
How to Use I2C: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with I2C in Cirkit Designer
Design with I2C in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a serial communication protocol developed by Inter Integrated Circuit. It is designed for short-distance communication between devices on a single bus. I2C supports multiple masters and multiple slaves, making it highly versatile for embedded systems. The protocol uses only two wires: a data line (SDA) and a clock line (SCL), which simplifies circuit design and reduces pin usage.
Explore Projects Built with I2C
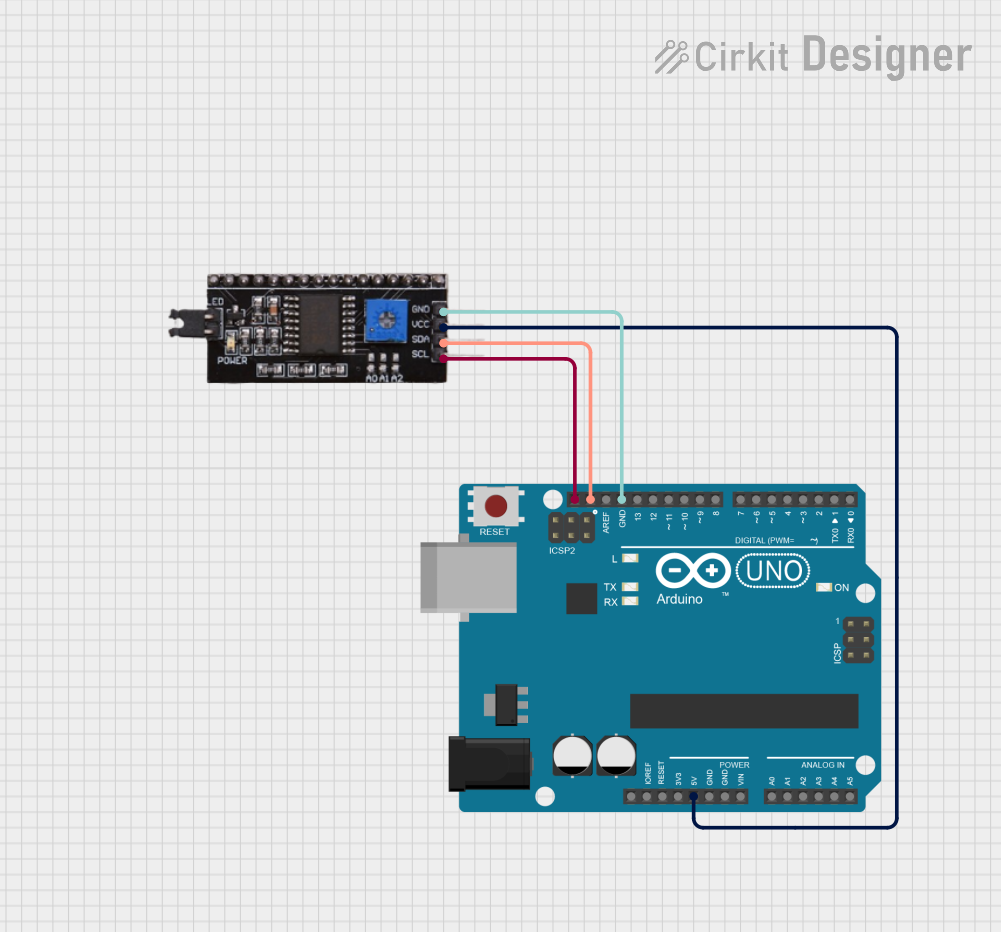
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer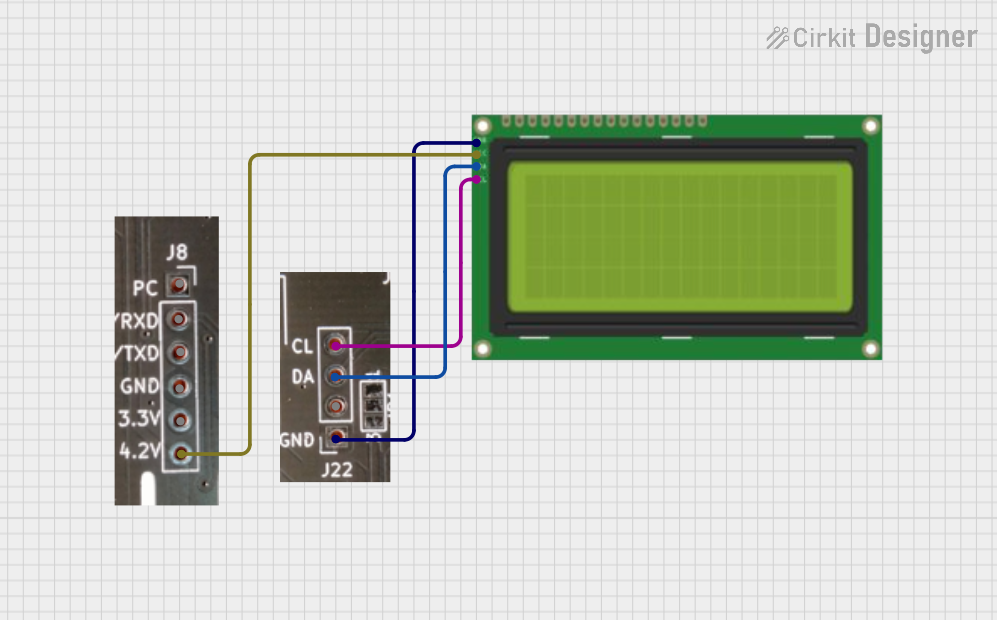
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer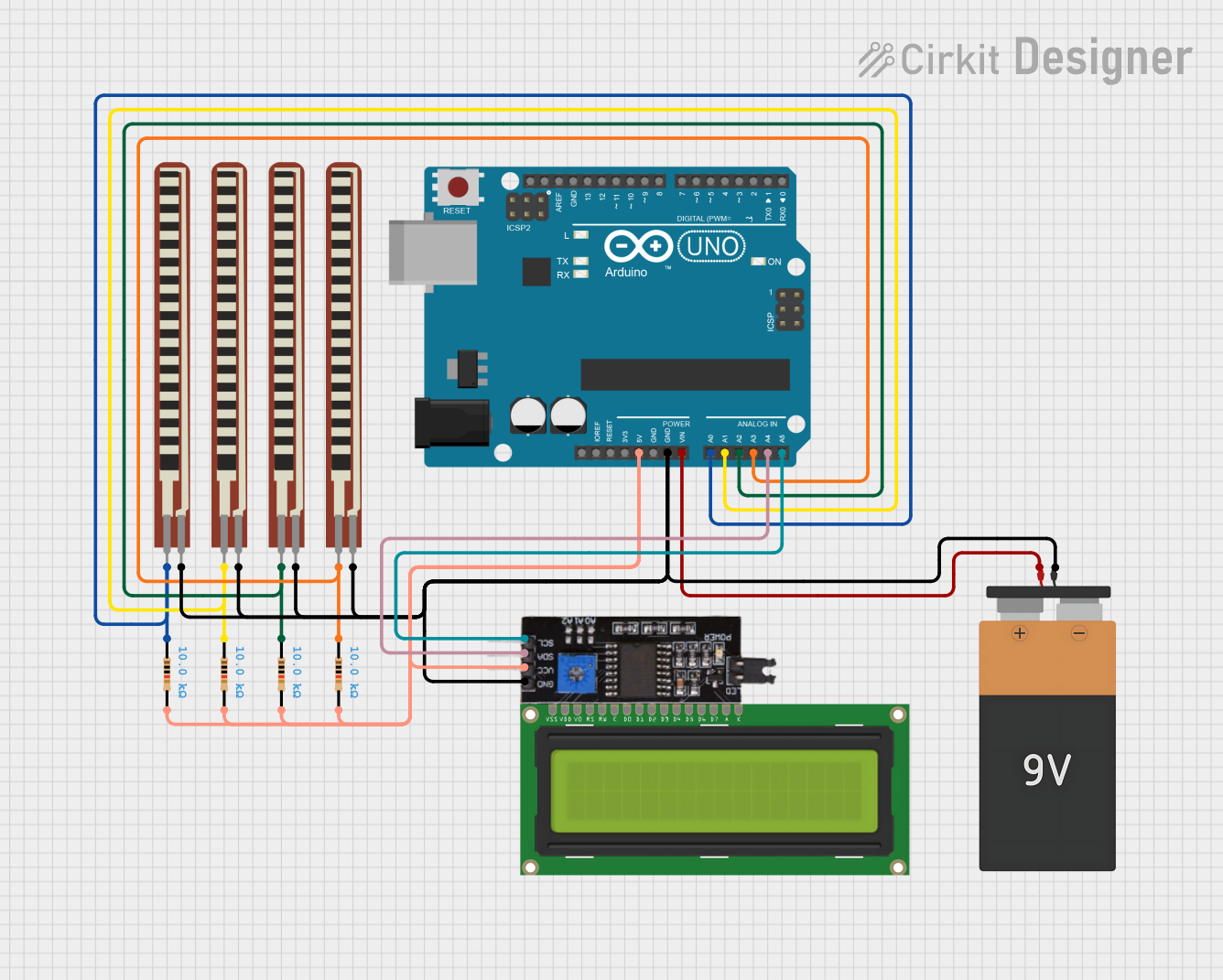
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer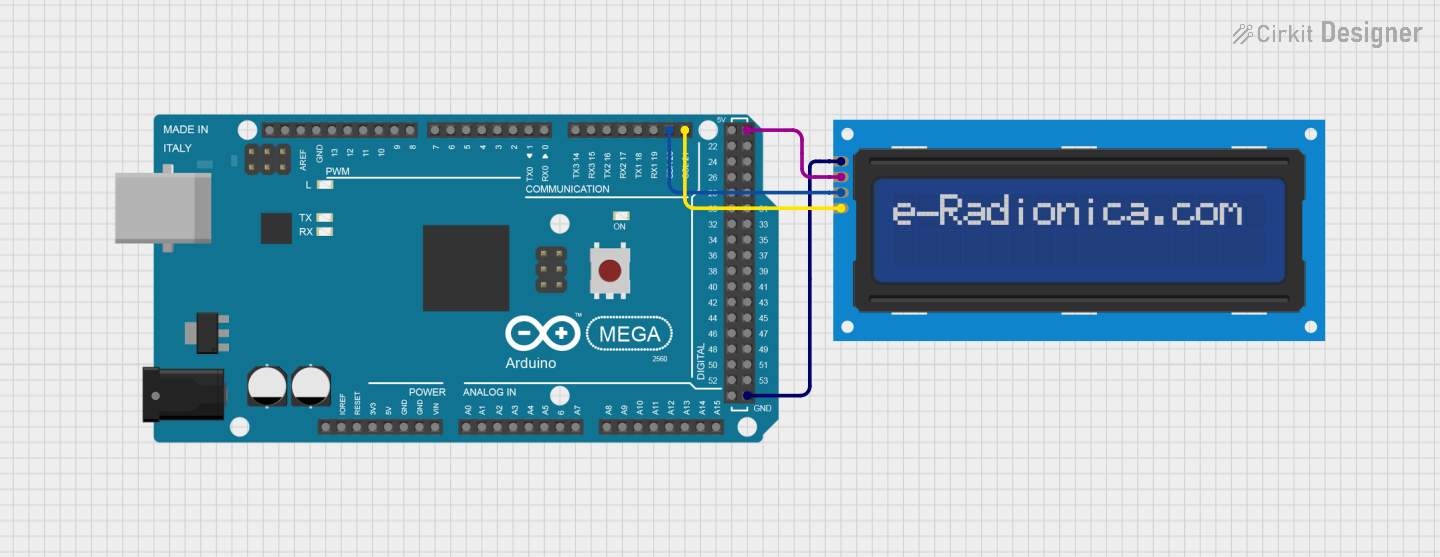
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with I2C

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Communication with sensors (e.g., temperature, pressure, and accelerometers)
- Interfacing with EEPROMs and real-time clocks
- Connecting microcontrollers and peripheral devices
- Display modules like OLEDs and LCDs
- Embedded systems requiring low-speed, short-distance communication
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Manufacturer: Inter Integrated Circuit
- Part ID: i2c
- Communication Type: Serial, synchronous
- Number of Wires: 2 (SDA - Serial Data, SCL - Serial Clock)
