
How to Use Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor (Manufacturer Part ID: SEN0193/SEN0308) by DFRobot is a reliable and non-invasive sensor designed to measure the volumetric water content in soil. Unlike resistive soil moisture sensors, this capacitive sensor detects changes in soil capacitance, making it less prone to corrosion and ensuring a longer lifespan. It is ideal for applications requiring accurate and durable soil moisture monitoring.
Explore Projects Built with Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor
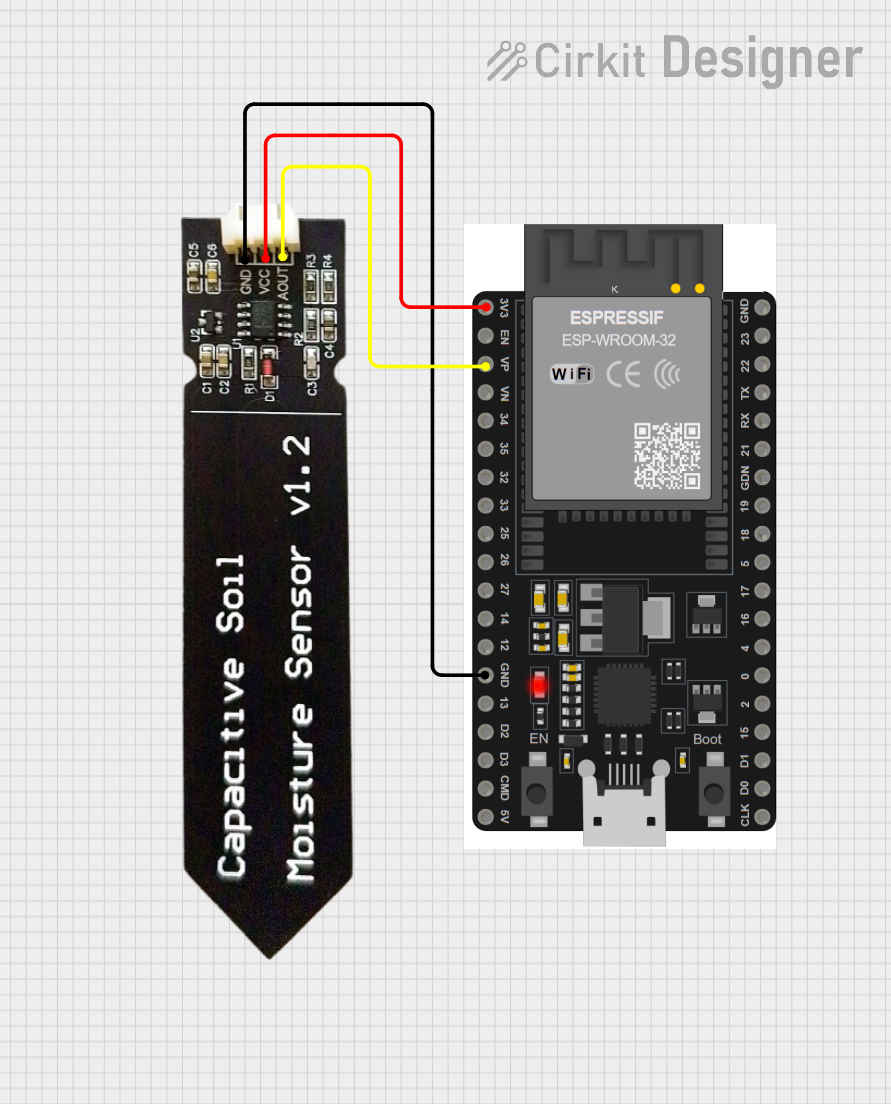
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer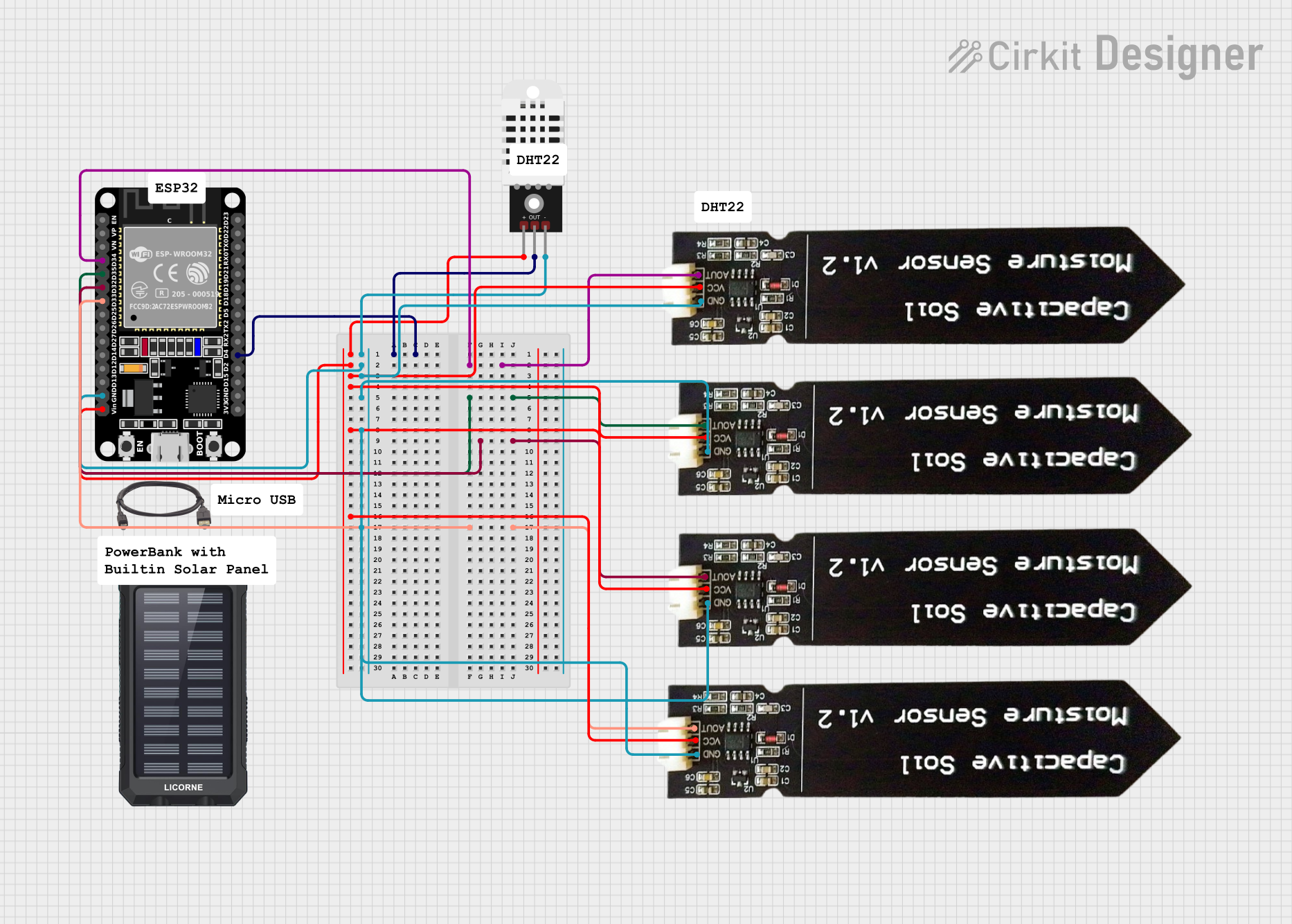
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer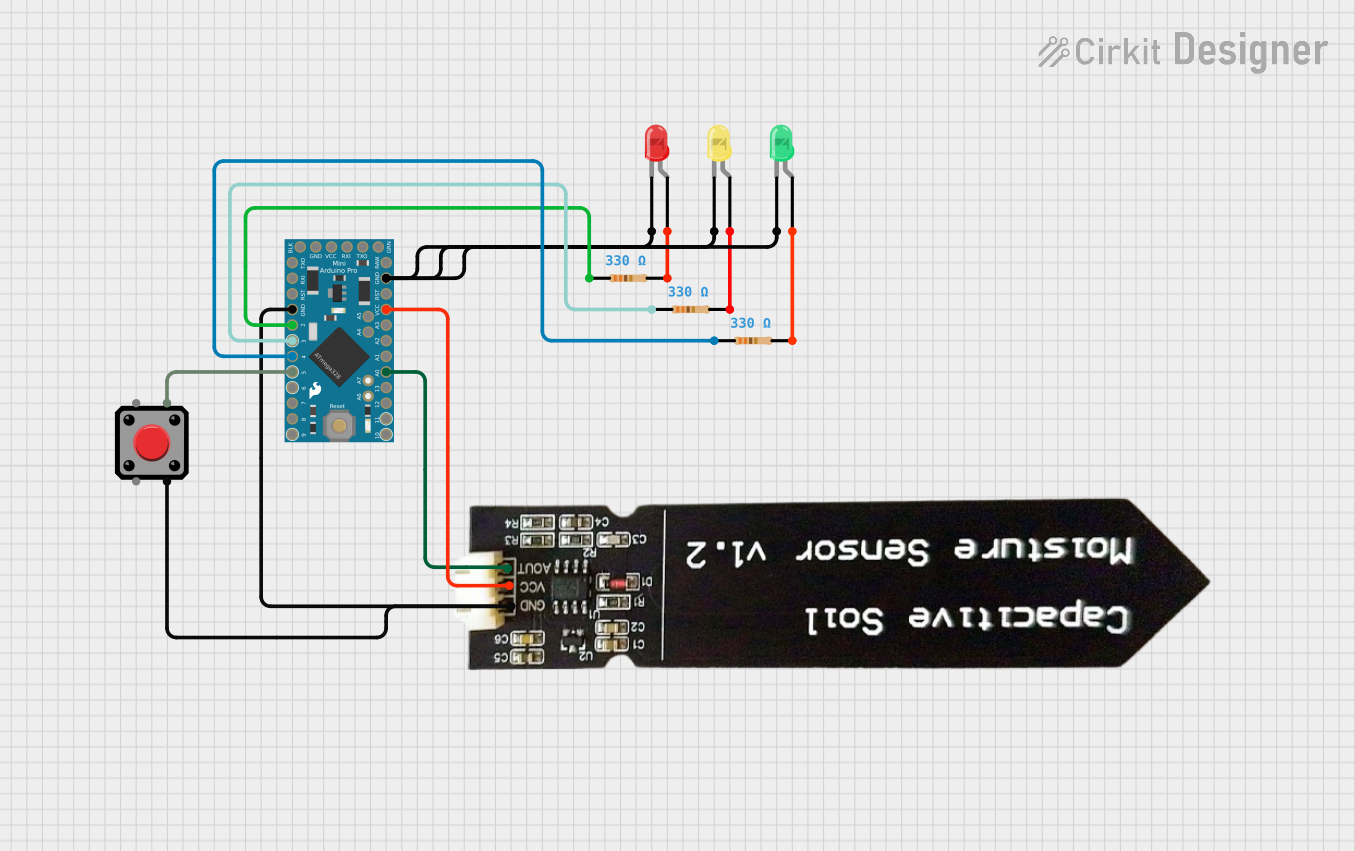
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer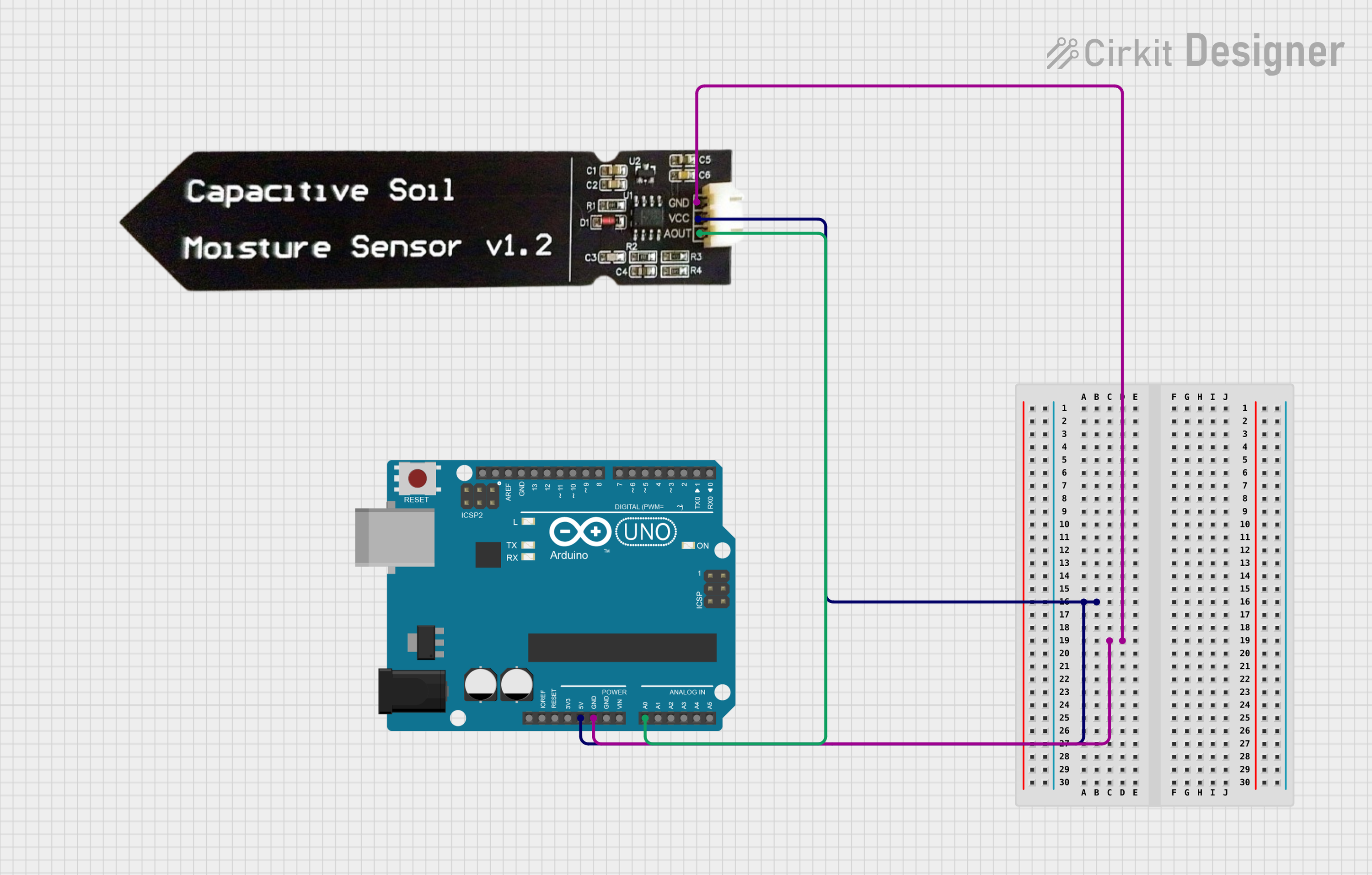
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Smart irrigation systems
- Agricultural automation
- Gardening and horticulture
- Environmental monitoring
- DIY electronics and IoT projects
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5.5V |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (0-3.0V typical) |
