
How to Use CO2 sensor : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with CO2 sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with CO2 sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A CO2 sensor detects the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air. It is commonly used for monitoring air quality and ensuring proper ventilation in indoor environments such as offices, homes, greenhouses, and industrial facilities. These sensors are essential for maintaining healthy air quality, optimizing energy usage in HVAC systems, and ensuring compliance with safety standards in enclosed spaces.
Explore Projects Built with CO2 sensor
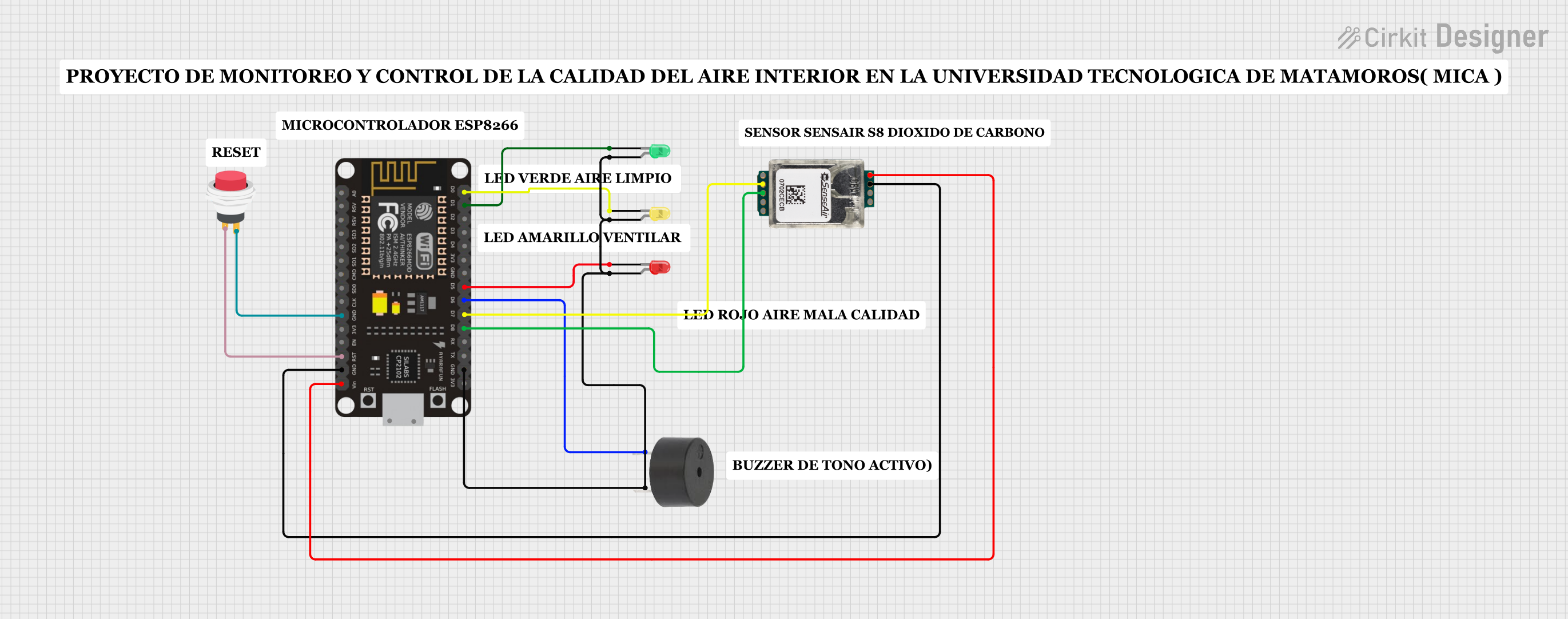
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer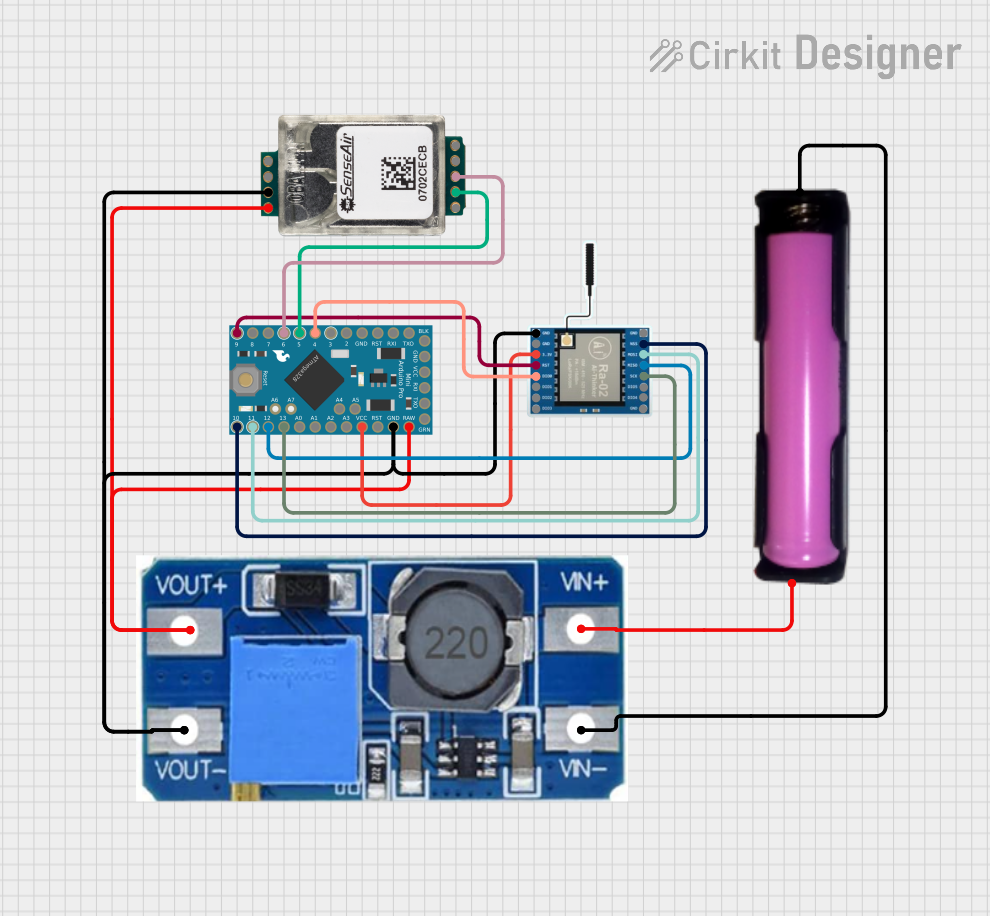
