
How to Use LCD: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with LCD in Cirkit Designer
Design with LCD in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a flat-panel display technology that uses liquid crystals to modulate light. It is widely used in various electronic devices, including televisions, computer monitors, mobile devices, and embedded systems. LCDs are popular due to their low power consumption, lightweight design, and ability to produce sharp and clear images.
In electronics, smaller LCD modules, such as the 16x2 or 20x4 character displays, are commonly used for displaying text or simple graphics in embedded systems. These modules are often integrated into projects involving microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or other development boards.
Explore Projects Built with LCD
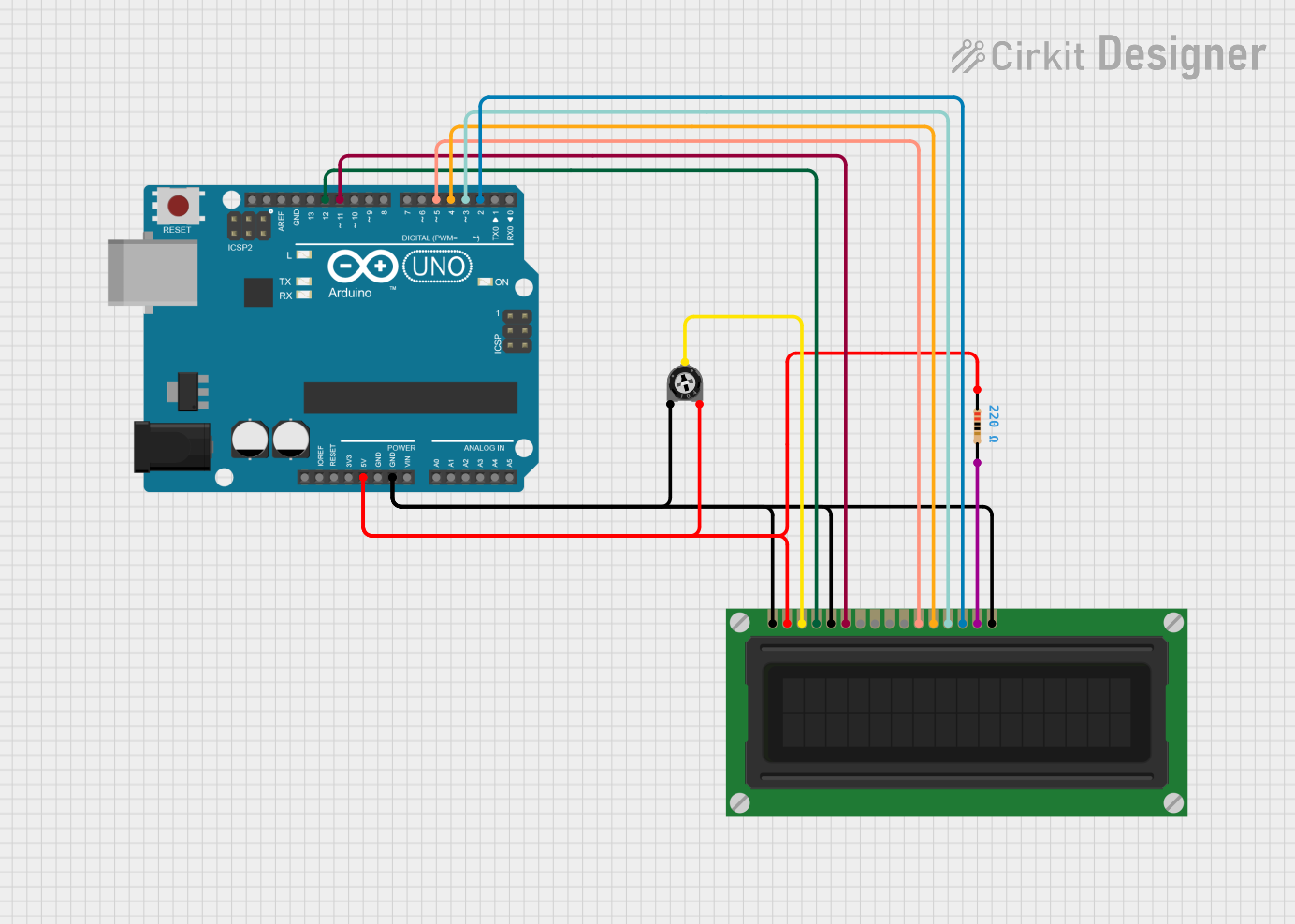
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer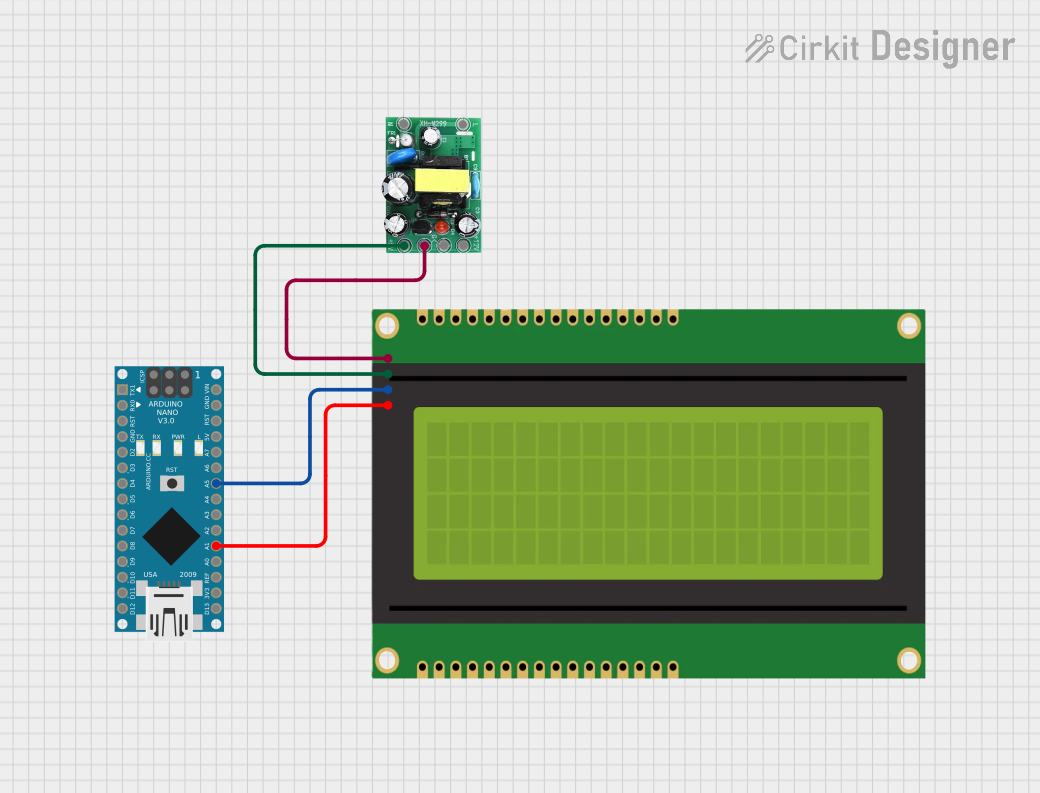
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer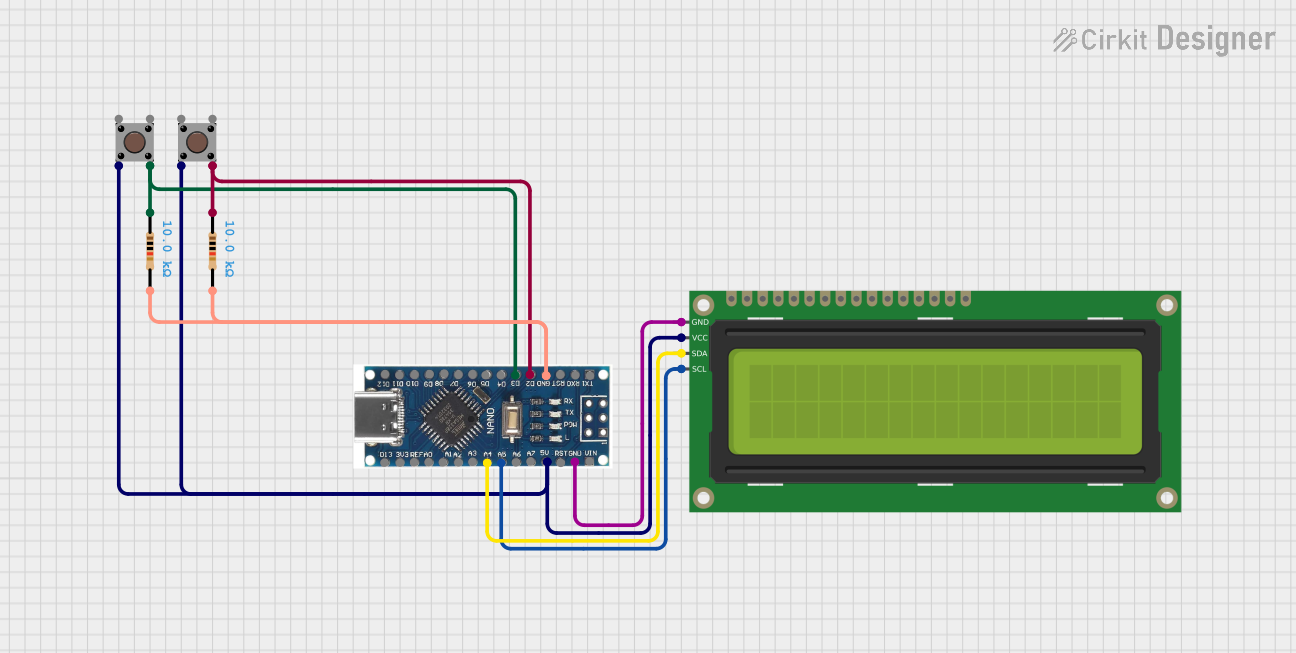
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer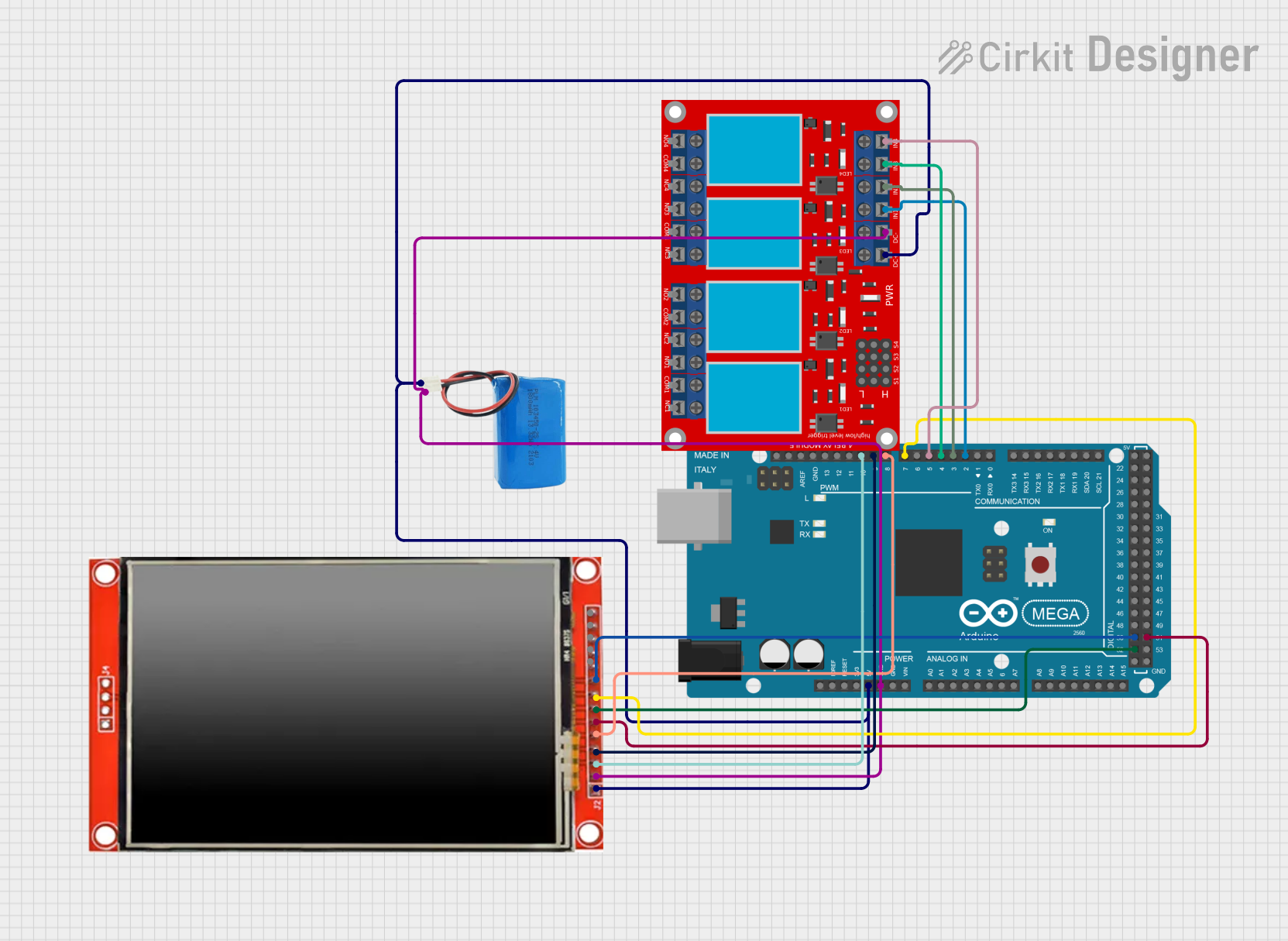
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with LCD

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Digital clocks and timers
- Home appliances (e.g., microwave ovens, washing machines)
- Embedded systems and IoT devices
- Industrial control panels
- Educational and hobbyist projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard 16x2 LCD module (HD44780-compatible):
