
How to Use 4 DIGIT DISPLAY: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 4 DIGIT DISPLAY in Cirkit Designer
Design with 4 DIGIT DISPLAY in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 4 digit display is an electronic component used to visually represent numerical values using four individual digits, typically in a seven-segment format. Each digit consists of seven LEDs (segments) arranged in a pattern to form numbers from 0 to 9. Some displays also include a decimal point for additional functionality.
This component is widely used in applications such as:
- Digital clocks
- Counters
- Timers
- Measurement devices (e.g., voltmeters, thermometers)
- Scoreboards and other numerical displays
Its compact design and ease of use make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with 4 DIGIT DISPLAY
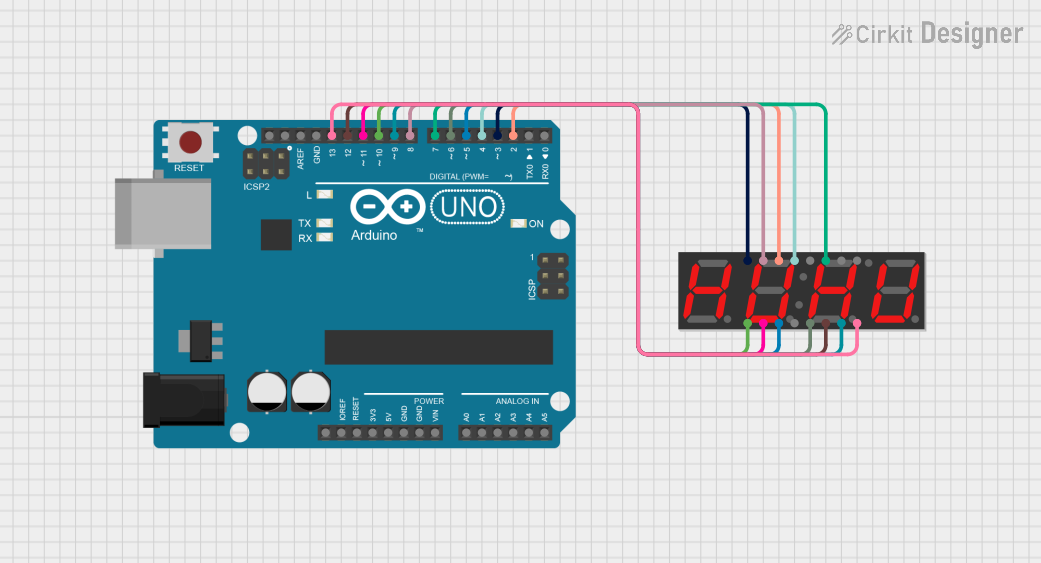
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer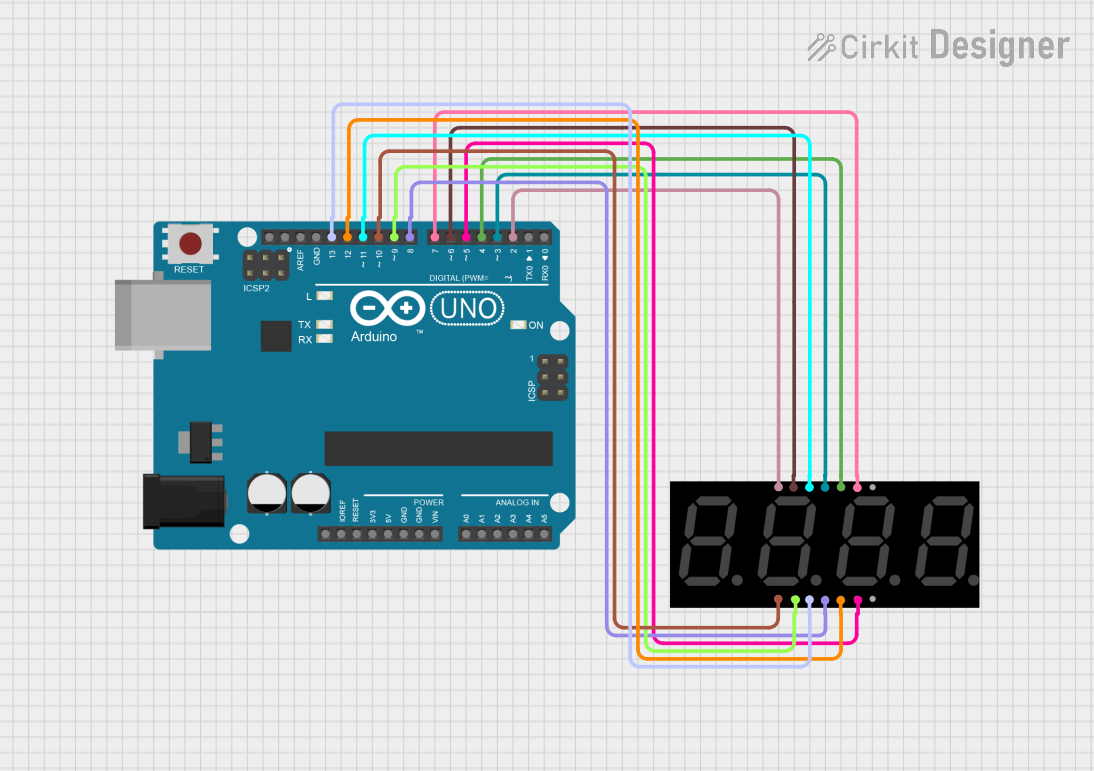
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer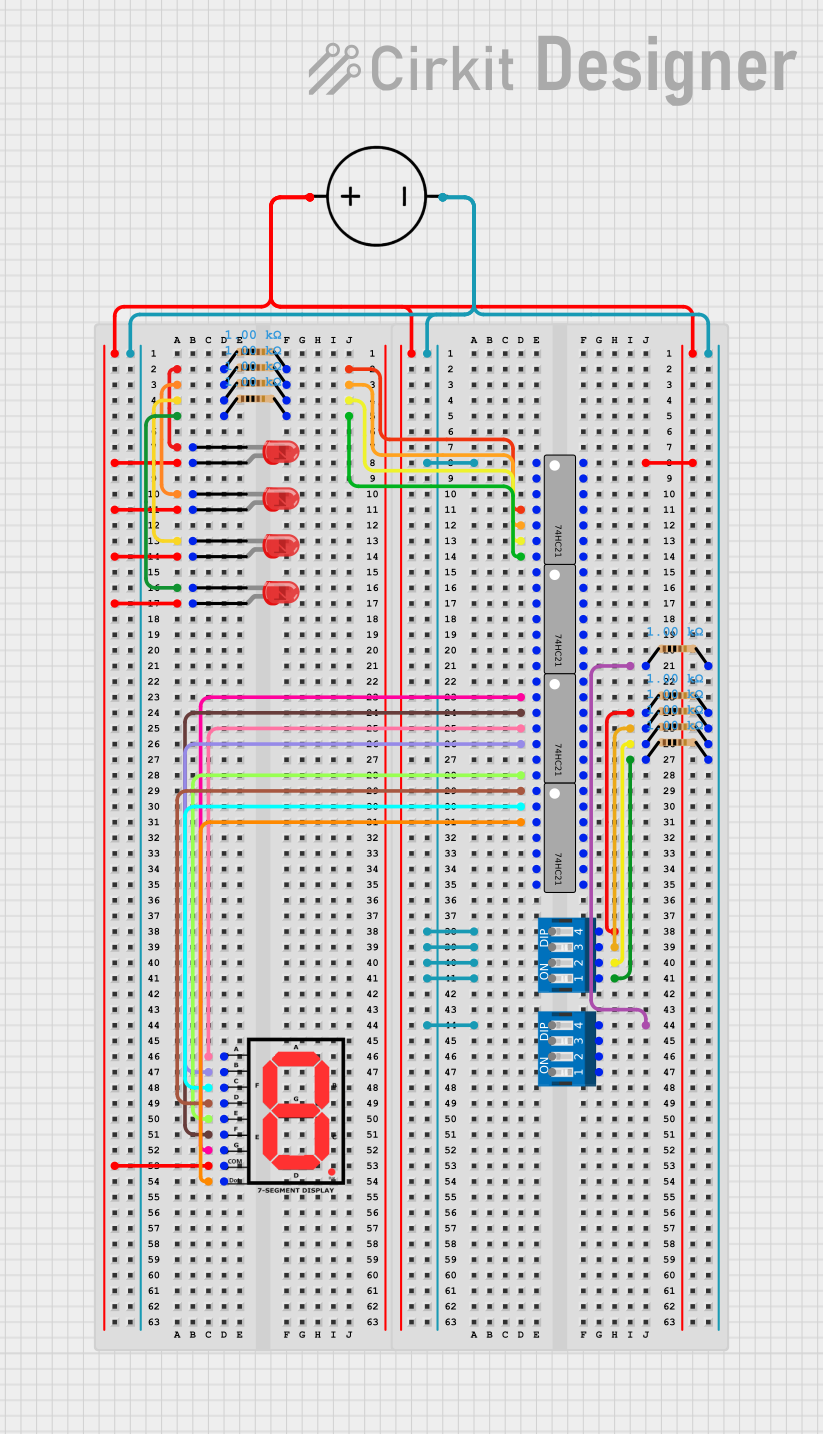
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer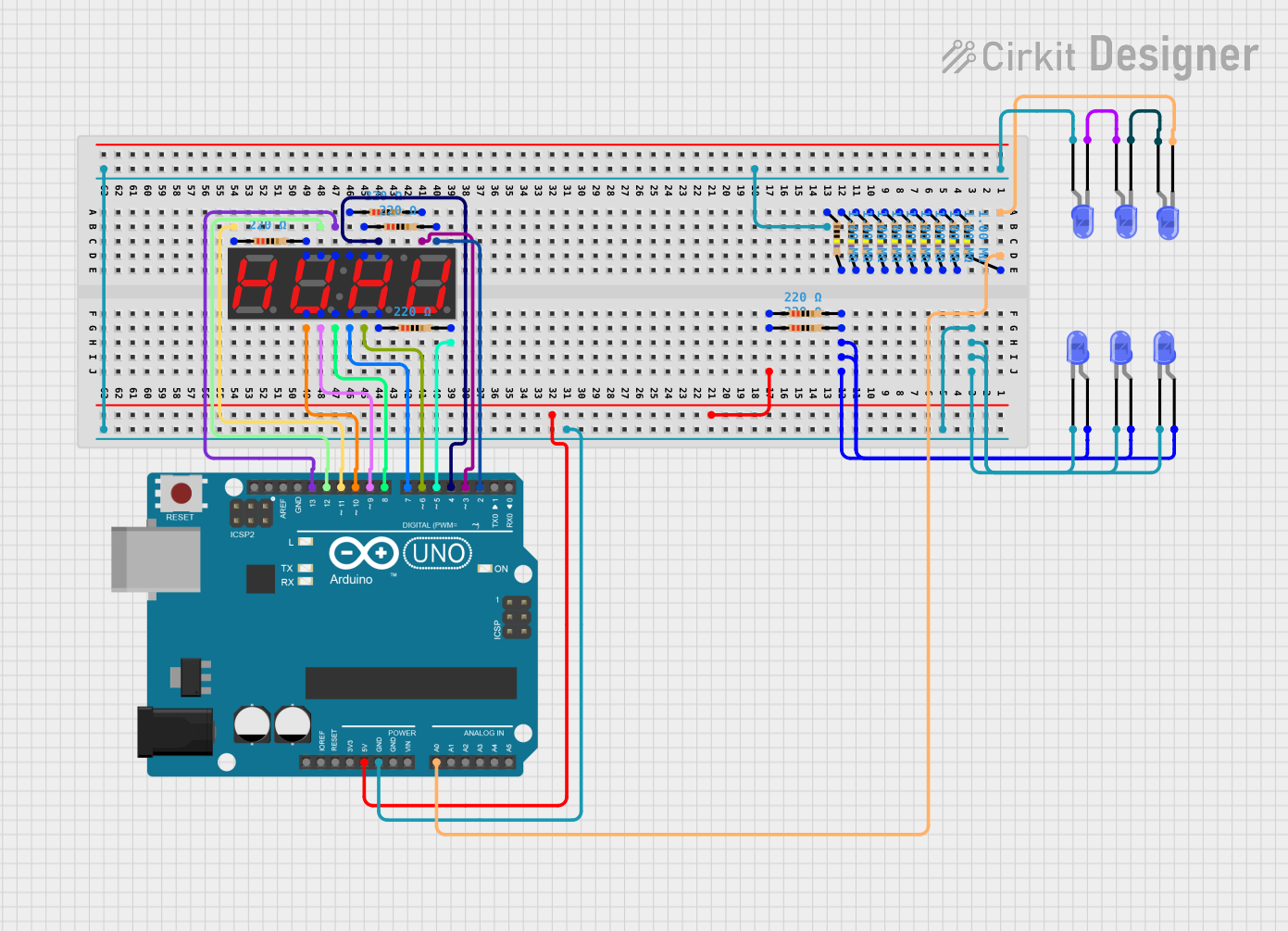
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 4 DIGIT DISPLAY

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a typical 4 digit display:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Current | ~20mA per segment (typical) |
| Display Type | Common Cathode or Common Anode |
| Number of Digits | 4 |
| Segment Type | Seven-segment with optional DP |
