
How to Use Battery Charging Module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
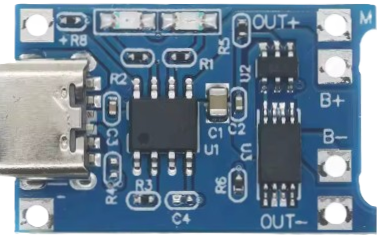
 Design with Battery Charging Module in Cirkit Designer
Design with Battery Charging Module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TP4056 Module (Type C), manufactured by Shenzhen Technology Co., is a compact and efficient battery charging module designed for charging single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries. It ensures safe and efficient charging by incorporating features such as overcharge protection, short-circuit protection, and automatic charge termination. The module is equipped with a Type-C USB input for convenience and ease of use.
Explore Projects Built with Battery Charging Module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer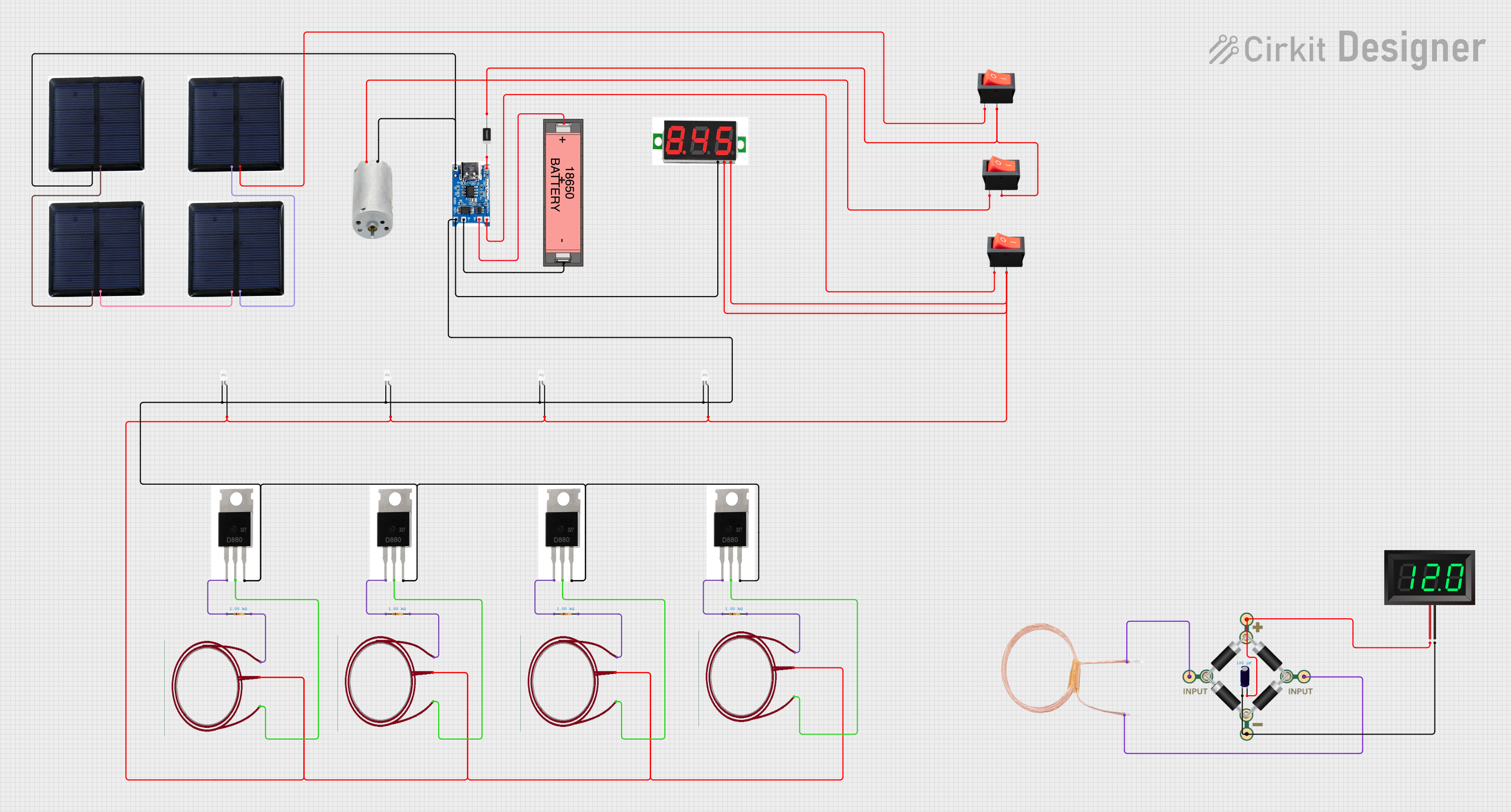
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer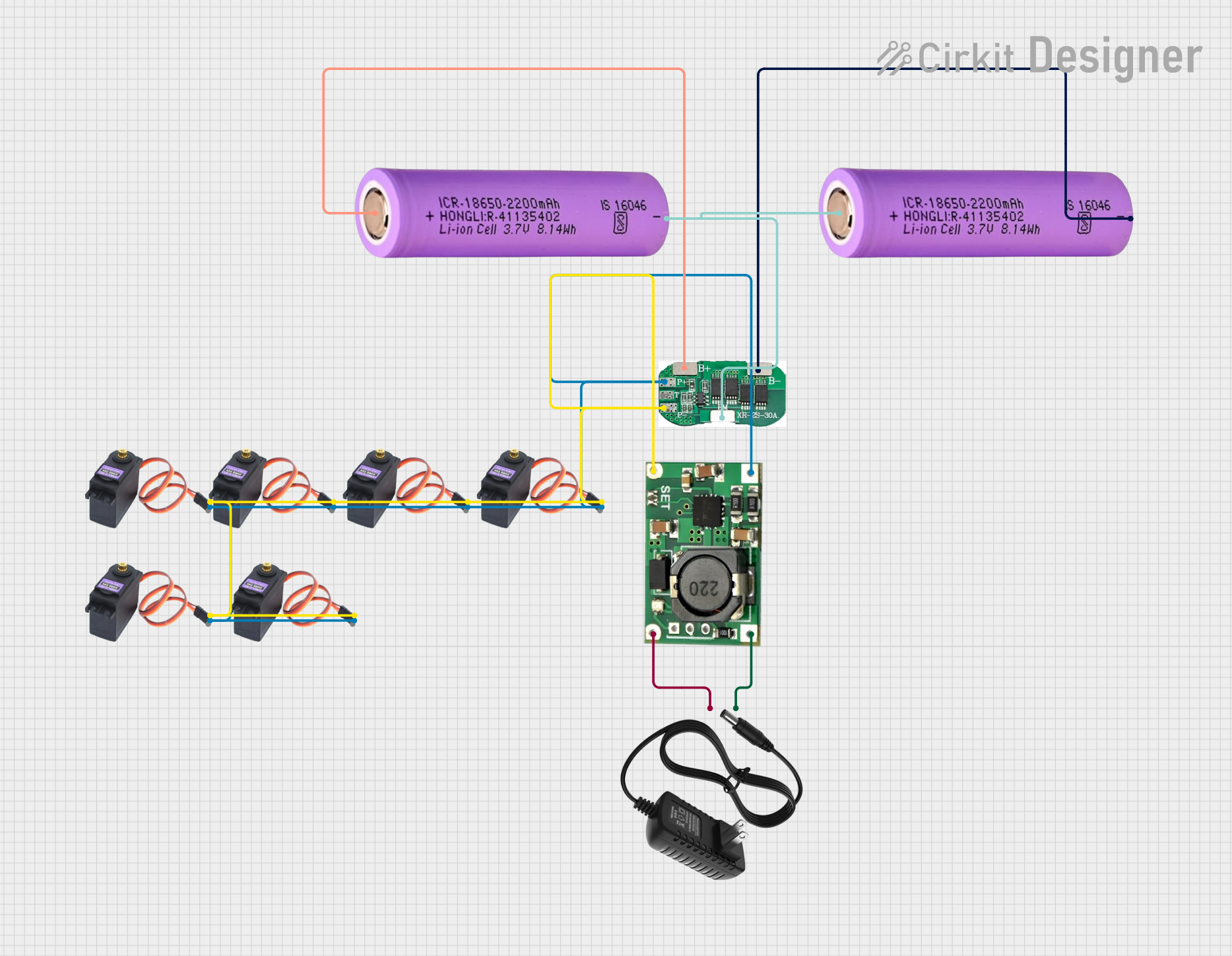
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Battery Charging Module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries in portable devices
- Power banks and battery-powered projects
- DIY electronics and prototyping
- Wearable devices and IoT applications
- Backup power systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the TP4056 Module (Type C):
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 4.5V to 5.5V |
| Charging Current | Adjustable (default: 1A) |
| Battery Type | Single-cell Li-ion/LiPo (3.7V) |
| Charge Cut-off Voltage | 4.2V ± 1% |
| Protection Features | Overcharge, Over-discharge, |
| Short-circuit, Reverse polarity | |
| Connector Type | Type-C USB |
| Dimensions | 25mm x 19mm x 10mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TP4056 Module has the following pins and connections:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BAT+ | Positive terminal for the battery connection |
| BAT- | Negative terminal for the battery connection |
| IN+ | Positive terminal for external power input (alternative to Type-C USB input) |
| IN- | Negative terminal for external power input |
| OUT+ | Positive terminal for output to the load (optional, depending on use case) |
| OUT- | Negative terminal for output to the load (optional, depending on use case) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TP4056 Module in a Circuit
Connect the Battery:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the
BAT+pin. - Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the
BAT-pin.
