
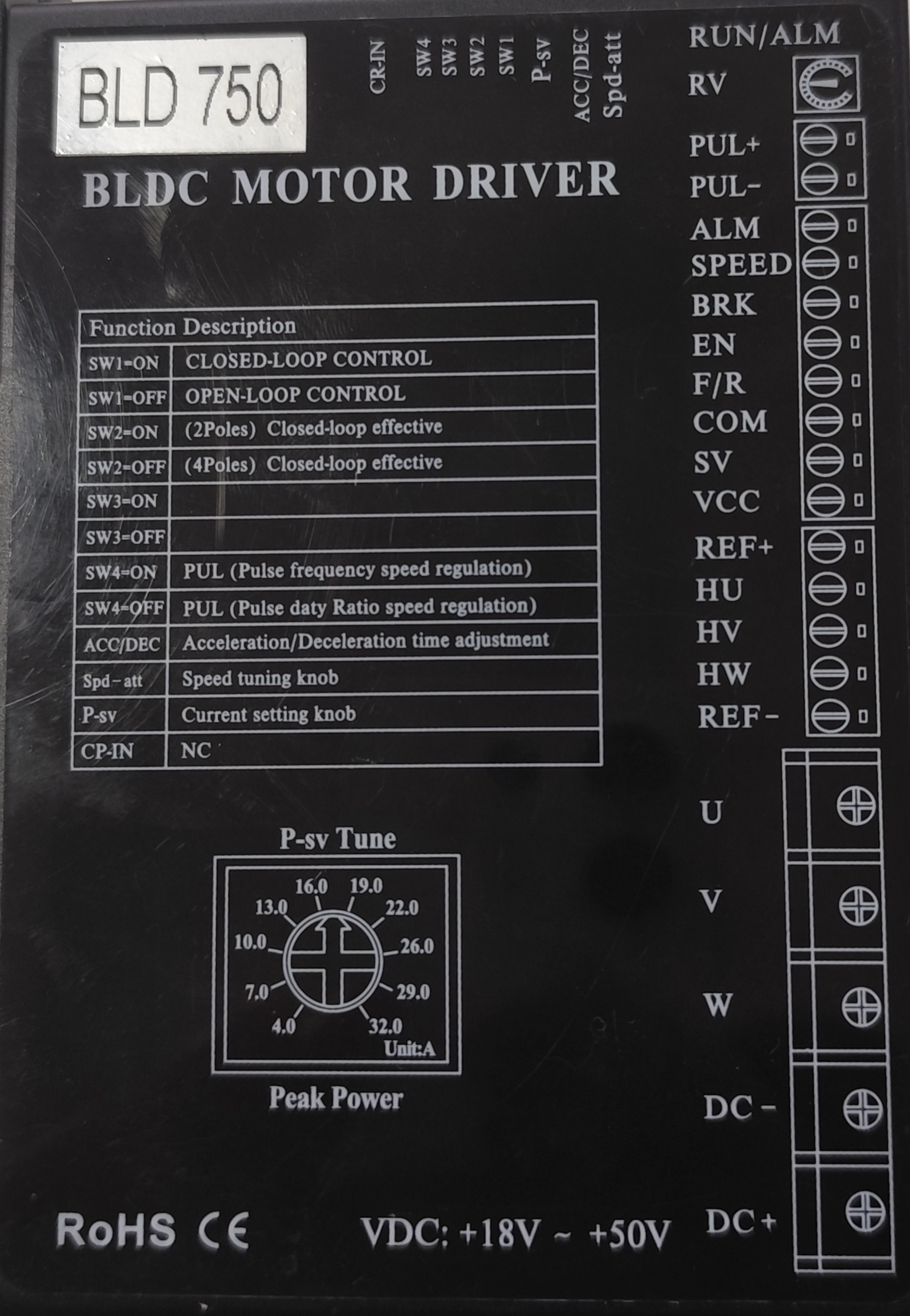
How to Use BLD 750: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with BLD 750 in Cirkit Designer
Design with BLD 750 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BLD 750 is a high-performance battery load tester designed for evaluating the condition and capacity of batteries. It provides accurate readings of voltage, current, and resistance, making it an essential tool for maintenance and troubleshooting in various applications. The BLD 750 is widely used in automotive, industrial, and renewable energy systems to ensure battery reliability and performance.
Explore Projects Built with BLD 750

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer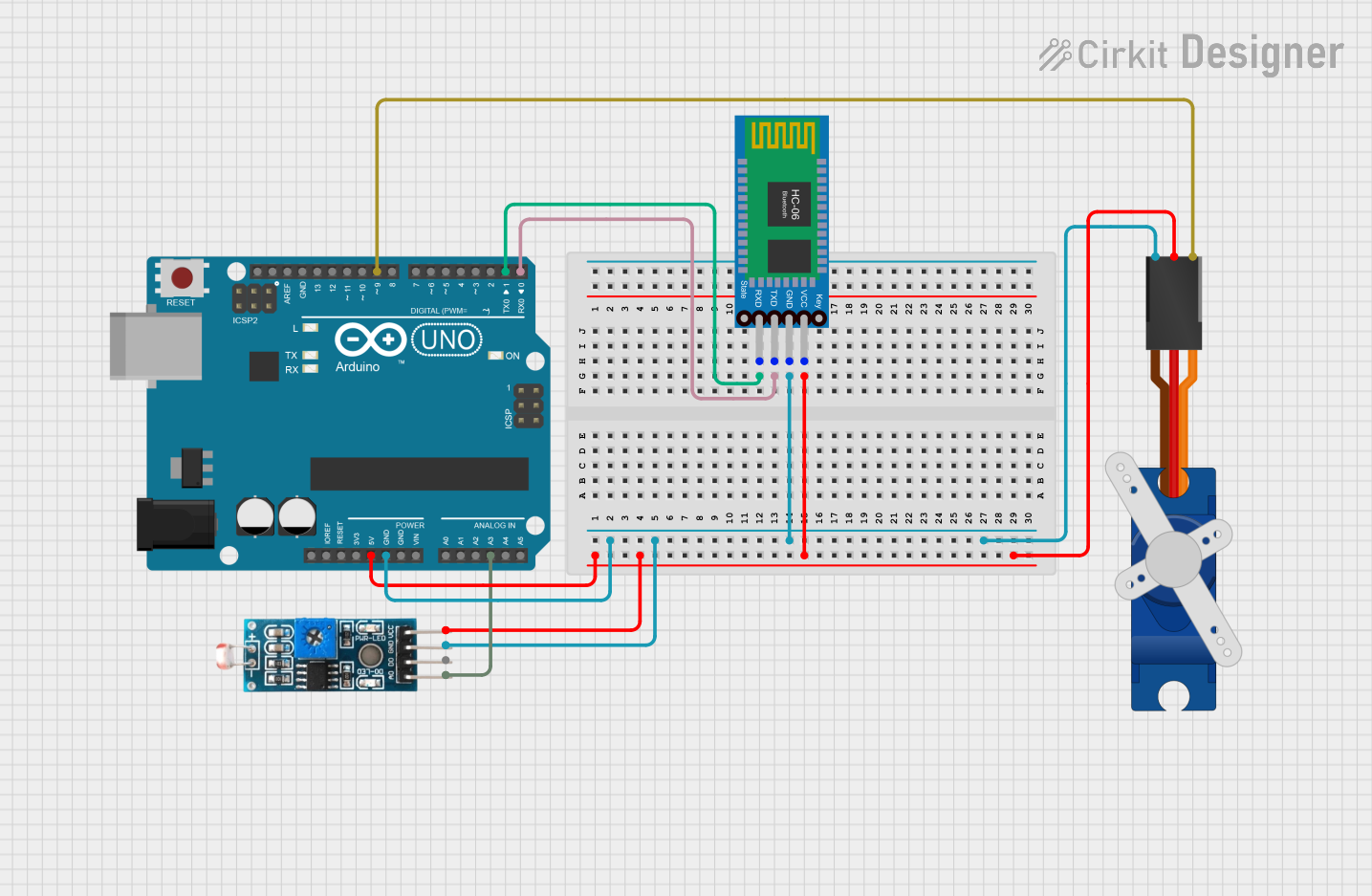
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer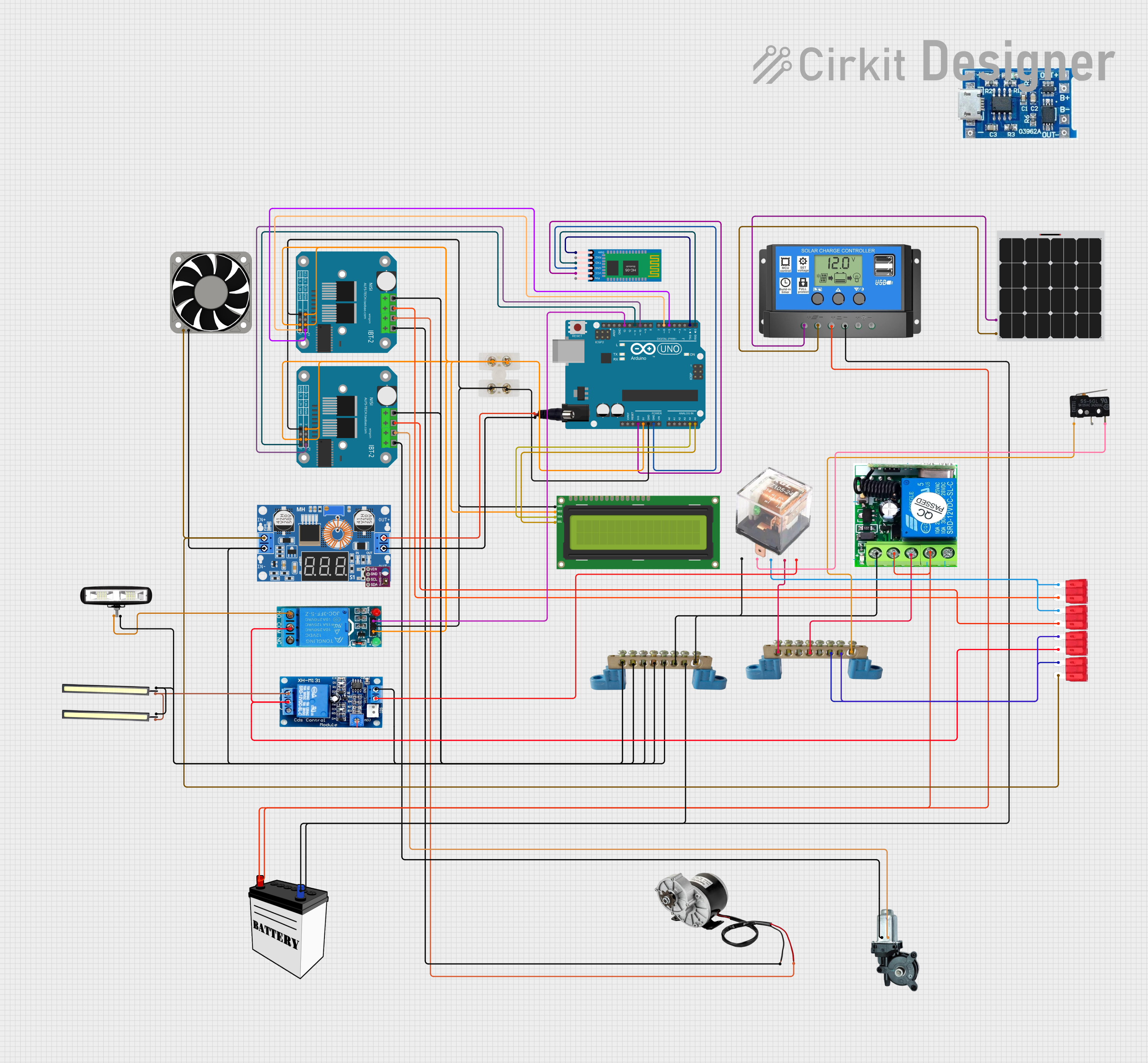
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer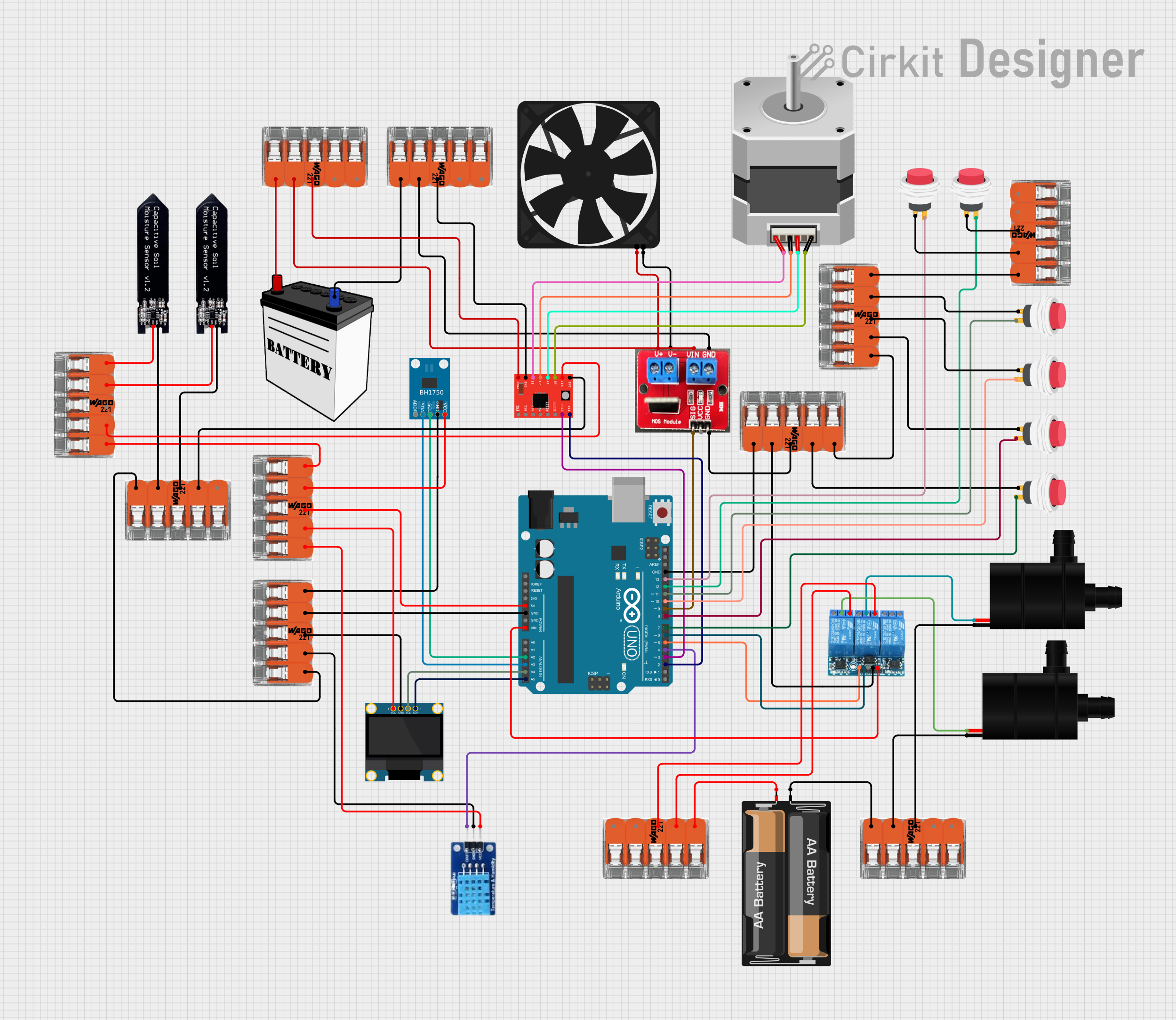
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BLD 750

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive battery testing for cars, trucks, and motorcycles
- Industrial battery maintenance in UPS systems and backup power supplies
- Renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind, for battery health monitoring
- Troubleshooting battery-related issues in portable electronics
- Evaluating deep-cycle batteries in marine and RV applications
Technical Specifications
The BLD 750 is designed to handle a wide range of battery types and capacities. Below are its key technical specifications:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage Range | 6V to 48V |
| Load Current Range | 0A to 750A |
| Resistance Measurement | 0.001Ω to 10Ω |
| Display Type | Digital LCD with backlight |
| Accuracy | ±1% for voltage and current |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 50°C |
| Storage Temperature | -20°C to 60°C |
| Dimensions | 200mm x 150mm x 80mm |
