
How to Use Shunt 75MV/20A: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
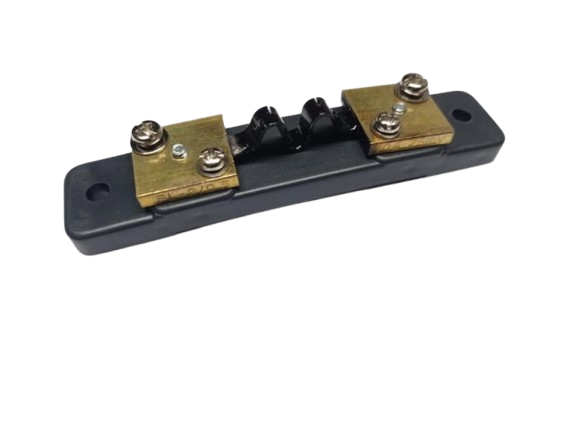

 Design with Shunt 75MV/20A in Cirkit Designer
Design with Shunt 75MV/20A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A shunt is a precision resistor designed to measure current by generating a small, proportional voltage drop across its terminals. The Shunt 75MV/20A is specifically calibrated to produce a voltage drop of 75 millivolts (mV) when a current of 20 amperes (A) flows through it. This makes it an ideal component for current measurement in high-power circuits, where direct current measurement is impractical.
Explore Projects Built with Shunt 75MV/20A
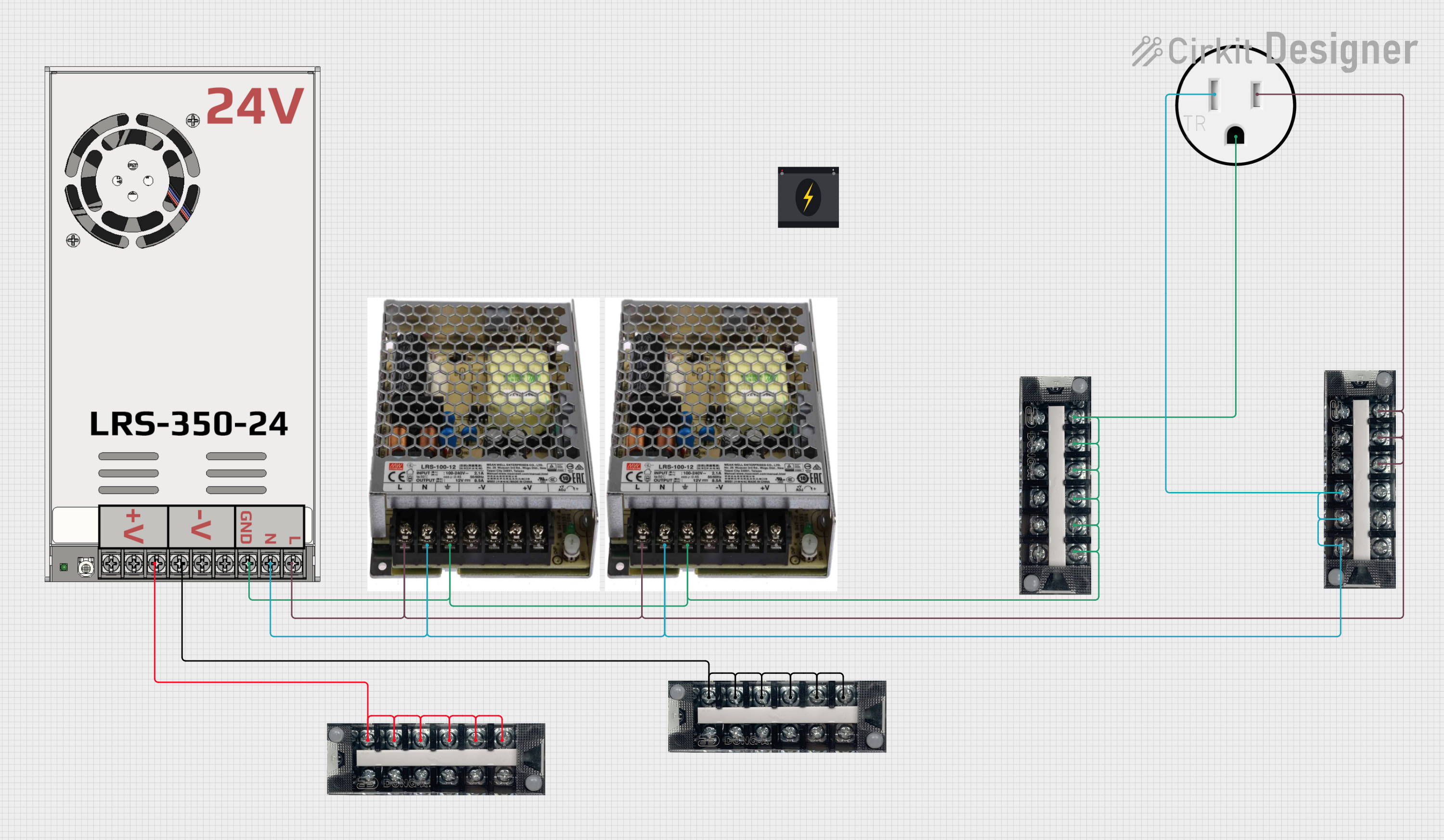
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer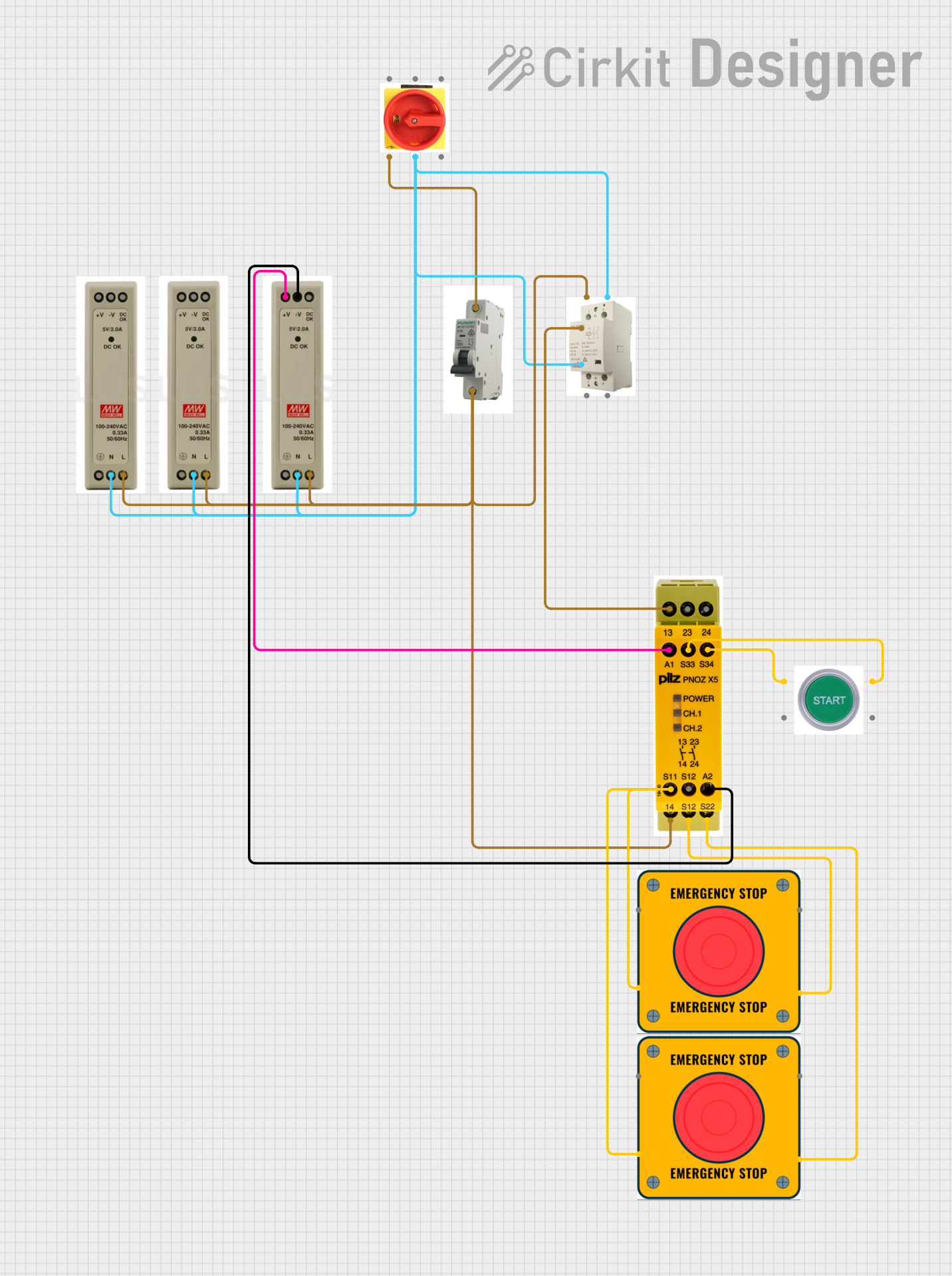
