
How to Use mpi3508: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
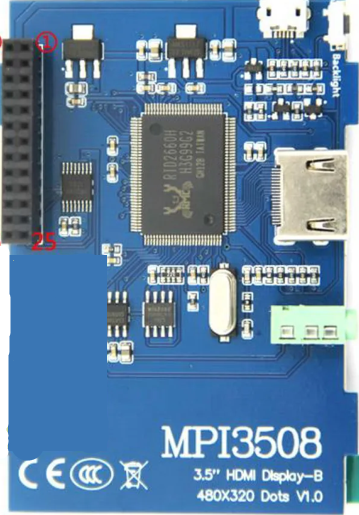
 Design with mpi3508 in Cirkit Designer
Design with mpi3508 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MPI3508 is a high-performance, low-power microcontroller designed for embedded applications. It features multiple I/O ports, analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) capabilities, and support for various communication protocols, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of projects. Its compact design and energy efficiency make it ideal for applications such as IoT devices, robotics, industrial automation, and consumer electronics.
Explore Projects Built with mpi3508

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer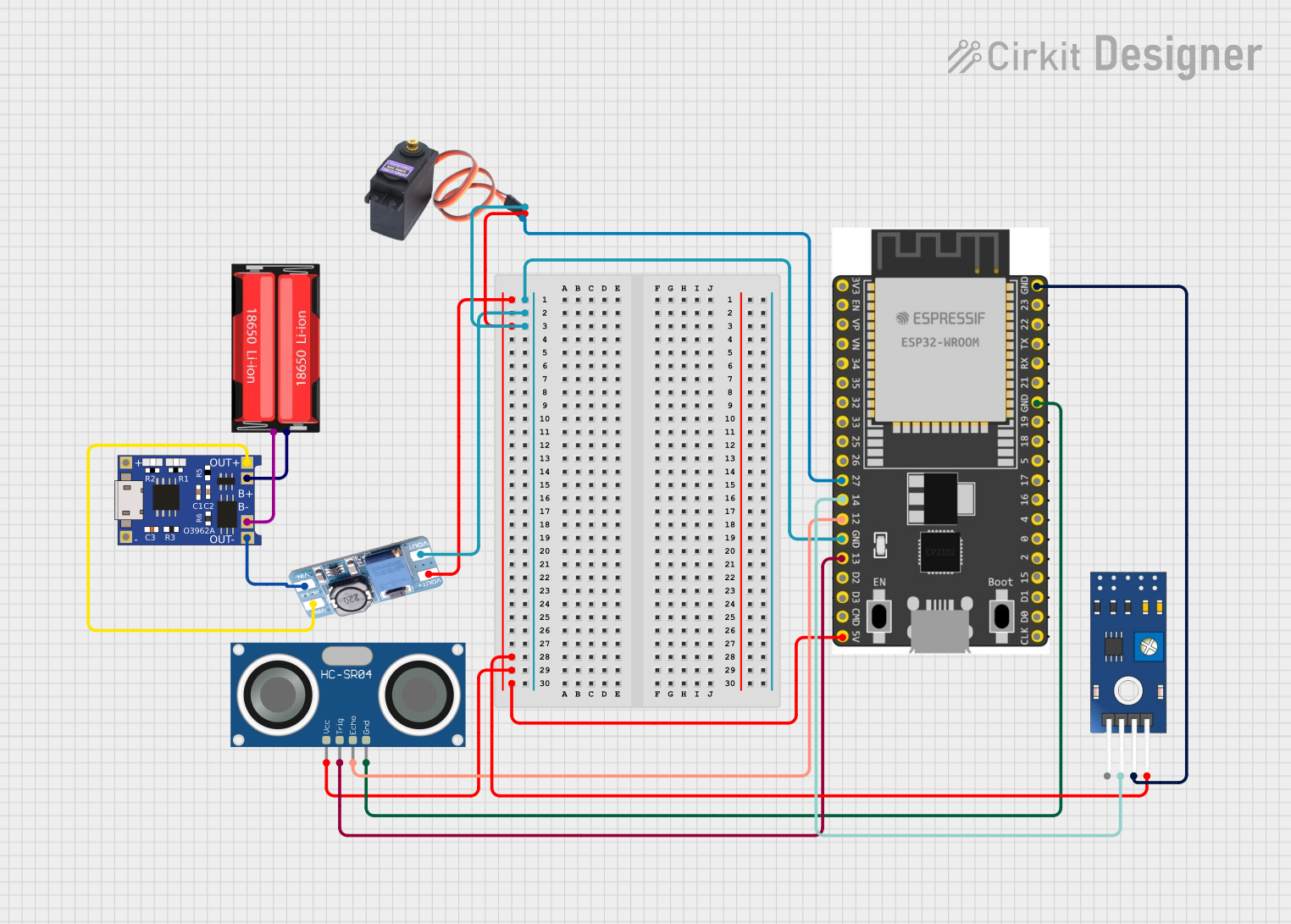
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer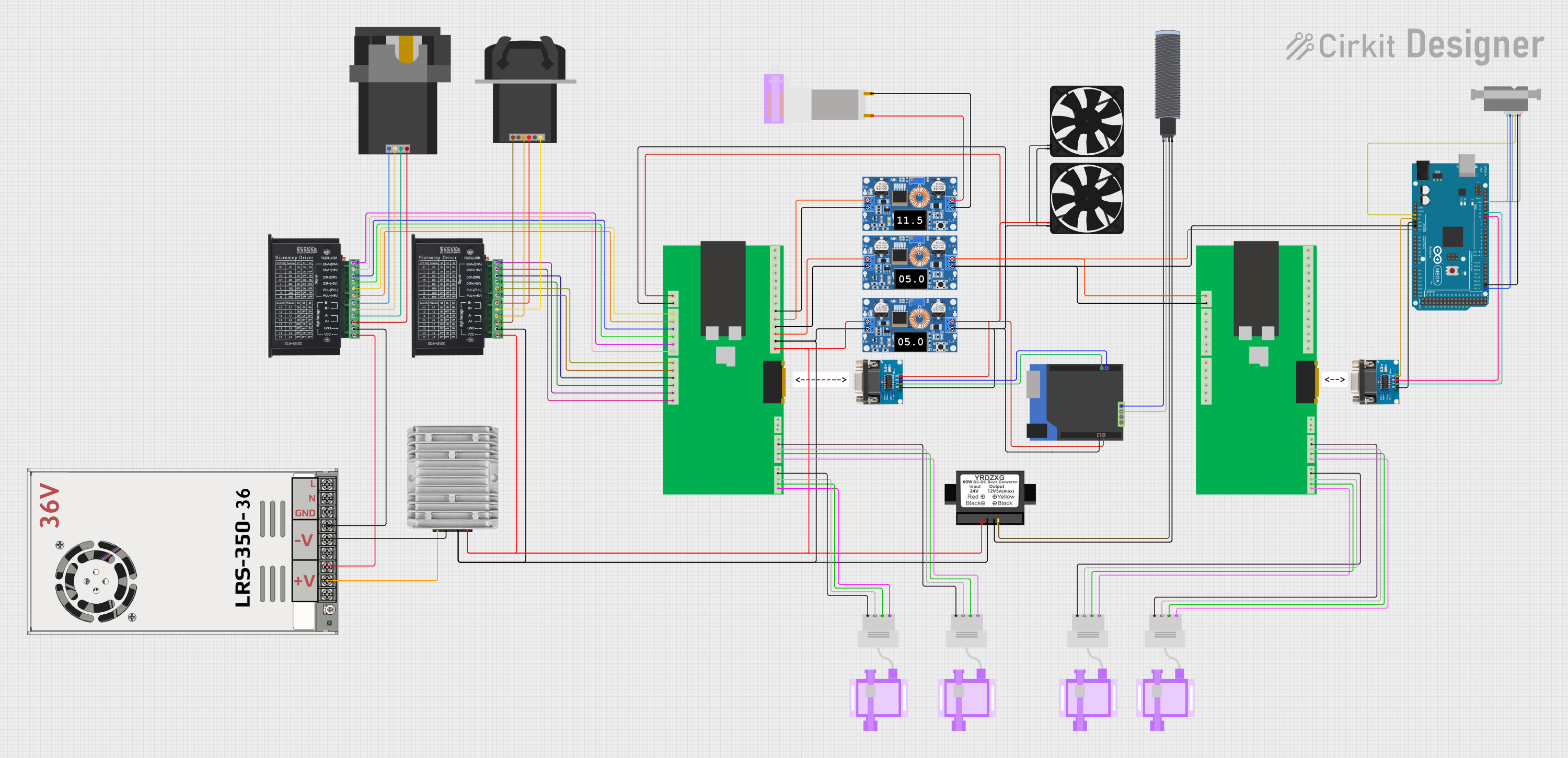
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with mpi3508

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Robotics and automation systems
- Data acquisition and sensor interfacing
- Home automation and smart appliances
- Educational and prototyping projects
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 1.8V to 3.6V |
| Maximum Clock Frequency | 48 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 64 KB |
| SRAM | 8 KB |
| GPIO Pins | Up to 32 |
| ADC Resolution | 12-bit |
| Communication Protocols | I2C, SPI, UART |
| Power Consumption (Active) | 5 mA (typical) |
| Power Consumption (Sleep) | 1 µA (typical) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | QFN-32 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MPI3508 comes in a 32-pin QFN package. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Power supply (1.8V to 3.6V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | GPIO0 | General-purpose I/O |
| 4 | GPIO1 | General-purpose I/O |
| 5 | ADC_IN0 | Analog input channel 0 |
| 6 | ADC_IN1 | Analog input channel 1 |
| 7 | UART_TX | UART transmit |
| 8 | UART_RX | UART receive |
| 9 | SPI_MOSI | SPI Master Out Slave In |
| 10 | SPI_MISO | SPI Master In Slave Out |
| 11 | SPI_SCK | SPI Clock |
| 12 | SPI_CS | SPI Chip Select |
| 13 | I2C_SCL | I2C Clock |
| 14 | I2C_SDA | I2C Data |
| 15-30 | GPIO2-17 | General-purpose I/O |
| 31 | RESET | Reset input (active low) |
| 32 | NC | Not connected |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MPI3508 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a stable power source (1.8V to 3.6V) and the GND pin to ground.
- GPIO Configuration: Configure the GPIO pins as input or output based on your application. Unused GPIO pins should be left floating or pulled to ground through a resistor.
- Communication Protocols: Use the appropriate pins for I2C, SPI, or UART communication. Ensure proper pull-up resistors for I2C lines.
- ADC Usage: Connect analog sensors to the ADC_IN pins. Ensure the input voltage does not exceed the operating voltage range.
- Reset: Use the RESET pin to initialize the microcontroller. This pin is active low.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place a 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor close to the VDD pin to reduce noise and stabilize the power supply.
- Clock Source: If an external clock is required, connect it to the appropriate GPIO pin configured as a clock input.
- Programming: Use an appropriate programmer or development board to upload firmware to the microcontroller.
- ESD Protection: Add ESD protection diodes to sensitive pins in environments prone to electrostatic discharge.
Example: Connecting the MPI3508 to an Arduino UNO
The MPI3508 can be interfaced with an Arduino UNO via I2C. Below is an example code snippet:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define MPI3508_ADDRESS 0x48 // Replace with the actual I2C address of the MPI3508
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Send a test command to the MPI3508
Wire.beginTransmission(MPI3508_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x01); // Example command