- Data Transfer Rate:
- Standard Mode: Up to 100 kbit/s
- Fast Mode: Up to 400 kbit/s
- Fast Mode Plus: Up to 1 Mbit/s
- High-Speed Mode: Up to 3.4 Mbit/s
- Voltage Levels: Typically 3.3V or 5V (depending on the system)
- Addressing: 7-bit or 10-bit addressing modes
- Maximum Devices on Bus: Limited by bus capacitance (typically up to 127 devices with 7-bit addressing)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The I2C protocol does not have a specific physical pinout since it is implemented in microcontrollers and devices. However, the two key lines are:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SDA | Serial Data Line: Used for bidirectional data transfer between devices. |
| SCL | Serial Clock Line: Provides the clock signal for synchronizing data transfer. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the SDA and SCL Lines:
- Connect the SDA line of the master device to the SDA line of the slave device(s).
- Similarly, connect the SCL line of the master to the SCL line of the slave(s).
Pull-Up Resistors:
- Add pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ or 10kΩ) to both the SDA and SCL lines. These resistors are necessary to ensure proper signal levels on the bus.
Power Supply:
- Ensure all devices on the I2C bus operate at the same voltage level (e.g., 3.3V or 5V). Use level shifters if devices operate at different voltage levels.
Addressing:
- Assign a unique address to each slave device. Most devices have configurable address pins or fixed addresses specified in their datasheets.
