
How to Use ADXL335: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
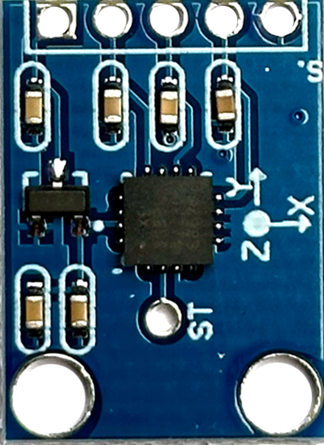
 Design with ADXL335 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ADXL335 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ADXL335 is a small, thin, low-power, 3-axis accelerometer with a measurement range of ±3g. It provides analog output signals proportional to acceleration along the X, Y, and Z axes. This component is widely used in applications such as motion sensing, tilt detection, vibration monitoring, and gaming devices. Its compact size and low power consumption make it ideal for portable and battery-powered devices.
Explore Projects Built with ADXL335
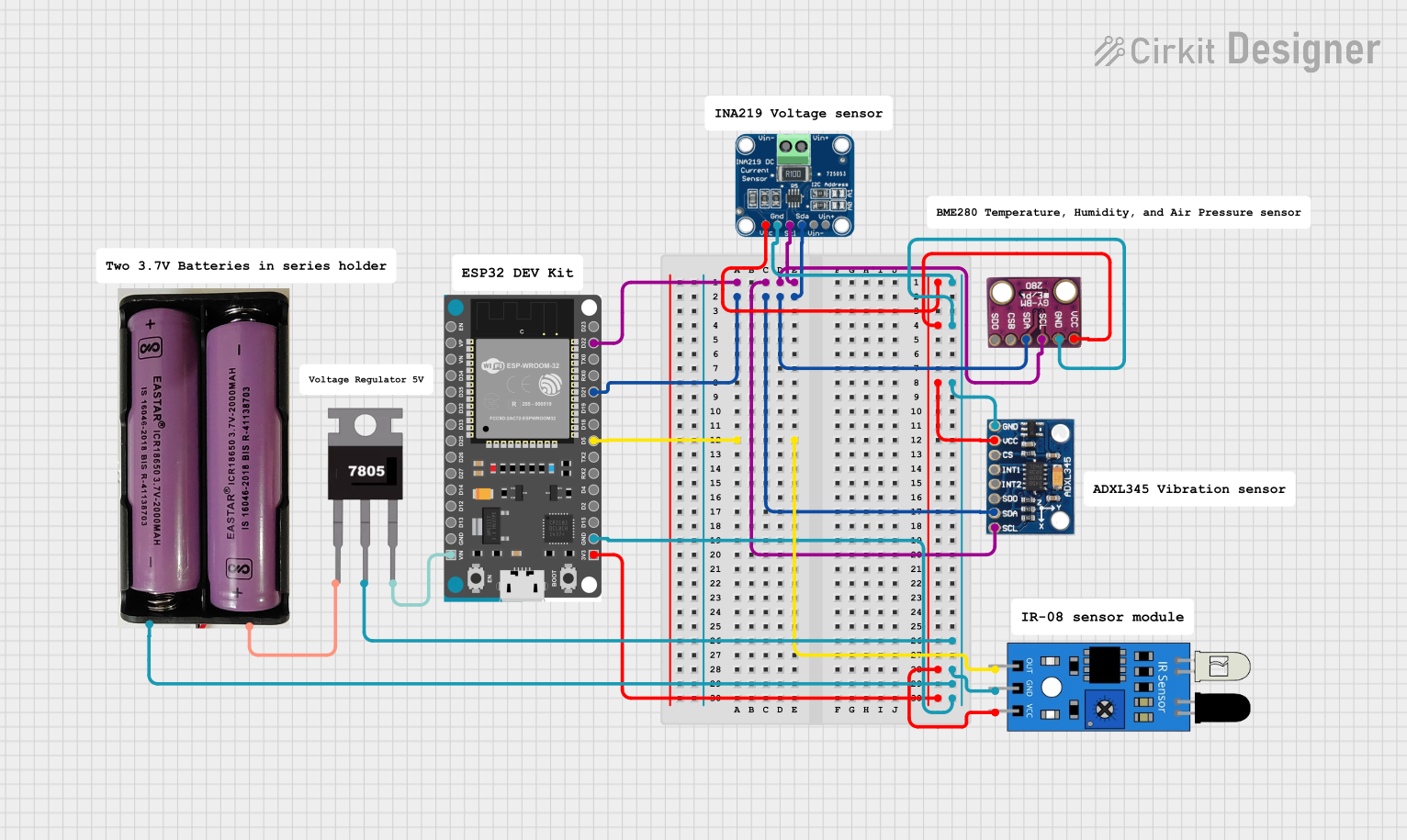
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer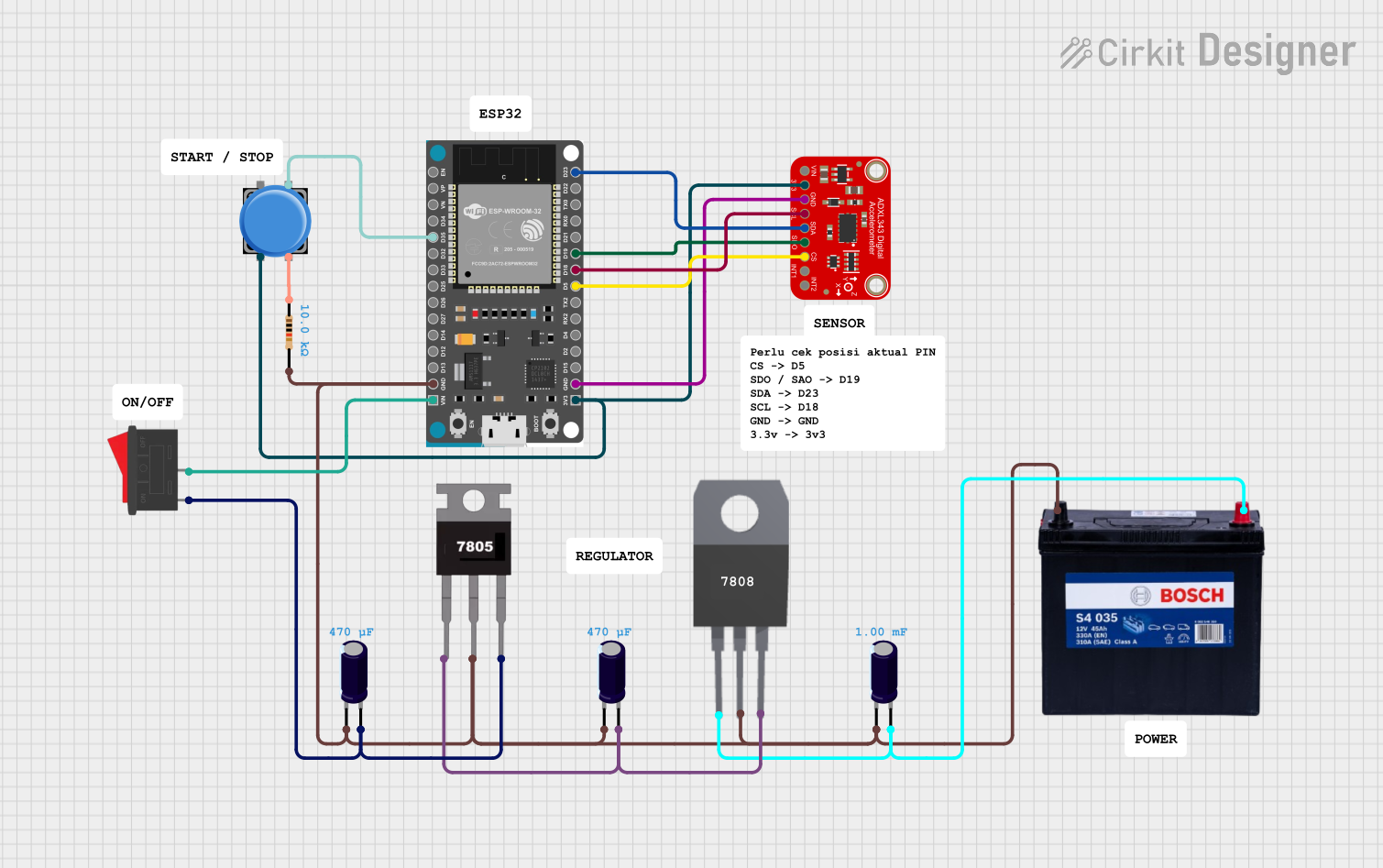
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer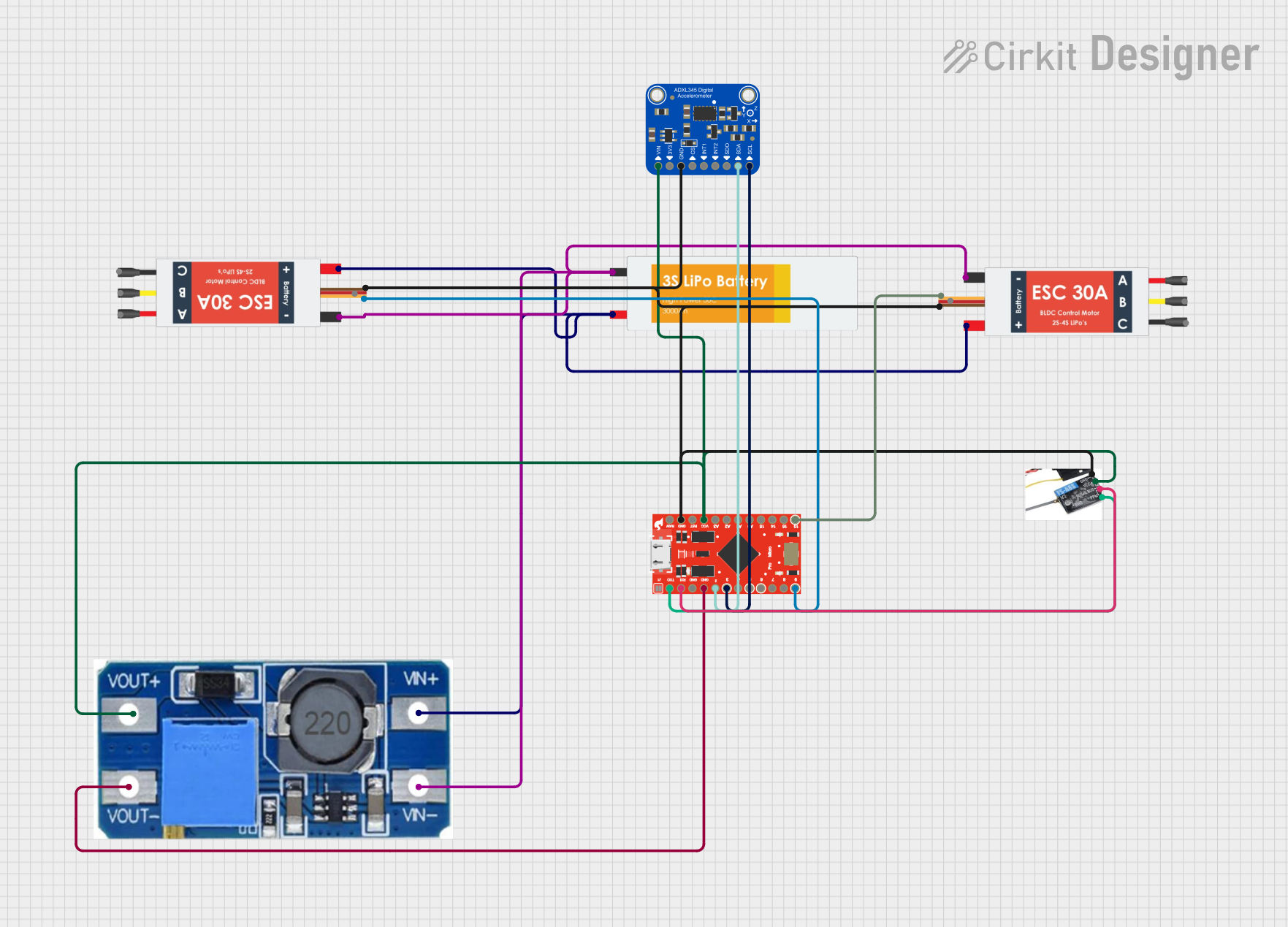
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer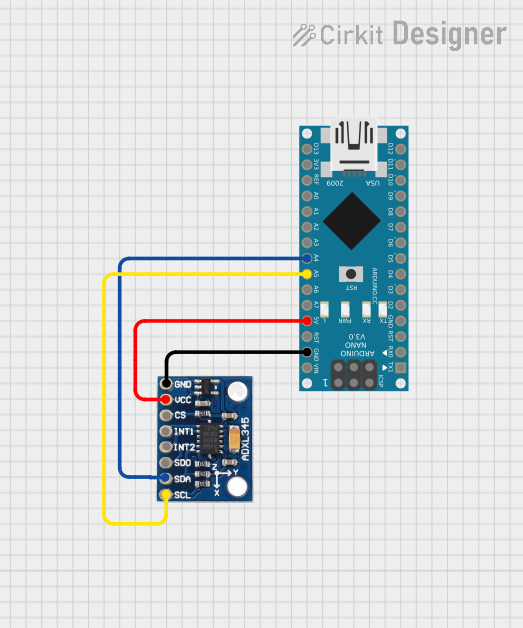
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ADXL335

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Motion sensing in mobile devices
- Tilt detection in robotics and industrial equipment
- Vibration monitoring in machinery
- Gaming controllers and user interface devices
- Wearable technology and fitness trackers
Technical Specifications
The ADXL335 is designed to provide reliable and accurate acceleration measurements. Below are its key technical details:
Key Specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Measurement Range | ±3g |
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 1.8V to 3.6V |
| Typical Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Output Type | Analog |
| Sensitivity | 300 mV/g (typical at 3.3V) |
| Bandwidth (X, Y, Z axes) | 0.5 Hz to 1600 Hz (adjustable) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Power Consumption | 350 µA (typical) |
| Dimensions | 4 mm × 4 mm × 1.45 mm |
Pin Configuration:
The ADXL335 has a total of 5 pins. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 1 | Power supply input (1.8V to 3.6V) |
| GND | 2 | Ground |
| XOUT | 3 | Analog output voltage proportional to X-axis |
| YOUT | 4 | Analog output voltage proportional to Y-axis |
| ZOUT | 5 | Analog output voltage proportional to Z-axis |
Usage Instructions
The ADXL335 outputs analog voltages proportional to the acceleration along the X, Y, and Z axes. These outputs can be read using an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) on a microcontroller, such as an Arduino UNO.
Connecting the ADXL335 to an Arduino UNO:
- Power the ADXL335: Connect the VCC pin to the 3.3V pin on the Arduino and the GND pin to the Arduino's GND.
- Connect the Output Pins: Connect the XOUT, YOUT, and ZOUT pins to the Arduino's analog input pins (e.g., A0, A1, A2).
- Read the Analog Values: Use the Arduino's
analogRead()function to read the voltage values from the X, Y, and Z axes.
Sample Arduino Code:
// Define the analog input pins connected to the ADXL335