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer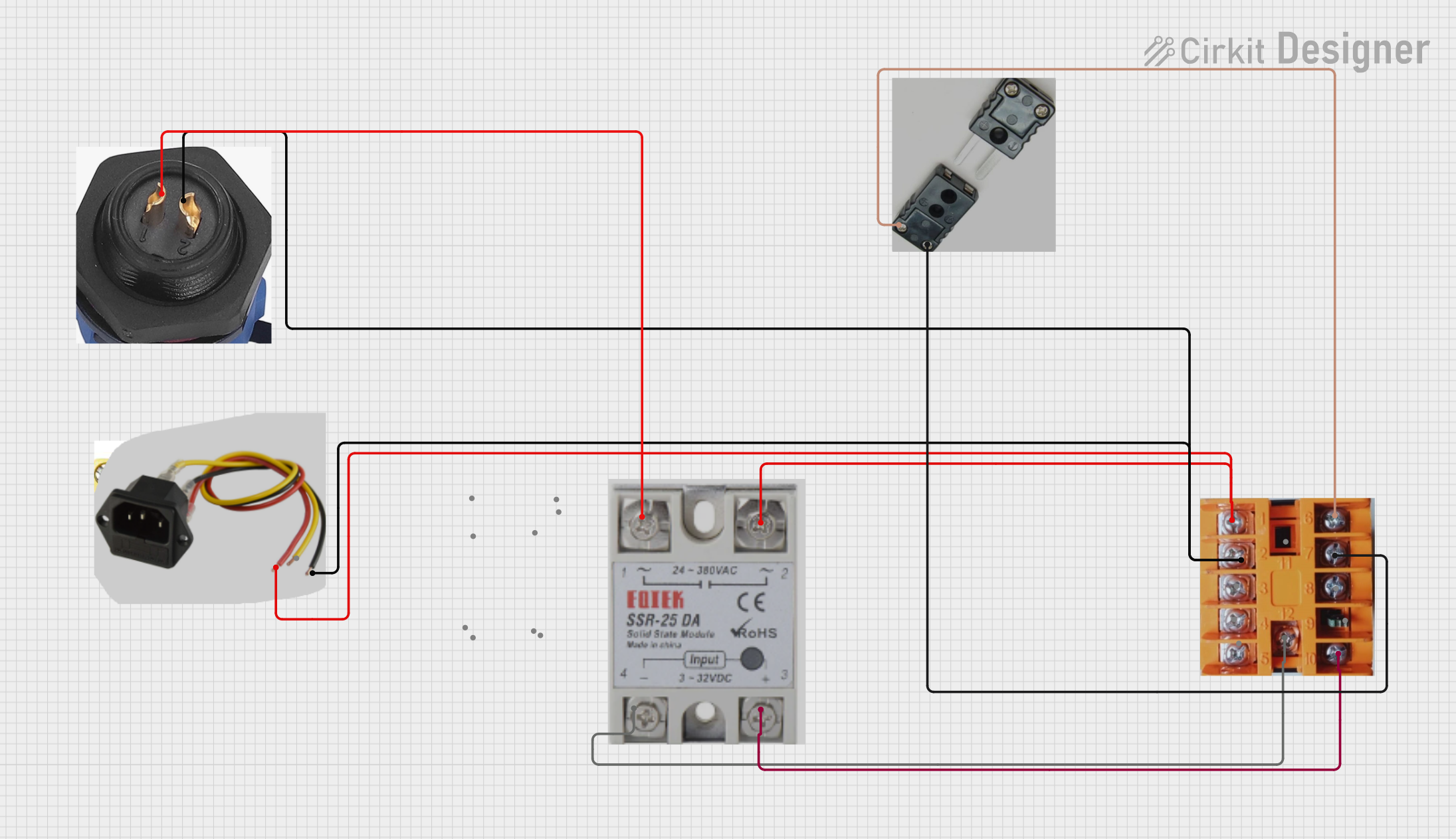
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Shunt 75MV/20A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Current measurement in power supply systems
- Battery monitoring and management systems
- Industrial equipment and motor control
- Energy meters and power monitoring devices
- Integration with microcontrollers and data acquisition systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Maximum Current Rating: 20A
- Voltage Drop at Maximum Current: 75mV
- Resistance: 3.75 milliohms (calculated as 75mV / 20A)
- Accuracy: Typically ±0.5% or better
- Material: Manganin or similar low-temperature-coefficient alloy
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
- Mounting Style: Screw terminals or solderable connections
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Shunt 75MV/20A typically has two main terminals for current flow and two smaller terminals for voltage measurement. These are described in the table below:
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Current Input (+) | Connect to the positive side of the current source or load. |
| Current Output (-) | Connect to the negative side of the current source or load. |
| Voltage Sense (+) | Connect to the positive input of a voltmeter or ADC for voltage measurement. |
| Voltage Sense (-) | Connect to the negative input of a voltmeter or ADC for voltage measurement. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Shunt in a Circuit
Placement in the Circuit:
- Place the shunt in series with the load whose current you want to measure.
