
How to Use driver motor single l293: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
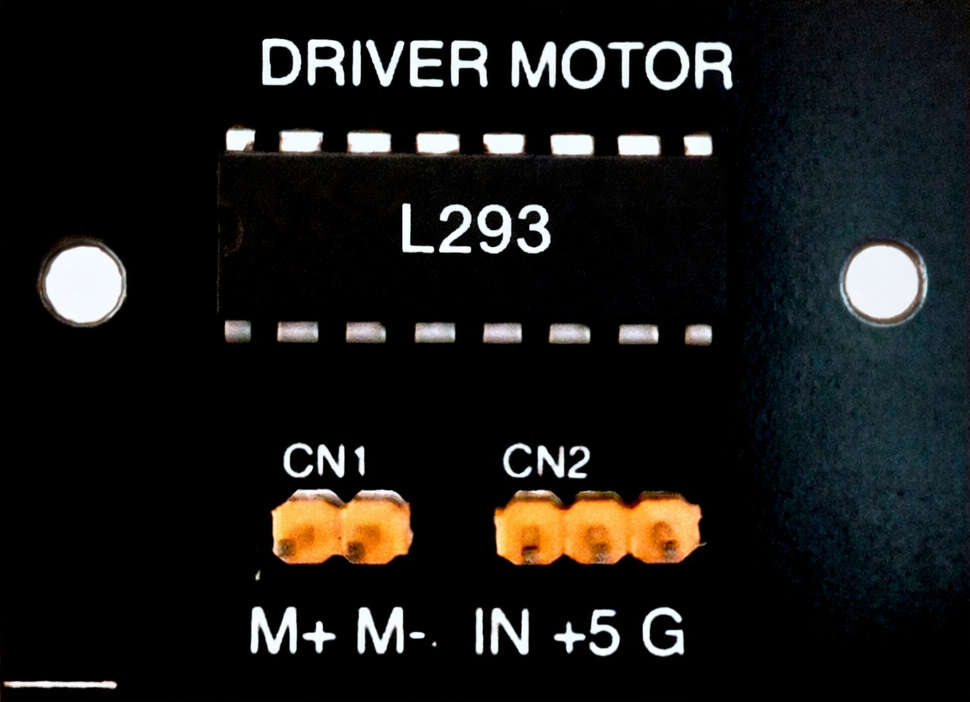
 Design with driver motor single l293 in Cirkit Designer
Design with driver motor single l293 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The L293 is a dual H-bridge motor driver IC manufactured by L293D. It is designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors and stepper motors. The IC can drive two motors simultaneously, making it a versatile choice for robotics, automation, and motor control applications. Its ability to handle bidirectional control of motors makes it a popular component in projects requiring precise motor operation.
