
How to Use SMD RGB LED: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with SMD RGB LED in Cirkit Designer
Design with SMD RGB LED in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SMD RGB LED is a surface-mount device that integrates red, green, and blue LEDs into a single compact package. By varying the intensity of each LED, this component can produce a wide spectrum of colors, making it ideal for applications requiring dynamic lighting effects. Its small size and versatility make it a popular choice for modern electronics, including wearables, displays, and decorative lighting.
Explore Projects Built with SMD RGB LED
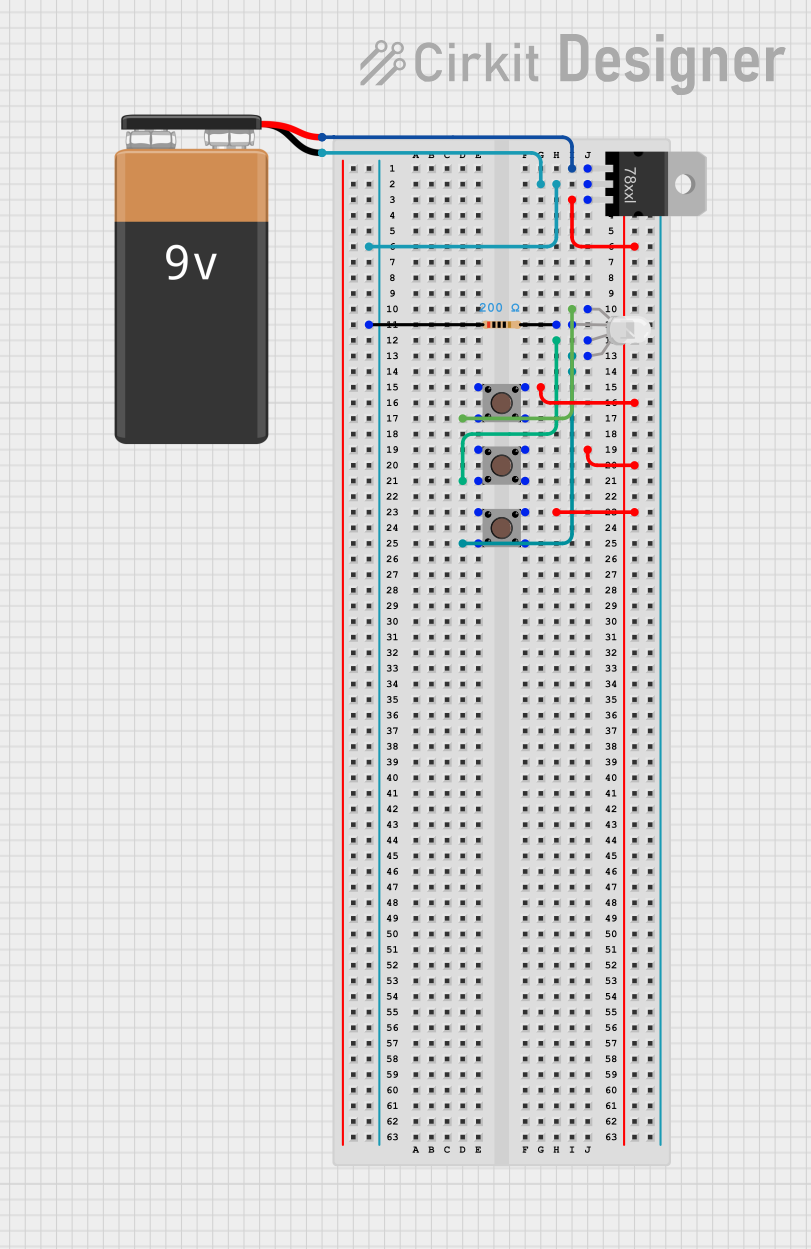
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer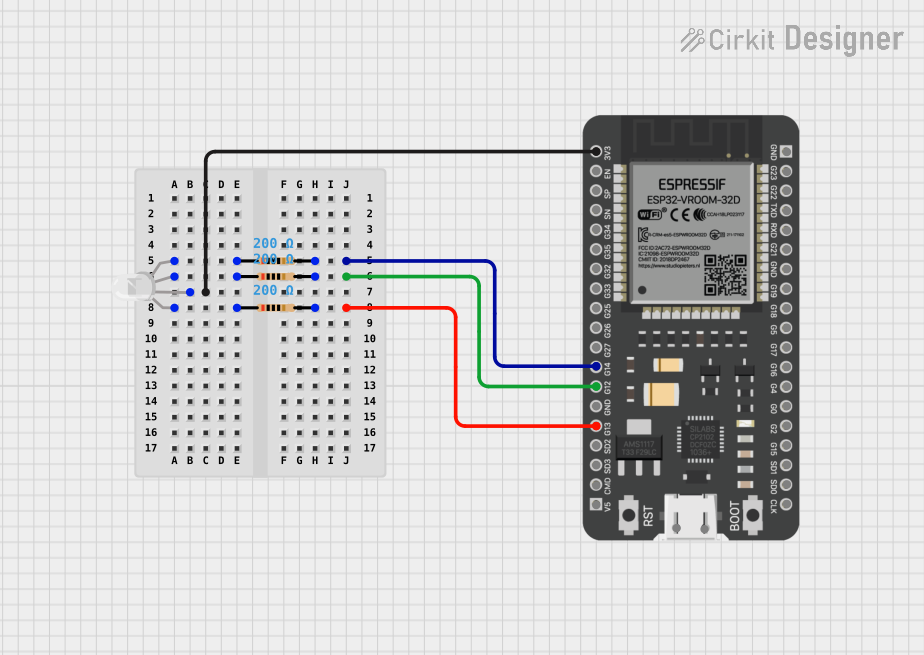
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer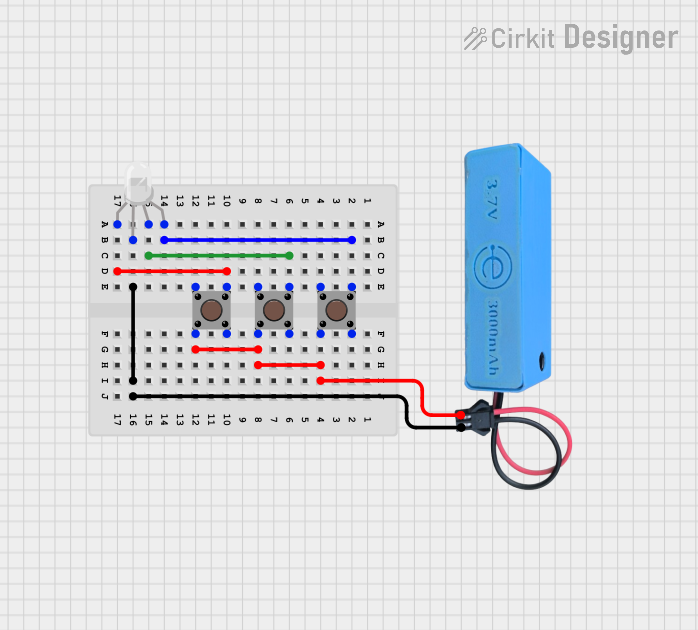
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer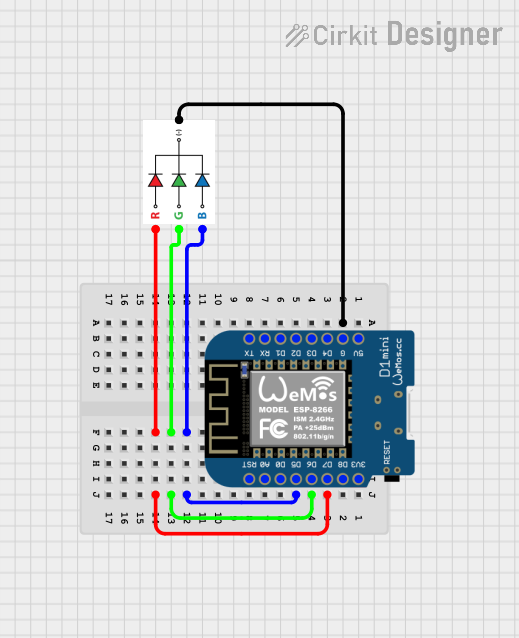
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SMD RGB LED

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- LED displays and signage
- Backlighting for screens and keyboards
- Wearable devices and smart gadgets
- Decorative and ambient lighting
- IoT devices with visual feedback
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a typical SMD RGB LED. Note that specific values may vary depending on the manufacturer.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Forward Voltage (Red) | 1.8V - 2.2V |
| Forward Voltage (Green) | 2.8V - 3.2V |
| Forward Voltage (Blue) | 2.8V - 3.2V |
| Forward Current | 20mA (per color channel) |
| Power Dissipation | ~60mW (total) |
| Viewing Angle | 120° |
| Package Type | 5050 or 3528 (common SMD sizes) |
Pin Configuration
The SMD RGB LED typically has four pins: one common cathode or anode and three individual pins for the red, green, and blue LEDs. Below is the pinout for a common cathode configuration:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Pin 1 | Red LED (-) Cathode |
| Pin 2 | Common Cathode (-) |
| Pin 3 | Green LED (-) Cathode |
| Pin 4 | Blue LED (-) Cathode |
For a common anode configuration, Pin 2 would serve as the common anode (+), and the other pins would connect to the cathodes of the individual LEDs.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the SMD RGB LED in a Circuit
- Determine the Configuration: Identify whether the SMD RGB LED is common cathode or common anode. This will affect how you connect it to your circuit.
