
How to Use thermocouple: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
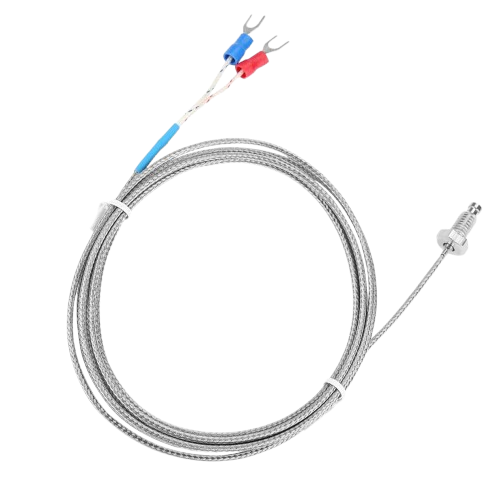
 Design with thermocouple in Cirkit Designer
Design with thermocouple in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor that consists of two dissimilar metal wires joined at one end. It generates a voltage that is proportional to the temperature difference between the joined end (hot junction) and the other ends of the wires (cold junction). This voltage can be measured and converted into a temperature reading using appropriate circuitry or microcontrollers.
Thermocouples are widely used in industrial, scientific, and household applications due to their simplicity, durability, and ability to measure a wide range of temperatures. Common use cases include:
- Industrial temperature monitoring in furnaces, kilns, and engines.
- Scientific experiments requiring precise temperature measurements.
- Household appliances like ovens and water heaters.
Explore Projects Built with thermocouple
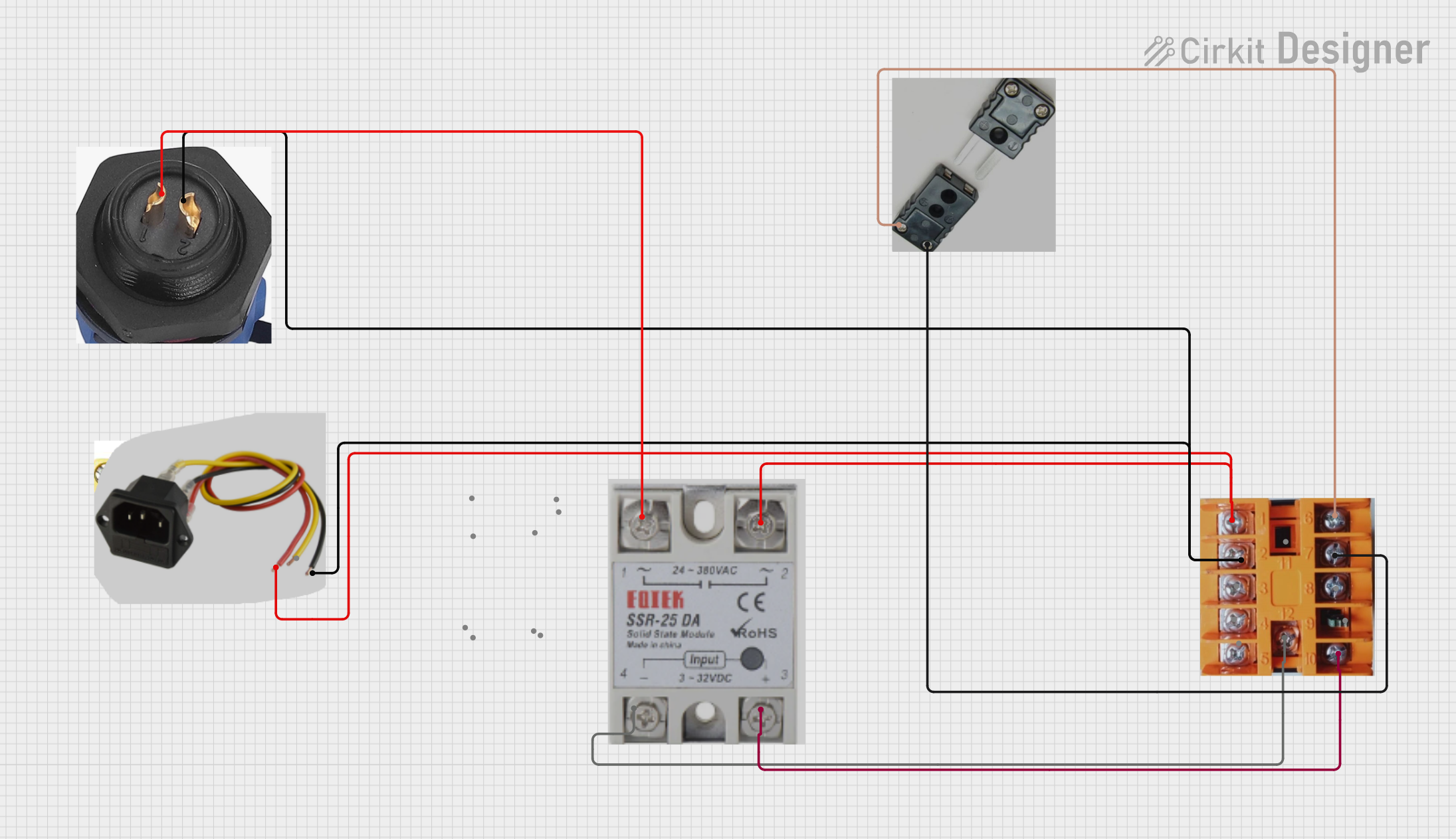
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer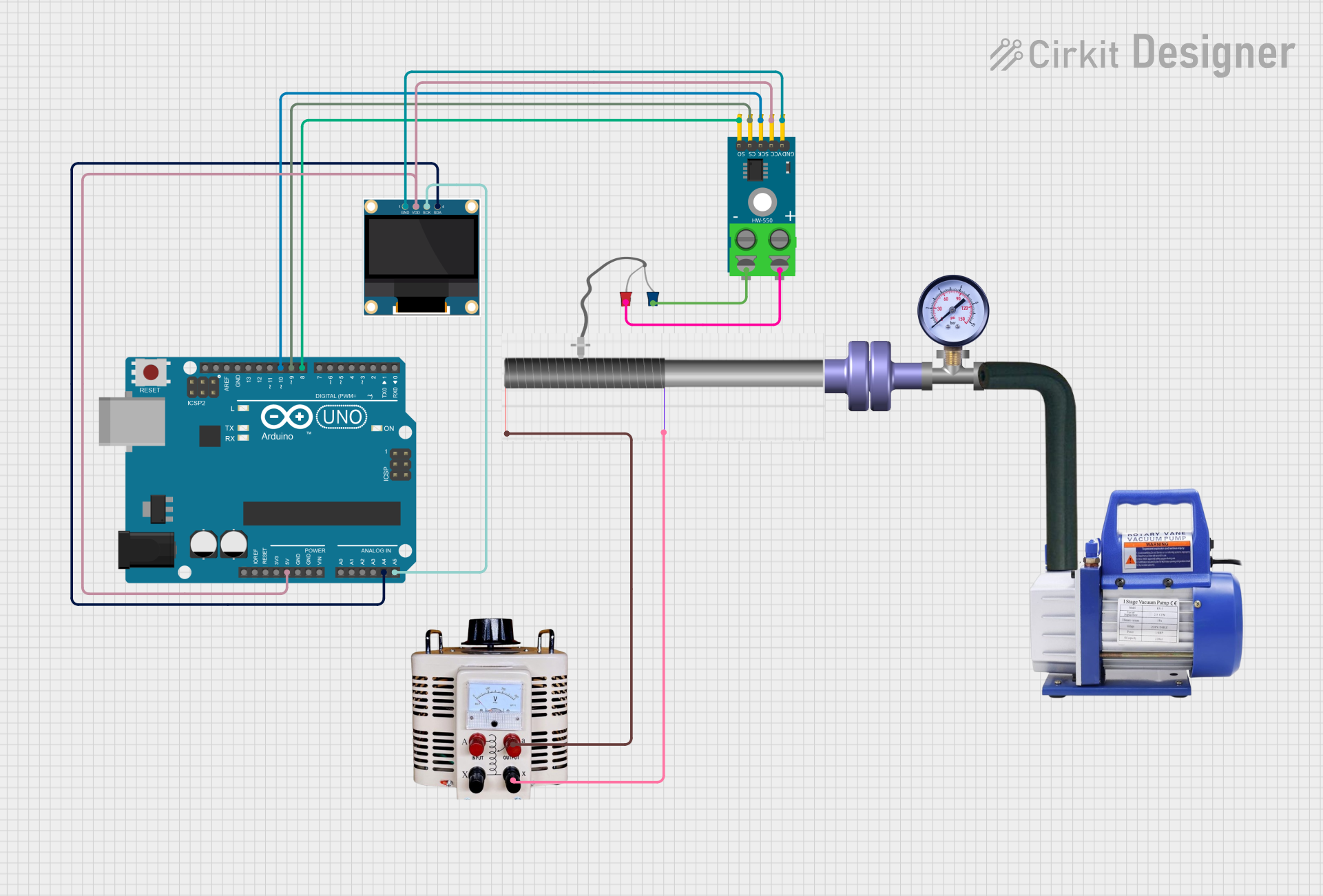
