
How to Use Lonely Binary ESP32-S3 DevKitC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
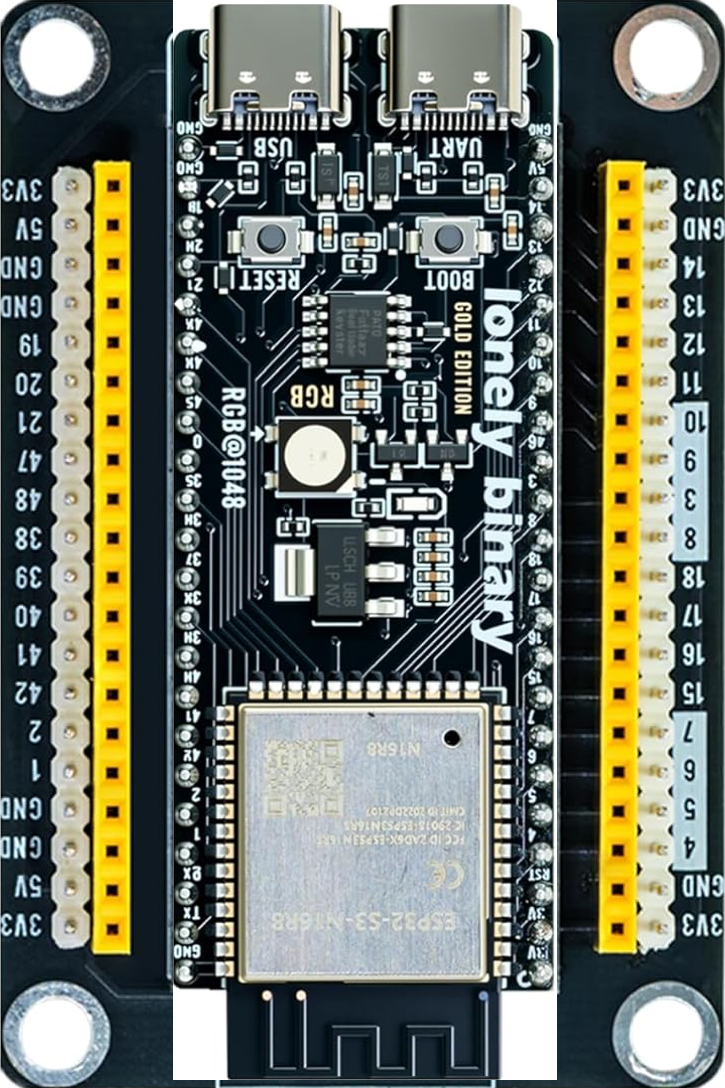
 Design with Lonely Binary ESP32-S3 DevKitC in Cirkit Designer
Design with Lonely Binary ESP32-S3 DevKitC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Lonely Binary ESP32-S3 DevKitC is a versatile development board built around the ESP32-S3 chip. This board is designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, offering integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity. It is ideal for prototyping and developing smart devices, wearables, and other connected systems. The board supports a wide range of peripherals and interfaces, making it a powerful tool for both beginners and experienced developers.
