
How to Use GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay in Cirkit Designer
Design with GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay (Manufacturer Part ID: GM-002) is a single-channel relay module designed and manufactured by PCBCUPID. This module allows users to control high-voltage devices (e.g., appliances, lights, motors) using low-voltage control signals from microcontrollers or other logic circuits. It features opto-isolation for enhanced safety and reliability, making it ideal for applications where electrical isolation is critical.
Explore Projects Built with GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay
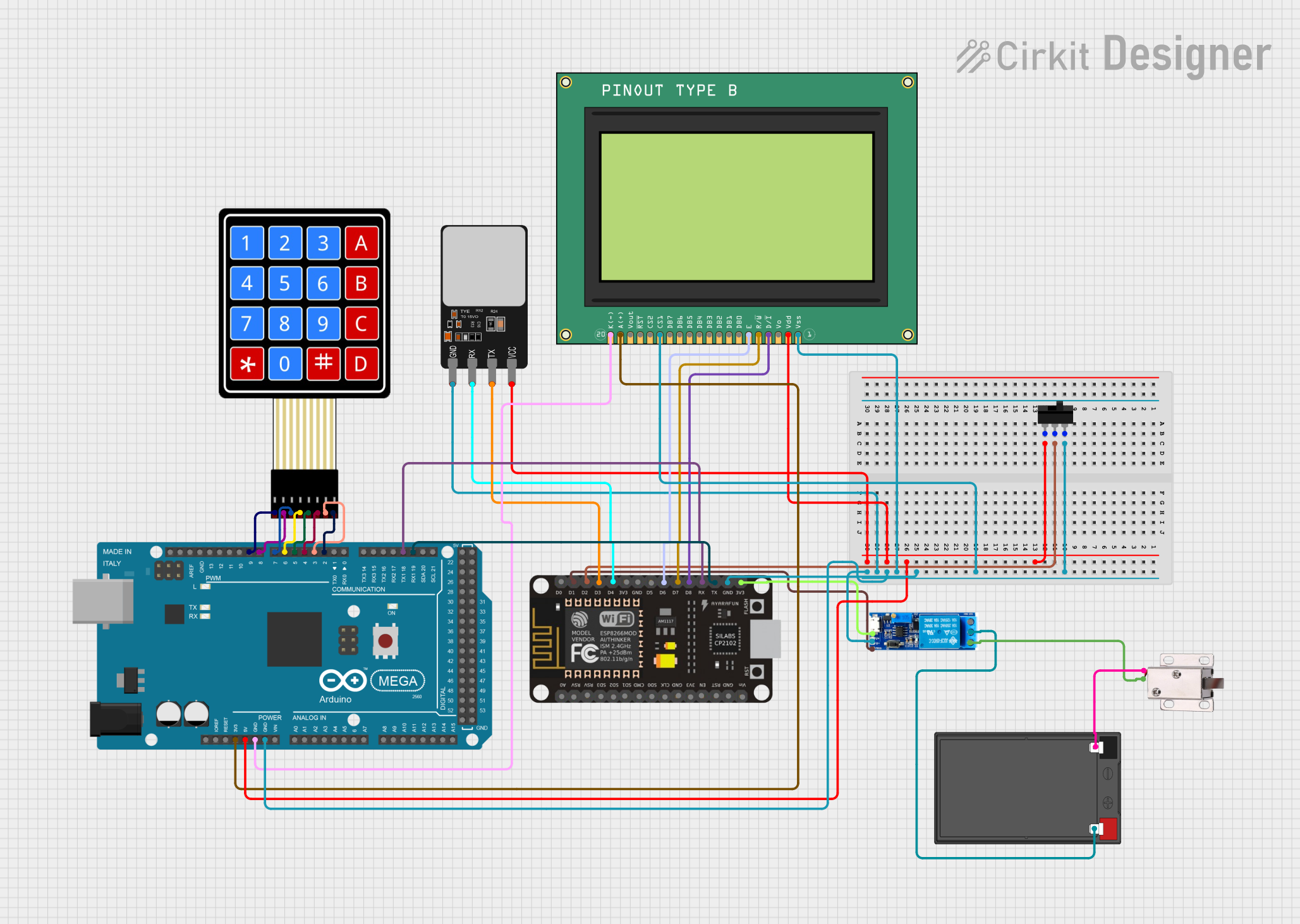
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer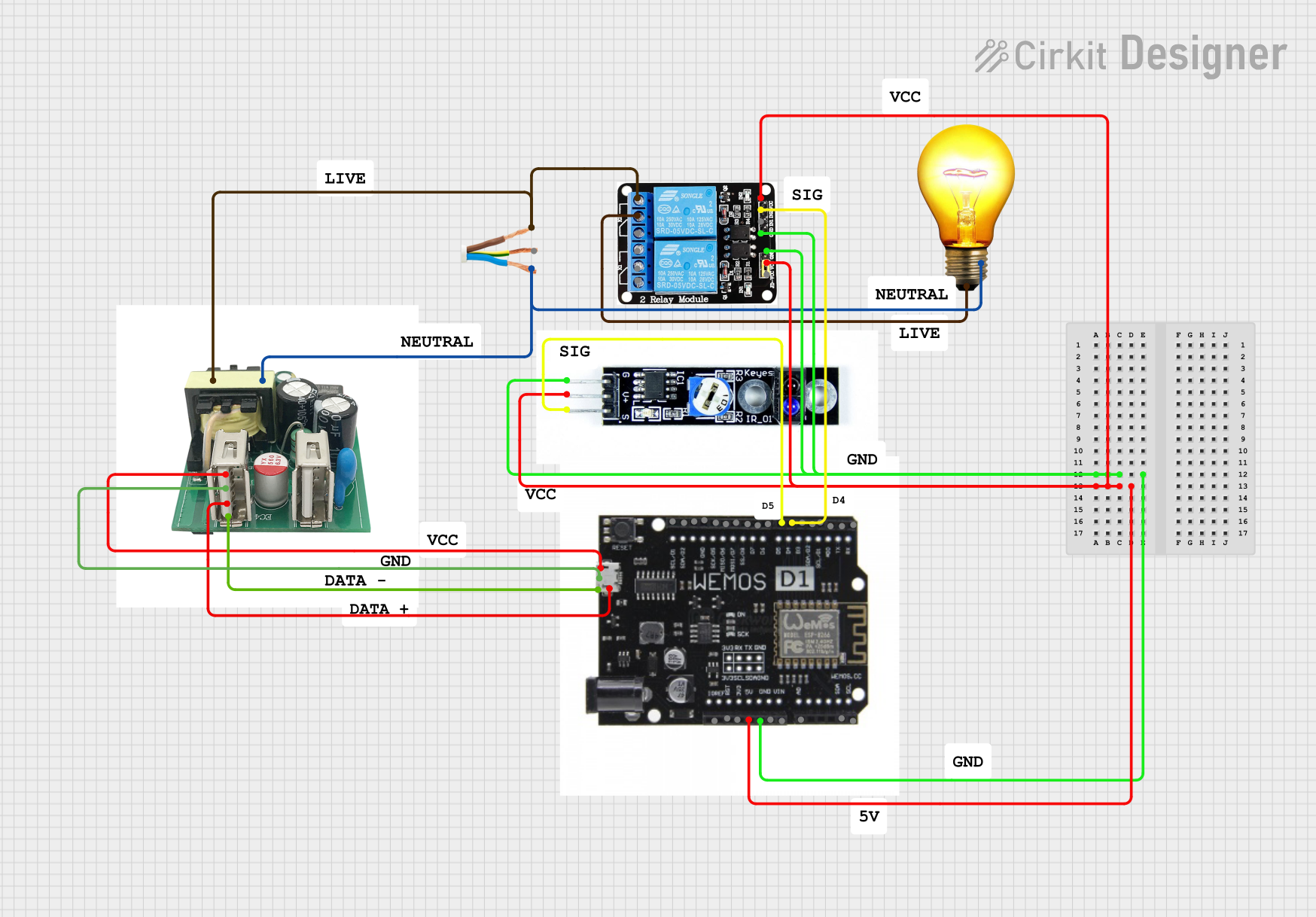
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer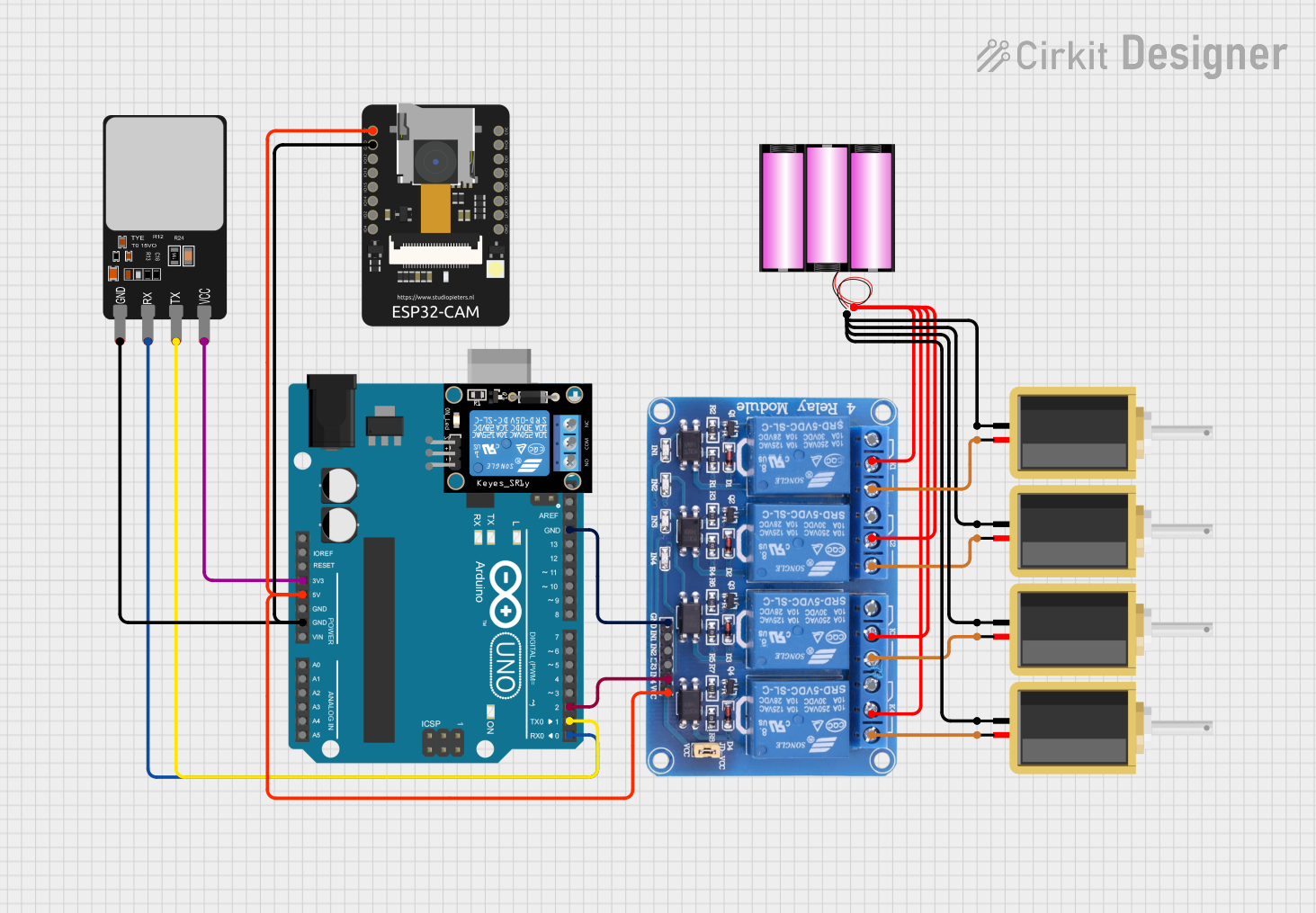
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer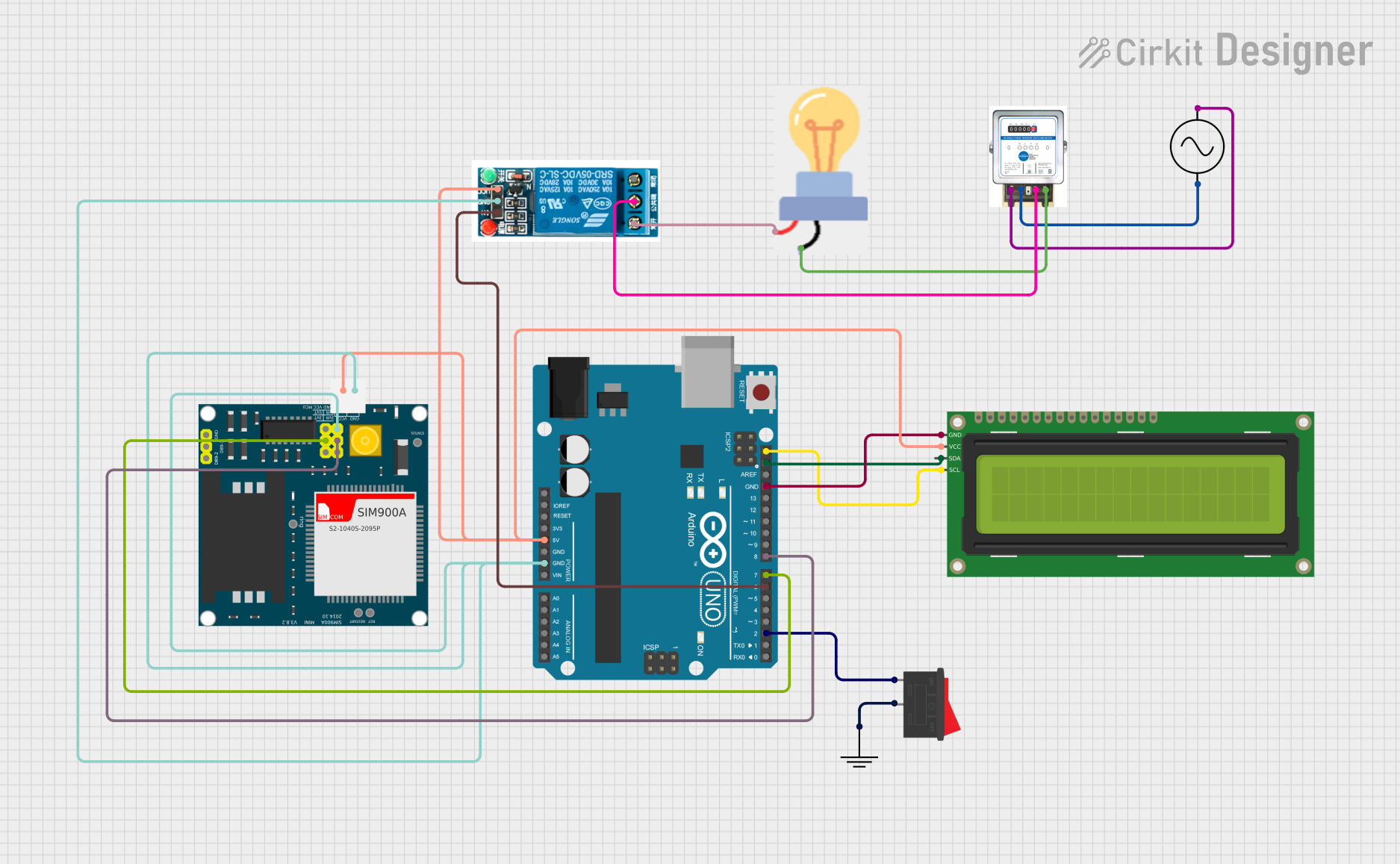
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems (e.g., controlling lights or fans)
- Industrial control systems
- IoT projects for remote device control
- Robotics and motor control
- Prototyping and educational projects