const int xPin = A0; // X-axis output connected to A0
const int yPin = A1; // Y-axis output connected to A1
const int zPin = A2; // Z-axis output connected to A2
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog values from the ADXL335
int xValue = analogRead(xPin); // Read X-axis value
int yValue = analogRead(yPin); // Read Y-axis value
int zValue = analogRead(zPin); // Read Z-axis value
// Convert the analog values to voltages (assuming 5V reference)
float xVoltage = xValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
float yVoltage = yValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
float zVoltage = zValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Print the voltages to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("X Voltage: ");
Serial.print(xVoltage);
Serial.print(" V, Y Voltage: ");
Serial.print(yVoltage);
Serial.print(" V, Z Voltage: ");
Serial.println(zVoltage);
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Important Considerations:
- Power Supply: Ensure the ADXL335 is powered with a voltage within its operating range (1.8V to 3.6V). Using a voltage higher than 3.6V can damage the component.
- Filtering: The ADXL335 allows bandwidth adjustment using external capacitors on the XOUT, YOUT, and ZOUT pins. This can help reduce noise in the output signal.
- Calibration: For accurate measurements, calibrate the accelerometer to account for any offsets or variations in sensitivity.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues:
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the VCC pin is receiving the correct voltage.
Noisy Output:
- Cause: High-frequency noise or lack of filtering capacitors.
- Solution: Add external capacitors to the XOUT, YOUT, and ZOUT pins to filter noise.
Inaccurate Readings:
- Cause: Misalignment or lack of calibration.
- Solution: Calibrate the accelerometer by measuring the output at known orientations and adjusting for offsets.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive voltage applied to the VCC pin.
- Solution: Ensure the supply voltage does not exceed 3.6V.
FAQs:
Q1: Can the ADXL335 be used with a 5V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, but you must use a voltage regulator or level shifter to step down the 5V to 3.3V for the ADXL335's VCC pin. The analog output signals can still be read by the 5V microcontroller.
Q2: How do I adjust the bandwidth of the ADXL335?
A2: The bandwidth can be adjusted by adding external capacitors to the XOUT, YOUT, and ZOUT pins. Refer to the datasheet for recommended capacitor values for specific bandwidths.
Q3: What is the sensitivity of the ADXL335?
A3: The typical sensitivity is 300 mV/g when powered at 3.3V. This means a 1g acceleration will produce a 0.3V change in the output signal.
Q4: Can the ADXL335 measure static acceleration (e.g., gravity)?
A4: Yes, the ADXL335 can measure both static acceleration (e.g., tilt due to gravity) and dynamic acceleration (e.g., motion or vibration).