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("MPI3508 initialized.");
}
void loop() {
Wire.requestFrom(MPI3508_ADDRESS, 2); // Request 2 bytes of data from the MPI3508
if (Wire.available() == 2) {
int data = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); // Combine two bytes into a single value
Serial.print("Received data: ");
Serial.println(data);
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next request
}
Notes:
- Replace
MPI3508_ADDRESSwith the actual I2C address of your device. - Ensure proper pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ) are connected to the I2C lines.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Microcontroller Not Powering On
- Cause: Incorrect power supply voltage or missing decoupling capacitor.
- Solution: Verify the power supply voltage is within the 1.8V to 3.6V range. Add a 0.1 µF capacitor near the VDD pin.
No Communication via I2C/SPI/UART
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or configuration.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the correct pins are used. Verify the communication settings (e.g., baud rate, clock speed).
ADC Readings Are Inaccurate
- Cause: Noise or incorrect input voltage.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is within the ADC range. Add a low-pass filter to reduce noise.
Microcontroller Not Responding
- Cause: Firmware issue or incorrect reset configuration.
- Solution: Reprogram the microcontroller and verify the RESET pin is properly connected.
FAQs
Q: Can the MPI3508 operate at 5V?
A: No, the MPI3508 operates within a voltage range of 1.8V to 3.6V. Exceeding this range may damage the device.
Q: How many ADC channels are available?
A: The MPI3508 has two 12-bit ADC channels (ADC_IN0 and ADC_IN1).
Q: Is the MPI3508 compatible with 3.3V logic?
A: Yes, the MPI3508 is fully compatible with 3.3V logic levels.
Q: Can I use the GPIO pins for PWM output?
A: Yes, some GPIO pins can be configured for PWM output. Refer to the datasheet for details on PWM-capable pins.