
How to Use 12V to 5V Buck Converter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with 12V to 5V Buck Converter in Cirkit Designer
Design with 12V to 5V Buck Converter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 12V to 5V Buck Converter is a DC-DC step-down voltage regulator designed to efficiently convert a 12V input voltage to a stable 5V output. This component is widely used in power supply applications where a lower voltage is required to power devices such as microcontrollers, sensors, and USB-powered peripherals. Its high efficiency and compact design make it ideal for battery-powered systems, automotive electronics, and embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with 12V to 5V Buck Converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer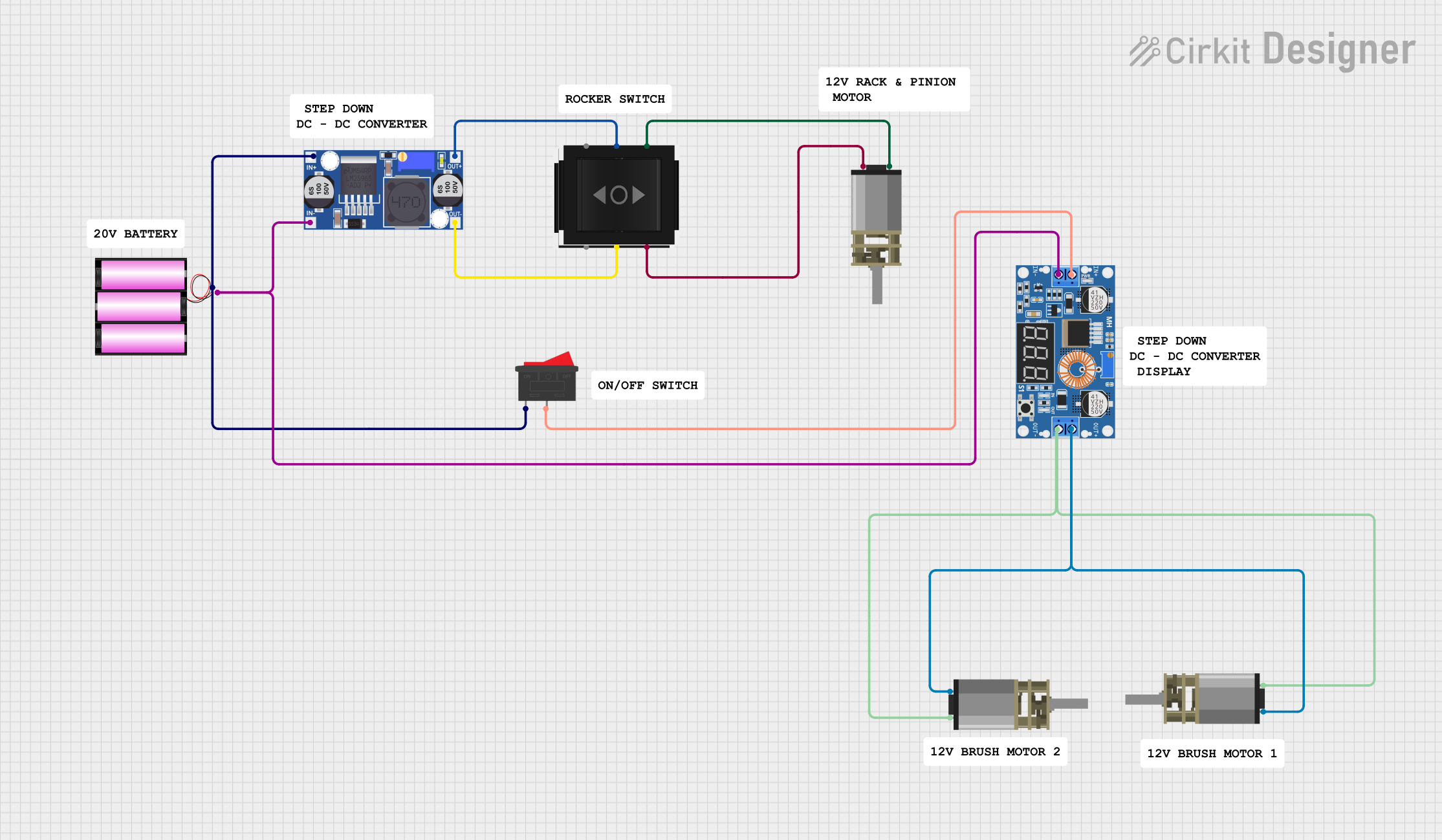
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 12V to 5V Buck Converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Powering microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- USB device power supplies
- Automotive electronics
- Battery-powered systems
- LED lighting systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the 12V to 5V Buck Converter:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 7V to 24V |
| Output Voltage | 5V ± 0.1V |
| Maximum Output Current | 3A (typical), 2A (continuous load) |
| Efficiency | Up to 95% |
| Switching Frequency | 150 kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | Varies (e.g., 22mm x 17mm x 4mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 12V to 5V Buck Converter typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin (connect to 12V power source) |
| GND | Ground pin (common ground for input and output) |
| VOUT | Output voltage pin (provides regulated 5V output) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage:
- Connect the VIN pin to a 12V DC power source. Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (7V to 24V).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the power source.
Connect the Output Load:
- Connect the VOUT pin to the device or circuit requiring 5V power.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the load.
Verify Connections:
- Double-check all connections to ensure proper polarity and avoid short circuits.
Power On:
- Turn on the 12V power source. The buck converter will regulate the input voltage and provide a stable 5V output.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: For high current loads (e.g., >1.5A), ensure proper heat dissipation by using a heatsink or providing adequate ventilation.
- Input Voltage Range: Do not exceed the maximum input voltage (24V) to avoid damaging the converter.
- Output Filtering: If the output voltage has noise, consider adding a capacitor (e.g., 100µF) across the VOUT and GND pins for additional filtering.
- Load Current: Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum continuous current rating (2A) to prevent overheating or damage.
Example: Using with an Arduino UNO
The 12V to 5V Buck Converter can be used to power an Arduino UNO from a 12V power source. Below is an example circuit and Arduino code:
Circuit Connections:
- Connect the VIN pin of the buck converter to a 12V DC power source.
- Connect the GND pin of the buck converter to the ground of the power source.
- Connect the VOUT pin of the buck converter to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the GND pin of the buck converter to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
Arduino Code:
// Example code to blink an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO
// Ensure the Arduino is powered via the 5V output of the buck converter
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient input voltage.
- Solution: Verify that the VIN and GND pins are correctly connected to the power source and that the input voltage is within the specified range.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive load current or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the load current or add a heatsink to the converter.
Output Voltage Fluctuations:
- Cause: Insufficient input power or high-frequency noise.
- Solution: Add a capacitor (e.g., 100µF) across the input and/or output pins to stabilize the voltage.
Damaged Converter:
- Cause: Input voltage exceeded the maximum rating or reverse polarity connection.
- Solution: Replace the converter and ensure proper input voltage and polarity in future use.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the buck converter to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, but ensure the converter can supply sufficient current (at least 2.5A) for the Raspberry Pi model you are using.
Q: Can I use this converter with a 24V input?
A: Yes, as long as the input voltage does not exceed 24V and the load current is within the specified range.
Q: Is the output voltage adjustable?
A: Most 12V to 5V buck converters provide a fixed 5V output. If you need an adjustable output, look for a model with a potentiometer for voltage adjustment.
Q: Can I use this converter for audio applications?
A: Yes, but you may need additional filtering capacitors to reduce noise for sensitive audio circuits.