
How to Use Wind Vane ( Wind Direction) RS485: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Wind Vane ( Wind Direction) RS485 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Wind Vane ( Wind Direction) RS485 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Wind Vane (Wind Direction) RS485 is a meteorological instrument designed to measure the direction of the wind. It utilizes an RS485 communication interface, which enables reliable, long-distance data transmission and seamless integration into networked systems. This makes it ideal for applications requiring precise wind direction monitoring in industrial, agricultural, and environmental settings.
Explore Projects Built with Wind Vane ( Wind Direction) RS485
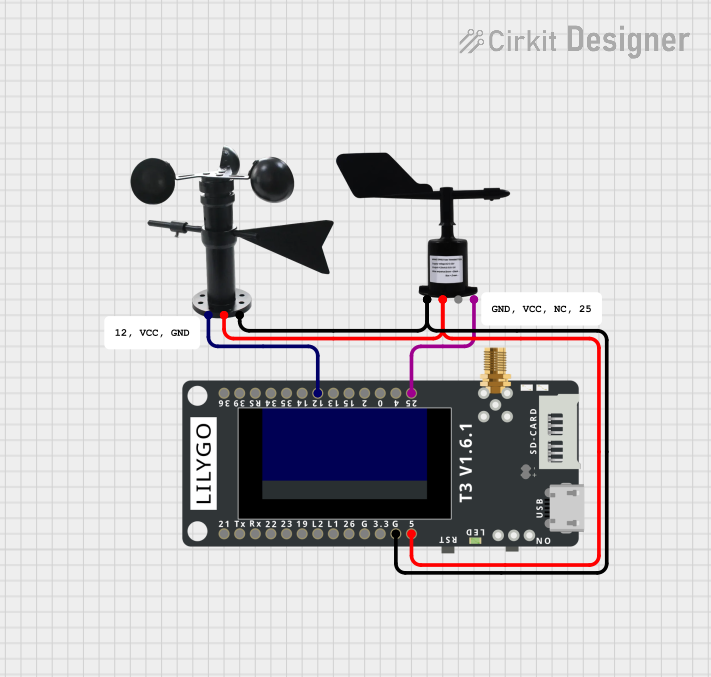
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer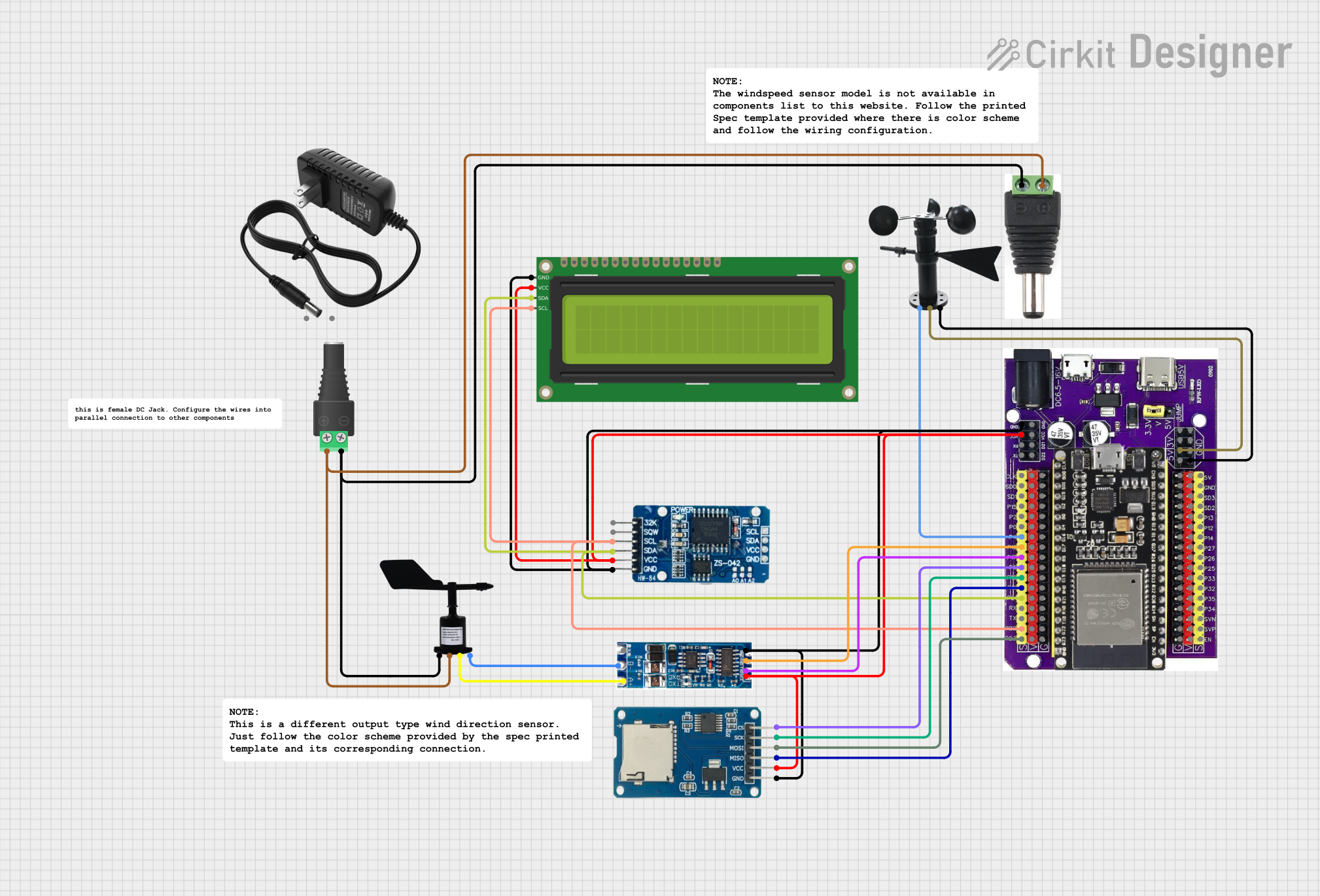