- Use Current-Limiting Resistors: To prevent damage, connect a resistor in series with each LED pin (red, green, and blue). Calculate the resistor value using Ohm's Law: [ R = \frac{V_{supply} - V_{forward}}{I_{forward}} ] For example, with a 5V supply and a forward voltage of 2.2V for the red LED, and a desired current of 20mA: [ R = \frac{5V - 2.2V}{0.02A} = 140\Omega ]
- Connect to a Microcontroller or Driver Circuit: Use GPIO pins or a dedicated LED driver IC to control the LED. Ensure the microcontroller can handle the required current or use transistors for higher currents.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control an SMD RGB LED using an Arduino UNO. This example assumes a common cathode configuration.
Circuit Connections
- Connect the common cathode pin to GND.
- Connect the red, green, and blue pins to Arduino digital pins (e.g., 9, 10, and 11) through 220Ω resistors.
Arduino Code
// Define pins for the RGB LED
const int redPin = 9; // Red LED connected to pin 9
const int greenPin = 10; // Green LED connected to pin 10
const int bluePin = 11; // Blue LED connected to pin 11
void setup() {
// Set the RGB LED pins as outputs
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Cycle through red, green, and blue colors
setColor(255, 0, 0); // Red
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 255, 0); // Green
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 0, 255); // Blue
delay(1000);
setColor(255, 255, 0); // Yellow
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 255, 255); // Cyan
delay(1000);
setColor(255, 0, 255); // Magenta
delay(1000);
setColor(255, 255, 255); // White
delay(1000);
}
// Function to set the RGB LED color
void setColor(int redValue, int greenValue, int blueValue) {
analogWrite(redPin, redValue); // Set red intensity (0-255)
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue); // Set green intensity (0-255)
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue); // Set blue intensity (0-255)
}
Important Considerations
- Heat Dissipation: Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating to prevent overheating.
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply voltage matches the LED's requirements.
- PWM Control: Use pulse-width modulation (PWM) to achieve smooth color transitions and dimming.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
LED Not Lighting Up
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or missing current-limiting resistors.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure resistors are in place.
Incorrect Colors
- Cause: Miswiring of the red, green, or blue pins.
- Solution: Verify the pin connections match the microcontroller's outputs.
Flickering or Dim Output
- Cause: Insufficient current or poor PWM signal.
- Solution: Check the power supply and ensure proper PWM settings.
Overheating
- Cause: Excessive current or insufficient heat dissipation.
- Solution: Use appropriate resistors and ensure the LED is not overdriven.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the SMD RGB LED without a microcontroller?
A: Yes, you can use simple switches or a pre-programmed LED driver IC to control the colors manually.
Q: How do I achieve custom colors?
A: Adjust the intensity of the red, green, and blue LEDs using PWM signals to mix colors.
Q: What is the difference between common cathode and common anode?
A: In a common cathode LED, all cathodes are connected to ground, while in a common anode LED, all anodes are connected to the positive supply.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the SMD RGB LED into your projects and create stunning lighting effects!