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer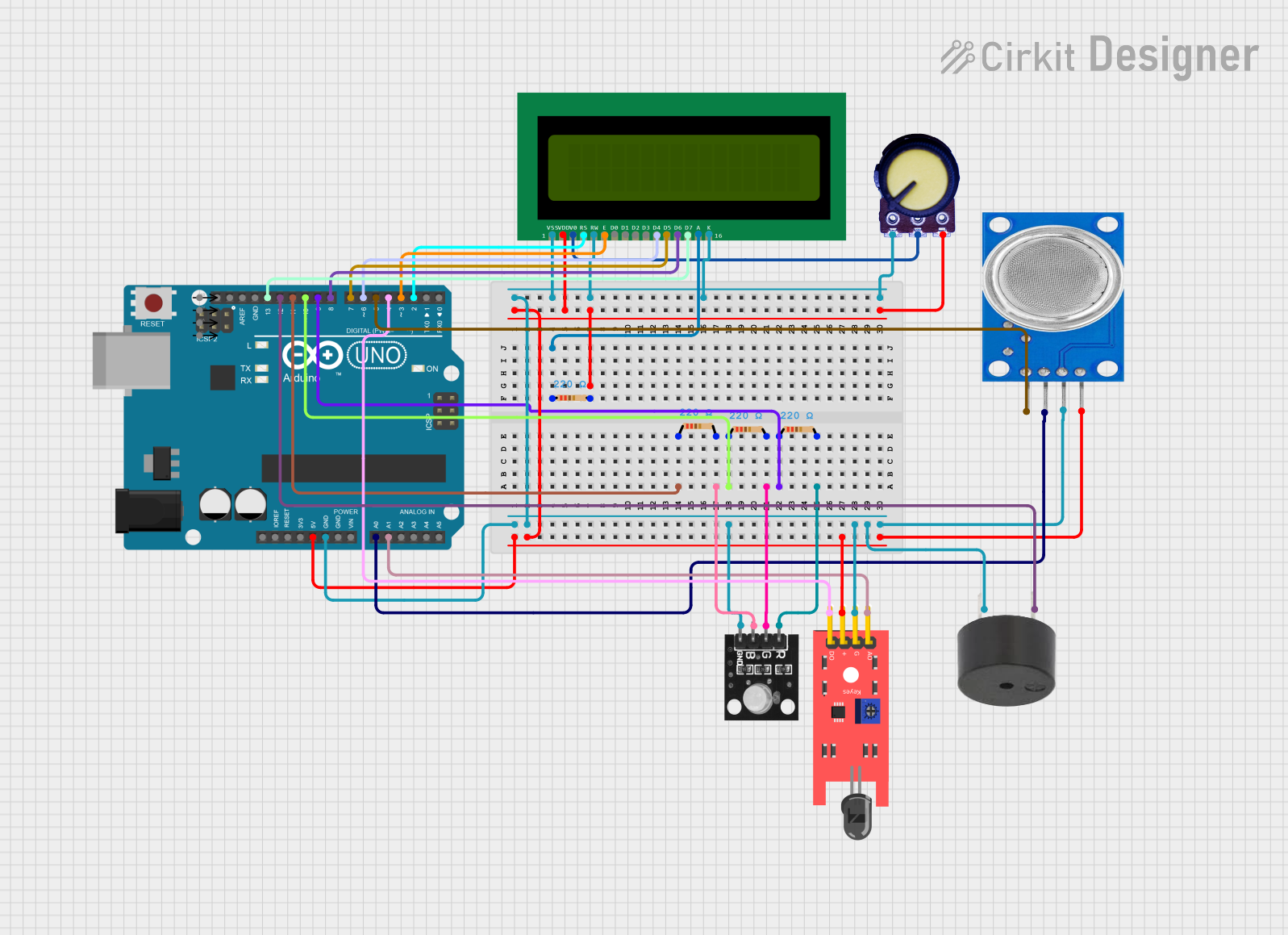
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer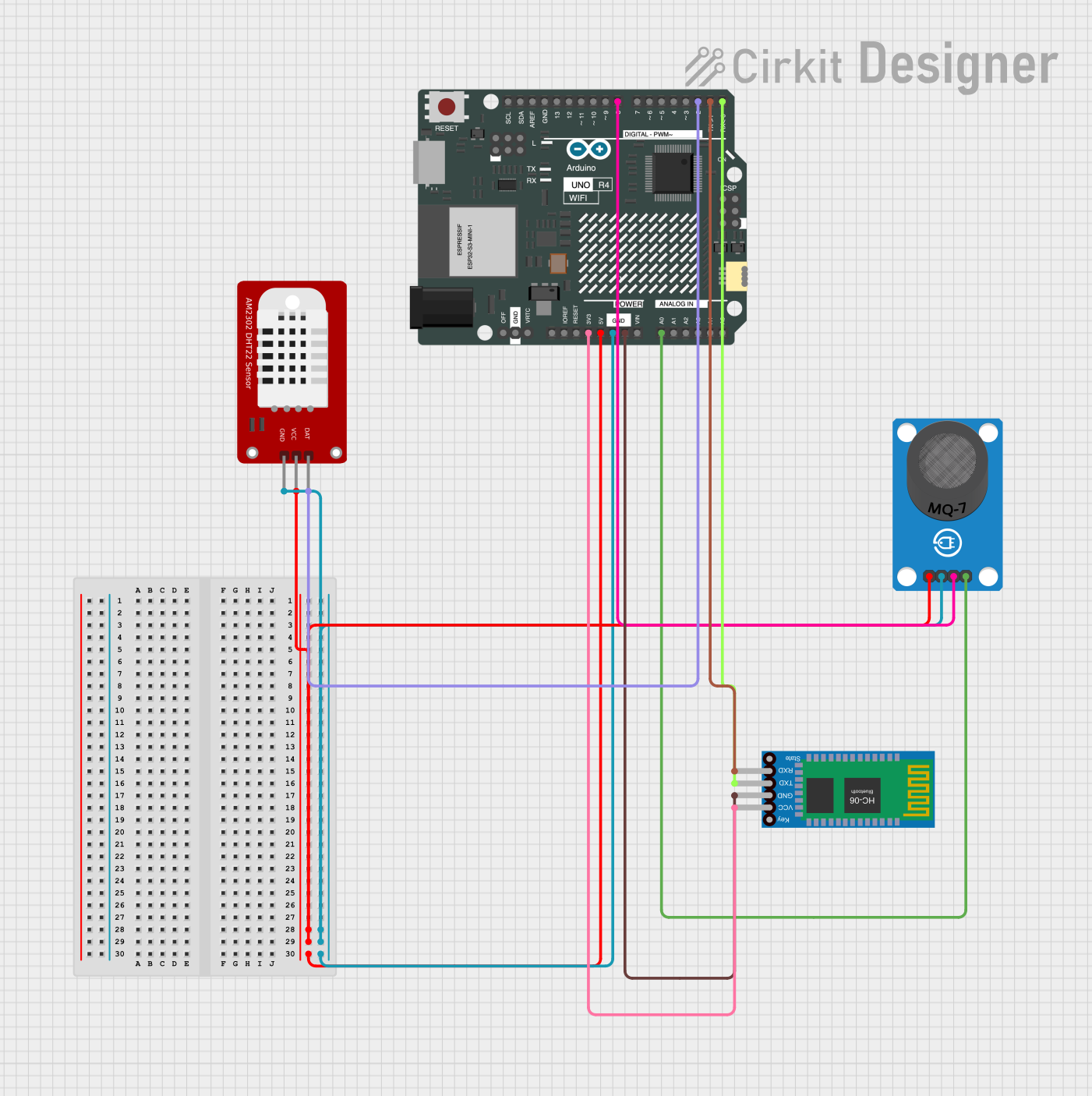
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with CO2 sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical CO2 sensor. Note that specific values may vary depending on the sensor model.
