
How to Use 2P Breaker: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 2P Breaker in Cirkit Designer
Design with 2P Breaker in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 2-pole circuit breaker (commonly referred to as a 2P breaker) is an essential safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. It is specifically engineered for dual-phase systems, where it can simultaneously disconnect power from both phases, ensuring comprehensive protection. The breaker automatically trips when it detects a fault, preventing damage to equipment and reducing the risk of electrical fires.
Explore Projects Built with 2P Breaker

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer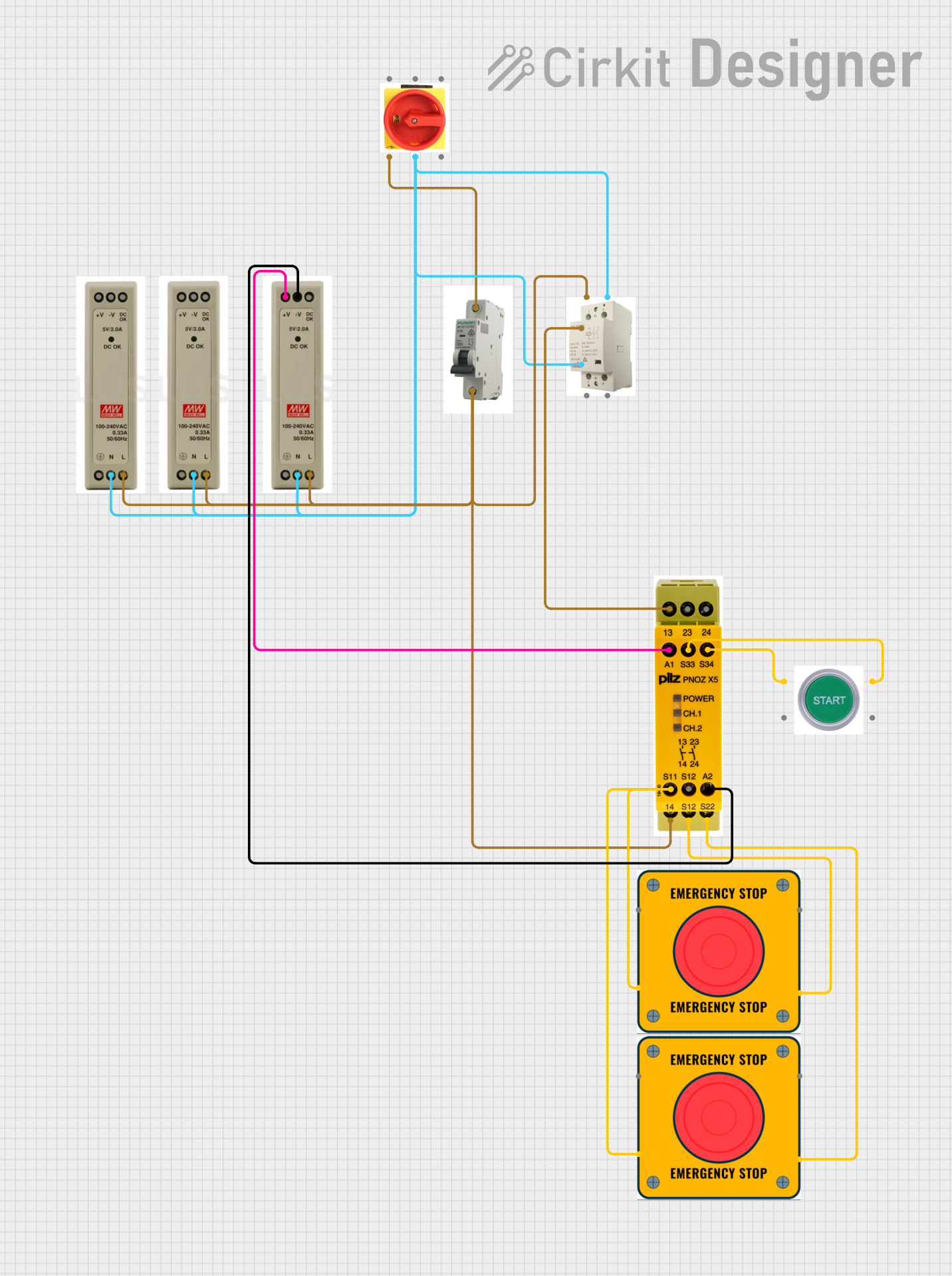
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer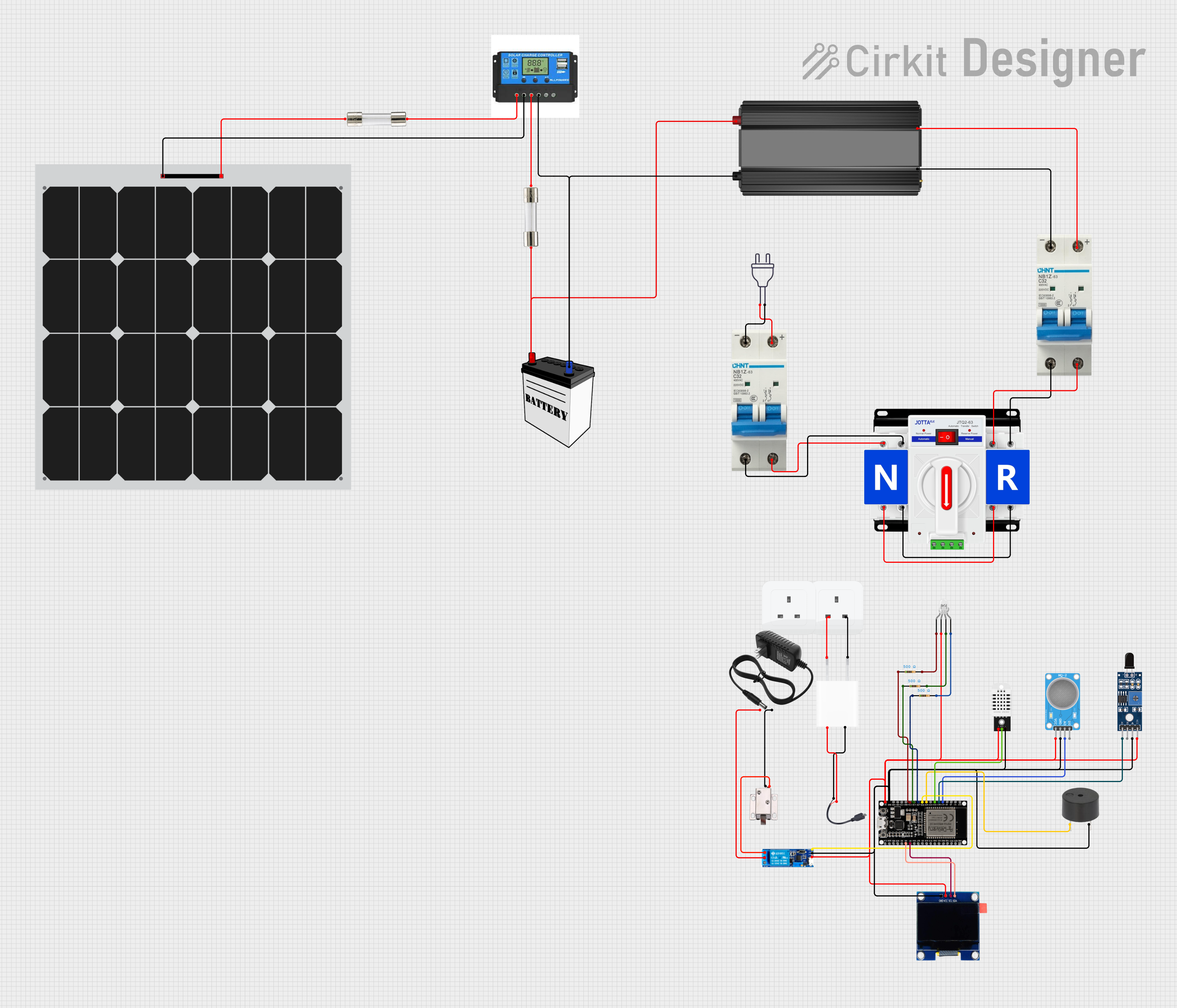
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer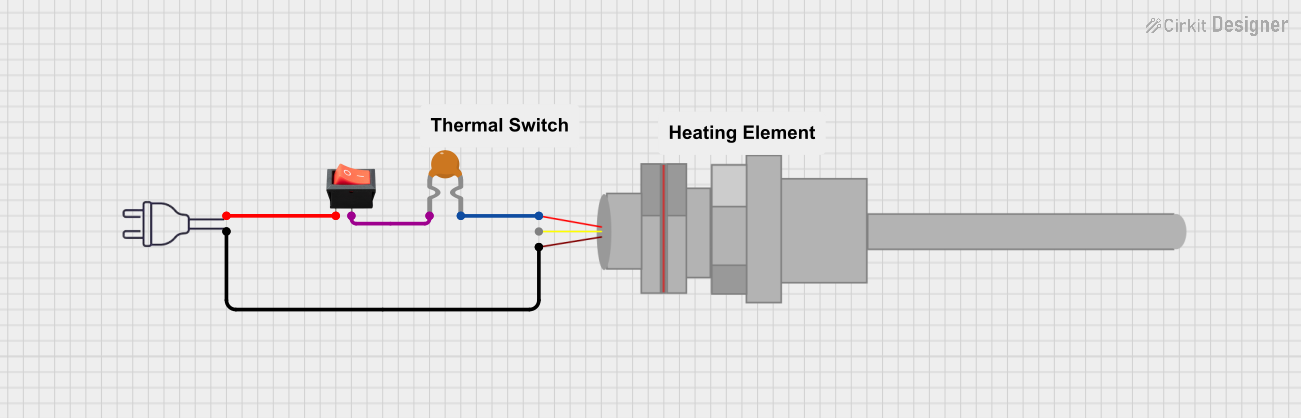
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 2P Breaker

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential and commercial electrical panels for dual-phase systems.