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer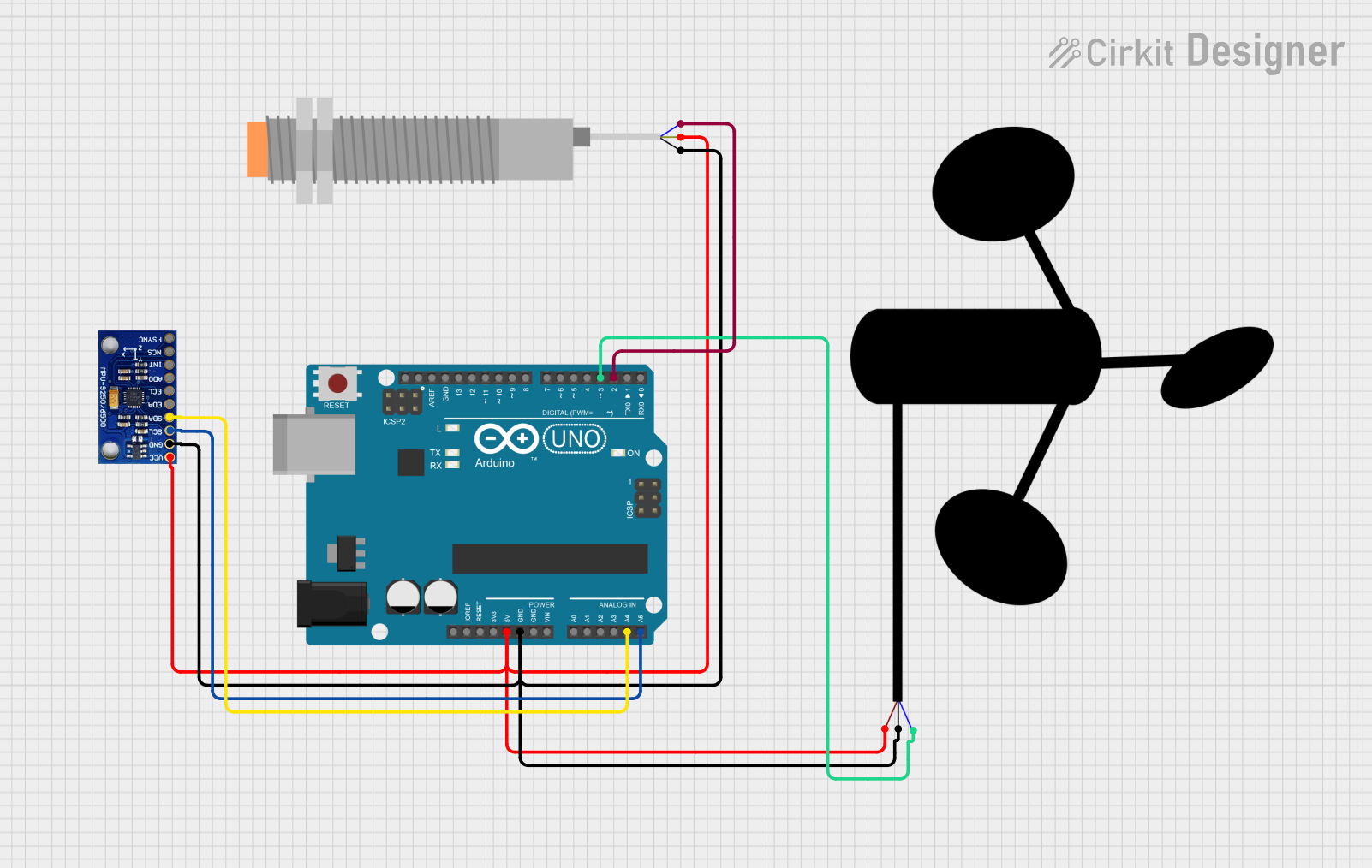
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer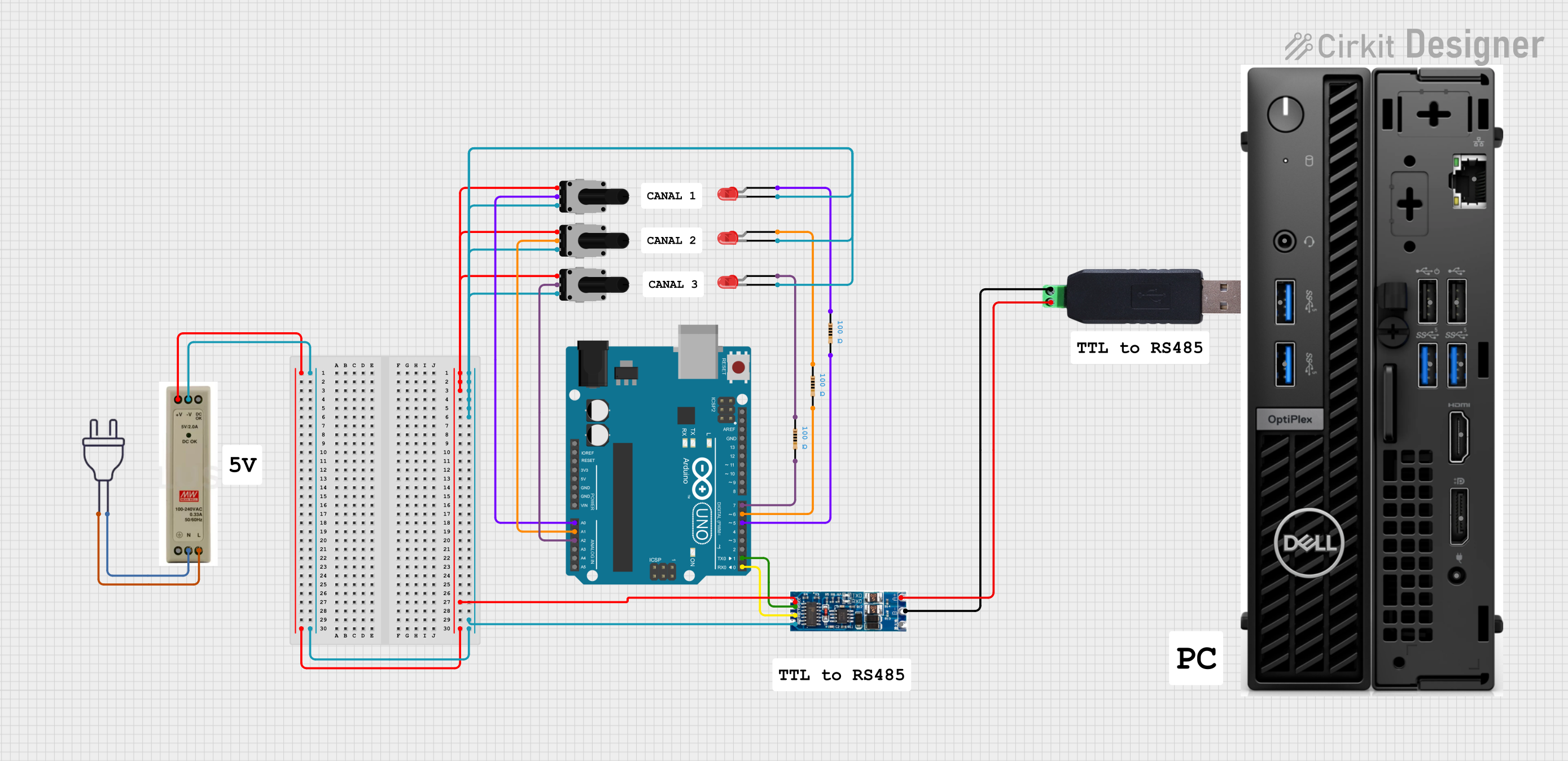
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Wind Vane ( Wind Direction) RS485

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Weather monitoring stations
- Agricultural automation systems
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., wind turbines)
- Industrial process control
- Environmental research and data collection
Technical Specifications
The Wind Vane (Wind Direction) RS485 is built for durability and accuracy in outdoor environments. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 12V DC (typical) |
| Communication Interface | RS485 (Modbus RTU protocol) |
| Measurement Range | 0° to 360° (full wind direction) |
| Accuracy | ±3° |
| Resolution | 1° |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
| Humidity Range | 0% to 100% RH (non-condensing) |
| Power Consumption | < 0.5W |
| Material | Corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy |
| Cable Length | 2 meters (extendable) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Wind Vane RS485 typically comes with a 4-wire cable for power and communication. The pinout is as follows:
| Wire Color | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Red | VCC (+12V) | Power supply input |
| Black | GND | Ground connection |
| Yellow | RS485-A | RS485 differential signal (A) |
| Green | RS485-B | RS485 differential signal (B) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Connection: Connect the red wire to a 12V DC power source and the black wire to ground.