Key Specifications:
- Display Type: Character-based (16 columns x 2 rows)
- Operating Voltage: 4.7V to 5.3V (typical 5V)
- Current Consumption: ~1mA (without backlight), ~15mA (with backlight)
- Interface: Parallel (4-bit or 8-bit mode)
- Character Size: ~5.2mm x 8.5mm
- Backlight: LED (commonly white, green, or blue)
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to +70°C
Pin Configuration:
The standard 16x2 LCD module has 16 pins. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VSS | Ground (0V) connection |
| 2 | VDD | Power supply (4.7V to 5.3V) |
| 3 | V0 | Contrast adjustment (connect to a potentiometer for contrast control) |
| 4 | RS | Register Select (0: Command mode, 1: Data mode) |
| 5 | RW | Read/Write (0: Write to LCD, 1: Read from LCD) |
| 6 | E | Enable pin (triggers data read/write) |
| 7-14 | D0-D7 | Data pins (used for 4-bit or 8-bit communication) |
| 15 | LED+ | Backlight anode (connect to 5V via a resistor) |
| 16 | LED- | Backlight cathode (connect to ground) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the LCD to an Arduino UNO
The LCD can be connected to an Arduino UNO using the 4-bit mode to save pins. Below is a typical wiring configuration for a 16x2 LCD:
| LCD Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VSS | GND |
| VDD | 5V |
| V0 | Middle pin of a 10kΩ potentiometer (other two pins to 5V and GND) |
| RS | Digital Pin 12 |
| RW | GND |
| E | Digital Pin 11 |
