
How to Use Diode: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Diode in Cirkit Designer
Design with Diode in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A diode is a fundamental semiconductor device known for its ability to conduct electrical current in one direction while blocking current in the opposite direction. This unidirectional behavior makes diodes essential in various applications, including rectification, signal demodulation, overvoltage protection, and as a component in more complex devices like photodiodes and light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Common applications of diodes include:
- Power supply rectification to convert AC to DC.
- Voltage regulation and reference.
- Signal mixing and detection in RF applications.
- Overvoltage protection in circuits.
- Logic gates and digital circuits.
Explore Projects Built with Diode
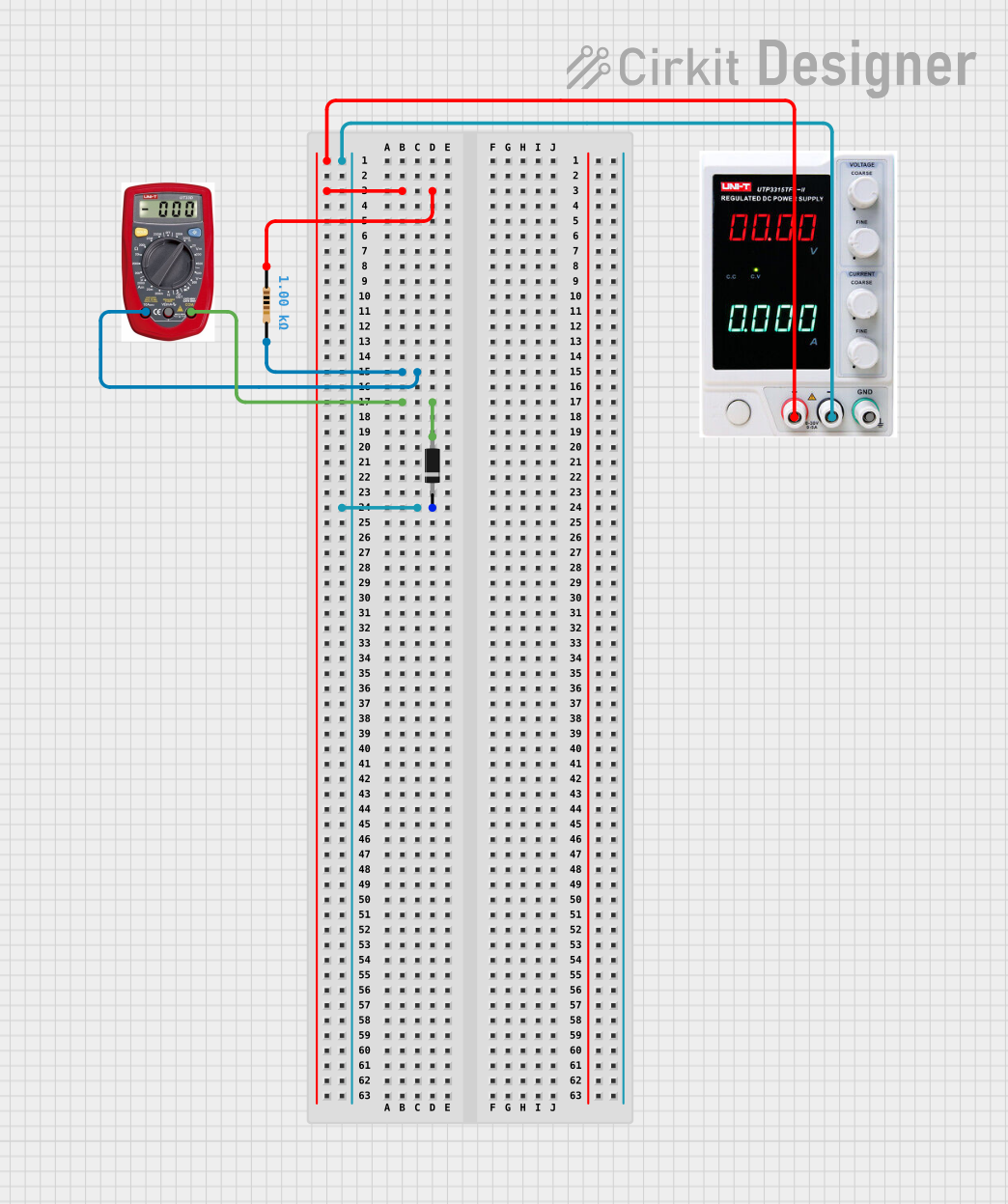
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer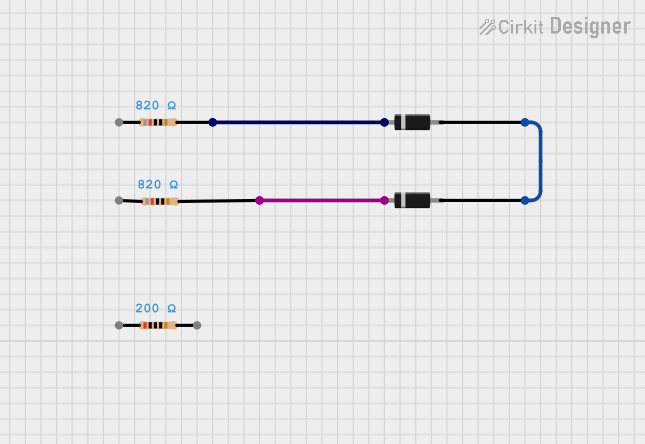
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer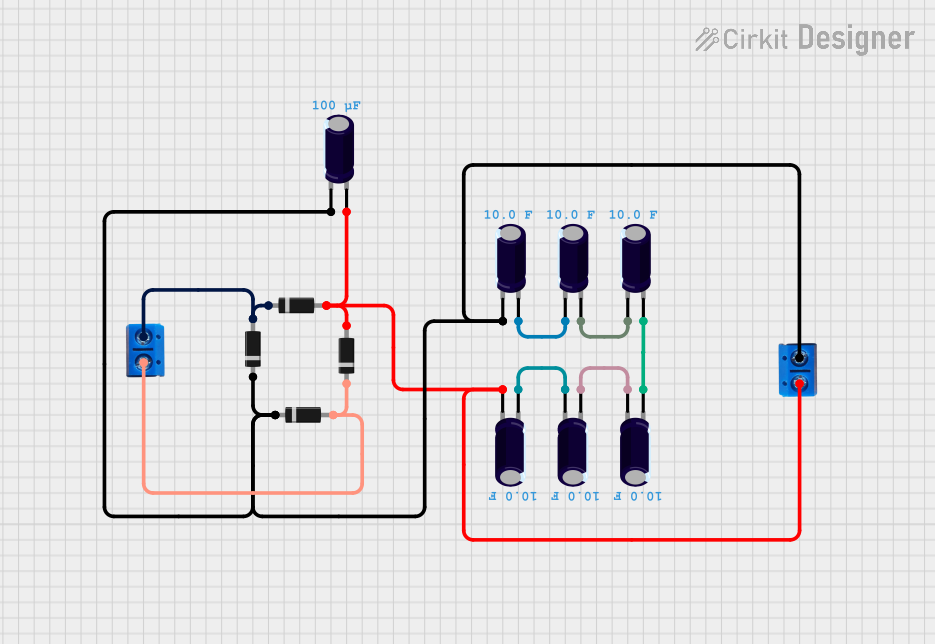
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer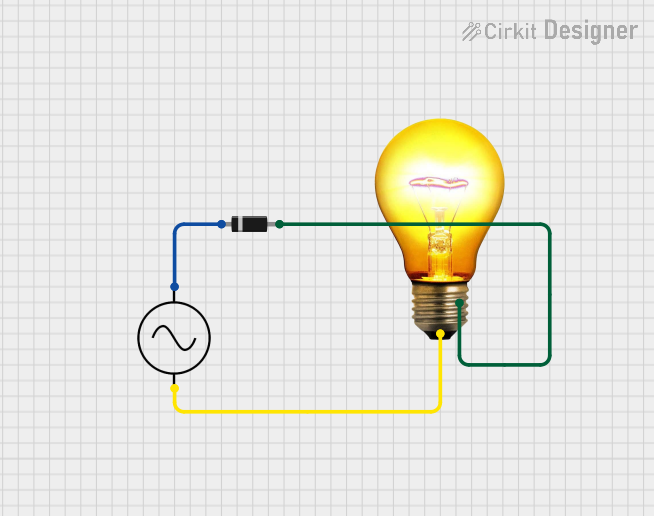
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Diode

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Forward Voltage (Vf): Typically around 0.7V for silicon diodes.
- Reverse Breakdown Voltage (Vr): The maximum voltage the diode can withstand in the reverse direction without breaking down.
- Forward Current (If): The maximum current the diode can conduct in the forward direction.
- Reverse Current (Ir): The small leakage current that flows when the diode is reverse-biased.
- Power Dissipation (Pd): The maximum power the diode can dissipate without damage.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode (A) | Positive terminal, connects to the higher potential side in forward bias. |
| 2 | Cathode (K) | Negative terminal, connects to the lower potential side in forward bias. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Diode in a Circuit
- Identify the Anode and Cathode: The anode is typically marked by a longer lead or a plus sign; the cathode is marked by a band on the diode's body.
- Forward Bias Connection: Connect the anode to the positive voltage and the cathode to the negative voltage or ground.