- Ensure the current flows from the Current Input (+) terminal to the Current Output (-) terminal.
Voltage Measurement:
- Use a high-impedance voltmeter or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to measure the voltage across the Voltage Sense (+) and Voltage Sense (-) terminals.
- The measured voltage will be proportional to the current flowing through the shunt, based on the formula: [ I = \frac{V}{R} ] where ( I ) is the current, ( V ) is the measured voltage, and ( R ) is the shunt resistance (3.75 milliohms).
Connection to Microcontrollers:
- If using a microcontroller like an Arduino UNO, connect the Voltage Sense (+) terminal to an analog input pin and the Voltage Sense (-) terminal to the ground (GND).
- Use the ADC to read the voltage and calculate the current.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Dissipation: Ensure the shunt's power dissipation does not exceed its rating. For the Shunt 75MV/20A, the maximum power dissipation is: [ P = I^2 \times R = 20^2 \times 0.00375 = 1.5 , \text{W} ]
- Wiring: Use thick, low-resistance wires for the current-carrying terminals to minimize additional resistance.
- Temperature Effects: Avoid placing the shunt near heat sources, as temperature changes can affect its resistance and accuracy.
- Calibration: Periodically verify the shunt's accuracy using a known current source and a precision voltmeter.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The following code demonstrates how to measure current using the Shunt 75MV/20A and an Arduino UNO:
// Define the analog pin connected to the Voltage Sense (+) terminal
const int shuntPin = A0;
// Shunt resistance in ohms (3.75 milliohms)
const float shuntResistance = 0.00375;
// ADC reference voltage (5V for Arduino UNO)
const float adcReferenceVoltage = 5.0;
// ADC resolution (10-bit ADC for Arduino UNO)
const int adcResolution = 1024;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the raw ADC value
int adcValue = analogRead(shuntPin);
// Convert ADC value to voltage
float shuntVoltage = (adcValue * adcReferenceVoltage) / adcResolution;
// Calculate current using Ohm's Law (I = V / R)
float current = shuntVoltage / shuntResistance;
// Print the measured current to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current, 2); // Print current with 2 decimal places
Serial.println(" A");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Voltage Reading Across the Shunt:
- Cause: Improper wiring or no current flowing through the shunt.
- Solution: Verify the connections and ensure the shunt is in series with the load.
Inaccurate Current Measurement:
- Cause: High resistance in the wiring or incorrect ADC reference voltage.
- Solution: Use thick wires for current connections and ensure the ADC reference voltage is correctly set in the code.
Overheating of the Shunt:
- Cause: Current exceeds the shunt's maximum rating.
- Solution: Ensure the current does not exceed 20A. Use a higher-rated shunt if necessary.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Cause: Electrical noise or poor connections.
- Solution: Use shielded cables for voltage sense lines and ensure all connections are secure.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the Shunt 75MV/20A for AC current measurement?
A1: No, this shunt is designed for DC current measurement. For AC, you would need additional circuitry, such as a rectifier and filter.
Q2: What happens if I exceed the 20A current rating?
A2: Exceeding the current rating can cause excessive heat, damage the shunt, and reduce measurement accuracy. Always stay within the specified limits.
Q3: Can I use this shunt with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A3: Yes, but ensure the voltage drop across the shunt does not exceed the ADC input range of the microcontroller. Adjust the code accordingly for the 3.3V reference voltage.
Q4: How do I improve measurement accuracy?
A4: Use a high-resolution ADC, minimize noise in the circuit, and ensure proper calibration of the shunt and measurement system.