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer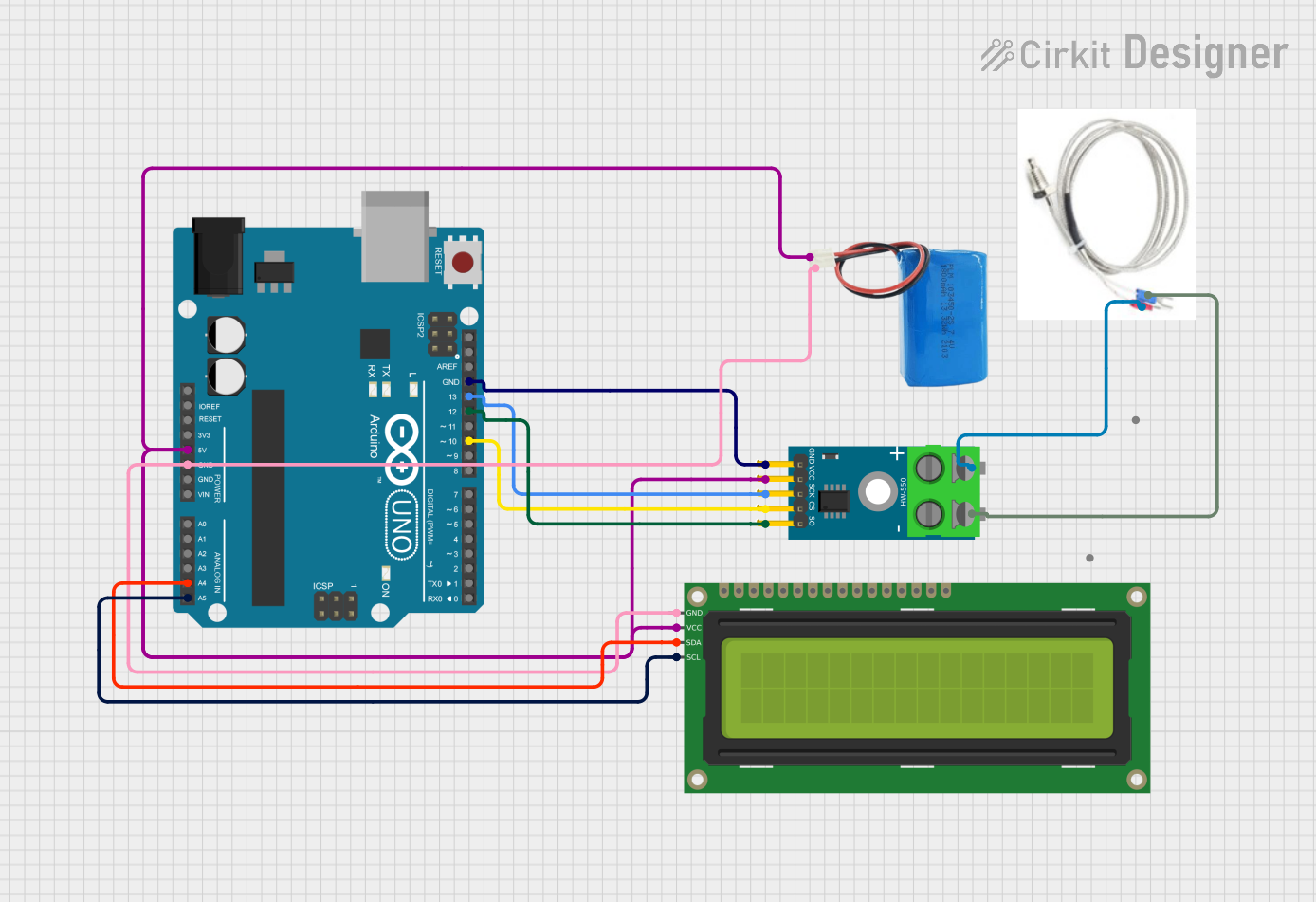
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer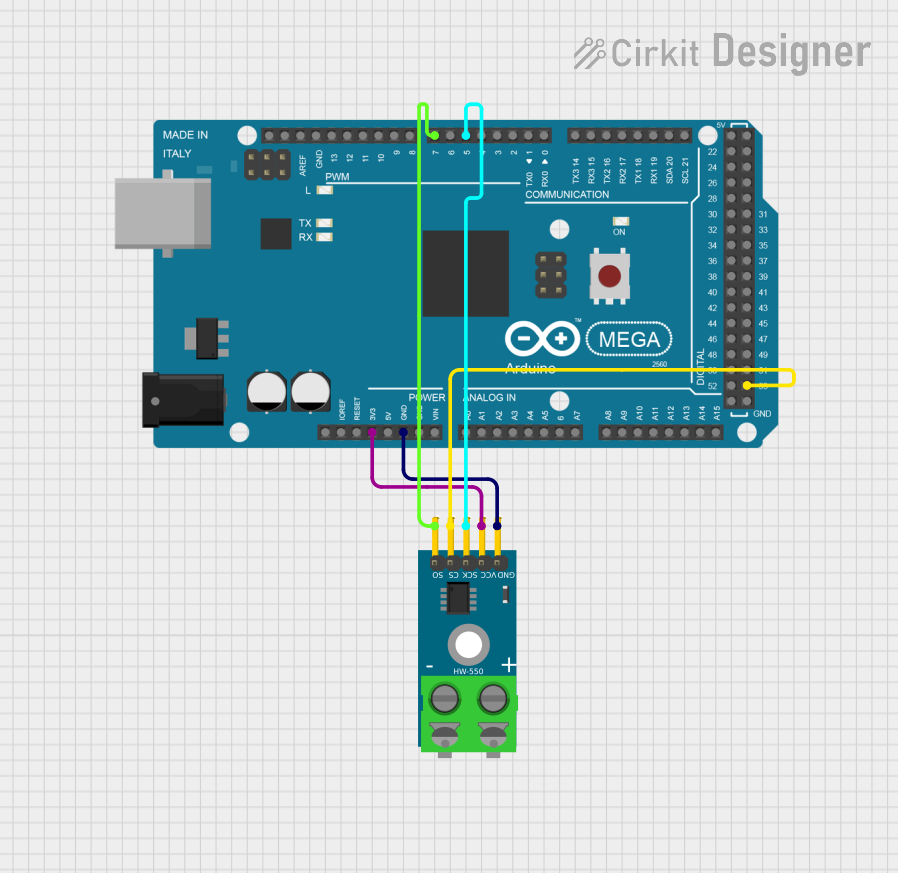
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with thermocouple

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Temperature Range: Varies by thermocouple type (e.g., Type K: -200°C to 1350°C).