Explore Projects Built with driver motor single l293
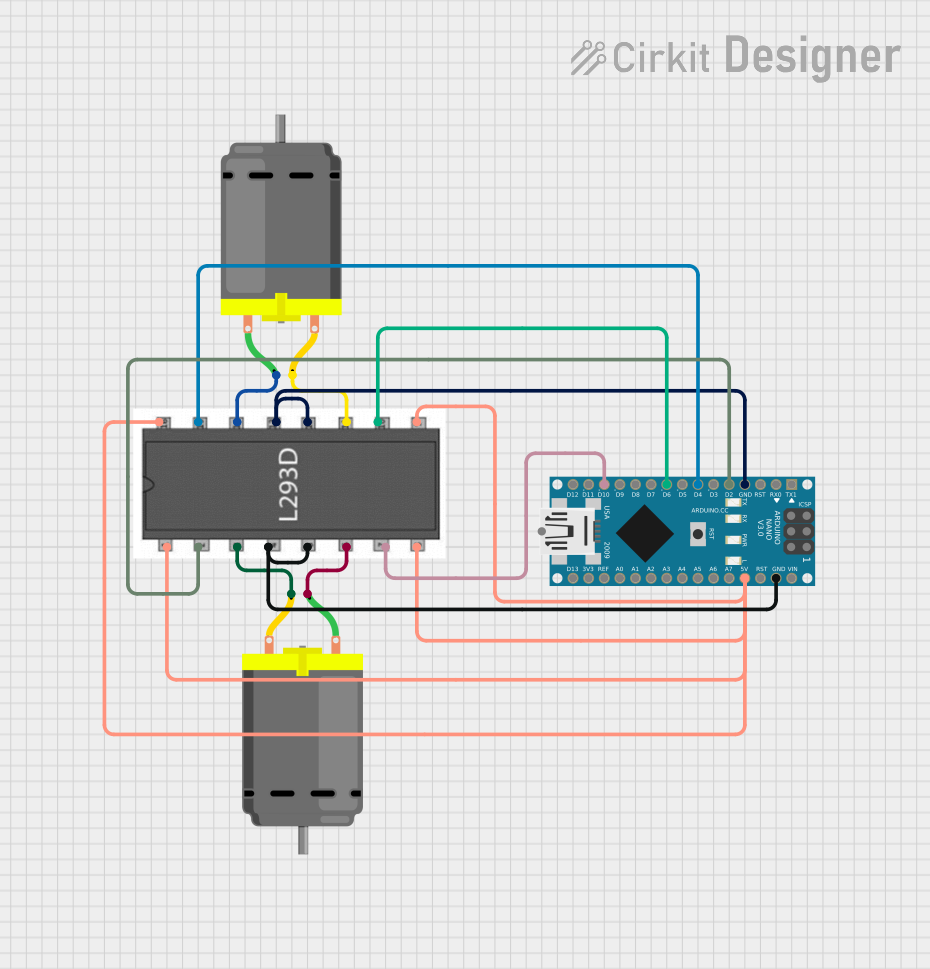
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer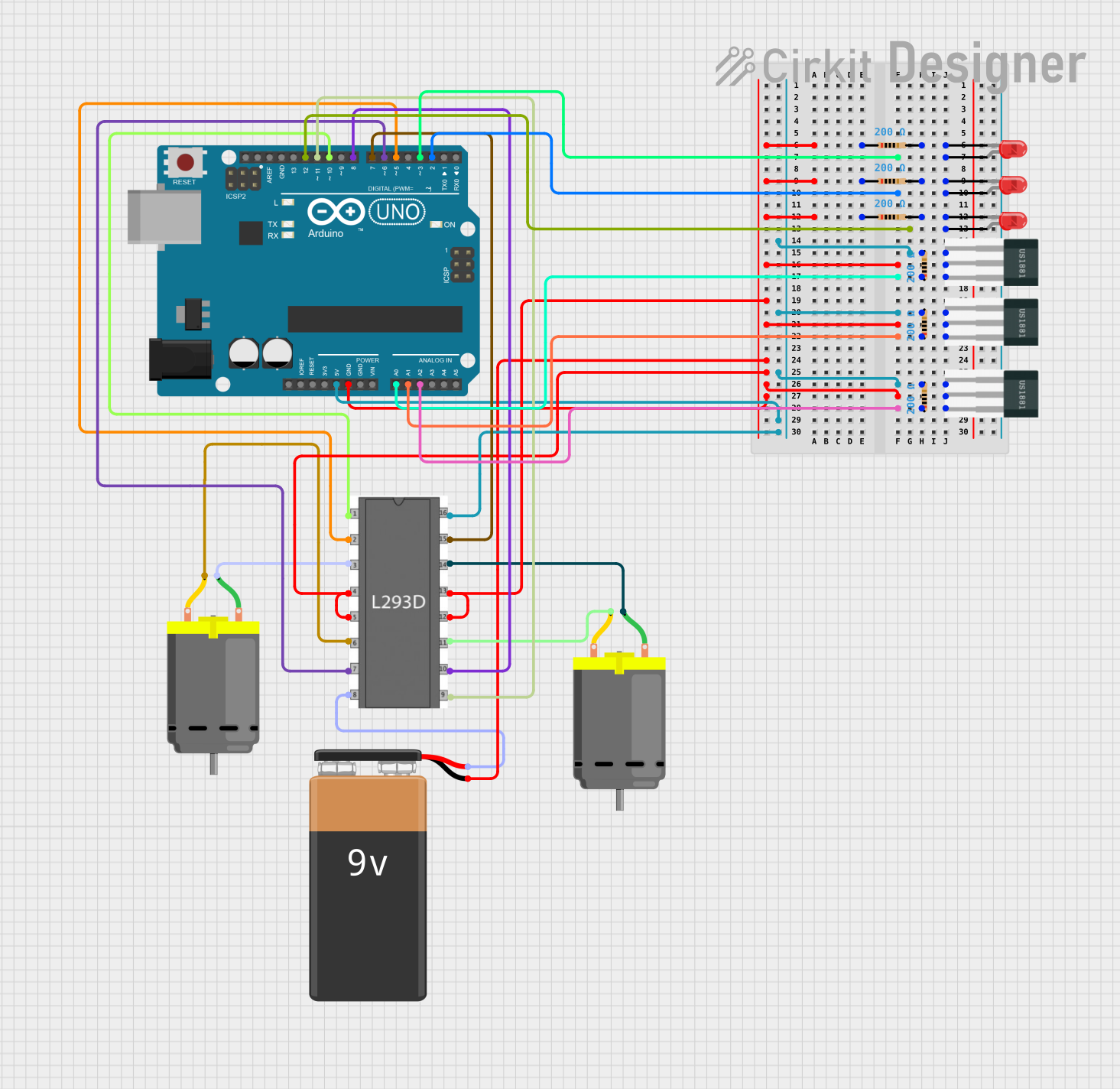
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer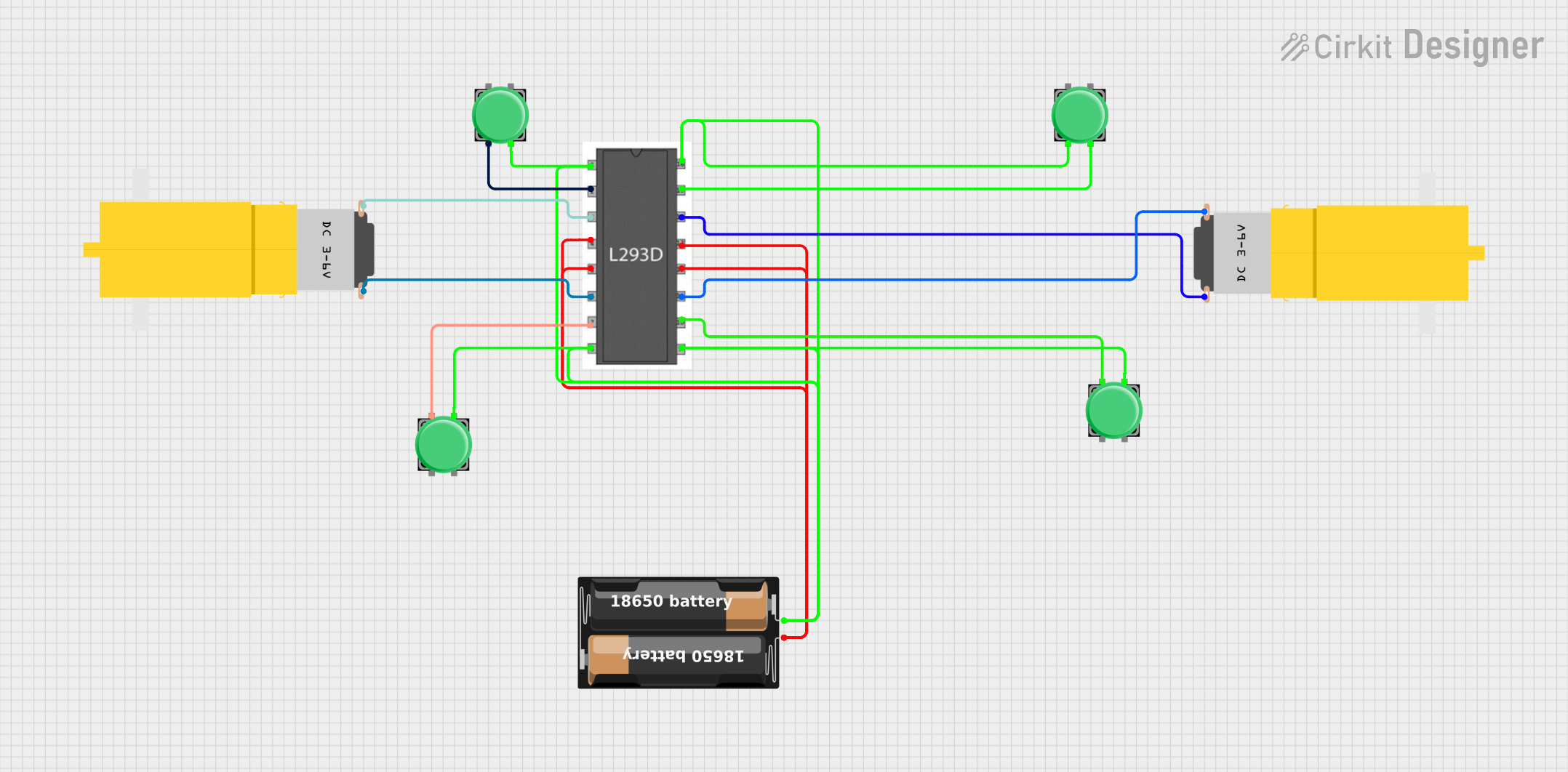
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer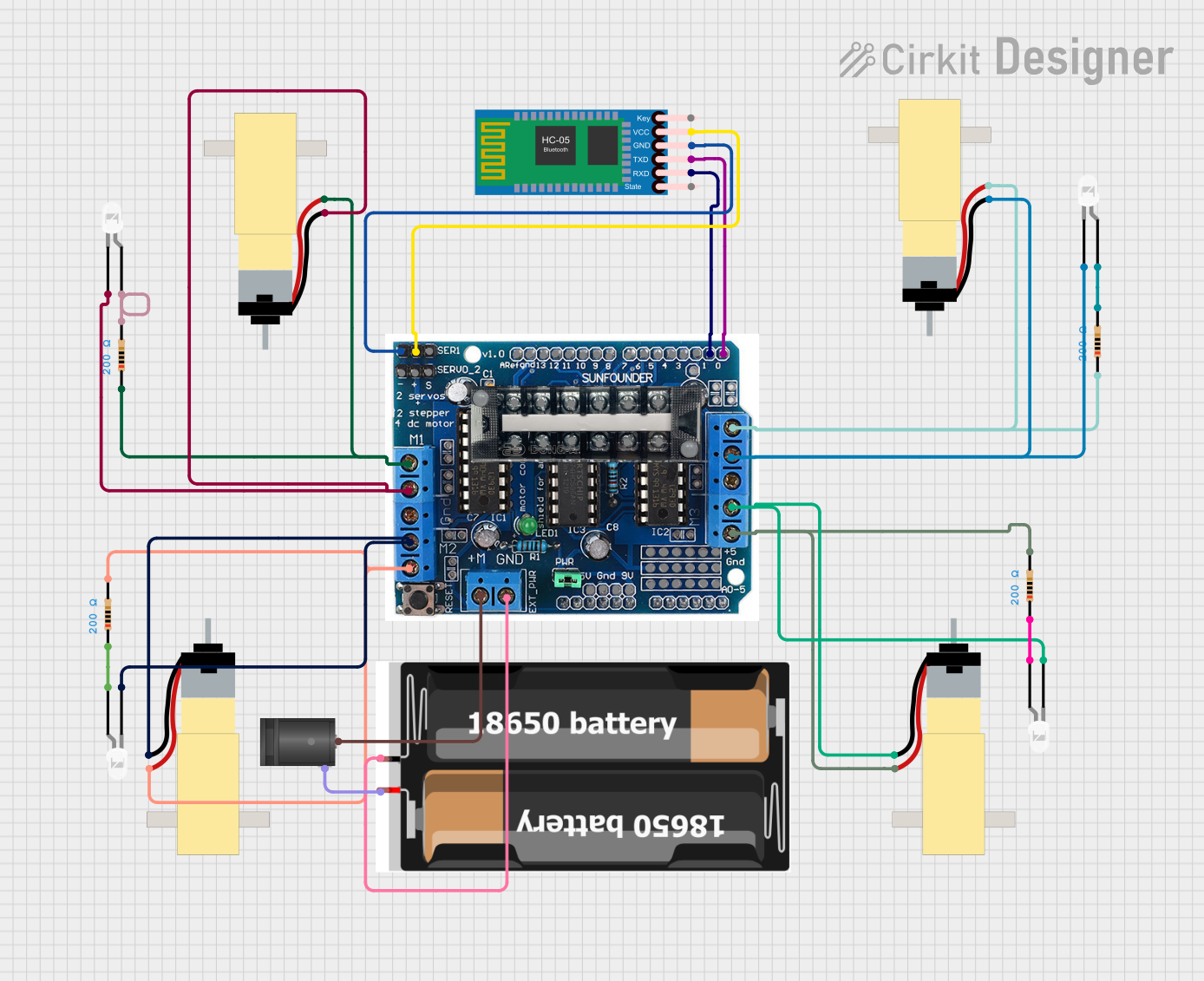
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with driver motor single l293

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics and automation systems
- Motorized toys and vehicles