Explore Projects Built with Lonely Binary ESP32-S3 DevKitC
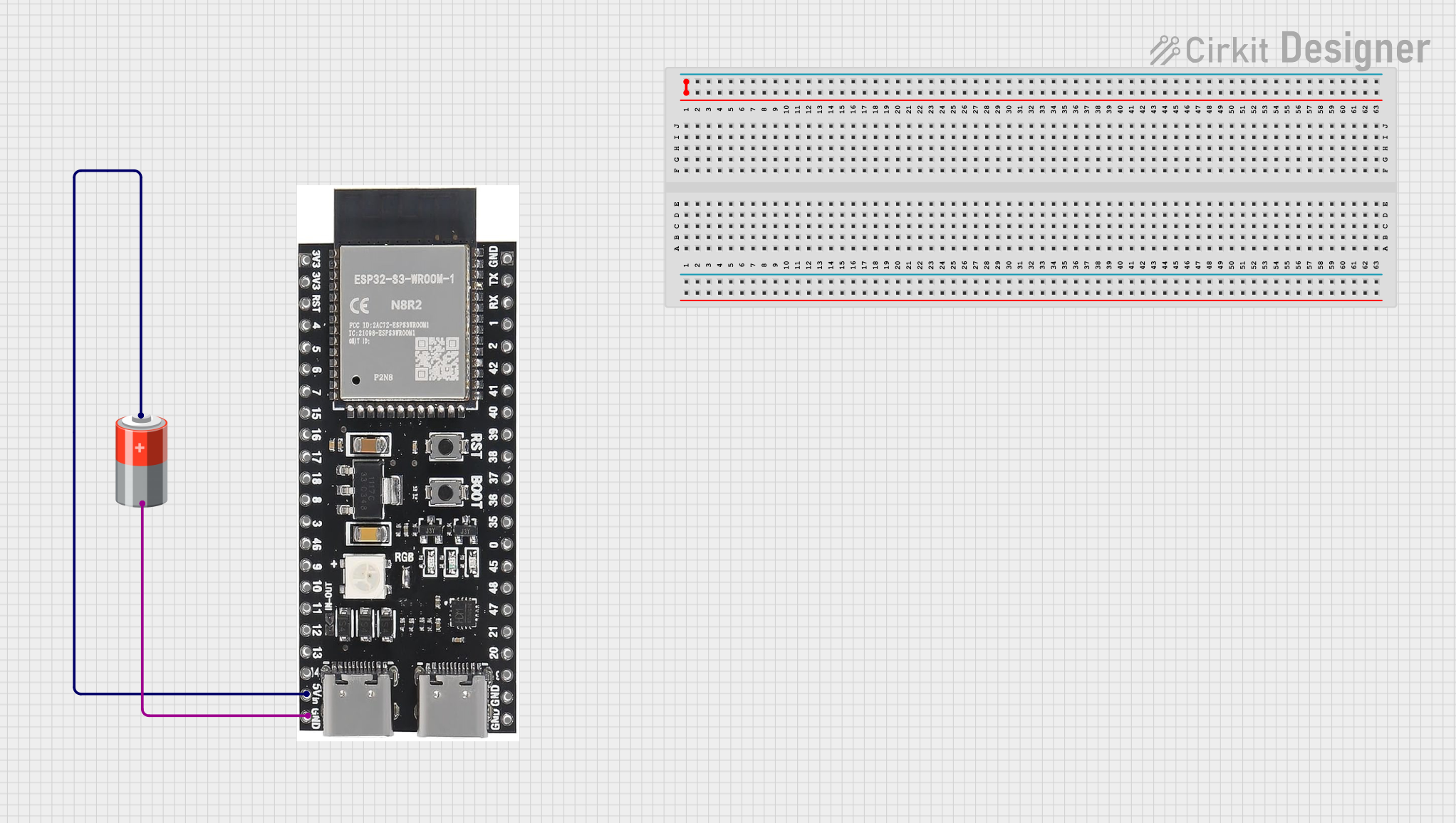
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer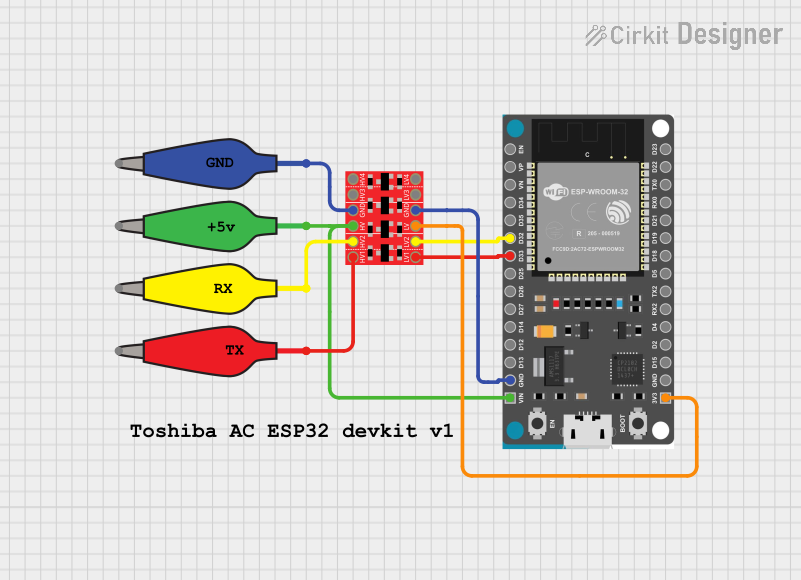
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer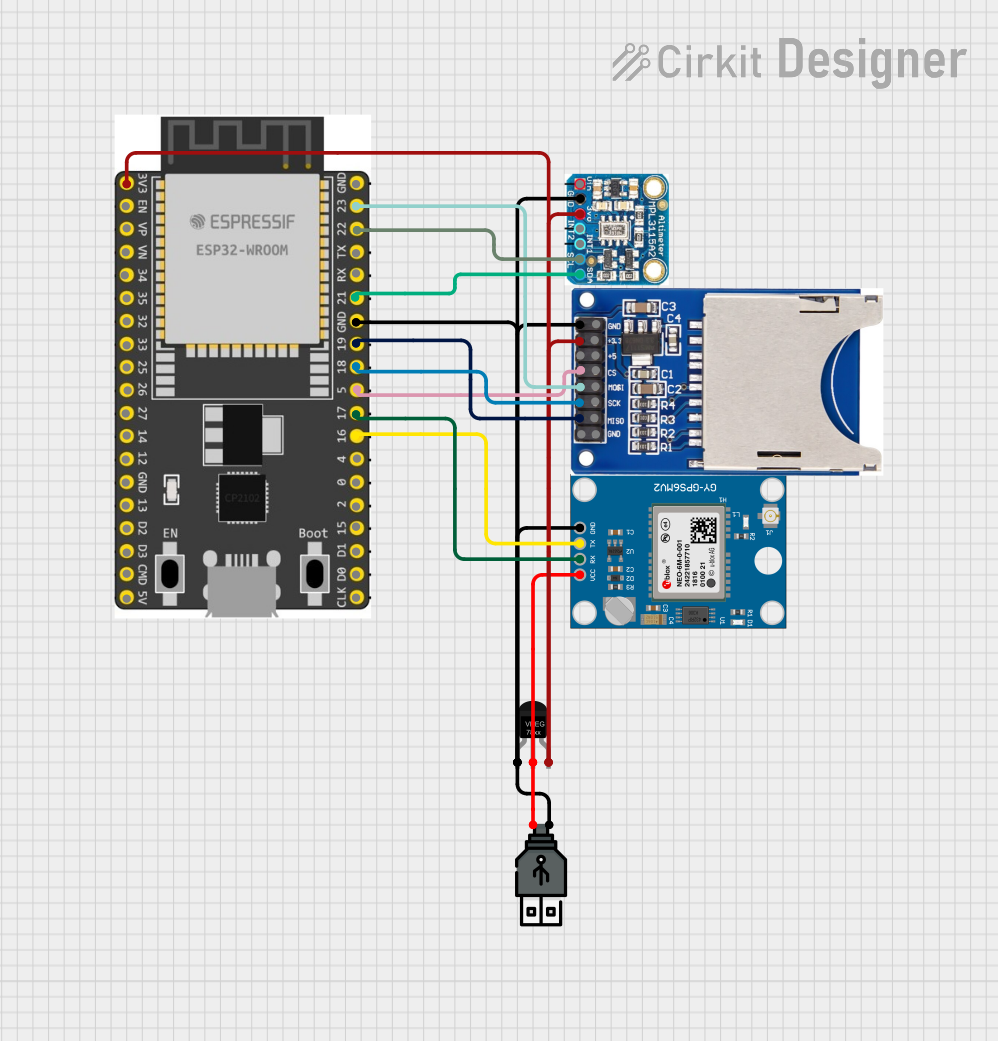
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer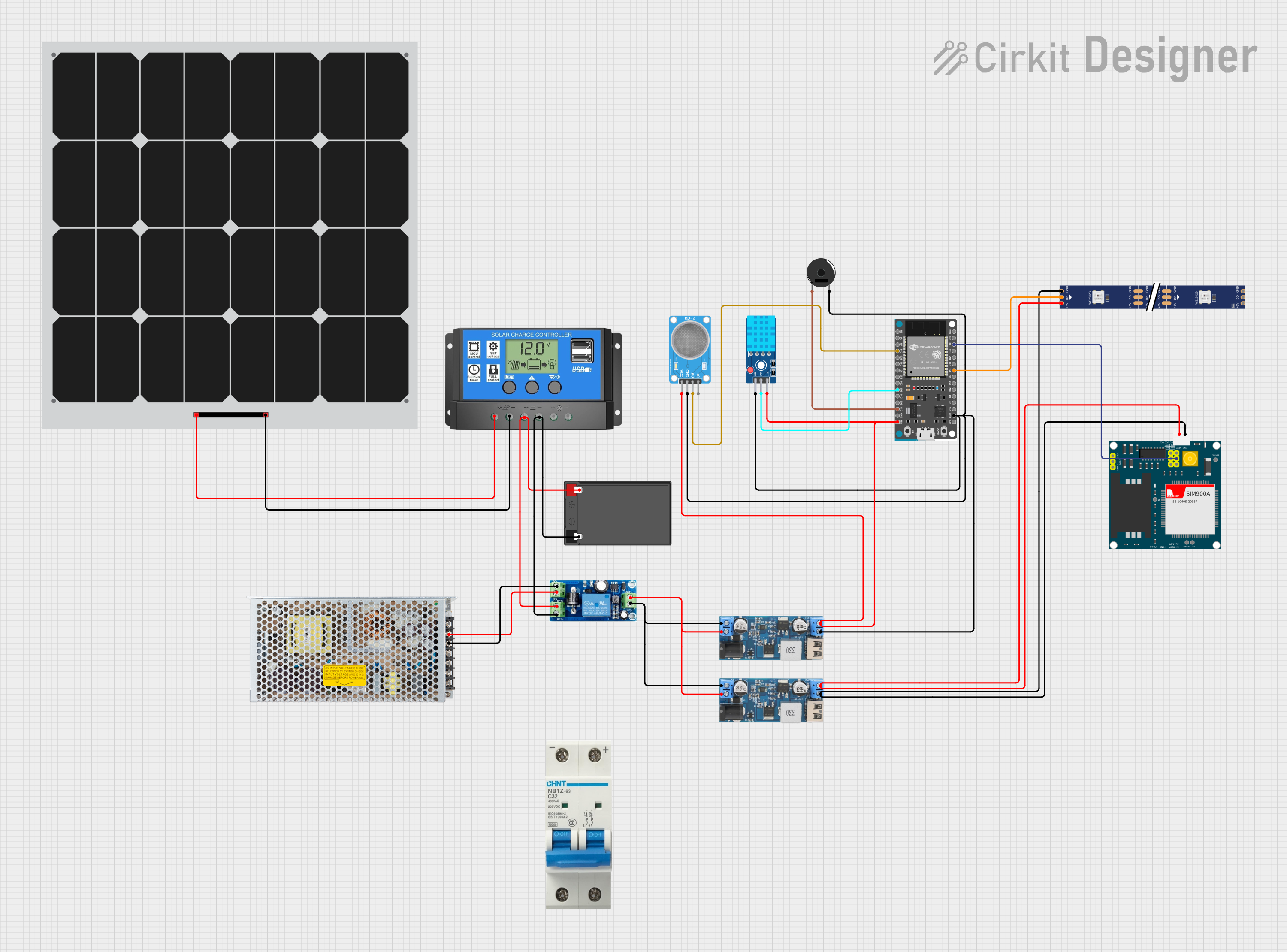
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Lonely Binary ESP32-S3 DevKitC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home systems
- Wearable technology
- Wireless sensor networks
- Industrial automation
- Prototyping AI and machine learning applications at the edge
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons and gateways
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the ESP32-S3 DevKitC:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ESP32-S3 (Xtensa® 32-bit LX7 dual-core processor) |
| Clock Speed | Up to 240 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 8 MB (external SPI flash) |
| RAM | 512 KB SRAM + 2 MB PSRAM |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n (2.4 GHz), Bluetooth 5.0 LE |
| GPIO Pins | 21 GPIO pins |
| Interfaces | UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, PWM, ADC, DAC |
| USB Connectivity | USB Type-C (supports programming and power supply) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Power Supply | 5V via USB Type-C or external power source |
