
How to Use Rainfall Sensor DFRobot: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Rainfall Sensor DFRobot in Cirkit Designer
Design with Rainfall Sensor DFRobot in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Rainfall Sensor DFRobot (Gravity_12C_UART) is a versatile sensor designed to detect and measure rainfall. It provides both analog and digital outputs, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. The sensor can detect the presence of rain and measure its intensity, making it an essential component in weather monitoring systems, smart irrigation systems, and other environmental monitoring projects.
This sensor is part of DFRobot's Gravity series, which is known for its ease of use and compatibility with microcontrollers like Arduino. Its robust design ensures reliable performance in outdoor environments.
Explore Projects Built with Rainfall Sensor DFRobot
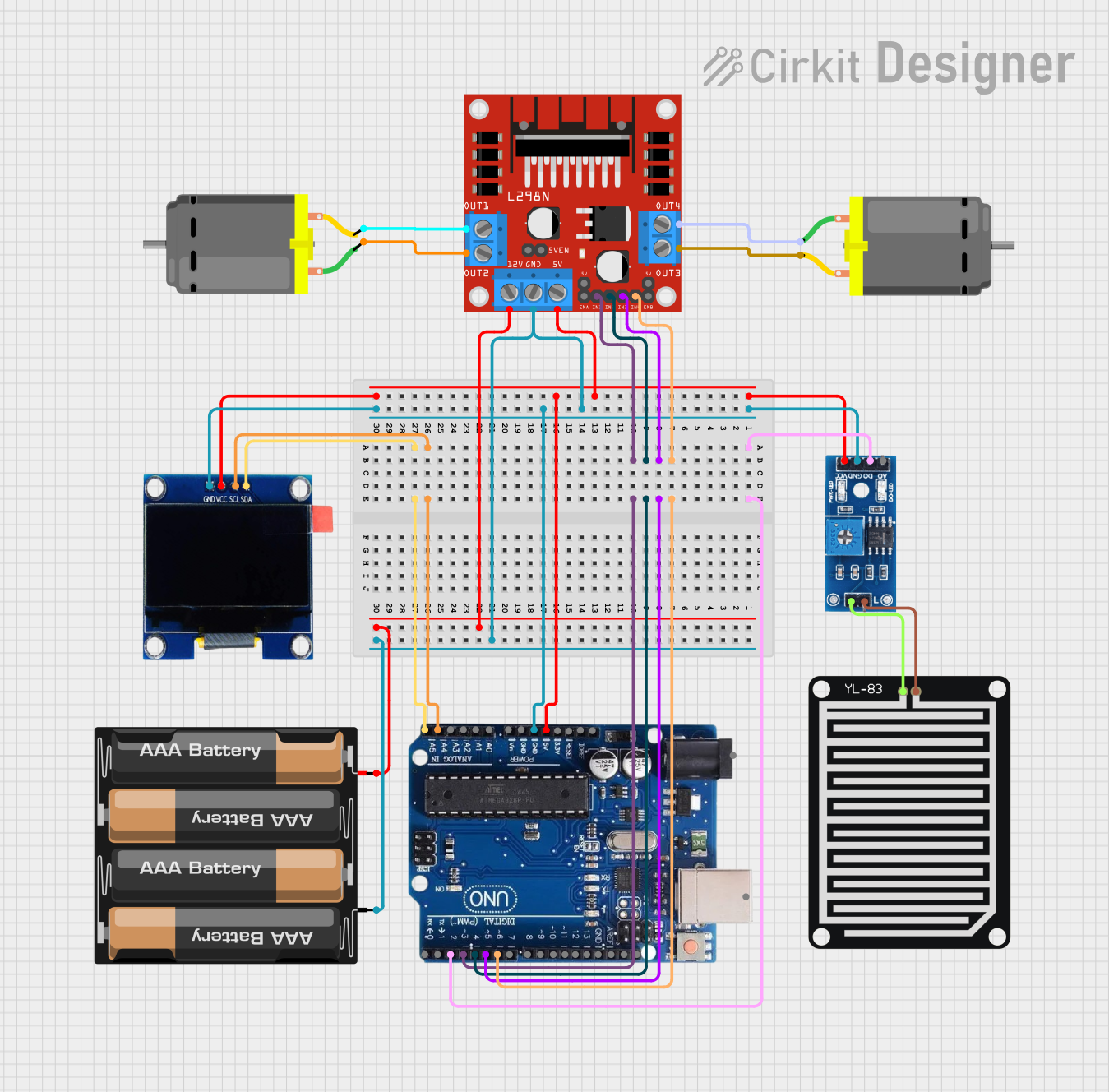
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer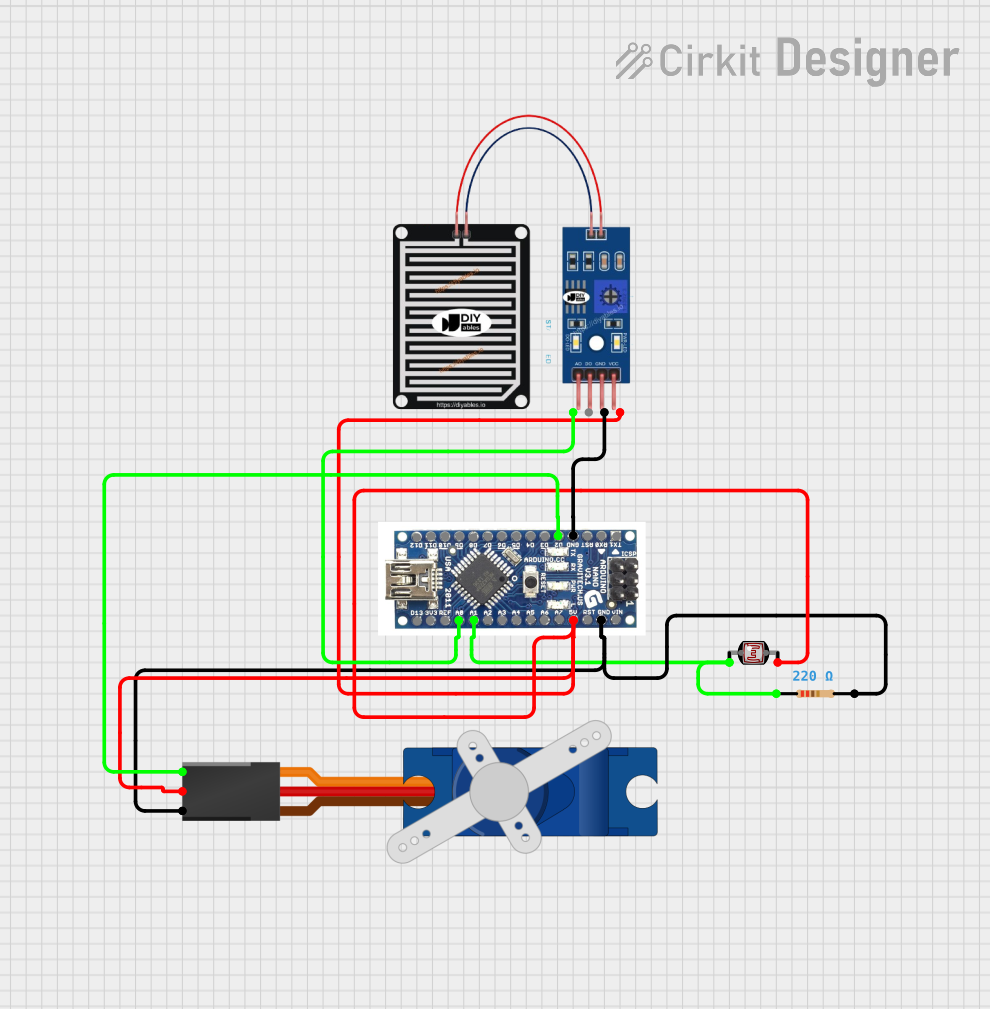
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer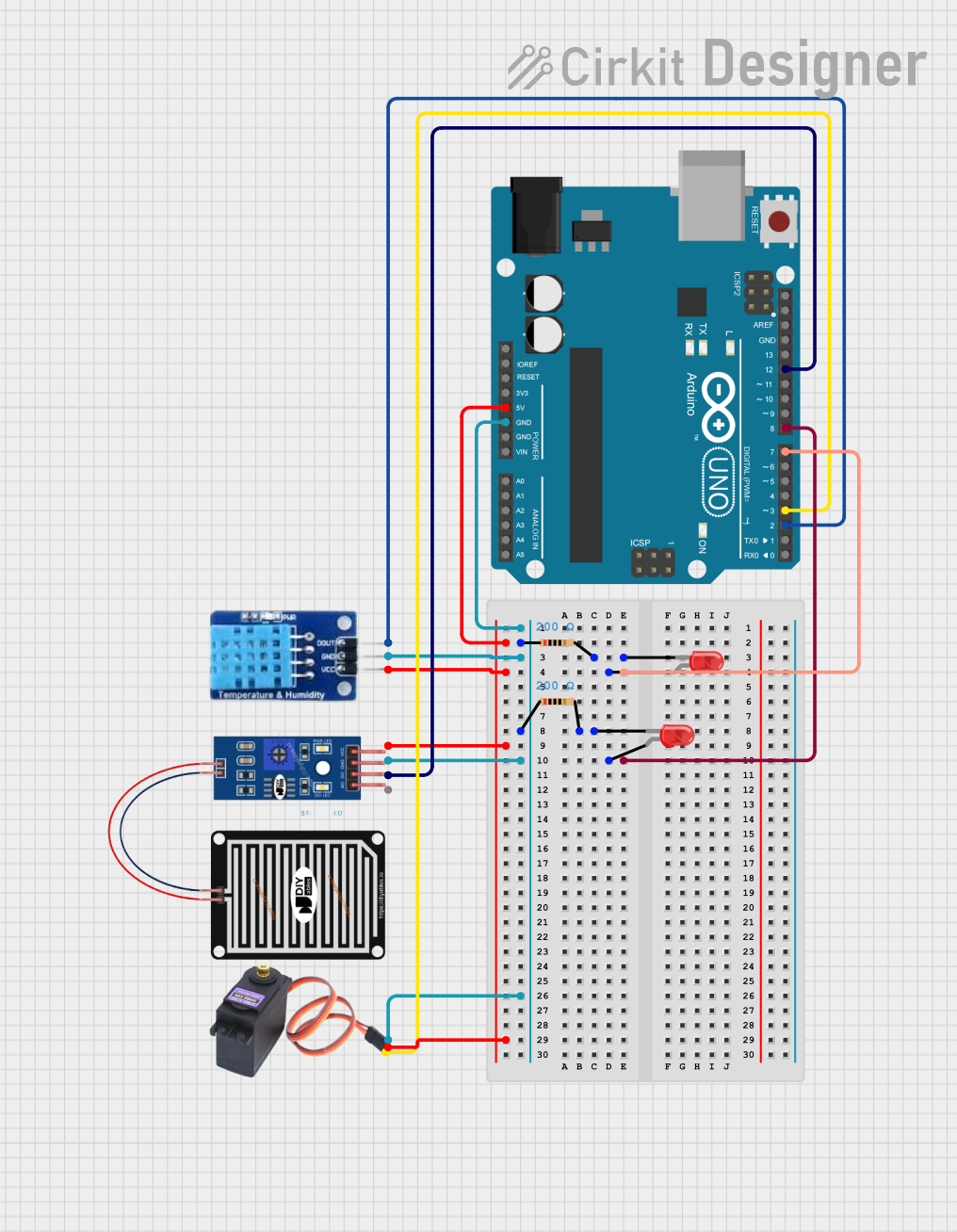
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer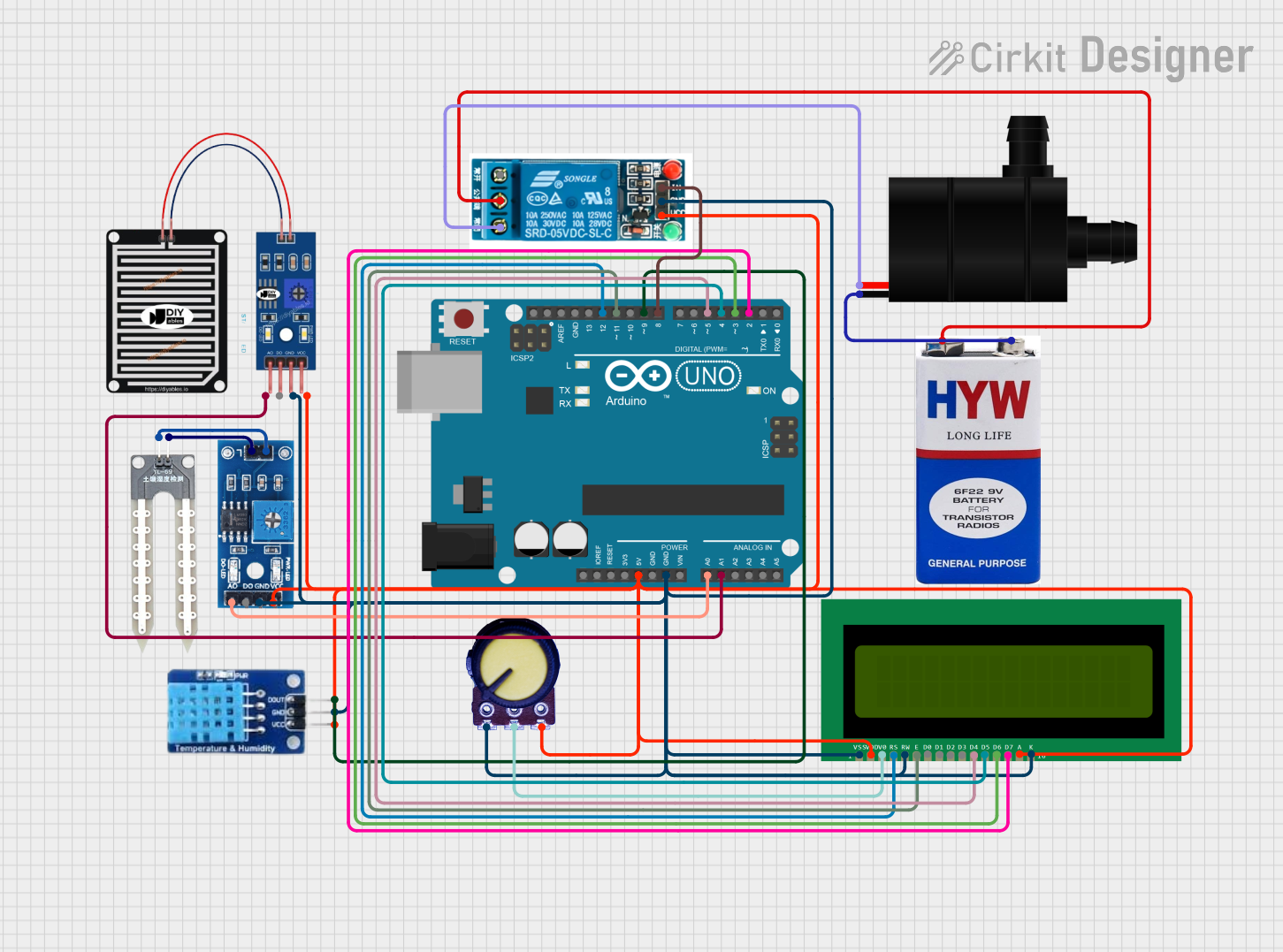
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Rainfall Sensor DFRobot

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Weather monitoring stations