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay module:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V DC |
| Trigger Voltage | 3.3V to 5V DC |
| Relay Type | SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) |
| Maximum Load Voltage | 250V AC / 30V DC |
| Maximum Load Current | 10A |
| Isolation Method | Opto-isolator |
| Dimensions | 50mm x 26mm x 18mm |
| Mounting | PCB mount or screw holes |
| Indicator LED | Yes (indicates relay activation) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay module has a total of 6 pins and terminals. The table below describes each pin:
Input Pins (Control Side)
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Connect to 5V DC power supply. |
| GND | Connect to ground of the power supply. |
| IN | Control signal input (3.3V to 5V logic level). |
Output Terminals (Load Side)
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| COM | Common terminal for the relay. |
| NO | Normally Open terminal (connected to COM when |
| the relay is activated). | |
| NC | Normally Closed terminal (connected to COM |
| when the relay is not activated). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the VCC pin to a 5V DC power supply and the GND pin to the ground of the same power supply.
- Control Signal: Connect the IN pin to a digital output pin of a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO). The relay will activate when the control signal is HIGH (3.3V to 5V).
- Load Connection:
- Connect the device you want to control to the relay's output terminals (COM, NO, and NC).
- For example, connect one wire of a light bulb to the COM terminal and the other wire to the NO terminal. When the relay is activated, the circuit will close, and the light bulb will turn on.
- Indicator LED: Observe the onboard LED, which lights up when the relay is activated.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Isolation: Ensure proper electrical isolation between the control side (low voltage) and the load side (high voltage) to prevent damage to your microcontroller or other control circuits.
- Current Rating: Do not exceed the maximum load current of 10A to avoid damaging the relay.
- Flyback Diode: If controlling an inductive load (e.g., motor, solenoid), use a flyback diode across the load to suppress voltage spikes.
- Secure Connections: Use proper screw terminals or soldered connections for high-voltage loads to ensure safety and reliability.