| Dimensions | 54 mm x 25 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32-S3 DevKitC features a 2x19 pin header layout. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | 3V3 | 3.3V power output |
| 3 | EN | Enable pin (active high) |
| 4 | IO0 | GPIO0, used for boot mode selection |
| 5 | IO1 | GPIO1, general-purpose I/O |
| 6 | IO2 | GPIO2, general-purpose I/O |
| 7 | IO3 | GPIO3, general-purpose I/O |
| 8 | IO4 | GPIO4, general-purpose I/O |
| 9 | IO5 | GPIO5, general-purpose I/O |
| 10 | IO6 | GPIO6, general-purpose I/O |
| ... | ... | ... (remaining GPIO pins follow similar use) |
For a complete pinout diagram, refer to the official datasheet provided by Lonely Binary.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
Connect the board to your computer or a power source using a USB Type-C cable. The board operates at 3.3V internally but requires a 5V input via USB or an external power source.Programming the Board:
- Install the ESP32-S3 board support package in the Arduino IDE or use the ESP-IDF (Espressif IoT Development Framework) for advanced development.
- Select the correct board and port in the IDE.
- Write your code and upload it to the board.
Connecting Peripherals:
Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, actuators, or other peripherals. Ensure that the voltage levels of connected devices are compatible with the 3.3V logic of the ESP32-S3.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Boot Mode Selection: To enter bootloader mode, hold the BOOT button while pressing the EN button.
- Voltage Levels: Avoid applying voltages higher than 3.3V to the GPIO pins to prevent damage.
- Power Supply: If using an external power source, ensure it provides a stable 5V input.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Antenna: Keep the onboard antenna area clear of obstructions for optimal wireless performance.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
Below is an example of how to use the ESP32-S3 DevKitC to read data from a DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor and send it to a serial monitor:
#include <DHT.h>
// Define the GPIO pin connected to the DHT11 sensor
#define DHTPIN 4 // GPIO4 on the ESP32-S3
// Define the type of DHT sensor
#define DHTTYPE DHT11
// Initialize the DHT sensor
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Start the serial communication
dht.begin(); // Initialize the DHT sensor
Serial.println("DHT11 Sensor Example with ESP32-S3");
}
void loop() {
// Read temperature and humidity values
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
// Check if the readings are valid
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
// Print the readings to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.print("% Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println("°C");
delay(2000); // Wait 2 seconds before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Board Not Detected by the Computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
- Verify that the correct drivers for the ESP32-S3 are installed.
Code Upload Fails:
- Check that the correct board and port are selected in the IDE.
- Enter bootloader mode by holding the BOOT button while pressing the EN button.
Wi-Fi or Bluetooth Connectivity Issues:
- Ensure the antenna area is unobstructed.
- Verify that the correct SSID and password are used for Wi-Fi connections.
GPIO Pin Malfunction:
- Confirm that the connected peripherals are operating within the 3.3V logic level.
- Avoid using reserved pins for general-purpose I/O.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to check power supply voltages and continuity of connections.
- Refer to the official datasheet and pinout diagram for detailed information on pin functions.
- Update the ESP32-S3 firmware and development tools to the latest versions for improved stability and compatibility.
For further assistance, consult the official documentation and support resources provided by Lonely Binary.