
How to Use abl: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
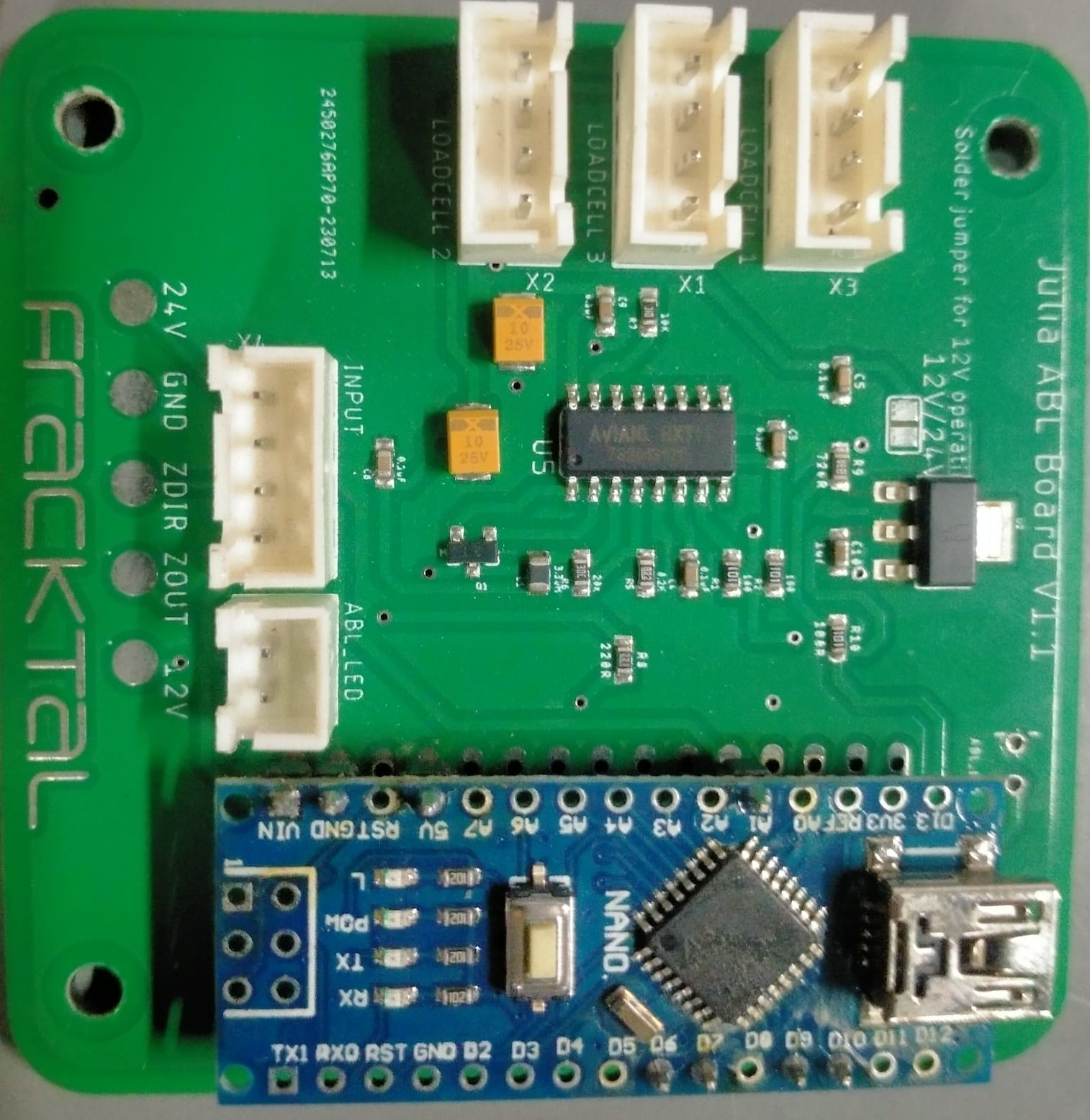
 Design with abl in Cirkit Designer
Design with abl in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An Active Bus Load (ABL) is a critical component in power distribution systems designed to manage and balance electrical loads across multiple circuits. By dynamically adjusting the load, the ABL ensures efficient operation, prevents overloads, and maintains system stability. It is commonly used in industrial power systems, renewable energy setups, and data centers where load balancing is essential for optimal performance and safety.