| D4 | Digital Pin 5 |
| D5 | Digital Pin 4 |
| D6 | Digital Pin 3 |
| D7 | Digital Pin 2 |
| LED+ | 5V (via a 220Ω resistor) |
| LED- | GND |
Arduino Code Example
Below is an example Arduino sketch to display "Hello, World!" on a 16x2 LCD:
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
// Initialize the library with the pins connected to the LCD
// (RS, E, D4, D5, D6, D7)
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
void setup() {
// Set up the LCD's number of columns and rows
lcd.begin(16, 2);
// Print a message to the LCD
lcd.print("Hello, World!");
}
void loop() {
// Move the cursor to the second row, first column
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
// Print a dynamic message
lcd.print("LCD Tutorial!");
delay(1000);
// Clear the second row
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" "); // Clear text by overwriting with spaces
delay(1000);
}
Important Considerations:
- Contrast Adjustment: Use a 10kΩ potentiometer to adjust the contrast of the display. Connect the middle pin of the potentiometer to the V0 pin of the LCD.
- Backlight Resistor: Use a 220Ω resistor in series with the LED+ pin to limit the current and protect the backlight.
- 4-bit vs. 8-bit Mode: The 4-bit mode is commonly used to save microcontroller pins. If you need faster data transfer, use the 8-bit mode by connecting all D0-D7 pins.
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable 5V power supply to avoid flickering or malfunctioning of the LCD.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues:
No Display on LCD:
- Check the power connections (VSS to GND, VDD to 5V).
- Adjust the contrast using the potentiometer connected to V0.
- Ensure the backlight is connected properly.
Garbage Characters or No Text:
- Verify the wiring of the data pins (D4-D7) and control pins (RS, E).
- Ensure the correct pin numbers are defined in the Arduino code.
- Check for loose or faulty connections.
Flickering or Dim Backlight:
- Use a proper current-limiting resistor (220Ω) for the backlight.
- Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current.
LCD Not Responding to Commands:
- Confirm the RW pin is connected to GND for write operations.
- Ensure the Enable (E) pin is toggled correctly in the code.
FAQs:
Q1: Can I use the LCD with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Most LCD modules require 5V for proper operation. However, you can use a level shifter or voltage divider to interface the data pins with a 3.3V microcontroller.
Q2: How do I display custom characters on the LCD?
A2: You can create custom characters using the createChar() function in the LiquidCrystal library. Refer to the library documentation for details.
Q3: Can I use multiple LCDs with one Arduino?
A3: Yes, but you will need additional pins or an I2C interface module to control multiple LCDs efficiently.
By following this documentation, you can successfully integrate and troubleshoot an LCD module in your projects!