For example:
- 250mV corresponds to 25°C.
- 1V corresponds to 100°C.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply Stability: Ensure the power supply is stable and within the specified range to avoid inaccurate readings.
- Placement: Place the sensor in a location where it can accurately measure the desired temperature without interference from heat sources or airflow.
- Decoupling Capacitor: Add a small decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) between VCC and GND to reduce noise.
- Avoid Overheating: Do not exceed the maximum operating temperature to prevent damage to the sensor.
Example: Using the LM35 with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example code to read temperature data from an LM35 sensor using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the analog pin connected to the LM35 sensor
const int sensorPin = A0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the analog value from the sensor
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert ADC value to voltage
float temperature = voltage * 100.0; // Convert voltage to temperature in °C
// Print the temperature to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Notes:
- The
analogRead()function reads a value between 0 and 1023, corresponding to 0V to 5V. - The conversion factor
5.0 / 1023.0is used to calculate the actual voltage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Inaccurate Readings:
- Cause: Unstable power supply or electrical noise.
- Solution: Use a decoupling capacitor and ensure a stable power source.
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or damaged sensor.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and replace the sensor if necessary.
Output Voltage Stuck at a Fixed Value:
- Cause: Sensor operating outside its temperature range or faulty sensor.
- Solution: Ensure the sensor is within its specified temperature range and replace it if needed.
Slow Response Time:
- Cause: Poor thermal contact or incorrect placement.
- Solution: Place the sensor closer to the heat source or improve thermal coupling.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the LM35 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, the LM35 can operate with a supply voltage as low as 4V. However, for 3.3V systems, consider using a sensor designed for lower voltage operation, or use a level shifter.
Q2: How do I measure negative temperatures with the LM35?
A2: The LM35 outputs 0V at 0°C. To measure negative temperatures, you need to use a negative voltage reference or a sensor variant like the LM35C.
Q3: Can I use the LM35 in a waterproof application?
A3: The LM35 itself is not waterproof. For such applications, use a waterproof housing or a sensor designed for immersion, such as the DS18B20.
Q4: What is the maximum cable length for the LM35?
A4: The maximum cable length depends on the environment and noise levels. For long distances, use shielded cables or consider a digital temperature sensor like the DS18B20.