Example: Using the GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay with an Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to control the relay using an Arduino UNO:
// Example: Controlling the GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay with Arduino UNO
// Define the pin connected to the relay module's IN pin
const int relayPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the relay pin as an output
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT);
// Ensure the relay is off at startup
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the relay on (activate)
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay on for 1 second
// Turn the relay off (deactivate)
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the relay off for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Relay Not Activating
- Cause: Insufficient control signal voltage.
- Solution: Ensure the IN pin receives a voltage between 3.3V and 5V. Check the microcontroller's output pin configuration.
Indicator LED Not Lighting Up
- Cause: No power to the module.
- Solution: Verify the VCC and GND connections. Ensure the power supply provides 5V DC.
Load Not Turning On/Off
- Cause: Incorrect wiring of the load terminals.
- Solution: Double-check the connections to the COM, NO, and NC terminals. Ensure the load is within the relay's voltage and current ratings.
Microcontroller Resetting When Relay Activates
- Cause: Voltage spikes from the load affecting the control circuit.
- Solution: Use a flyback diode across inductive loads and ensure proper grounding.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, the relay module is compatible with 3.3V control signals, but ensure the VCC pin is powered with 5V DC.
Q2: Is the relay module safe for high-voltage applications?
A2: Yes, the module is designed for high-voltage applications up to 250V AC or 30V DC. However, always follow proper safety precautions when working with high voltages.
Q3: Can I control multiple relays with one microcontroller?
A3: Yes, you can control multiple relay modules by connecting each module's IN pin to a separate digital output pin on the microcontroller.
Q4: What is the purpose of the opto-isolator?
A4: The opto-isolator provides electrical isolation between the control circuit and the high-voltage load, protecting the microcontroller from voltage spikes or surges.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use the GLYPHMOD-1-CH-Relay module in your projects.