- Smart irrigation systems
- Rain detection for automated systems
- Environmental monitoring projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Rainfall Sensor DFRobot:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Output Type | Analog and Digital |
| Interface | Gravity 3-pin interface |
| Detection Area | 5cm x 4cm |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (rain intensity) |
| Digital Output Threshold | Adjustable via onboard potentiometer |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
| Dimensions | 54mm x 40mm |
Pin Configuration
The sensor has a 3-pin interface for easy connection. Below is the pin description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V - 5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | SIG | Signal output (analog or digital, depending on mode) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the Sensor
- Power Supply: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to ground. - Signal Output: Connect the
SIGpin to an analog or digital input pin on your microcontroller.- For analog output, read the voltage to determine rain intensity.
- For digital output, adjust the sensitivity using the onboard potentiometer.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the Rainfall Sensor to an Arduino UNO:
- VCC → 5V on Arduino
- GND → GND on Arduino
- SIG → A0 (analog input) or D2 (digital input) on Arduino
Sample Code
The following Arduino code demonstrates how to read both analog and digital outputs from the sensor:
// Define pin connections
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to SIG
const int digitalPin = 2; // Digital pin connected to SIG
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT); // Set digital pin as input
}
void loop() {
// Read analog value (rain intensity)
int analogValue = analogRead(analogPin);
Serial.print("Analog Value (Rain Intensity): ");
Serial.println(analogValue);
// Read digital value (rain detected or not)
int digitalValue = digitalRead(digitalPin);
Serial.print("Digital Value (Rain Detected): ");
if (digitalValue == LOW) {
Serial.println("Yes"); // Rain detected
} else {
Serial.println("No"); // No rain detected
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before next reading
}
Important Considerations
- Sensitivity Adjustment: Use the onboard potentiometer to adjust the digital output threshold for rain detection.
- Placement: Ensure the sensor is placed in an open area where it can directly detect rainfall.
- Waterproofing: While the sensor is designed for outdoor use, ensure proper sealing of connections to prevent water damage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Output Signal
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply is within the specified range (3.3V - 5V).
Inconsistent Readings
- Cause: Dirt or debris on the sensor surface.
- Solution: Clean the sensor surface gently with a soft cloth.
Digital Output Always HIGH or LOW
- Cause: Incorrect sensitivity adjustment.
- Solution: Adjust the potentiometer to set the desired threshold.
Analog Output Not Changing
- Cause: Faulty sensor or improper placement.
- Solution: Verify the sensor's placement and test with a known water source.
FAQs
Q: Can this sensor detect the amount of rainfall over time?
A: The sensor provides real-time rain intensity data. To measure cumulative rainfall, you would need to integrate the data over time using a microcontroller.
Q: Is the sensor waterproof?
A: The sensor is designed for outdoor use, but the connections should be properly sealed to prevent water damage.
Q: Can I use this sensor with a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, the sensor can be connected to a Raspberry Pi using its GPIO pins. Use an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) module for reading analog signals.
Q: How do I clean the sensor?
A: Use a soft, damp cloth to gently clean the sensor surface. Avoid using abrasive materials.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Rainfall Sensor DFRobot into your projects and ensure reliable performance.