- Reverse Bias Connection: Reverse the connections to block current flow.
- Current Limiting: Always use a current-limiting resistor to protect the diode from excessive current.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Reverse Voltage Protection: Use a diode in reverse bias across the power supply to protect against reverse polarity.
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure adequate heat sinking if the diode is expected to dissipate significant power.
- Snubber Circuits: Use a diode in parallel with inductive loads to prevent voltage spikes during turn-off.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Diode Not Conducting: Ensure the diode is forward-biased and that the forward voltage is sufficient.
- Diode Conducting in Reverse: The diode may be damaged or incorrectly installed.
- Excessive Heat: Check for overcurrent or insufficient heat sinking.
Solutions and Tips
- Check Polarity: Verify that the diode is installed with the correct orientation.
- Measure Voltage Drop: Use a multimeter to measure the forward voltage drop across the diode.
- Replace if Damaged: If the diode is not functioning as expected, replace it with a new one.
FAQs
Q: Can I use any diode for my application? A: No, you must select a diode with appropriate ratings for your specific application.
Q: What happens if I reverse the connections to a diode? A: The diode will block current flow unless the reverse breakdown voltage is exceeded, which can damage the diode.
Q: How can I tell if a diode is damaged? A: A damaged diode may conduct in both directions or not conduct at all. Use a multimeter in diode test mode to check its functionality.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Example code for using a diode with an Arduino UNO
// This code assumes a diode is used for simple overvoltage protection.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn off the LED
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
// Note: The diode itself does not require code to operate.
// It functions as a passive component in the circuit.
Please note that the diode does not interact with the Arduino UNO in a way that requires specific code to operate. The example provided is a simple blink sketch to demonstrate how a diode might be included in a circuit with an LED to prevent reverse current from damaging the LED or the microcontroller.