| Weight | 1.5 kg |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BLD 750 features input terminals for connecting to the battery under test. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Connects to the positive terminal of the battery |
| Negative (-) | Connects to the negative terminal of the battery |
| Ground (GND) | Optional grounding for enhanced safety |
Usage Instructions
The BLD 750 is straightforward to use for testing and evaluating batteries. Follow the steps below to ensure accurate and safe operation:
Step-by-Step Instructions
Preparation:
- Ensure the BLD 750 is powered off before connecting it to a battery.
- Verify that the battery voltage is within the supported range (6V to 48V).
Connection:
- Connect the positive terminal of the BLD 750 to the positive terminal of the battery.
- Connect the negative terminal of the BLD 750 to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Optionally, connect the ground terminal to a safe grounding point.
Operation:
- Power on the BLD 750 using the main switch.
- Select the desired test mode (e.g., voltage, current, or resistance) using the mode selector.
- Apply the load as needed by adjusting the load control knob or buttons.
- Observe the readings on the digital LCD display.
Completion:
- After testing, power off the BLD 750.
- Disconnect the terminals in reverse order (negative first, then positive).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always ensure proper polarity when connecting the BLD 750 to a battery to avoid damage.
- Do not exceed the maximum load current rating of 750A.
- Avoid prolonged testing at high currents to prevent overheating.
- Use the device in a well-ventilated area to dissipate heat effectively.
- Regularly inspect the test leads and terminals for wear or damage.
Arduino UNO Integration
While the BLD 750 is not directly designed for microcontroller integration, you can use an Arduino UNO to monitor the voltage and current readings via external sensors. Below is an example code snippet for reading battery voltage using an analog input pin:
// Arduino code to read battery voltage using an analog input pin
const int voltagePin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage sensor
const float voltageDividerRatio = 11.0; // Adjust based on your voltage divider
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(voltagePin, INPUT); // Set the voltage pin as input
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(voltagePin); // Read the analog value
float batteryVoltage = (sensorValue * 5.0 / 1023.0) * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to scale down the battery voltage to a safe range (0-5V) for the Arduino's analog input.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No display or power on the BLD 750 | Battery voltage is too low or no power | Check the battery connection and voltage |
| Incorrect readings | Loose or corroded connections | Ensure all connections are secure and clean |
| Overheating during testing | Prolonged high-current testing | Allow the device to cool down before resuming |
| Device does not apply load | Internal fault or load control issue | Contact the manufacturer for support |
FAQs
Can the BLD 750 test lithium-ion batteries?
- Yes, the BLD 750 supports lithium-ion batteries as long as their voltage is within the 6V to 48V range.
What safety precautions should I follow?
- Always wear protective gear, ensure proper polarity, and avoid testing in flammable environments.
How do I clean the BLD 750?
- Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the device. Avoid using water or solvents.
Can I use the BLD 750 for continuous load testing?
- The BLD 750 is designed for intermittent testing. Avoid prolonged high-current testing to prevent overheating.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the BLD 750 for battery testing and maintenance while ensuring safety and accuracy.