- Accuracy: Typically ±1°C to ±2°C, depending on the type and calibration.
- Output Voltage: Microvolts per degree Celsius (varies by type).
- Response Time: Fast, typically in milliseconds.
- Durability: Resistant to high temperatures and harsh environments.
Common Thermocouple Types
| Type | Composition (Metals) | Temperature Range | Sensitivity (µV/°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K | Chromel (+) / Alumel (-) | -200°C to 1350°C | ~41 |
| J | Iron (+) / Constantan (-) | -40°C to 750°C | ~55 |
| T | Copper (+) / Constantan (-) | -200°C to 350°C | ~43 |
| E | Chromel (+) / Constantan (-) | -200°C to 900°C | ~68 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Thermocouples do not have traditional "pins" but consist of two wires:
| Wire Color (Type K) | Description |
|---|---|
| Yellow | Positive (Chromel) |
| Red | Negative (Alumel) |
Note: Wire colors may vary by region or thermocouple type. Always refer to the manufacturer's datasheet.
Usage Instructions
How to Use a Thermocouple in a Circuit
- Connect the Thermocouple: Attach the positive and negative wires to the appropriate input terminals of a thermocouple amplifier or microcontroller with a thermocouple interface.
- Amplify the Signal: Use a thermocouple amplifier (e.g., MAX31855 or MAX6675) to amplify the small voltage signal and convert it into a digital or readable format.
- Cold Junction Compensation: Ensure the circuit compensates for the cold junction temperature, as the thermocouple measures only the temperature difference.
- Read the Data: Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) to read the temperature data from the amplifier.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate the thermocouple for accurate readings.
- Shielding: Use shielded cables to minimize noise interference in high-EMI environments.
- Polarity: Ensure correct polarity when connecting the thermocouple wires.
- Environment: Select a thermocouple type suitable for the temperature range and environment.
Example: Using a Type K Thermocouple with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of interfacing a Type K thermocouple with an Arduino UNO using the MAX6675 amplifier module:
#include <SPI.h>
#include "Adafruit_MAX6675.h"
// Define pins for the MAX6675 module
int thermoDO = 4; // Data Out pin
int thermoCS = 5; // Chip Select pin
int thermoCLK = 6; // Clock pin
// Create a MAX6675 object
Adafruit_MAX6675 thermocouple(thermoCLK, thermoCS, thermoDO);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
Serial.println("Thermocouple Test");
delay(500); // Allow time for initialization
}
void loop() {
// Read temperature from the thermocouple
double temperature = thermocouple.readCelsius();
// Check if the reading is valid
if (isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Error: Thermocouple not connected!");
} else {
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Notes:
- Ensure the MAX6675 module is properly connected to the Arduino UNO.
- The
Adafruit_MAX6675library must be installed in the Arduino IDE.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Temperature Reading:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Verify connections and ensure proper polarity.
Inaccurate Readings:
- Cause: Lack of cold junction compensation or calibration.
- Solution: Use a thermocouple amplifier with built-in compensation and calibrate the system.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Cause: Electrical noise or interference.
- Solution: Use shielded cables and keep the thermocouple away from high-EMI sources.
Thermocouple Not Detected:
- Cause: Damaged thermocouple or amplifier module.
- Solution: Test with a multimeter or replace the faulty component.
FAQs
Q1: Can I extend the thermocouple wires?
A1: Yes, but use thermocouple extension wires made of the same materials to avoid introducing errors.
Q2: How do I choose the right thermocouple type?
A2: Consider the temperature range, environment, and required accuracy. For general use, Type K is a popular choice.
Q3: Can I connect a thermocouple directly to an Arduino?
A3: No, the voltage output of a thermocouple is too small. Use an amplifier like the MAX6675 or MAX31855.
Q4: How do I protect a thermocouple in harsh environments?
A4: Use a thermocouple with a protective sheath or coating designed for the specific environment.