
How to Use Arduino Mega 2560: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
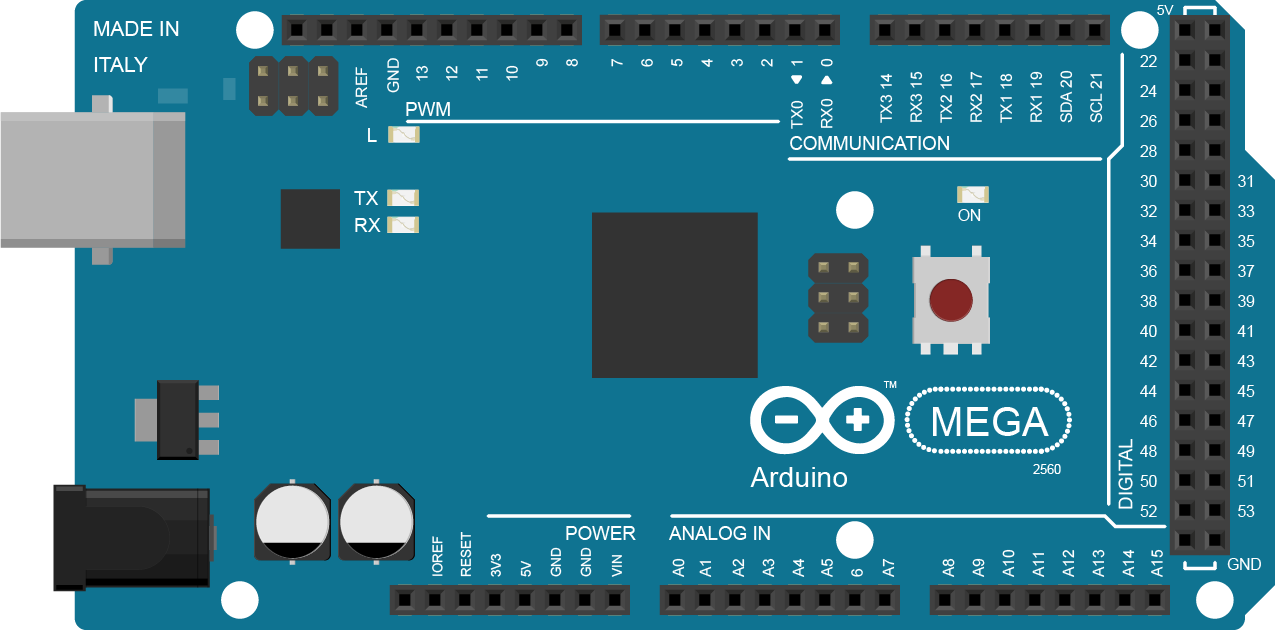
 Design with Arduino Mega 2560 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Arduino Mega 2560 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Arduino Mega 2560 is a powerful microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It is designed for projects requiring a large number of input/output pins and greater processing power. With 54 digital input/output pins (15 of which can be used as PWM outputs), 16 analog inputs, 4 UARTs (hardware serial ports), and a USB connection for programming and power, the Arduino Mega 2560 is ideal for complex projects and prototypes.
Explore Projects Built with Arduino Mega 2560
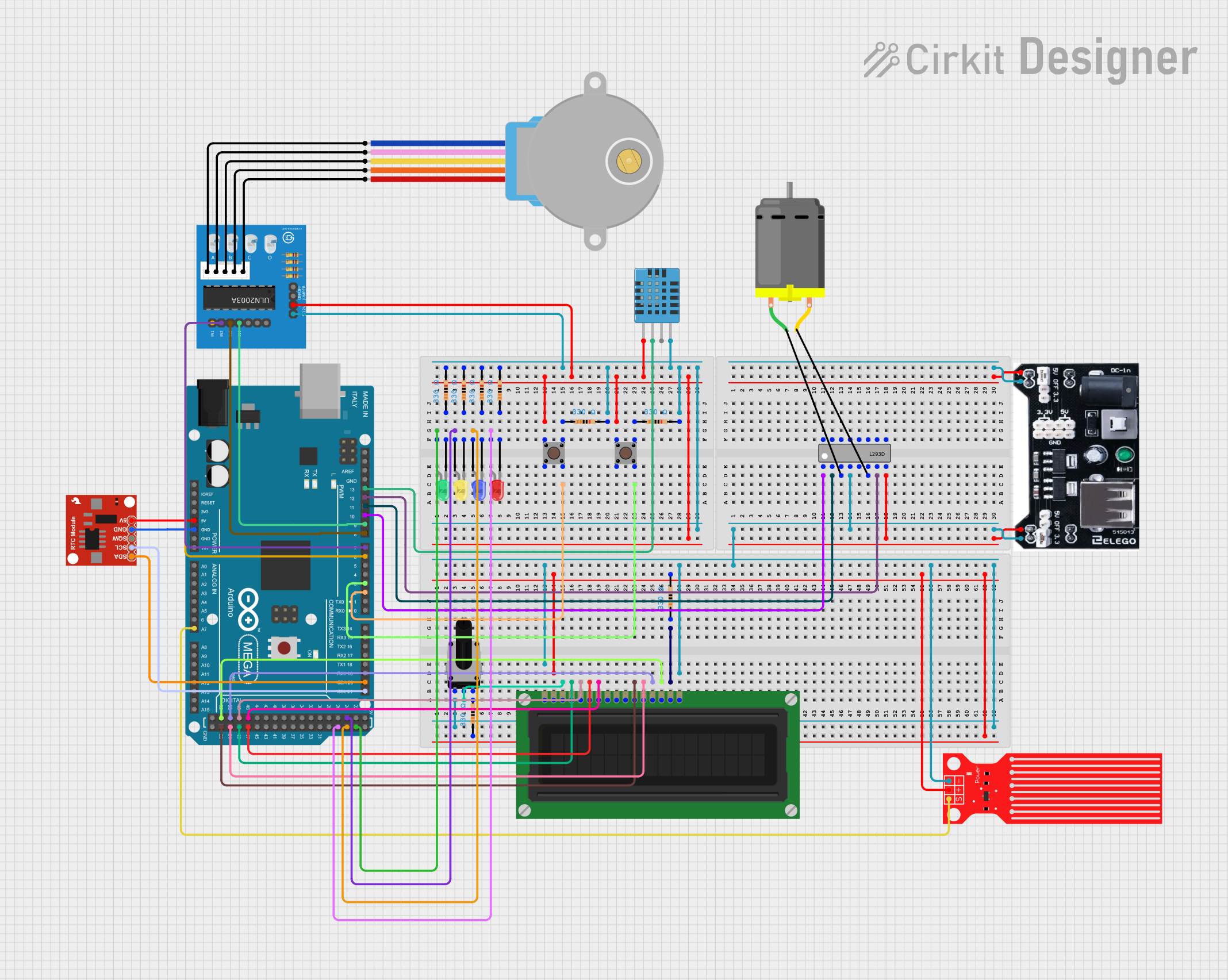
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer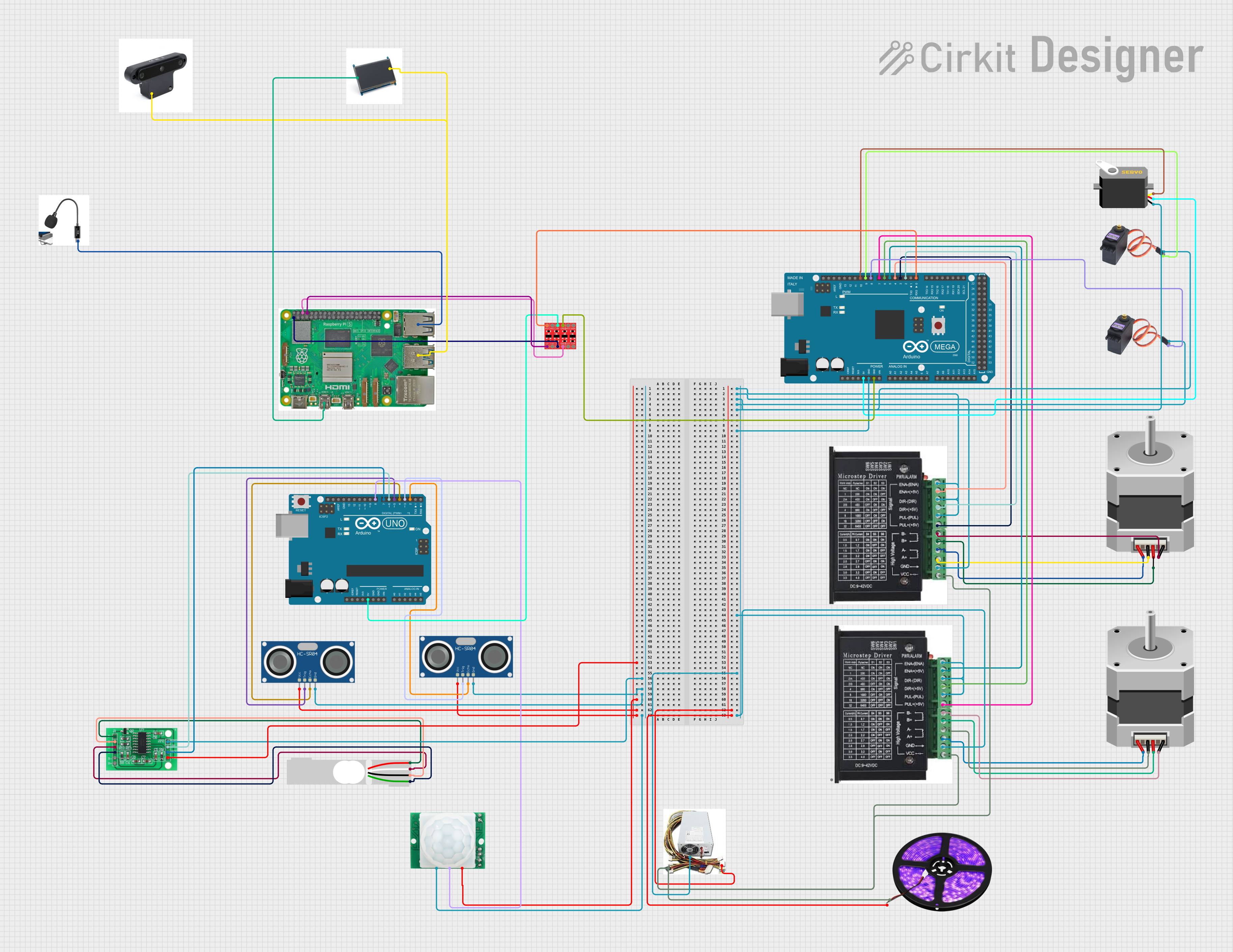
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer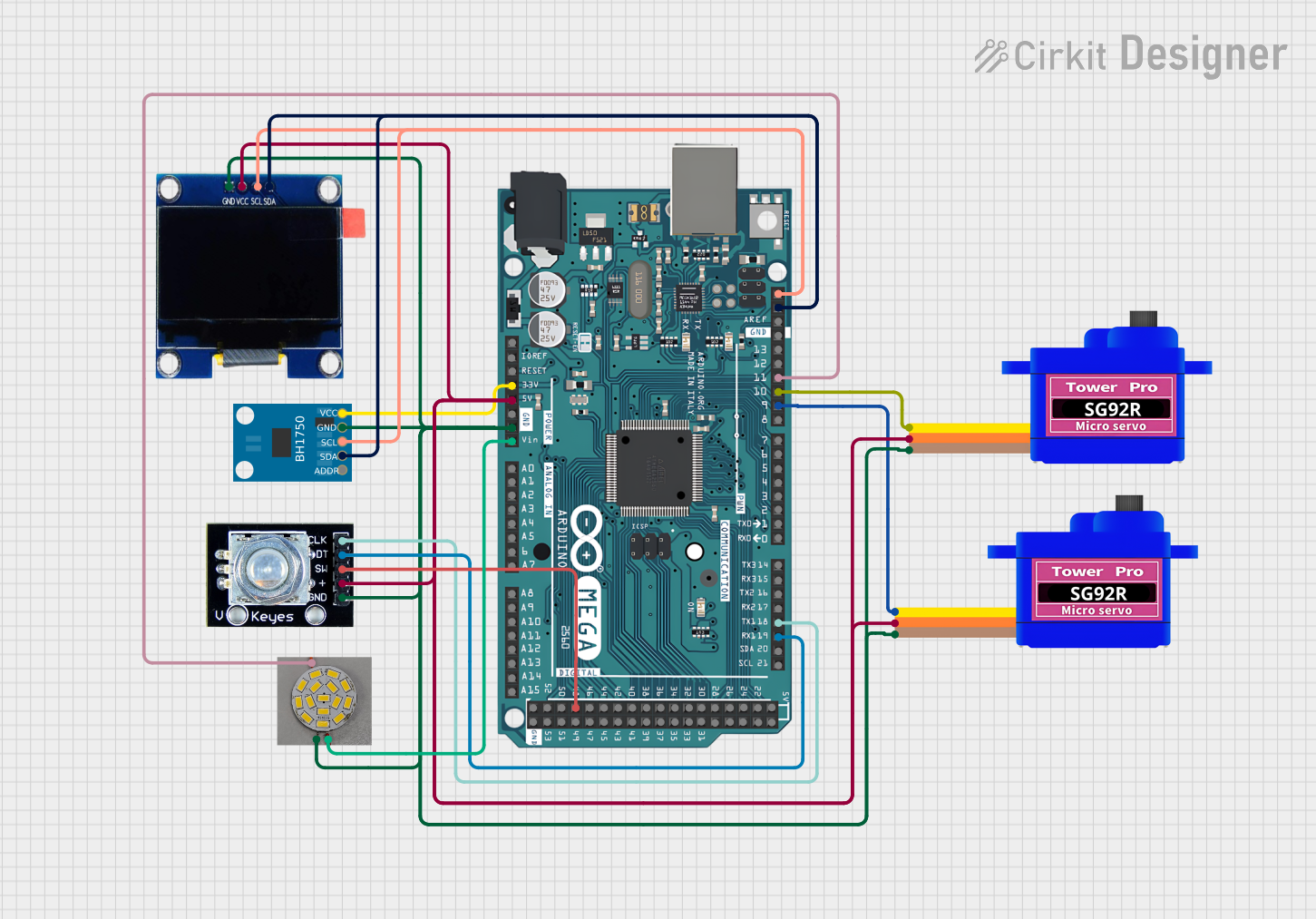
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer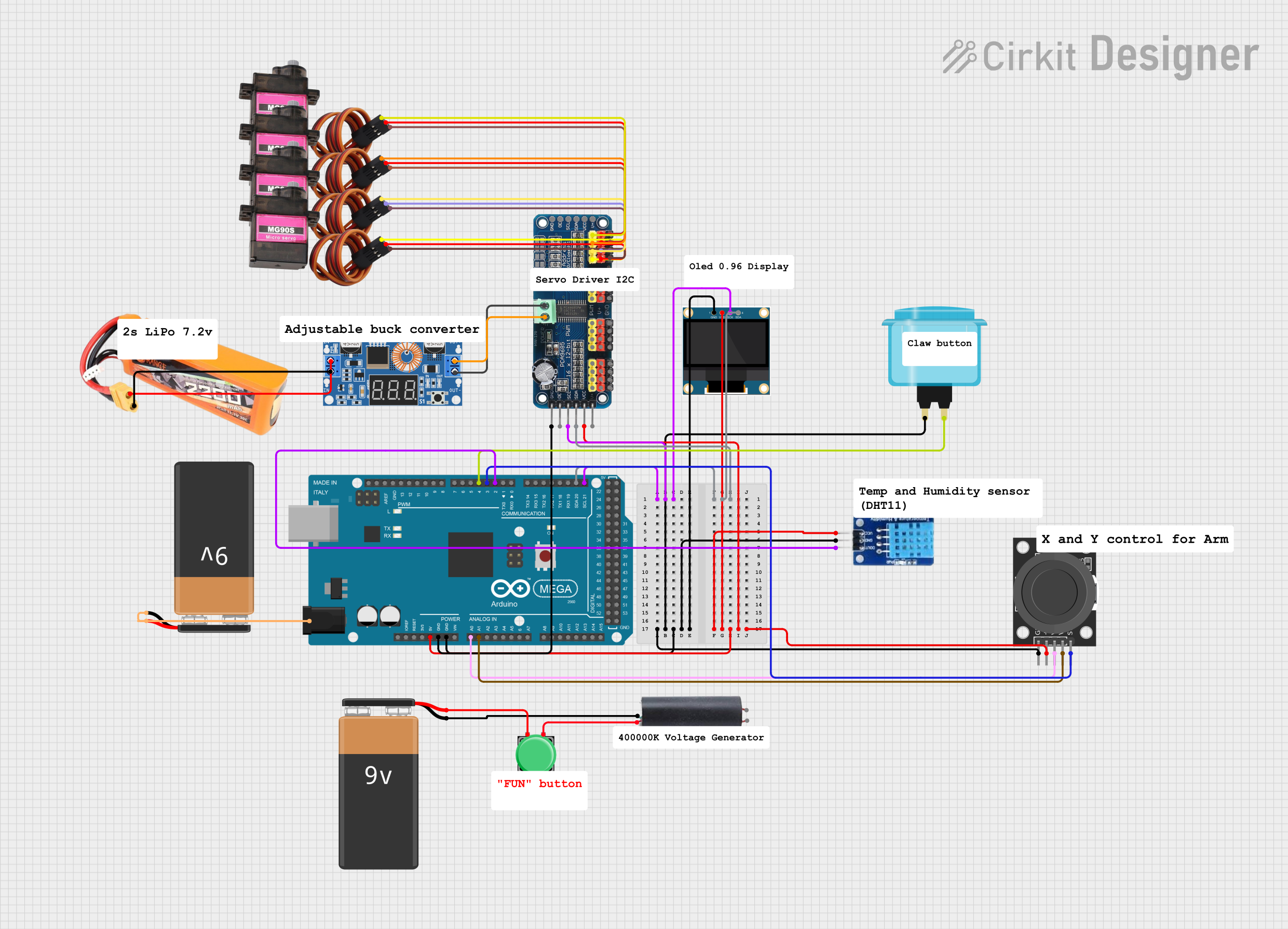
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Arduino Mega 2560

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics and automation systems
- IoT (Internet of Things) devices
- Data acquisition and logging
- Large-scale LED matrix control
- Advanced sensor integration
- Prototyping for industrial and academic projects
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ATmega2560 |
| Operating Voltage | 5V |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12V |
| Input Voltage (limit) | 6-20V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 54 (15 PWM outputs) |
| Analog Input Pins | 16 |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 20 mA |
| Flash Memory | 256 KB (8 KB used by bootloader) |
| SRAM | 8 KB |
| EEPROM | 4 KB |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| USB Connection | Type-B |
| Dimensions | 101.52 mm x 53.3 mm |
| Weight | 37 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Digital Pins
| Pin Number | Functionality |
|---|---|
| 0-1 | UART0 (Serial communication) |
| 2-13 | General-purpose digital I/O |
| 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11 | PWM outputs |
| 20-21 | I2C (SDA, SCL) |
| 22-53 | General-purpose digital I/O |
Analog Pins
| Pin Number | Functionality |
|---|---|
| A0-A15 | Analog inputs (10-bit resolution) |
Power Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage to the board |
| 5V | Regulated 5V output |
| 3.3V | Regulated 3.3V output |
| GND | Ground |
| IOREF | Voltage reference for I/O pins |
| RESET | Resets the microcontroller |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Arduino Mega 2560 in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the board to your computer using a USB Type-B cable for programming and power.
- Alternatively, use an external power supply (7-12V) via the barrel jack or VIN pin.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE from the official website.
- Select "Arduino Mega 2560" as the board type in the Tools menu.
- Choose the correct COM port for the board.
- Write or load your sketch and click the upload button.
Connecting Components:
- Use the digital pins for digital sensors, actuators, or communication modules.
- Use the analog pins for sensors that output analog signals.
- Ensure proper grounding and voltage levels for all connected components.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating (20 mA per I/O pin) to prevent damage.
- Use external power for high-current devices like motors or large LED arrays.
- Use pull-up or pull-down resistors for stable digital input signals.
- Always double-check connections to avoid short circuits or incorrect wiring.
- Use decoupling capacitors for noise-sensitive circuits.
Example: Blinking an LED
Here is a simple example to blink an LED connected to pin 13:
// This sketch blinks an LED connected to pin 13 on the Arduino Mega 2560.
// The LED will turn on for 1 second, then off for 1 second, repeatedly.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Example: Reading an Analog Sensor
This example reads a value from an analog sensor connected to pin A0:
// This sketch reads an analog value from a sensor connected to pin A0
// and prints the value to the Serial Monitor.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0); // Read the analog value from pin A0
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the value to the Serial Monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500 milliseconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The board is not recognized by the computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is properly connected and functional.
- Install the correct USB driver for the Arduino Mega 2560.
- Try a different USB port or cable.
Sketch upload fails:
- Verify that the correct board and COM port are selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Press the reset button on the board before uploading.
- Check for conflicting processes using the COM port (e.g., Serial Monitor).
Components not working as expected:
- Double-check wiring and connections.
- Ensure components are compatible with the Arduino Mega 2560.
- Verify that the power supply is sufficient for all connected devices.
Board resets unexpectedly:
- Check for power supply issues or excessive current draw.
- Avoid connecting high-current devices directly to the board.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the Arduino Mega 2560 with shields designed for the Arduino Uno?
A: Yes, the Arduino Mega 2560 is compatible with most Arduino Uno shields. However, ensure that the shield does not rely on specific pins that differ between the two boards.
Q: How do I expand the number of I/O pins?
A: You can use I/O expanders like the MCP23017 or shift registers like the 74HC595 to increase the number of available pins.
Q: Can the Arduino Mega 2560 be powered by batteries?
A: Yes, you can use a battery pack (7-12V) connected to the barrel jack or VIN pin. Ensure the battery voltage is within the recommended range.
Q: What is the maximum length for connecting sensors or modules?
A: For digital signals, the maximum cable length depends on the signal frequency and environmental noise. For analog signals, shorter cables are recommended to minimize noise and signal degradation.