Explore Projects Built with abl
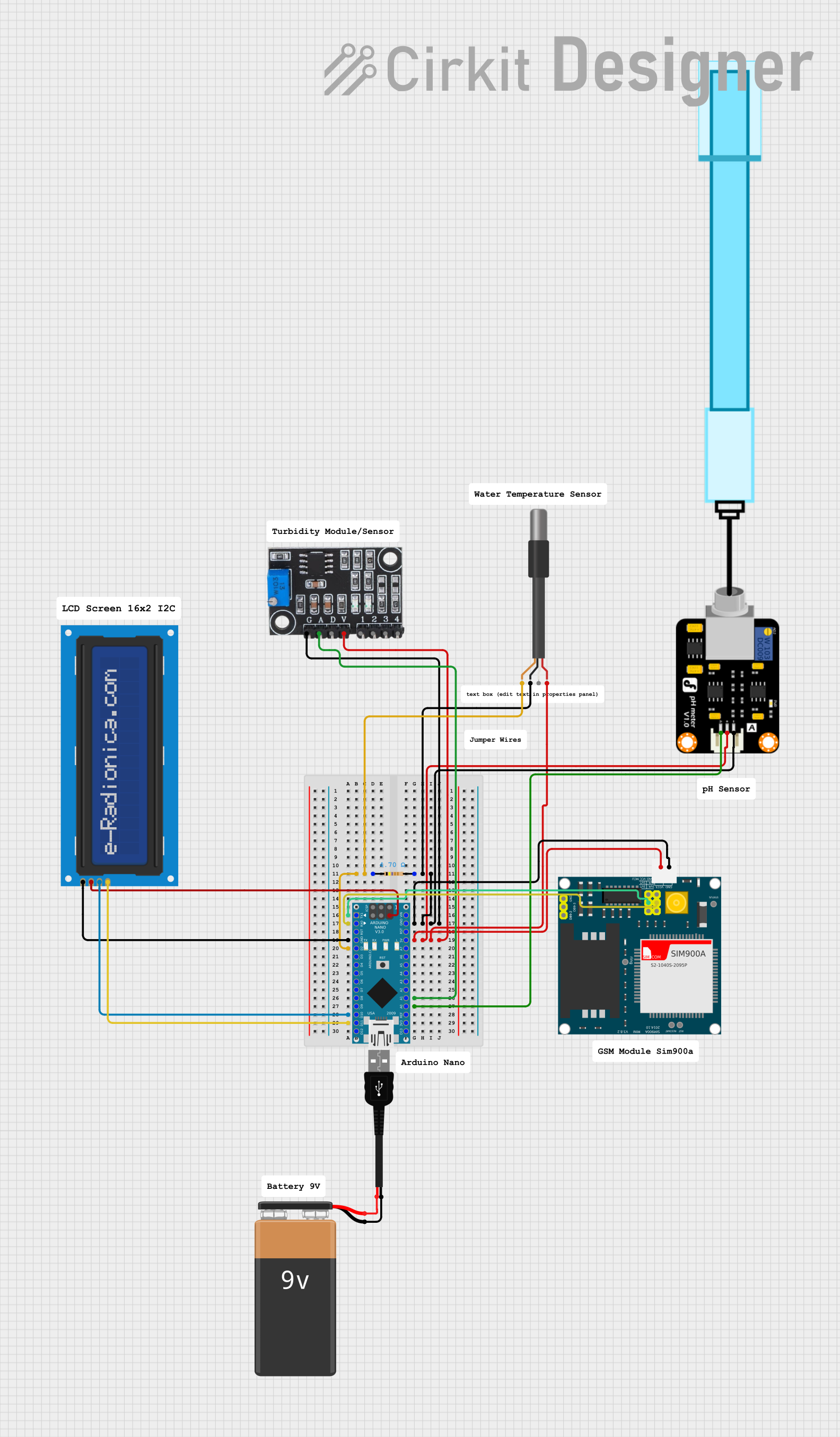
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer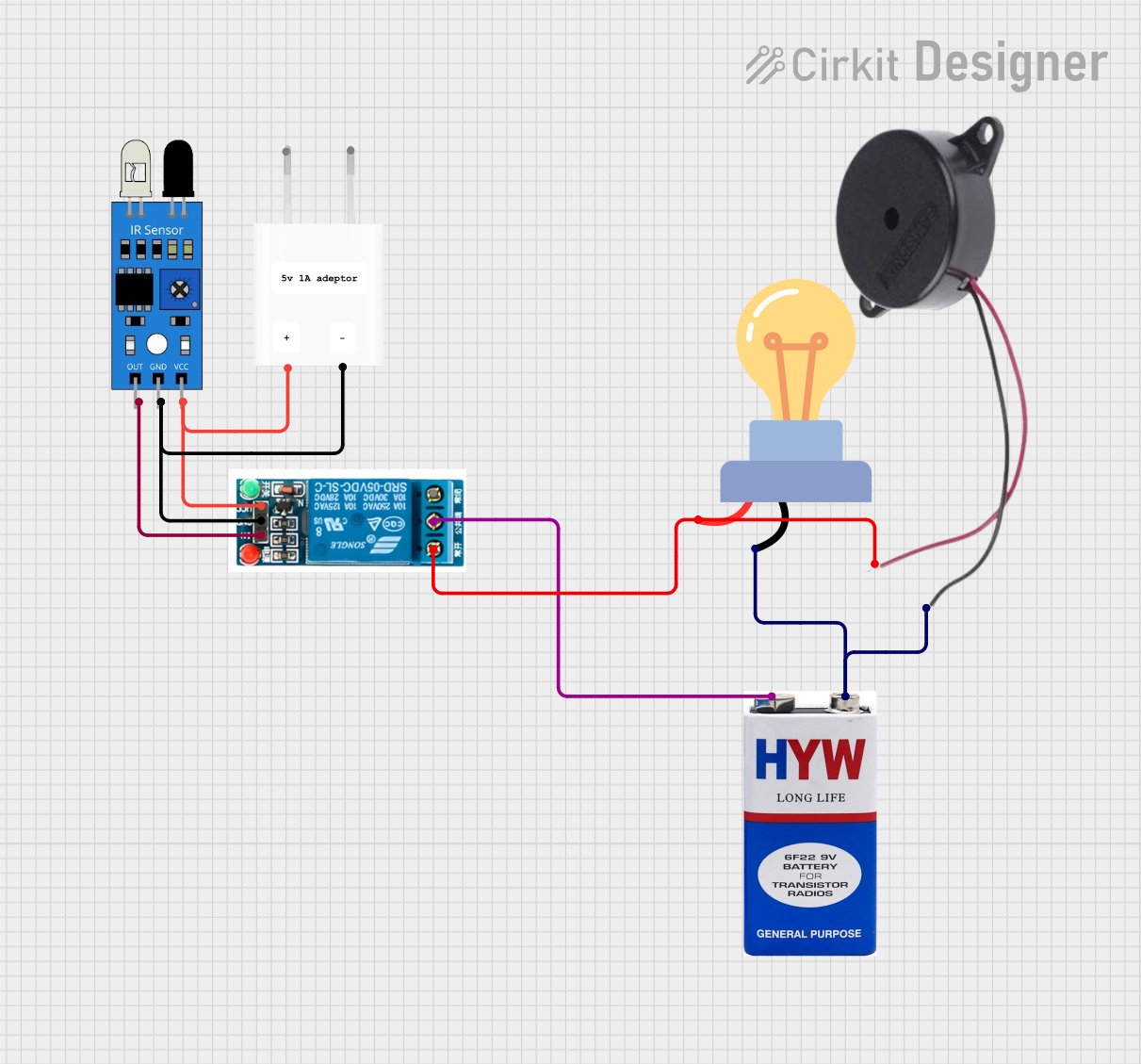
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer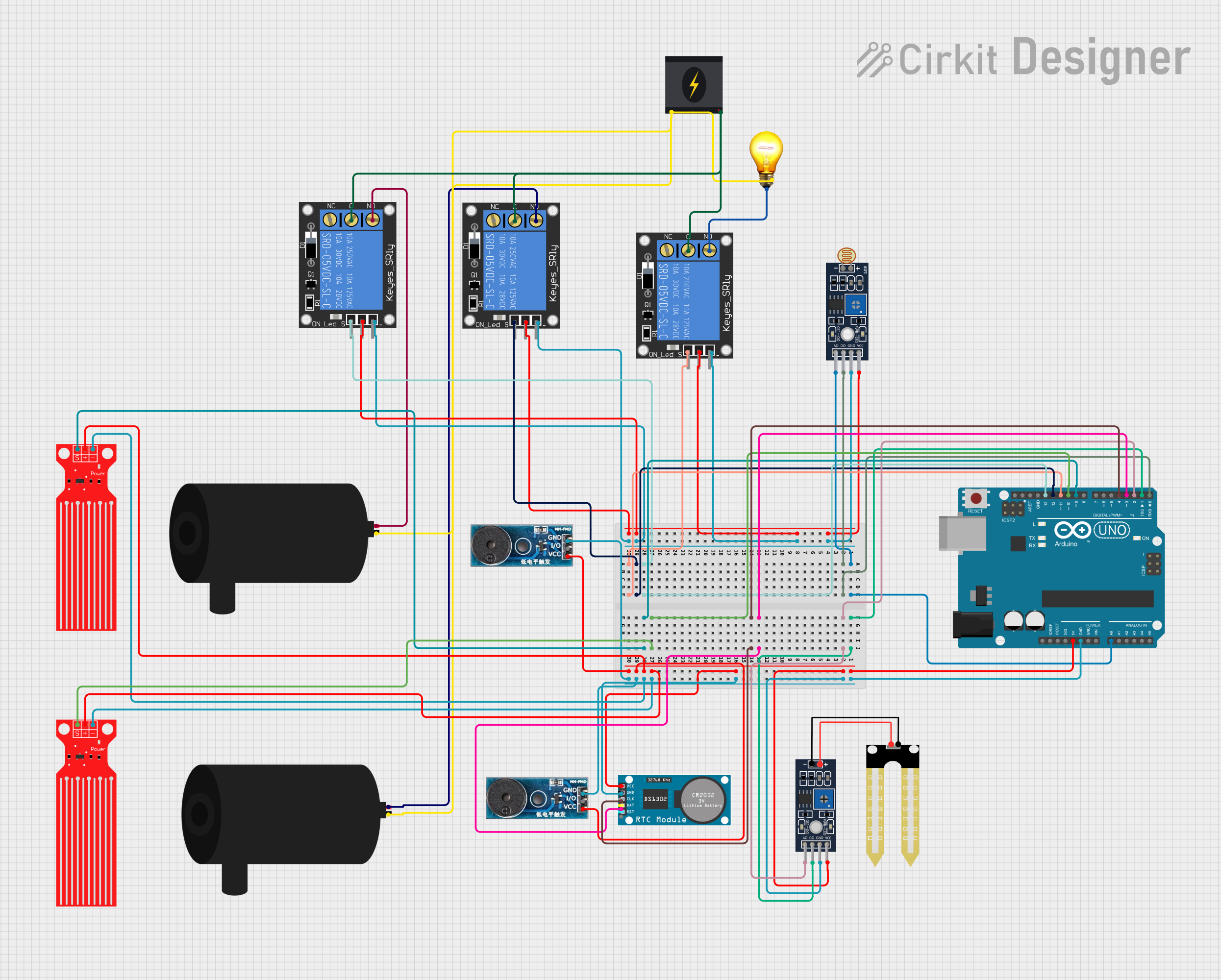
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with abl

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial Power Systems: Balancing loads across multiple circuits to prevent overloading and ensure efficient energy distribution.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Managing power distribution in solar, wind, or hybrid energy systems.
- Data Centers: Ensuring stable power delivery to critical IT infrastructure.
- Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Distributing power evenly across multiple charging points.