- Conveyor belt systems
- Stepper motor control in CNC machines
- Home automation projects
- Educational electronics projects
Technical Specifications
The following are the key technical details of the L293 motor driver IC:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc1) | 4.5V to 7V |
| Motor Supply Voltage (Vcc2) | 4.5V to 36V |
| Output Current (per channel) | 600mA (continuous), 1.2A (peak) |
| Logic Input Voltage | 0V to 7V |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +85°C |
| Number of Channels | 2 (dual H-bridge) |
| Control Logic | TTL compatible |
| Package Type | 16-pin DIP or SOIC |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The L293 IC has 16 pins, which are configured as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enable 1,2 | Enables H-bridge 1 (active high) |
| 2 | Input 1 | Logic input for H-bridge 1 (controls motor direction) |
| 3 | Output 1 | Output for H-bridge 1 (connect to motor terminal) |
| 4 | Ground (GND) | Ground connection |
| 5 | Ground (GND) | Ground connection |
| 6 | Output 2 | Output for H-bridge 1 (connect to motor terminal) |
| 7 | Input 2 | Logic input for H-bridge 1 (controls motor direction) |
| 8 | Vcc2 (Motor V+) | Motor supply voltage (4.5V to 36V) |
| 9 | Enable 3,4 | Enables H-bridge 2 (active high) |
| 10 | Input 3 | Logic input for H-bridge 2 (controls motor direction) |
| 11 | Output 3 | Output for H-bridge 2 (connect to motor terminal) |
| 12 | Ground (GND) | Ground connection |
| 13 | Ground (GND) | Ground connection |
| 14 | Output 4 | Output for H-bridge 2 (connect to motor terminal) |
| 15 | Input 4 | Logic input for H-bridge 2 (controls motor direction) |
| 16 | Vcc1 (Logic V+) | Logic supply voltage (4.5V to 7V) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the L293 in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect pin 16 (Vcc1) to a 5V logic supply.
