
How to Use 20A Buck 300W cc cv: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
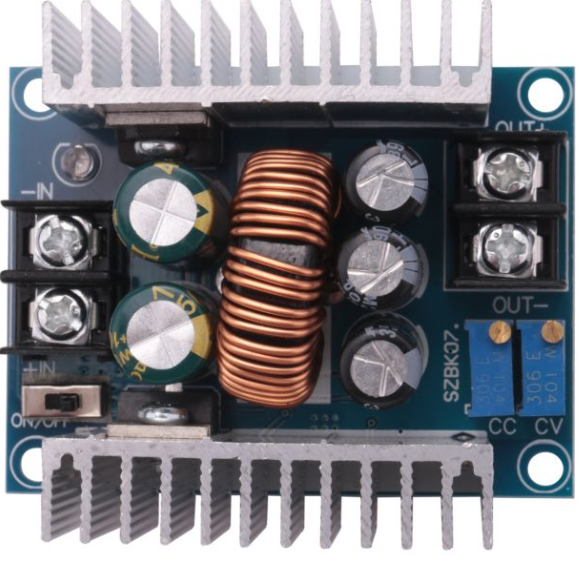
 Design with 20A Buck 300W cc cv in Cirkit Designer
Design with 20A Buck 300W cc cv in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 20A Buck 300W cc cv is a high-performance DC-DC buck converter manufactured by Sene. It is designed to step down a higher DC input voltage to a lower DC output voltage while maintaining high efficiency. This module supports both constant current (cc) and constant voltage (cv) modes, making it ideal for applications requiring precise voltage and current regulation.
Explore Projects Built with 20A Buck 300W cc cv

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer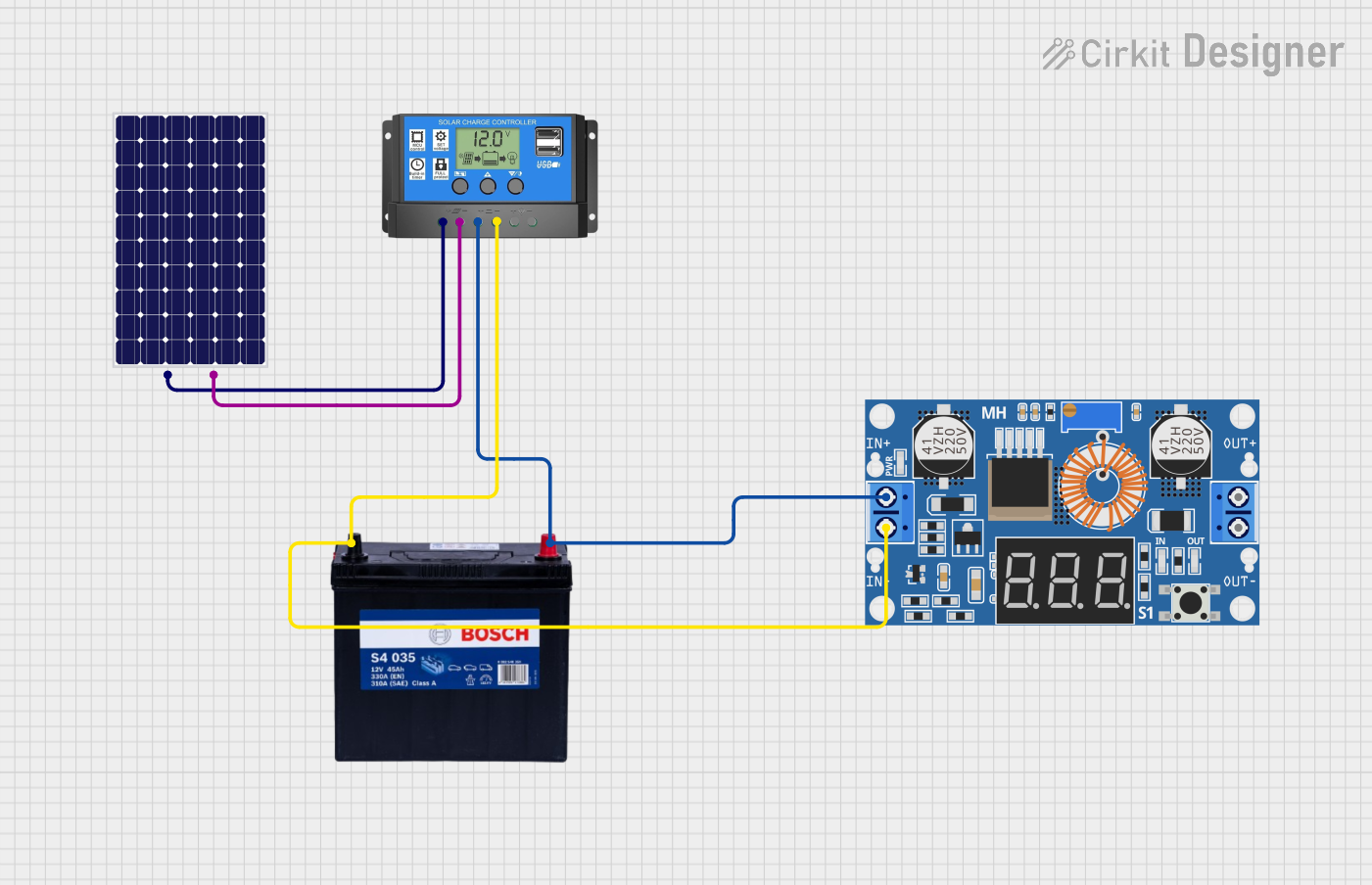
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer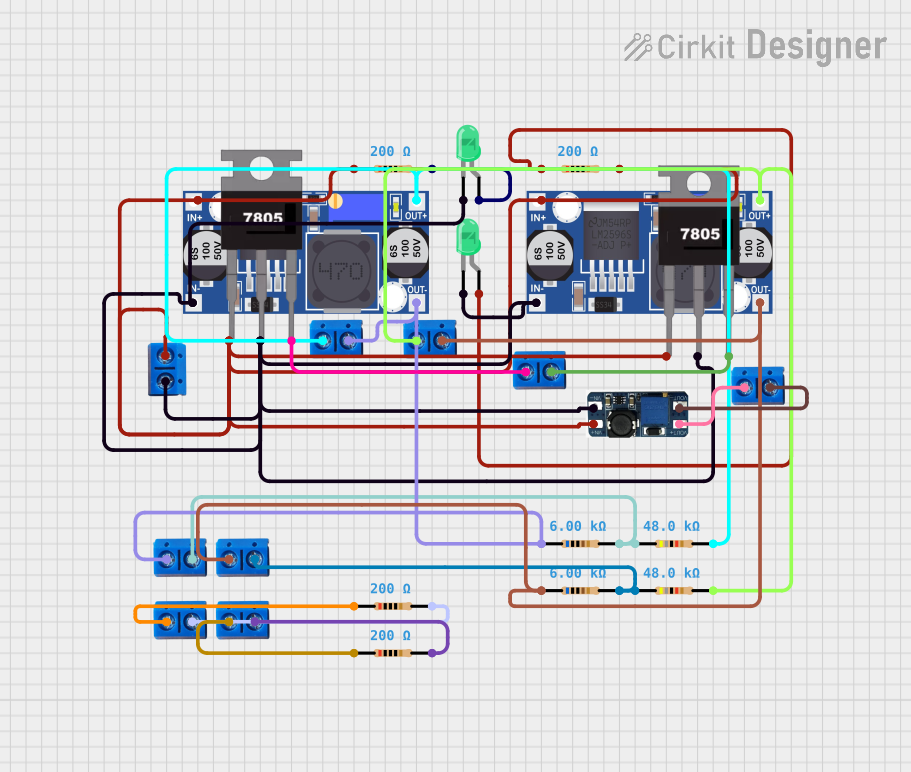
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 20A Buck 300W cc cv

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Battery charging (e.g., lithium-ion, lead-acid batteries)
- LED drivers and lighting systems
- Power supply for electronic devices
- Solar power systems
- Laboratory power supplies
- Motor speed control
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the 300W 20A cc cv module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 6V to 40V DC |
| Output Voltage Range | 1.2V to 36V DC |
| Output Current | Up to 20A (adjustable) |
| Output Power | Up to 300W |
| Efficiency | Up to 95% |
| Operating Modes | Constant Voltage (CV), Constant Current (CC) |
| Voltage Regulation | ±1% |
| Current Regulation | ±2% |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 60mm x 52mm x 22mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The module has input and output terminals for easy integration into circuits. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN+ | Positive input voltage terminal (connect to the DC power source) |
| VIN- | Negative input voltage terminal (connect to the DC power source ground) |
| VOUT+ | Positive output voltage terminal (connect to the load) |
| VOUT- | Negative output voltage terminal (connect to the load ground) |
| CC Adjust | Potentiometer to adjust the constant current limit |
| CV Adjust | Potentiometer to adjust the constant voltage output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage:
- Connect the VIN+ and VIN- terminals to a DC power source within the input voltage range (6V to 40V).