Key Specifications
- Measurement Range: 0 to 5000 ppm (parts per million)
- Accuracy: ±50 ppm or ±5% of reading (whichever is greater)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
- Current Consumption: 10 mA to 150 mA (depending on the sensor type)
- Output Signal: Analog voltage, PWM, or digital (I2C/UART)
- Response Time: <30 seconds
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to 50°C
- Humidity Range: 0% to 95% RH (non-condensing)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Below is a typical pinout for a CO2 sensor with digital and analog output capabilities:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V or 5V DC, depending on the sensor model). |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection. |
| 3 | OUT/ANALOG | Analog output signal proportional to CO2 concentration. |
| 4 | PWM/DIGITAL | Digital output (PWM or UART/I2C, depending on the sensor model). |
| 5 | RX | UART receive pin (used for communication with microcontrollers, if applicable). |
| 6 | TX | UART transmit pin (used for communication with microcontrollers, if applicable). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the CO2 Sensor in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Choose Output Type: Depending on your application, use either the analog output (OUT/ANALOG pin) or the digital output (PWM/DIGITAL pin). For UART communication, connect the RX and TX pins to the corresponding pins on your microcontroller.
- Read the Output:
- For analog output, measure the voltage on the OUT/ANALOG pin using an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) on your microcontroller.
- For digital output, read the PWM signal or use UART/I2C communication to retrieve CO2 concentration data.
- Calibrate the Sensor: Some CO2 sensors require periodic calibration to maintain accuracy. Refer to the sensor's datasheet for calibration instructions.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Preheat Time: Allow the sensor to warm up for 1-2 minutes after powering it on to ensure accurate readings.
- Ventilation: Place the sensor in a location with good airflow to avoid stagnant air affecting the readings.
- Avoid Contaminants: Keep the sensor away from dust, water, and volatile chemicals, as these can damage the sensor or affect its accuracy.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to prevent fluctuations in the sensor's output.
Example: Connecting a CO2 Sensor to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and read data from a CO2 sensor with an analog output using an Arduino UNO.
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the VCC pin of the sensor to the 5V pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the sensor to the GND pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the OUT/ANALOG pin of the sensor to the A0 pin on the Arduino.
Arduino Code
// CO2 Sensor Example Code for Arduino UNO
// This code reads the analog output of a CO2 sensor and prints the CO2 level
// to the Serial Monitor. Ensure the sensor is connected to pin A0.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor's output
float voltage; // Variable to store the sensor's output voltage
float co2Concentration; // Variable to store the calculated CO2 concentration
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage (assuming 5V reference)
voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Convert the voltage to CO2 concentration (ppm)
// Example formula: CO2 (ppm) = (voltage - 0.4) * 2000
// Adjust the formula based on your sensor's datasheet
co2Concentration = (voltage - 0.4) * 2000;
// Print the CO2 concentration to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("CO2 Concentration: ");
Serial.print(co2Concentration);
Serial.println(" ppm");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings:
- Solution: Check the power supply voltage and ensure proper connections to the sensor.
- Tip: Verify that the sensor's preheat time has elapsed before taking readings.
Fluctuating or Unstable Readings:
- Solution: Ensure the sensor is placed in a well-ventilated area and away from heat sources or drafts.
- Tip: Use a capacitor across the power supply pins to filter out noise.
Sensor Not Responding to UART/I2C Commands:
- Solution: Double-check the baud rate and communication protocol settings in your code.
- Tip: Refer to the sensor's datasheet for the correct communication parameters.
Sensor Requires Frequent Calibration:
- Solution: Follow the calibration procedure outlined in the sensor's datasheet.
- Tip: Use a known CO2 concentration environment for accurate calibration.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the CO2 sensor outdoors?
- A: Most CO2 sensors are designed for indoor use. Outdoor use may expose the sensor to extreme temperatures, humidity, and contaminants, which can affect its performance.
Q: How often should I calibrate the sensor?
- A: Calibration frequency depends on the sensor model and usage conditions. Refer to the manufacturer's recommendations, but typically, calibration is required every 6-12 months.
Q: Can I use the sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
- A: Yes, as long as the sensor supports a 3.3V power supply. Check the datasheet to confirm compatibility.
Q: What is the lifespan of a CO2 sensor?
- A: The lifespan varies by model but is typically 5-10 years under normal operating conditions.