- Connect pin 8 (Vcc2) to the motor supply voltage (4.5V to 36V, depending on the motor).
- Connect pins 4, 5, 12, and 13 to ground (GND).
Motor Connections:
- Connect the motor terminals to the output pins (e.g., Output 1 and Output 2 for Motor 1).
- Use the corresponding input pins (e.g., Input 1 and Input 2) to control the motor direction.
Enable Pins:
- Set the enable pins (Enable 1,2 and Enable 3,4) to HIGH to activate the H-bridges.
Control Logic:
- Use the input pins to control the motor direction:
- Input 1 HIGH and Input 2 LOW: Motor rotates in one direction.
- Input 1 LOW and Input 2 HIGH: Motor rotates in the opposite direction.
- Both inputs LOW: Motor stops.
- Use the input pins to control the motor direction:
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a DC motor using the L293 and an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections
- Connect pin 16 (Vcc1) to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- Connect pin 8 (Vcc2) to an external motor power supply (e.g., 12V).
- Connect pins 4, 5, 12, and 13 to GND.
- Connect Enable 1,2 (pin 1) to Arduino pin 9.
- Connect Input 1 (pin 2) to Arduino pin 2.
- Connect Input 2 (pin 7) to Arduino pin 3.
- Connect the motor terminals to Output 1 (pin 3) and Output 2 (pin 6).
Arduino Code
// Define pin connections
const int enablePin = 9; // Enable pin for H-bridge 1
const int input1 = 2; // Input 1 for H-bridge 1
const int input2 = 3; // Input 2 for H-bridge 1
void setup() {
// Set pin modes
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(input1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(input2, OUTPUT);
// Initialize motor in stopped state
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW); // Disable motor
digitalWrite(input1, LOW); // Set input1 LOW
digitalWrite(input2, LOW); // Set input2 LOW
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in one direction
digitalWrite(enablePin, HIGH); // Enable motor
digitalWrite(input1, HIGH); // Set input1 HIGH
digitalWrite(input2, LOW); // Set input2 LOW
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop motor
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW); // Disable motor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Rotate motor in the opposite direction
digitalWrite(enablePin, HIGH); // Enable motor
digitalWrite(input1, LOW); // Set input1 LOW
digitalWrite(input2, HIGH); // Set input2 HIGH
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop motor
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW); // Disable motor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the motor supply voltage (Vcc2) matches the motor's rated voltage.
- Use a heat sink if the IC gets too hot during operation.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating to prevent damage to the IC.
- Decouple the power supply with capacitors to reduce noise and voltage spikes.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Running:
- Check if the enable pin is set HIGH.
- Verify the input pin logic levels.
- Ensure the motor supply voltage (Vcc2) is connected and within the specified range.
IC Overheating:
- Reduce the motor load or use a heat sink.
- Check for short circuits in the motor connections.
Motor Running in the Wrong Direction:
- Swap the logic levels of the input pins (e.g., Input 1 and Input 2).
No Output Voltage:
- Verify the power supply connections (Vcc1 and Vcc2).
- Ensure the ground pins are properly connected.
FAQs
Q: Can the L293 drive stepper motors?
A: Yes, the L293 can drive stepper motors by controlling the sequence of inputs to the H-bridges.
Q: What is the difference between Vcc1 and Vcc2?
A: Vcc1 powers the logic circuitry (4.5V to 7V), while Vcc2 powers the motors (4.5V to 36V).
Q: Can I use the L293 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: The L293 requires a minimum logic voltage of 4.5V, so it is not directly compatible with 3.3V logic. Use a level shifter or a 5V microcontroller.
Q: How many motors can the L293 control?
A: The L293 can control two DC motors or one stepper motor.