- Protection of high-power appliances such as HVAC systems, water heaters, and electric ranges.
- Industrial equipment requiring dual-phase power.
- Backup power systems and generators.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a standard 2P breaker:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 120/240V AC (typical) |
| Rated Current | 10A to 100A (varies by model) |
| Breaking Capacity | 10kA to 25kA (depending on model) |
| Number of Poles | 2 |
| Trip Mechanism | Thermal-magnetic |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
| Mounting Type | DIN rail or panel-mounted |
| Compliance Standards | IEC 60898, UL 489 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Line 1 (L1) | Connects to the first phase of the power supply. |
| Line 2 (L2) | Connects to the second phase of the power supply. |
| Load 1 | Connects to the load for the first phase. |
| Load 2 | Connects to the load for the second phase. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 2P Breaker in a Circuit
- Determine the Load Requirements: Ensure the breaker’s rated current and voltage match the requirements of your circuit.
- Turn Off Power: Before installation, disconnect power to the circuit to avoid electrical shock.
- Connect the Breaker:
- Connect the power supply lines to the
Line 1 (L1)andLine 2 (L2)terminals. - Connect the load wires to the
Load 1andLoad 2terminals.
- Connect the power supply lines to the
- Secure the Breaker: Mount the breaker onto a DIN rail or panel as per the installation requirements.
- Test the Circuit: After installation, restore power and test the breaker by manually tripping it to ensure proper operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Select the Correct Rating: Always choose a breaker with a current rating slightly higher than the maximum expected load current.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not connect loads that exceed the breaker’s rated capacity.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically inspect the breaker for signs of wear, damage, or overheating.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure the circuit is properly grounded to enhance safety.
- Use in Dual-Phase Systems Only: This breaker is designed for dual-phase systems and should not be used in single-phase applications.
Example: Connecting a 2P Breaker to an Arduino-Controlled System
While a 2P breaker is not directly connected to an Arduino, it can be used to protect circuits that include Arduino-based systems. For example, if you are controlling a dual-phase motor with an Arduino, the 2P breaker can safeguard the motor and associated wiring.
// Example Arduino code for controlling a dual-phase motor via a relay
// Ensure the 2P breaker is installed to protect the motor circuit
const int relayPin = 7; // Pin connected to the relay module
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set relay pin as output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure relay is off at startup
}
void loop() {
// Turn on the motor
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Activate relay to power the motor
delay(5000); // Run motor for 5 seconds
// Turn off the motor
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Deactivate relay to cut power
delay(5000); // Wait for 5 seconds before restarting
}
Note: The 2P breaker should be installed between the power source and the motor to protect against overloads or short circuits.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Breaker trips frequently | Overloaded circuit | Reduce the load or use a higher-rated breaker. |
| Breaker does not trip during faults | Faulty breaker or incorrect wiring | Inspect wiring and replace the breaker if necessary. |
| Breaker feels hot to the touch | Loose connections or overload | Tighten connections and ensure the load is within limits. |
| Breaker will not reset | Persistent fault in the circuit | Identify and fix the fault before resetting. |
FAQs
Can I use a 2P breaker in a single-phase system?
- No, a 2P breaker is designed for dual-phase systems. For single-phase systems, use a single-pole breaker.
What happens if I exceed the breaker’s rated current?
- The breaker will trip to protect the circuit. Repeated overloading can damage the breaker.
How do I know if my breaker is faulty?
- If the breaker does not trip during a fault or trips without any load, it may be faulty and should be replaced.
Can I install a 2P breaker myself?
- Installation should be performed by a qualified electrician to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes.