
How to Use NEMA23: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with NEMA23 in Cirkit Designer
Design with NEMA23 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The NEMA23 stepper motor is a widely used actuator that converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements. The motor is named after its frame size, which is compliant with the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) standards. This stepper motor is commonly employed in CNC machines, 3D printers, robotics, and other applications where precise positioning is crucial.
Explore Projects Built with NEMA23

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer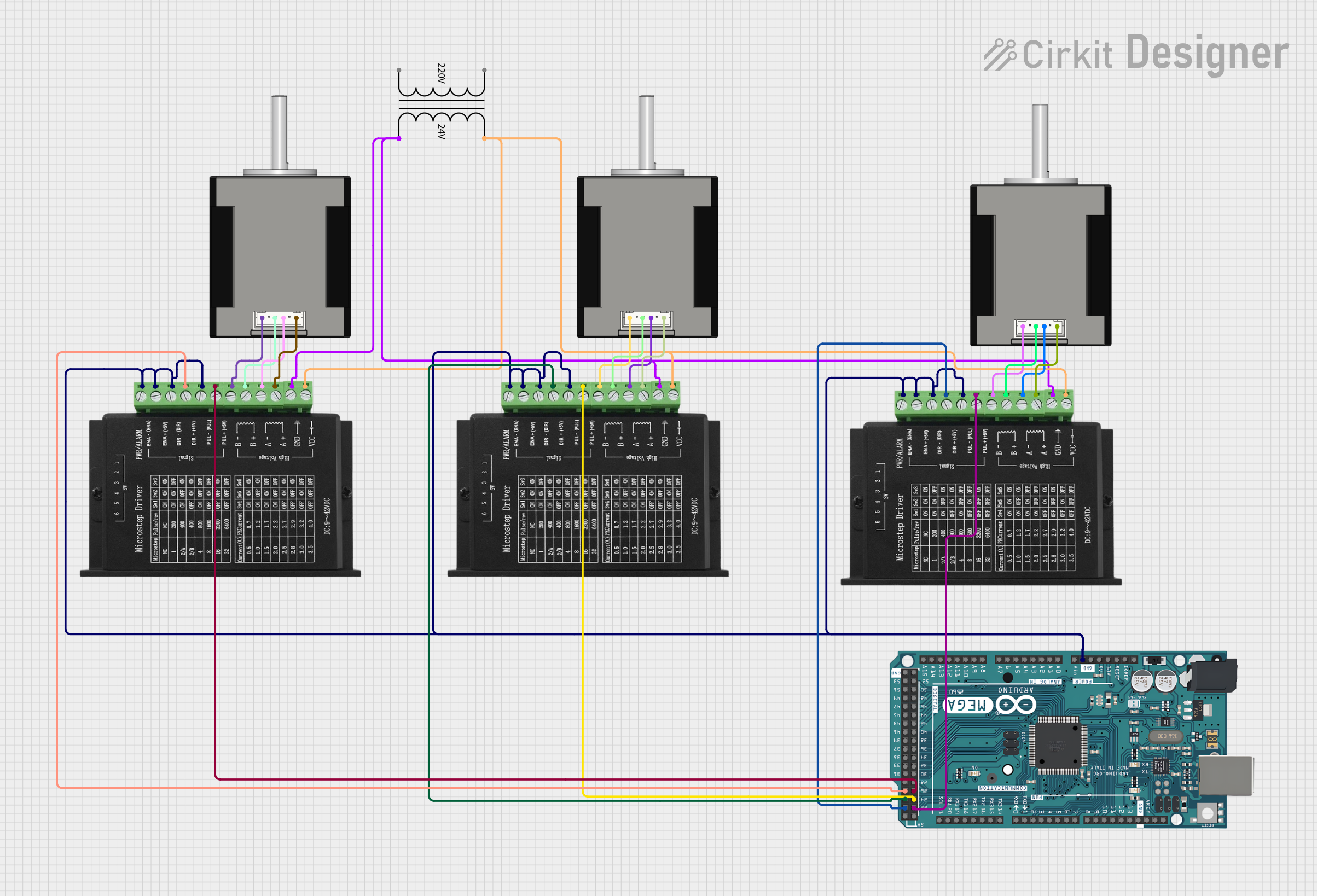
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with NEMA23

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- CNC milling machines and lathes
- 3D printers
- Robotic arms and actuators
- Precision camera controls
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs)
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications for the NEMA23 stepper motor manufactured by AutomationTechnologies with the part ID of 2.8 Amp.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Step Angle | 1.8° |
| Voltage | 3.0V |
| Current per Phase | 2.8A |
| Holding Torque | 1.26 Nm |
| Resistance per Phase | 1.13 Ohms |
| Inductance per Phase | 5.4 mH |
| Frame Size | 2.3" (58.4 mm) square |
| Shaft Diameter | 0.25" (6.35 mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Coil A+ |
| 2 | Coil A- |
| 3 | Coil B+ |
| 4 | Coil B- |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply can deliver the necessary voltage and current. For the NEMA23, a supply that can provide at least 3.0V and 2.8A per phase is required.
- Driver Selection: Choose a stepper motor driver capable of handling the current requirements of the NEMA23. The driver should also be compatible with the control signals from the controller (e.g., an Arduino UNO).
- Wiring: Connect the motor to the driver according to the pin configuration. Ensure that the coil wires are connected to the correct terminals on the driver.
- Microstepping: Configure the driver for the desired microstepping resolution. Microstepping allows for smoother and more precise motor movements.
- Control Signal: Connect the control signals from the controller to the driver. This typically includes step (pulse) and direction signals.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Adjust the current limit on the stepper motor driver to match the motor's rated current to prevent overheating.
- Heat Management: Monitor the motor temperature during operation. If the motor gets too hot, consider adding a heat sink or cooling fan.
- Mechanical Load: Do not exceed the motor's rated torque to avoid missed steps or motor damage.
- Voltage Spike Protection: Use flyback diodes or a similar method to protect the driver and motor from voltage spikes caused by inductive kickback.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Motor Does Not Move: Check the wiring connections, ensure the power supply is adequate, and verify that the driver is receiving the correct control signals.
- Motor Vibrates but Does Not Rotate: This could be due to incorrect wiring or a misconfiguration of the driver's microstepping settings.
- Motor Misses Steps: This can occur if the motor is overloaded, the current limit is set too low, or if there is mechanical binding in the system.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and correct according to the motor and driver datasheets.
- Adjust Current Limit: If the motor is stalling or overheating, adjust the current limit on the driver.
- Reduce Load: If the motor cannot handle the load, reduce the load or use a motor with a higher torque rating.
Example Arduino Code
#include <Stepper.h>
// Define the number of steps per revolution
const int stepsPerRevolution = 200;
// Initialize the stepper library on pins 8 through 11
Stepper myStepper(stepsPerRevolution, 8, 9, 10, 11);
void setup() {
// Set the speed at 60 rpm
myStepper.setSpeed(60);
}
void loop() {
// Move one revolution in one direction
myStepper.step(stepsPerRevolution);
delay(500);
// Move one revolution in the other direction
myStepper.step(-stepsPerRevolution);
delay(500);
}
Note: The above code is a simple example to control a NEMA23 stepper motor using an Arduino UNO. Make sure to adjust the pin numbers and steps per revolution to match your specific motor and driver setup.