| Current Consumption | < 20mA |
| Measurement Range | 0% - 100% soil moisture |
| Interface Type | Analog |
| Dimensions | 98mm x 23mm x 3mm |
| Cable Length | 200mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
Pin Configuration
The sensor has a 3-pin interface for easy connection. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V - 5.5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | AOUT | Analog output signal proportional to soil moisture |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the Sensor
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source, depending on your microcontroller.
- Ground: Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Analog Output: Connect the AOUT pin to an analog input pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
Example Circuit
Below is an example of how to connect the sensor to an Arduino UNO:
- VCC → 5V pin on Arduino
- GND → GND pin on Arduino
- AOUT → A0 pin on Arduino
Sample Arduino Code
The following code reads the analog output from the sensor and converts it into a soil moisture percentage:
// Define the analog pin connected to the sensor
const int sensorPin = A0;
// Variable to store the sensor reading
int sensorValue = 0;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Map the sensor value to a percentage (0% to 100%)
// Adjust the range (e.g., 0-1023) based on your sensor's calibration
int moisturePercent = map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 100);
// Print the moisture percentage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Soil Moisture: ");
Serial.print(moisturePercent);
Serial.println("%");
// Wait for 1 second before the next reading
delay(1000);
}
Important Considerations
- Calibration: The sensor's output may vary depending on soil type. Calibrate the sensor for your specific soil by testing it in dry and saturated conditions.
- Placement: Insert the sensor into the soil vertically, ensuring the sensing area is fully covered by soil for accurate readings.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid fluctuations in the analog output.
- Waterproofing: While the sensor is corrosion-resistant, avoid submerging the entire sensor in water. Only the sensing area should contact the soil.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Inconsistent Readings:
- Cause: Unstable power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Ensure all connections are secure and use a regulated power source.
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or damaged sensor.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and test the sensor with a multimeter.
Output Always at Maximum or Minimum:
- Cause: Sensor not properly inserted into the soil or soil too dry/wet.
- Solution: Ensure the sensor is fully inserted into the soil and test in different moisture conditions.
FAQs
Q: Can this sensor be used outdoors?
A: Yes, the sensor is designed for outdoor use, but ensure the connections are protected from water and weather.
Q: How do I calibrate the sensor?
A: Measure the sensor's output in completely dry soil (0% moisture) and fully saturated soil (100% moisture). Use these values to map the sensor's output range in your code.
Q: Can I use this sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the sensor operates within a voltage range of 3.3V to 5.5V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems like ESP32 or Raspberry Pi.
Q: Is the sensor affected by soil type?
A: Yes, different soil types may affect the sensor's readings. Calibration is recommended for accurate results.