- Smart Grids: Enhancing grid stability by dynamically adjusting loads.
Technical Specifications
The ABL is designed to operate in a wide range of power distribution systems. Below are its key technical specifications:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage Range | 100V to 600V AC/DC |
| Maximum Current Rating | 50A |
| Power Rating | Up to 30 kW |
| Efficiency | ≥ 95% |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
| Communication Protocols | Modbus, CAN, RS485 |
| Dimensions | 150mm x 100mm x 50mm |
| Weight | 1.2 kg |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ABL typically features a terminal block for power connections and a communication interface for control. Below is the pin configuration:
Power Terminal Block
| Pin Number | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | L (Line) | Connect to the live wire of the power source. |
| 2 | N (Neutral) | Connect to the neutral wire of the power source. |
| 3 | GND | Ground connection for safety. |
Communication Interface (RS485 Example)
| Pin Number | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | RS485 Data Line A |
| 2 | B | RS485 Data Line B |
| 3 | GND | Ground for communication interface. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ABL in a Circuit
Power Connection:
- Connect the live (L) and neutral (N) wires of the power source to the corresponding terminals on the ABL.
- Ensure the ground (GND) terminal is properly connected to the system ground for safety.
Load Connection:
- Connect the output terminals of the ABL to the load(s) you wish to manage.
- Verify that the total load does not exceed the ABL's maximum current and power ratings.
Communication Setup:
- If using a communication protocol (e.g., Modbus or RS485), connect the ABL's communication pins to the corresponding controller or monitoring system.
- Configure the communication settings (e.g., baud rate, device address) as per the system requirements.
Configuration:
- Use the ABL's software interface or hardware controls to set load balancing parameters, such as maximum current per circuit or priority levels for specific loads.
Testing:
- Power on the system and monitor the ABL's operation to ensure proper load balancing and communication.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Safety First: Always disconnect power before wiring or modifying connections.
- Load Ratings: Ensure the connected loads do not exceed the ABL's rated capacity.
- Ventilation: Install the ABL in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly check for firmware updates to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
- Communication Protocols: Use shielded cables for communication lines to minimize interference.
Example: Connecting an ABL to an Arduino UNO
The ABL can be integrated with an Arduino UNO for monitoring and control via RS485. Below is an example code snippet:
#include <ModbusMaster.h>
// Create an instance of the ModbusMaster library
ModbusMaster node;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
node.begin(1, Serial); // Set Modbus slave ID to 1 and use Serial for communication
}
void loop() {
uint8_t result;
uint16_t data;
// Read the current load value from the ABL (register address 0x0001)
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x0001, 1);
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
data = node.getResponseBuffer(0); // Get the value from the response buffer
Serial.print("Current Load: ");
Serial.println(data); // Print the load value to the serial monitor
} else {
Serial.println("Error reading from ABL"); // Print error message if communication fails
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next read
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: ABL does not power on.
- Solution: Check the power connections and ensure the input voltage is within the specified range.
Issue: Load balancing is not functioning correctly.
- Solution: Verify the load connections and ensure the total load does not exceed the ABL's capacity. Check the configuration settings.
Issue: Communication with the ABL fails.
- Solution: Ensure the communication cables are properly connected and not damaged. Verify the communication settings (e.g., baud rate, device address) match those of the controller.
Issue: ABL overheats during operation.
- Solution: Check for proper ventilation and ensure the ambient temperature is within the operating range. Reduce the load if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can the ABL handle both AC and DC loads?
A: Yes, the ABL is designed to support both AC and DC loads within its specified voltage and current ratings.Q: How do I update the ABL's firmware?
A: Refer to the manufacturer's instructions for firmware updates. Typically, this involves connecting the ABL to a computer via a USB or communication interface.Q: Is the ABL compatible with renewable energy systems?
A: Yes, the ABL is ideal for managing and balancing loads in renewable energy setups such as solar or wind power systems.Q: Can I use the ABL without a communication interface?
A: Yes, the ABL can operate in standalone mode, but using a communication interface allows for advanced monitoring and control.
This concludes the documentation for the ABL (Active Bus Load). For further assistance, refer to the manufacturer's support resources.