- RS485 Communication: Connect the yellow (RS485-A) and green (RS485-B) wires to the corresponding RS485 terminals on your microcontroller or RS485-to-USB converter.
- Termination Resistor: If the wind vane is at the end of the RS485 bus, add a 120-ohm termination resistor between RS485-A and RS485-B to prevent signal reflections.
- Data Reading: Use the Modbus RTU protocol to query the wind vane for wind direction data. The device typically responds with a 16-bit value representing the wind direction in degrees.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Mounting: Install the wind vane on a stable, vertical pole in an open area free from obstructions to ensure accurate wind direction measurements.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding to protect the device from electrical surges.
- Cable Extension: If extending the cable, use shielded twisted-pair cables to minimize noise and signal degradation.
- RS485 Network: When connecting multiple devices on the RS485 bus, assign unique Modbus addresses to each device to avoid communication conflicts.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the Wind Vane RS485 with an Arduino UNO using an RS485-to-TTL module:
#include <ModbusMaster.h>
// Instantiate ModbusMaster object
ModbusMaster node;
// RS485 communication pins
#define RE_DE 2 // Pin to control RS485 module (RE/DE)
void preTransmission() {
digitalWrite(RE_DE, HIGH); // Enable RS485 transmission
}
void postTransmission() {
digitalWrite(RE_DE, LOW); // Disable RS485 transmission
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(RE_DE, OUTPUT); // Set RE/DE pin as output
digitalWrite(RE_DE, LOW); // Set RS485 to receive mode
// Initialize Modbus communication
node.begin(1, Serial); // Set Modbus ID to 1
node.preTransmission(preTransmission);
node.postTransmission(postTransmission);
}
void loop() {
uint8_t result;
uint16_t windDirection;
// Read wind direction (register 0x0000)
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x0000, 1);
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
windDirection = node.getResponseBuffer(0); // Get wind direction in degrees
Serial.print("Wind Direction: ");
Serial.print(windDirection);
Serial.println("°");
} else {
Serial.println("Error reading wind direction");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before next reading
}
Notes:
- Use a compatible RS485-to-TTL module to connect the wind vane to the Arduino UNO.
- Ensure the Modbus ID of the wind vane matches the ID specified in the code (
node.begin(1, Serial)).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data Received
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or RS485 termination.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure a 120-ohm termination resistor is used if the wind vane is at the end of the RS485 bus.
Incorrect Wind Direction Readings
- Cause: Obstructions or improper mounting.
- Solution: Install the wind vane in an open area and ensure it is level and aligned correctly.
Communication Errors
- Cause: Mismatched baud rate or Modbus ID.
- Solution: Check the device's baud rate and Modbus ID settings and ensure they match the configuration in your code.
Signal Noise
- Cause: Long cable runs or unshielded cables.
- Solution: Use shielded twisted-pair cables and ensure proper grounding.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a power supply other than 12V DC?
A: No, the wind vane is designed to operate at 12V DC. Using a different voltage may damage the device.
Q: How far can the RS485 signal travel?
A: RS485 supports communication distances of up to 1200 meters, depending on cable quality and environmental conditions.
Q: Can I connect multiple wind vanes to the same RS485 bus?
A: Yes, RS485 supports multi-drop communication. Assign unique Modbus addresses to each wind vane.
Q: How do I calibrate the wind vane?
A: The wind vane is factory-calibrated and does not require user calibration. Ensure proper installation for accurate readings.