| Dimensions | Varies (e.g., 50mm x 20mm) |
| LED Color | Red, Green, Blue, or White |
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration of a 4 digit display depends on whether it is a common cathode or common anode type. Below is a general pinout for a 12-pin 4 digit display:
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Segment A |
| 2 | Segment B |
| 3 | Segment C |
| 4 | Digit 1 (Common Cathode/Anode) |
| 5 | Segment D |
| 6 | Segment E |
| 7 | Segment F |
| 8 | Segment G |
| 9 | Digit 2 (Common Cathode/Anode) |
| 10 | Digit 3 (Common Cathode/Anode) |
| 11 | Digit 4 (Common Cathode/Anode) |
| 12 | Decimal Point (DP) |
Note: Always refer to the datasheet of your specific 4 digit display for exact pinout details.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Determine the Type: Identify whether your display is a common cathode or common anode type. This will affect how you connect it to your circuit.
- Connect the Pins:
- For a common cathode display, connect all cathode pins to ground.
- For a common anode display, connect all anode pins to the positive voltage supply.
- Use Current-Limiting Resistors: Connect a resistor (typically 220Ω to 1kΩ) in series with each segment to limit the current and prevent damage to the LEDs.
- Control the Digits: Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) or a driver IC (e.g., MAX7219) to control which segments light up and which digit is active.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and control a 4 digit display using an Arduino UNO and a MAX7219 driver IC:
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the 4 digit display to the MAX7219 driver IC.
- Connect the MAX7219 to the Arduino as follows:
- DIN (Data In) → Arduino Pin 11
- CS (Chip Select) → Arduino Pin 10
- CLK (Clock) → Arduino Pin 13
- VCC → 5V
- GND → GND
Arduino Code
#include <LedControl.h> // Include the library for MAX7219 control
// Create an instance of LedControl
// Parameters: DIN pin, CLK pin, CS pin, number of devices
LedControl lc = LedControl(11, 13, 10, 1);
void setup() {
lc.shutdown(0, false); // Wake up the MAX7219
lc.setIntensity(0, 8); // Set brightness level (0-15)
lc.clearDisplay(0); // Clear the display
}
void loop() {
// Display the number "1234" on the 4 digit display
lc.setDigit(0, 3, 1, false); // Digit 4 (leftmost), value 1
lc.setDigit(0, 2, 2, false); // Digit 3, value 2
lc.setDigit(0, 1, 3, false); // Digit 2, value 3
lc.setDigit(0, 0, 4, false); // Digit 1 (rightmost), value 4
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Note: The
LedControllibrary can be installed via the Arduino Library Manager.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply voltage matches the operating voltage of the display.
- Resistors: Always use current-limiting resistors to protect the LEDs.
- Multiplexing: If controlling the display directly (without a driver IC), use multiplexing to light up one digit at a time to reduce power consumption.
- Brightness Control: Use PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) or a driver IC to adjust the brightness of the display.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Problem: The display does not light up.
- Solution: Check the power supply and ensure all connections are secure. Verify that the common cathode or anode is correctly connected.
Problem: Some segments are dim or not lighting up.
- Solution: Check the current-limiting resistors. Ensure they are not too high in value. Verify the connections to the affected segments.
Problem: The display shows incorrect numbers.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure the correct pins are connected to the microcontroller or driver IC.
Problem: Flickering digits.
- Solution: If multiplexing manually, ensure the refresh rate is high enough (e.g., >60Hz). If using a driver IC, check the code for errors.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 4 digit display without a driver IC?
- A: Yes, but you will need to manually control the segments and multiplex the digits using a microcontroller.
Q: How do I know if my display is common cathode or common anode?
- A: Refer to the datasheet or test the display by connecting a single segment to power and ground.
Q: Can I control the brightness of the display?
- A: Yes, you can use PWM or a driver IC like the MAX7219 to adjust the brightness.
By following this documentation, you should be able to successfully integrate and troubleshoot a 4 digit display in your projects!