Master-Slave Communication:
- The master initiates communication by sending a start condition, followed by the slave address and read/write bit.
- Data is transferred in 8-bit packets, with an acknowledgment (ACK) bit after each byte.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Bus Capacitance: Ensure the total capacitance of the bus does not exceed 400pF to maintain signal integrity.
- Clock Stretching: Some slave devices may hold the SCL line low to delay communication. Ensure the master supports clock stretching if required.
- Noise and Interference: Use short wires and proper shielding to minimize noise on the bus.
Example: Using I2C with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of interfacing an I2C temperature sensor with an Arduino UNO:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define SENSOR_ADDRESS 0x48 // Replace with your sensor's I2C address
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication for debugging
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(SENSOR_ADDRESS); // Start communication with the sensor
Wire.write(0x00); // Send a command to read temperature (check sensor datasheet)
Wire.endTransmission(); // End transmission
Wire.requestFrom(SENSOR_ADDRESS, 2); // Request 2 bytes of data from the sensor
if (Wire.available() == 2) { // Check if 2 bytes are available
int temp = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); // Combine the two bytes
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.println(temp / 256.0); // Convert and print the temperature
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication on the Bus:
- Check the pull-up resistors on the SDA and SCL lines.
- Verify the wiring and ensure all devices share a common ground.
- Confirm the slave address matches the device's datasheet.
Data Corruption or Noise:
- Use shorter wires and proper shielding to reduce noise.
- Ensure the bus capacitance is within the acceptable range.
Clock Stretching Issues:
- Verify if the slave device uses clock stretching and ensure the master supports it.
Multiple Devices Not Responding:
- Check for address conflicts. Each device must have a unique address.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect devices with different voltage levels on the same I2C bus?
A: Yes, but you will need level shifters to safely interface devices operating at different voltage levels.
Q: How many devices can I connect to an I2C bus?
A: The number of devices is limited by the bus capacitance (typically up to 127 devices with 7-bit addressing).
Q: What happens if two masters try to communicate at the same time?
A: I2C includes an arbitration mechanism to prevent data collisions. The master with the higher priority (lower address) will take control of the bus.
Q: Do I always need pull-up resistors?
A: Yes, pull-up resistors are essential for proper operation of the I2C bus. Without them, the lines may not return to a high state.