- Ensure the input voltage is higher than the desired output voltage.
Connect the Load:
- Connect the VOUT+ and VOUT- terminals to the load (e.g., battery, LED, or motor).
Adjust the Output Voltage:
- Use the CV Adjust potentiometer to set the desired output voltage. Turn clockwise to increase the voltage and counterclockwise to decrease it.
Set the Current Limit:
- Use the CC Adjust potentiometer to set the maximum output current. This is particularly useful for applications like battery charging to prevent overcurrent.
Verify the Output:
- Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage and current to ensure they match the desired values.
Power On:
- Once all connections are secure and settings are verified, power on the module.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: The module can handle high power (up to 300W), so ensure adequate cooling using a heatsink or fan to prevent overheating.
- Input Voltage: Always ensure the input voltage is higher than the desired output voltage but within the specified range.
- Current Limiting: Set the current limit appropriately to protect the load and the module.
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of the input and output connections to avoid damage.
- Short Circuit Protection: The module includes short circuit protection, but avoid intentional shorting of the output.
Example: Using with Arduino UNO
The 20A Buck 300W cc cv module can be used to power an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to connect and use it:
- Set the output voltage of the module to 5V using the CV Adjust potentiometer.
- Connect the VOUT+ terminal to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- Connect the VOUT- terminal to the Arduino's GND pin.
Here is a simple Arduino sketch to read a sensor powered by the buck converter:
// Example: Reading a sensor powered by the 20A Buck 300W cc cv module
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor output
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the sensor reading
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Input voltage is not connected or is below the minimum required.
- Solution: Verify the input voltage is within the 6V to 40V range and properly connected.
Overheating:
- Cause: High power operation without adequate cooling.
- Solution: Attach a heatsink or use a cooling fan to dissipate heat.
Output Voltage Not Adjustable:
- Cause: Faulty potentiometer or incorrect input voltage.
- Solution: Check the input voltage and ensure it is higher than the desired output voltage. Inspect the potentiometer for damage.
Load Not Receiving Power:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or polarity.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure correct polarity.
Module Shuts Down Under Load:
- Cause: Current limit is set too low.
- Solution: Adjust the CC Adjust potentiometer to increase the current limit.
FAQs
Q1: Can this module charge a 12V battery?
A1: Yes, set the output voltage to 14.4V (for lead-acid batteries) and adjust the current limit to match the battery's charging specifications.
Q2: What happens if the input voltage exceeds 40V?
A2: The module may be damaged. Always ensure the input voltage stays within the specified range.
Q3: Can I use this module to power a Raspberry Pi?
A3: Yes, set the output voltage to 5V and ensure the current limit is sufficient for the Raspberry Pi's power requirements.
Q4: Is the module waterproof?
A4: No, the module is not waterproof. Use it in a dry environment or enclose it in a waterproof case if necessary.
Q5: How do I know if the module is in constant current mode?
A5: The module will enter constant current mode when the load tries to draw more current than the set limit. In this case, the output voltage will drop to maintain the current limit.