
How to Use Vcc: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
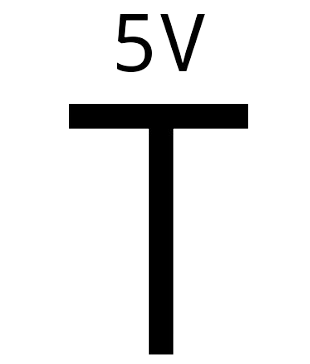
 Design with Vcc in Cirkit Designer
Design with Vcc in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
VCC, an acronym for Voltage at the Collector terminal, is a term commonly used in electronic circuits to denote the positive supply voltage with respect to the common ground. It is a critical parameter in the design and operation of circuits, particularly in digital electronics and microcontroller applications. VCC is not a component itself but a label used to indicate the positive voltage supply rail in a circuit diagram.
Explore Projects Built with Vcc
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer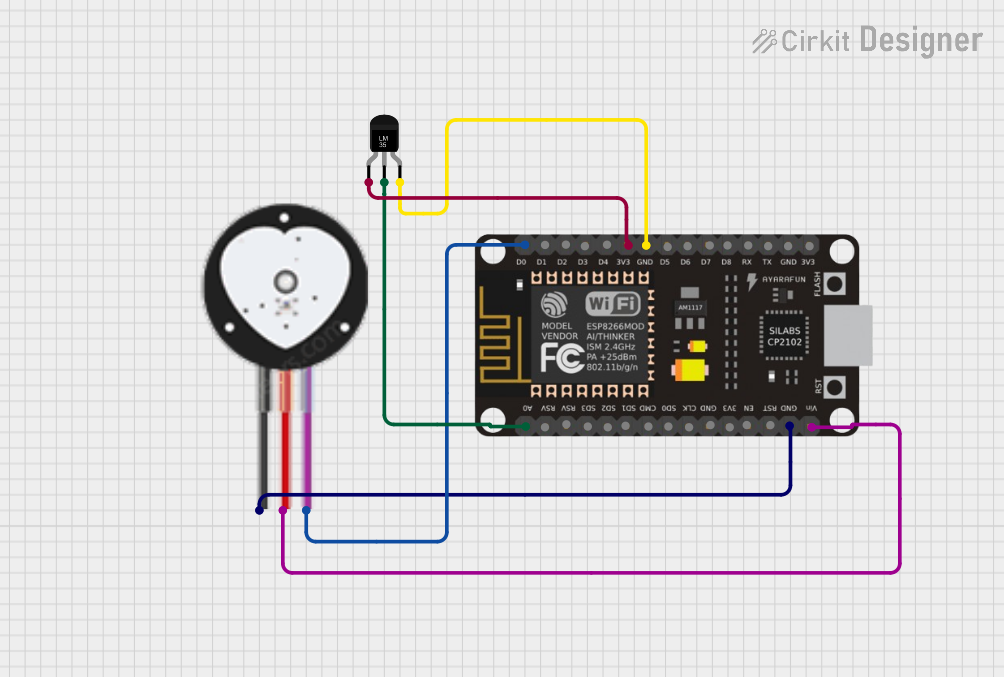
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Vcc

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering integrated circuits (ICs)
- Supplying voltage to microcontrollers, such as Arduino boards
- Biasing transistors in amplifiers and switches
- Providing the reference voltage for analog-to-digital converters (ADCs)
Technical Specifications
Since VCC is a concept rather than a physical component, the technical specifications will vary depending on the requirements of the electronic device or circuit. Below are general guidelines for VCC specifications in various contexts.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | Typically ranges from 3.3V to 5V for logic ICs, and up to 12V or higher for power circuits. |
| Current Rating | Depends on the total current consumption of the connected components. |
| Power Rating | Determined by the product of the voltage and the maximum current draw. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use VCC in a Circuit
- Identify the VCC Pin: Refer to the datasheet of the component to locate the VCC pin(s).
- Connect to Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to the positive terminal of a power supply that matches the voltage requirements.
- Ground Reference: Ensure that the ground (GND) of the power supply is connected to the common ground of the circuit.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors near the power pins of ICs to stabilize VCC and filter out noise.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure that the VCC supplied matches the voltage level required by the components in the circuit.
- Current Limitations: The power supply should be capable of providing sufficient current for all components without exceeding its rating.
- Heat Dissipation: Be mindful of heat generation if the current draw is significant; use appropriate heat sinks if necessary.
- Short Circuit Protection: Implement fuses or current-limiting resistors to protect against short circuits.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Voltage Drops: If the voltage at the VCC pin is lower than expected, check for poor connections or excessive current draw.
- Overheating: Components getting too hot may indicate that the VCC is too high or that there is excessive current flow.
- Intermittent Operation: This could be due to unstable VCC caused by insufficient decoupling or a noisy power supply.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Measure Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the voltage level at the VCC pin.
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion or damage.
- Review Decoupling: Verify that decoupling capacitors are correctly placed and of appropriate value.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 9V battery for VCC? A: Yes, if the circuit components can operate at 9V. However, voltage regulation may be necessary to provide a stable VCC.
Q: What happens if VCC is too high? A: Exceeding the voltage rating of components can lead to permanent damage or failure.
Q: Is VCC the same as VDD? A: VCC and VDD are similar concepts but are used in different contexts. VCC is typically used for bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), while VDD is used for field-effect transistors (FETs) and CMOS technology.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the VCC pin for Arduino UNO
const int VccPin = 5; // Assuming we use digital pin 5 as a VCC source
void setup() {
// Set the VccPin as OUTPUT to provide power
pinMode(VccPin, OUTPUT);
// Set the VccPin HIGH to supply 5V
digitalWrite(VccPin, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Your code here to interact with components powered by the VccPin
}
Note: The above code snippet demonstrates how to use an Arduino digital pin as a VCC source for low-power applications. Ensure that the current draw does not exceed the pin's maximum current rating (typically 20-40mA for Arduino UNO).