Ensure the battery is a single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer type with a nominal voltage of 3.7V.
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the
Provide Input Power:
- Use a Type-C USB cable to supply power to the module. Alternatively, connect an external power source (4.5V to 5.5V) to the
IN+andIN-pins.
- Use a Type-C USB cable to supply power to the module. Alternatively, connect an external power source (4.5V to 5.5V) to the
Monitor Charging Status:
- The module has two indicator LEDs:
- Red LED: Charging in progress.
- Blue LED: Charging complete.
- The module has two indicator LEDs:
Optional Load Connection:
- If you want to power a load while charging the battery, connect the load to the
OUT+andOUT-pins. Ensure the load does not exceed the module's current rating.
- If you want to power a load while charging the battery, connect the load to the
Important Considerations and Best Practices
Adjusting Charging Current:
The default charging current is 1A. To adjust it, replace the onboard resistor (Rprog) with a different value. Refer to the TP4056 datasheet for resistor values corresponding to desired current levels.Heat Dissipation:
The module may heat up during operation, especially at higher charging currents. Ensure proper ventilation or heat sinking if necessary.Battery Protection:
While the module includes overcharge and short-circuit protection, it is recommended to use batteries with built-in protection circuits for added safety.Avoid Reverse Polarity:
Always double-check the polarity of the battery and input connections to prevent damage to the module.
Example: Using the TP4056 Module with an Arduino UNO
The TP4056 Module can be used to charge a battery that powers an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to monitor the battery voltage using the Arduino:
// Example code to monitor battery voltage using Arduino UNO
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to BAT+ via a voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0; // Adjust based on your resistor values
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino UNO's reference voltage
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(batteryPin, INPUT); // Set the battery pin as input
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog value
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to step down the battery voltage to a safe level for the Arduino's analog input pins. For example, use two resistors with a 1:1 ratio to divide the voltage by half.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Overheating:
- Cause: High charging current or insufficient ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the charging current by replacing the Rprog resistor or improve heat dissipation.
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Incorrect connections or damaged battery.
- Solution: Verify the battery polarity and connections. Test the battery with a multimeter to ensure it is functional.
No LED Indicators:
- Cause: No input power or faulty module.
- Solution: Check the input power source and connections. Replace the module if necessary.
Load Not Powering On:
- Cause: Load current exceeds module's output capacity.
- Solution: Ensure the load current is within the module's specifications.
FAQs
Can I use the TP4056 Module to charge multiple batteries in series?
No, the TP4056 is designed for single-cell batteries only. Charging multiple batteries in series requires a specialized charging circuit.What happens if I leave the battery connected after it is fully charged?
The module automatically stops charging when the battery is fully charged, preventing overcharging.Can I use the module without a battery connected?
It is not recommended to use the module without a battery, as it may cause instability in the output voltage.How do I adjust the charging current?
Replace the onboard Rprog resistor with a different value. Refer to the TP4056 datasheet for the resistor-to-current mapping.
This concludes the documentation for the TP4056 Module (Type C). For further assistance, refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or contact Shenzhen Technology Co..